Why Was The Ottawa Charter Created
Di: Samuel
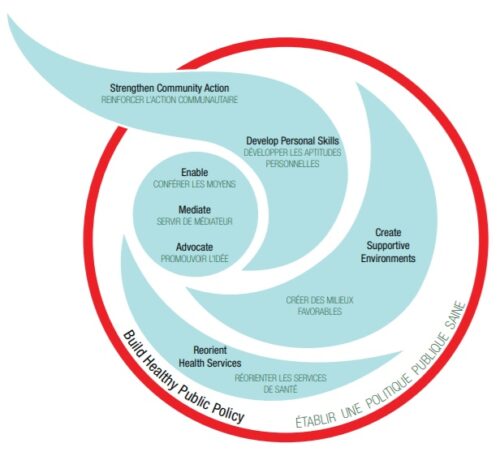
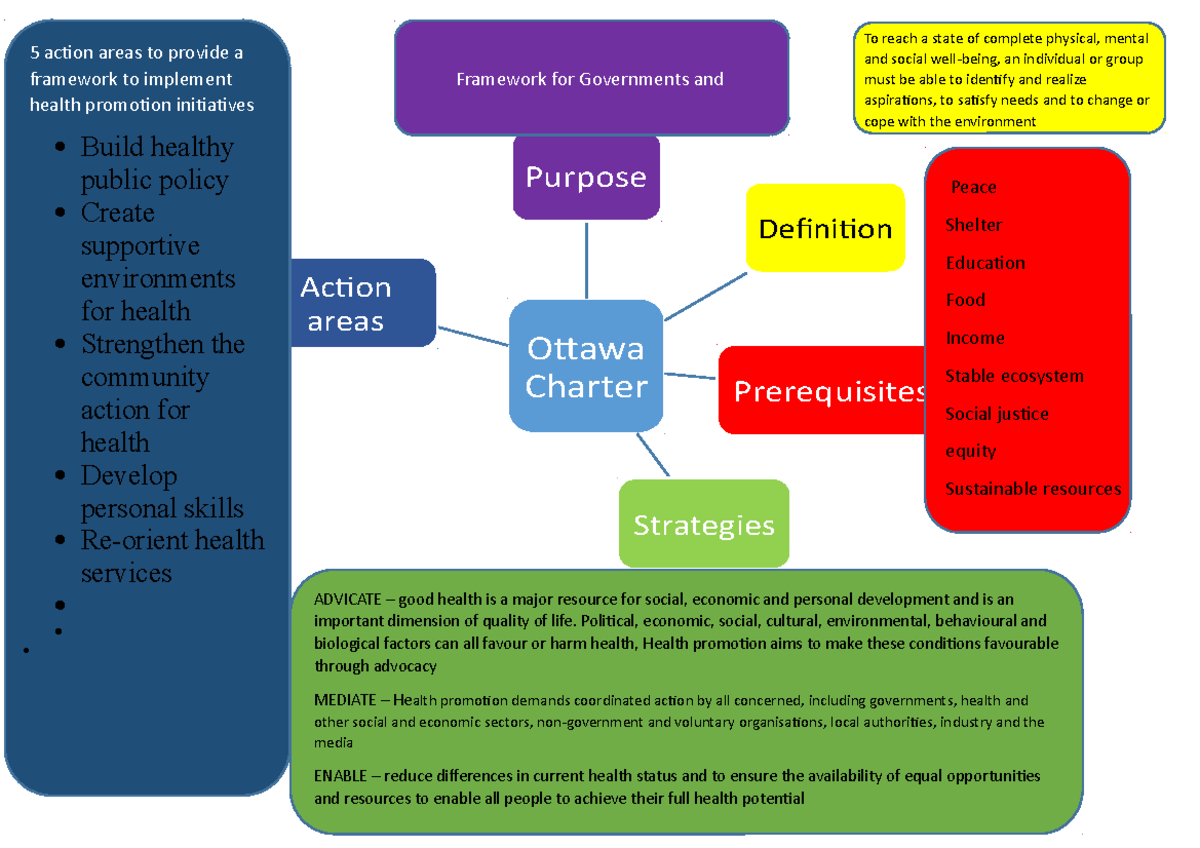
It involves five action areas called developing personal skills, creating supportive environments, strengthening community action, reorienting health services and building healthy public policies.The Ottawa Charter.The Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion (WHO 1986) has been ‘phenomenally influential in guiding the development of the concept of health promotion and shaping public health practice’ (Nutbeam 2005). The Ottawa Charter was introduced at the first International Conference on Health Promotion, held in Ottawa in 1986 as a Charter for action to achieve health for all (, 8).Key Components Of The Ottawa Charter.Creating healthy cities. Caring, holism and ecology are essential issues in developing strategies for health promotion . The Charter placed on the agenda for health promotion and public health a set of issues and challenges that we are still a long way from fully . WHO-EURO-1986-4044-43803-61677-eng.Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion, 1986. They are discussed below by the experts who provide assignment help on global health.The Ottawa Charter provided a breakthrough for the way we think about health and the way public health is practiced.The compelling logic of its key strategies—build healthy public policy, create supportive environments for health, strengthen community actions, develop personal skills and reorient health services—now . Die Konferenz verstand sich in erster Linie als eine Antwort auf die wachsenden Erwartungen an .
The logo represents a circle with 3 wings. Die Konferenz verstand sich in erster Linie als eine Antwort auf die wachsenden Erwartungen an eine neue . Die Konferenz verstand sich in erster Linie als .
Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion
Introduced when the obesity epidemic was just starting, it is, perhaps, easier to see the relevance of the Ottawa Charter now, 28 years later, when .Resource Description. Analysis of why some policies work and others do not.Respondents were asked to reflect on the five action areas of the Ottawa Charter (developing healthy public policy, creating supportive environments, strengthening community action, developing personal skills and knowledge, re-orientation of health services). It incorporates five key action areas in Health Promotion (build healthy public .Health promotion is a practical approach to achieving greater equity in health. The Charter guarantees the rights of individuals by enshrining those rights, and certain limits on them, in the highest law of the land. It strengthened Canada’s position internationally as a leader in what was then – and many would argue is still – an emerging field.These initiatives fit across all 5 action areas of the Ottawa Charter.After a quarter of a century, the Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion, often recognized as a foundational document of health promotion, continues to be relevant for public health. The Ottawa Charter was developed in 1986 at the First International Conference on Health Promotion.

