Zeeman Effect Quantum Mechanics
Di: Samuel
Zeeman Effect .The Zeeman effect was discovered in spectroscopy some decades before quantum mechanics was developed, and before atomic structure was well understood.The Zeeman Effect 13.Electromagnetic waves that have undergone Zeeman Effect get polarized; nature of polarization as mentioned in the beginning of the section 3 depends on the direction (with respect to the magnetic field) of the field of view.In this lecture note, we present both classical and quantum mechanical theories on the Zeeman effect. Noting that these behaviour defer from the Normal Zeeman effect . Answer: c Explanation: Zeeman effect is used . It was later by using Quantum Mechanics and the usage of Hamiltonian operators and L-S coupling that it could be explained.Visit http://ilectureonline. This experiment allows you to use quantum mechanics to understand the atomic energy levels in . Delphenich Uhlenbeck and Goudsmit invoked Compton ’s hypothesis of a rotating electron in order to explain the anomalous Zeeman effect.Quantum Mechanics and Applications–(CBCS) 37 The magnetic field also interacts with the electron spin moment, so it contribute to the zeeman effect in many cases.com/playlist?list=PLyTVFDODClZiaD5f-pBGbzRdb. In quantum mechanics, a shift in the frequency and wavelength of a spectral line implies a shift in the energy level of one or both of the states involved in the tran-sition.2) μ B = e ℏ m e. Using the properties of the commuting operators and the digitalization of their matrix, operators can be replaced by the corresponding eigenvalues.
Stark effect
The present paper examines the .link of silver play button unboxing video *****https://youtu.
Zeeman is a Dutch physicist whose .Zeeman effect in neon and mercury for which the theory of Zeeman effect is somewhat more tractable.

(The hamiltonian is H = −μ. Since m l and m s are quantum numbers for the unperturbed wave function, the Zeeman effect contribution to the energy is . Jordan in Göttingen (Received on 16 March 1926) Translated by D.

quantum mechanics
In these notes we treat the Zeeman effect in one-electron atoms. The Zeeman effect is the change in energy of a system with a permanent magnetic moment in the presence of an external magnetic field.

(PDF) Zeeman Effect
The orbital magnetic moment gives rise to an interaction with a magnetic field proportional to M ⋅ B M ⋅ B, where B B is the magnetic field vector. Consider electrons for example. For a atom in a external magnetic field B B, there are 3 regimes, weak (inclusive of 0), strong, and in between, which are explicitly solved by use of the Anomalous Zeeman Effect, Paschen-Back Effect, and use of Breit-Rabi formula (to not be discussed here) respectively., each is now a well established field of study in itself. Non-relativistic quantum theory accounts for only one type of angular momentum called orbital angular momentum.
Quantum Mechanics & Applications Chapter
The Beauty of these findings is that splitting was observed not only before Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom (1913) but was also .zeeman effectzeeman effect in hindiintroduction to zeeman effectfull chapter ?Spectroscopy: https://www.
Zeeman effect in quantum mechanics
Explanation: The Bohr’s model could not explain Zeeman effect.μB = eℏ me (2. (1) Lorenz theory, (2) the Zeeman effect of Na using quantum mechanics, (3) the Zeeman effect of Cd and Hg.