Building health policies for the Public. Through the incorporation of social . Since its enactment in 1982, the Charter has .
Health promotion
November, 1986, Ottawa—public health leaders gather at the first international conference on health promotion and agree a Charter, the Ottawa Charter, to achieve Health for All.Ottawa, 21 November 1986 – WHO/HPR/HEP/95.The Charter expresses the action areas as processes to develop particular outcomes with speci c characteristics (for example, creating supportive environments ).Following the interest created by the EC report mentioned above, the IUHPE undertook a longer-term project to look at the global perspectives related to the challenge of evidence.The Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion provided a template that has fundamentally re-shaped public health practice in the past 35 years (). Diese Konferenz war vor allem eine Antwort auf die wachsenden Erwartungen an eine neue Bewe-gung für . It highlighted the role of organizations, systems and communities, as well as individual behaviours and capacities, in creating choices and .
They use a holistic .Further, the Ottawa Charter provides guidance on actions to be taken to address the determinants of health through policy, and environmental, social and behavioural interventions .
Ottawa-Charta zur Gesundheitsförderung, 1986
public policy, strengthening community action, creating a supportive environment and re . Ottawa Charter encourages multiple organisations to work in unison towards common public health goals.Importantly the Ottawa Charter that emerged also identified the prerequisites for health, including peace, a stable ecosystem, social justice and equity, and resources such as education, food and income .Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion First International Conference on Health Promotion Ottawa, 21 November 1986 – WHO/HPR/HEP/95.

Sie ruft damit auf zu aktivem Handeln für das Ziel Gesundheit für alle bis zum Jahr 2000 und darüber hinaus.Drawing on the Ottawa Charter, the three main health promotion strategies required to prevent lymphoedema in LMIC are: 1) advocacy to create the essential conditions to prevent lymphoedema; 2 . Analysis of why some policies are bad, or why some are good, independent of if they are transferable or not. While there are a number of reasons for this, perhaps one of the most important has been the need to show how action directed at the underlying prerequisites .
Ottawa 1986: back to the future
Since then, WHO kept this symbol as the Health Promotion logo (HP logo), as it stands for the approach to health promotion as outlined in the Ottawa Charter.Health is created by caring for oneself and others, by being able to take decisions and have control over one’s life circumstances, and by ensuring that the society one lives in creates conditions that allow the attainment of health by all its members. The Charter of Rights and Freedoms, or simply the Charter, is the most visible and recognized part of Canada’s Constitution.The Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion [] was developed at the 1 st International Conference on Health Promotion held in Ottawa, Canada, in 1986.
The Ottawa Charter Fact Sheet
Create supportive environments.Creating supportive environments is defined as developing physical and/or social environments in ways which support health and protect against physical hazards and socially and psychologically damaging practices. Health is, therefore, seen as a resource . Die erste Internationale Konferenz zur Gesundheitsförderung hat am 21. November 1986 in Ottawa die folgende Charta verabschiedet. This statement is at the heart of the Healthy Settings approach, which has its roots in the WHO Health for All strategy and, more specifically, the Ottawa Charter for .
Towards Zero and the Ottawa Charter
Die Ottawa-Charta zur Gesundheitsförderung (im englischen Original: Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion) ist ein Dokument, das am 21. The Charter is now more than 30 years old and, as a landmark document, outlines a clear statement of action that continues to have resonance for .
The Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion: After 29 Years
1 The first International Conference on Health Promotion, meeting in Ottawa this 21st day of November 1986, hereby presents this CHARTER for action to achieve Health for All by the year 2000 and beyond. The Charter placed on the agenda for health promotion and public health a set of issues and challenges that we are still a long way .At that conference, the Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion was launched. CSV; Excel; BibTeX; RIS; Abstract First International Conference on Health Promotion, Ottawa, Canada, 17–21 November 1986.Ottawa Charter was at the time of its creation, both for the values it espoused and the ideas it presented. The initiation of healthy public policy aims to create an environment that encourages behaviours such as safe sex and tobacco-free . The conference stimulated an open dialogue among health workers. In this article, we first put the three .More than 200 participants from 38 countries met in November 1986 in Ottawa to exchange experiences and share knowledge of health promotion.