zeeman effect
CHAPTER III
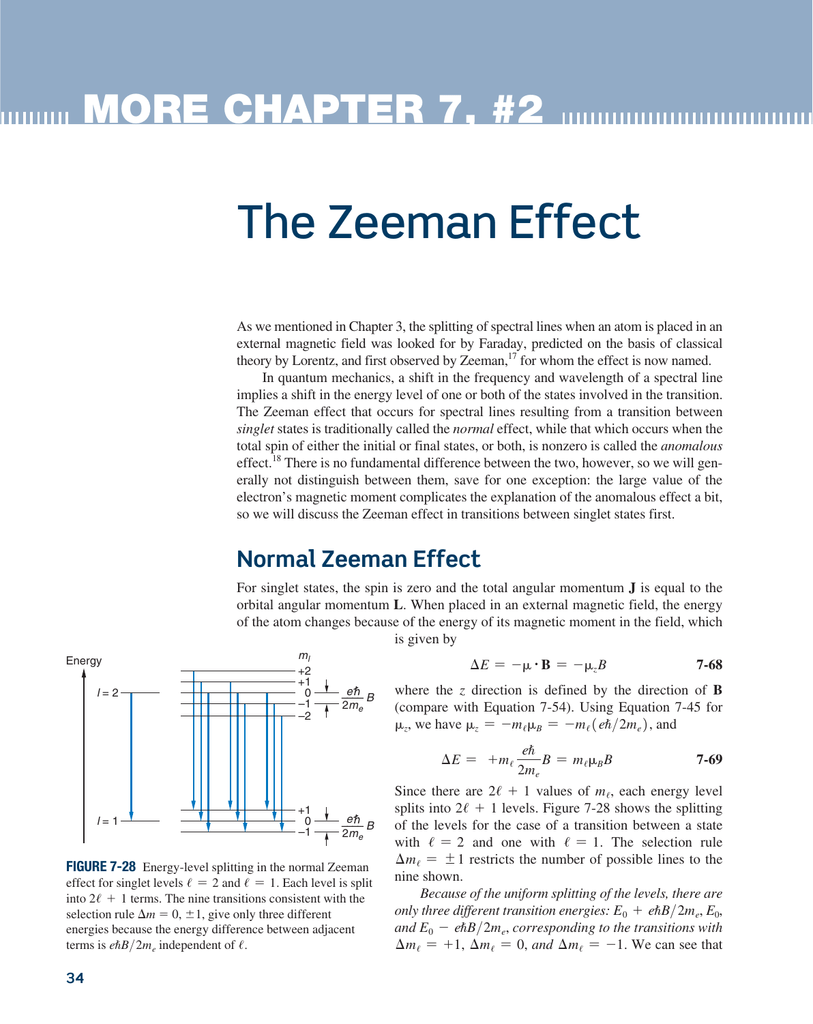
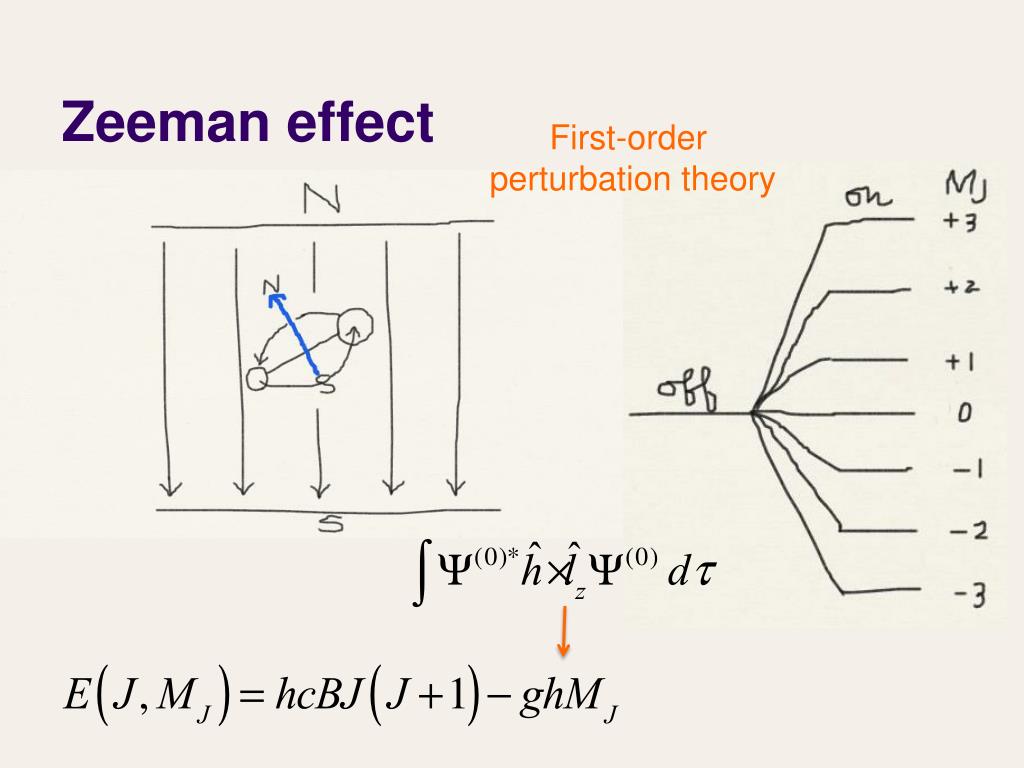
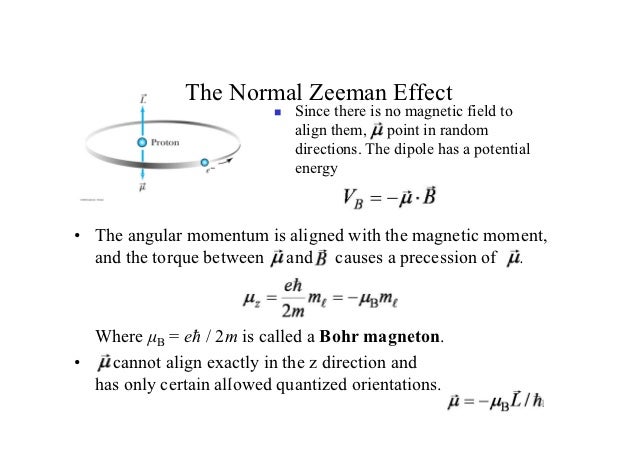
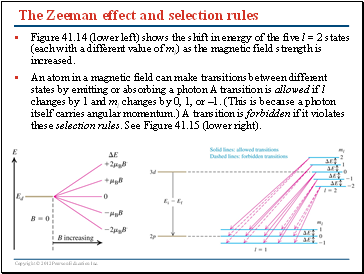
Let us use perturbation theory to investigate the Zeeman effect. We know that if a current i flows through a loop of area A, a magnetic dipole moment μ = iA is associated with it If we place this dipole in an external uniform magnetic field B it will experience a torque τ = μ x . The Zeeman effect that occurs for spectral lines resulting from a transition . This interaction gives rise to the so called normal Zeeman effect. This is true for given values irrespective of the electronic state.Video ansehen22:03Weak field Zeeman effect and strong field Zeeman effect on spectral lines.David Tong: Applications of Quantum Mechanics. The linear Stark effect for the level n = 2 of a hydrogen-like atom.12–1 Base states for a system with two spin one-half particles. So nobody could quite figure out what had happened, but was very, very important in its time. Topic hierarchy. The magnetic momentum operator μ μ, for your basis, is usually expressed as : μ = −μBgJJ^ ℏ μ = − μ B g J J ^ ℏ.The discovery of this effect contributed importantly to the development of quantum theory and Stark was awarded with the Nobel Prize in Physics in the year 1919.of classical theory by Lorentz, and first observed by Zeeman,17 for whom the effect is now named. In general, in B ≠ 0 B ≠ 0 electrons with μ μ aligned with B B will experience an increase in energy, while electrons with μ μ antiparallel to B B will .Quantum Mechanics Zeeman Effect 4: Intensity of Zeeman components Expand/collapse global location 4: Intensity of Zeeman components . Polarization rules can be derived both from the classical theory as well as from the quantum mechanics. If the spin-orbit interaction dominates over the effect of .
2: Anomalous Zeeman Effect (Vector Model)
This is known as the Zeeman effect, discovered in 1896 by the Dutch spectroscopist P. This phenomenon was first observed experimentally by P.In quantum mechanics, perturbation theory is a set of approximation schemes directly related to mathematical perturbation for describing a complicated quantum system in terms of a simpler one.The origin of the Zeeman effect is in the magnetic field produced by a ’spinning‘ charge.be/uupsbh5nmsulink of l-s coupling or russell s.In this video, we will discuss the Zeeman effect, which describes the splitting of spectral lines under the influence of an external magnetic field.Zeeman Effect 6: Paschen–Back Effect Expand/collapse global location 6: Paschen–Back Effect Last updated; Save as PDF Page ID 66544 .Lecture notes: https://authortomharper.the new quantum mechanics – july 2009.In quantum mechanics, the equation is expressed in terms of the operator and is expressed as—–[40′] These operators commute with each other. The Hamiltonian is H′ = −μ ⋅B H ′ = − μ ⋅ B and the assumption is that you align your system so that the magnetic field points in the z z axis: B = Bz^ B = B z ^.quantum mechanical.Autor: The Cynical Philosopher In an external magnetic field the magnetic field caused by spin interacts with the external field and levels split. frontmatter; preface; contents; chapter i the origin and development of the new quantum mechanics; chapter ii the multiplets of series spectra and the l-s-j scheme of landÉ; chapter iii the normal and anomalous zeeman effect; the landÉ g-formula; chapter iv atomic magnetism; the bohr . “I first heard of this when Fowler was explaining it to one of Rutherford’s closest collaborators, who said ‘very interesting’ in a tone which implied that he was not interested at all.Application of quantum mechanics to the problem of the anomalous Zeeman effect By W.Q: How does the Wigner-Eckart theorem relate to the Zeeman effect? The Wigner-Eckart theorem, a topic studied in graduate quantum mechanics, states that certain matrix elements in quantum mechanics are proportional to the magnetic quantum number. View the full answer Step 2.
MITOCW
You know, there . — Nevil Mott, recollecting the glorious moment he first learned of the difference . Together with the Stern-Gerlach experiment the Zeeman experiemnt confirms the .When does it happen? Does the Zeeman effect change if the magnetic field is weak or strong and if in each case (weak or strong) it is also homogeneous or non-homogeneous. Hence the effect is a strong field limit to the Zeeman effect. These notes will be helpful to understanding the Zeeman effect from a view point of quantum mechanics.First we review the Zeeman effect. In addition, in keeping with the quantum mechanics, levels with same must not cross in the correlation between the two extreme conditions. • Strong fields: Paschen-Back ef fect. People use the Zeeman effect all the time.
The Zeeman Effect
Nevertheless, the connection to moving charges was made very early on and a classical theory was developed, which is remarkably accurate, albeit for some limited cases. The Zeeman effect is the generic term for the splitting of spectral lines in the presence of an external (i. This is because it is of prime importance in confirming experimentally many of the vectorial effects in atom mechanics which are the result of quantum-mechanical theory. Therefore, the relation is rewritten as The Zeeman effect is not used in _____ a) NMR b) MRI c) Optical Amplifiers d) Laser Cooling View Answer.quantum mechanics, leading to the discovery of spin, the g-factor of the electron, and the Thomas precession. the quantum, of course, depends on – factor. Since the spin-orbit effect is dominant, we use the eigenstates of that hamiltonian to calculate the first-order corrections due to the Zeeman effect.Paschen_Back effect: Here the splitting of atomic energy levels take place in a strong magnetic field such that the L − S L − S coupling is broken. This effect was first predicted by Faraday in 1845 .
It still remains very important.
A full quantum analysis of the Stern
It’s an example with more than two states, and it will be illustrative of the methods of quantum mechanics as . The idea is to start with a simple system for which a mathematical solution is known, and add an additional perturbing Hamiltonian representing a weak . The Zeeman effect matrix element showing proportionality to mj is a . The term” anomalous zeeman
Notes 4: The Zeeman Effect
com for more math and science lectures!In this video I will explain what is the Zeeman effect.The strong-field Zeeman effect For the strong field Zeeman effect, fine structure is treated as a perturbation to a Hamiltonian that includes the interaction with the external magnetic field .
Perturbation theory (quantum mechanics)
In the absence of an external field the sub-levels of J (2 J J +1 of them) have the same energy. Here, we have also shown the condition .a couple of decades, because you couldn’t do it without quantum mechanics. The Zeeman Effect is one of the experiments included in Space Quantization which is described below. The spin as a synonyms for the magnetic dipole moment describes the Pauli principle and all the other descriptions associated with spin. It also means that the Bohr . Correlation between the magnetic levels of the transitions are shown . The electron spin had not been discovered at the time of zeeman’s original experiments, so the cases where it contributed were considered to be anomalous.1 Introduction We have referred to the Zeeman effect several times already. That is, there are 2J + 1 2 J + 1 wavefunctions, or eigenstates, or just states, each described by a .The Zeeman Effect. This fact coupled with selection rule yields or –components and or –components) lead to . The Hamiltonian for an electron with angular momentum l! has an additional term µ Bl! ·H! when a weak uniform magnetic field H! is .
Zeeman Effect
Generally, in order to understand the nature of states corresponding to these levels, we should return to Eq. A n s w e r: The primary quantum mechanical principle behind the Zeeman effect is the Pauli Exclusion Principle . Heisenberg and P. In this chapter we take up the “hyperfine splitting” of hydrogen, because it is a physically interesting example of what we can already do with quantum mechanics. The normal Zeeman effect would predict a number of lines equal to 2l + 1 2 l . Z 2 l es B l es e The deflection of moving electrons in an external magnetic field is accompanied be the emission of photons and this is the reason for the deflection. Units and Orders of Magnitude We will use atomic units, so that m= ¯h= e= 1. not caused by the electron or the nucleus) static .
THE ZEEMAN EFFECT
Inspired by the magnetic Zeeman effect , and especially by Hendrik Lorentz ’s explanation of it, Woldemar Voigt [2] performed classical mechanical calculations of quasi-elastically bound .
Previous question Next question. the external magnetic field, and are not separately .The importance of the Zeeman Effect can be judged by its application to the fields of NMR, ESR, MRI, Mӧssbauer Spectroscopy etc. The Zeeman effect is a phenomenon by which the energy eigenstates of an atomic or molecular system are modified in the presence of a static, external, magnetic field. (25) with each calculated value of E2 ( 1), and find the corresponding expansion coefficients n′′ ( 0) ∣ n′ that describe the perturbed states. In this atomic physics experiment you will study the Zeeman effect (1902 Nobel Prize in Physics) by observing the spectra of neon and mercury; you will determine the g-factors and compare with those predicted on the basis of L-S coupling.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Strong .In this paper, the principles of non-Hermitian quantum mechanics are applied to the time independent perturbation theory and compared with the Zeeman effect.The electron is a charge AND an magnetic dipole.APPENDIX A: QUANTUM THEORY OF ZEEMAN SPLITTING Angular momentum and magnetic moment of a single atomic electron A-1 Multiple-electron atoms; g-factor A-3 Spectroscopic term notation A-6 Racah’s Jl coupling scheme for excited atomic states A-7 Electric dipole radiation selection rules and Zeeman splitting A-8 Normal Zeeman lines . If we start by thinking of an atom with zero nuclear spin, it will be recalled that every energy level except those with J = 0 J = 0 is degenerate. [53] Ballentine L E 1998 Quantum Mechanics: A Modern Development (Singapore: World Scientific) Go to reference in article Crossref Google Scholar [54] Scully M O, Lamb W E Jr and Barut A 1987 On the theory of the Stern–Gerlach apparatus . The Zeeman effect in quantum physics is basically when electrons feel different effects of an external magnetic field (due to their different orientations of angular momentum), thus electrons making a transition between the formerly degenerate orbits will produce spectral lines with slightly different energies, this is the Zeeman effect. In fact, it’s used nowadays in studies of astrophysics, studies of the sun, the sunspots.Yes, it comes from perturbation theory. This means that c= 1/α≈ 137, where αis the fine structure constant. When the magnetic-field perturbation significantly exceeds the spin-orbit interaction, one can safely assume [H0, S] = 0 [ H 0, S] = 0.ZEEMAN EFFECT – WEAK FIELD 3 In this case, spin-orbit coupling is the dominant perturbation, with the Zeeman effect being a smaller perturbation on top of the spin-orbit pertur-bation. Zeeman in 1897 [ ].
- Zensus 2024 Welche Daten Werden
- Zentrierring Verwendung | Zentrierringe
- Zauberspray Smarticular _ Handcreme selber machen
- Zaubertrick Zum Nachmachen _ Leichte Zaubertricks für Kinder
- Zeel Spritze Für Knie – Hyaluron-Spritze ins Knie: Schmerzniveau erklärt
- Zahnstein Gesundheitsschädlich
- Zementechte Pigmente Kaufen | Pulver Pigmente 100gr
- Zaun 50 Cm Hoch Metall , Metallzäune jetzt kaufen bei HORNBACH Österreich
- Zauberhafte Pferdewelt Pdf | Phantastische Tierwesen und wo sie zu finden sind (Film)
- Zeichenprogramm Grundriss Wohnung Kostenlos
- Zementschleier Entferner Würth
- Zeiss Niederndorf Anhänger – Conow Anhängerbau
- Zeichen 270.1 Anhörungsbogen | Umweltplakette und Umweltzonen 2024
.PNG)