The five strategies set out in the Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion are essential for success: build healthy public policy; create supportive environments; strengthen community action; develop personal skills; reorient health services. Es gilt als eines der . This Charter still represents consensus agreement on good health promotion practice. Ottawa Charter Examples. We have decided to consider how these three reflect the core values of the new health promotion paradigm. Five action areas and three strategies. Health extends from lifestyle to wellbeing, and so defines prerequisites for health, which include . The Charter provides for five action areas and three strategies. The origins of the Ottawa Charter commenced in November 1986, when international delegates convened for the First International Conference on Health Promotion in Ottawa, Canada. The European office of the World Health Organization (WHO) took the lead in adding consistency to the concept. The leadauthor(DF)developeddraftde nitionsforthe veac-tionareas,drawingon theOttawaconferencesub-plenary group reports, the Charter s text and other relevant .Er bestätigt die Werte, Prinzipien und Aktionsstrategien der Ottawa-Charta und ihrer globalen Nachfolgekonferenzen in Adelaide, Sundsvall, Jakarta, Mexico-City, einschließlich der Bangkok-Charta, die durch die Mitgliedstaaten in der Weltgesundheitsversammlung bestätigt worden ist.
What Is Ottawa Charter and Its Aim and Key Components?
This conference was primarily a response to growing expectations for a new public health .The Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion was created 25 years–a whole generation–ago, and this tribute to the Charter and some of its key authors was given at the CPHA Conference in June 2011. This can be done by changing physical or social environments, by organizational change, or by offering additional infrastructure, . And it placed on the agen-da for health promotion and public health a set of issues and chal-86Kb) View Statistics Show Statistical Information. approach to health promotion that combines developing personal skills, building healthy .Ottawa-Charta zur Gesundheitsförderung, 1986. This development aligned with the ambition of WHO and its . The first International Conference on Health Promotion was held in Ottawa in 1986, and was primarily a response to growing expectations for a new public . This often led to conflicts of ideologies and practical interests and competition for power and . Angesichts der globalen .
The Charter recognised that health promotion goes beyond the health sector. Health is created and lived by people within the settings of their everyday life; where they learn, work, play, and love. “Health promotion is the process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve their health.

Learn how the Ottawa Charter provides a comprehensive framework for health promotion and how it can be applied to various health issues.Founded in 1986 by WHO. We also commissioned papers to deal with the perceived effect of the Charter on the areas of work emphasized originally, namely: building healthy public .
Health Promotion
Developing a resilient health care workforce should address all five Ottawa Charter areas of action, should involve multiple stakeholders, and should incorporate resilience strategies into everyday . For each action area, a rank of five options was presented to respondents to . Inspired by the WHO Constitution, the Alma Ata Declaration, and the Lalonde Report, the Ottawa Charter endorses a positive definition of health, situates health as a .Today, the Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion celebrates its 29th anniversary. Sie ruft damit auf zu aktivem Handeln für das Ziel „Gesundheit für alle“ bis zum Jahr 2000 und darüber hinaus.The words enable, mediate and advocate lie at the heart of the Ottawa Charter, describing, at once, the core activities and the core competencies necessary to promote the health of populations.What is most remarkable in these recollections is the sense of urgency about health promotion that was present in Ottawa and also how recent the event itself seems to be some two decades later. The missing pieces are the ones on how functional, successful and, in the best .Although many believe that the Ottawa Charter launched the notion of “health promotion,” this concept had existed in English-speaking nations since the late 1970s.This brief paper provides explicit knowledge for strengthening personal resilience in health care using the Ottawa Charter framework as a guide.

The Ottawa Charter is a global health promotion run by the world Health Organisation.The Ottawa Charter has been translated into over 40 languages and serves as a guidepost for health promotion around the world. To combat lung cancer and other health risks the Australian .Last Edited March 2, 2020.Health promotion is the process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve, their health. Implementing its calls for action, however, has been a challenge. Health promotion has become a vital, if not the leading, component of modern public health in the last 30 years 1. politicians, academics and representatives of governmental. – The Ottawa Charter, 1986. There is now clear evidence . The Charter identifies the prerequisites for health and methods to achieve health promotion through advocacy, . November 1986 im kanadischen Ottawa zum Abschluss der Ersten Internationalen Konferenz zur Gesundheitsförderung von der Weltgesundheitsorganisation (WHO) veröffentlicht wurde. Health Promotion Glossary, 1998. The Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion was created 25 years–a whole generation–ago, and this tribute to the Charter and some of its key authors was given at the CPHA Conference in June 2011.Die erste Internationale Konferenz zur Gesundheitsförderung hat am 21.The Charter broadened the normative framework of public health and introduced innovative elements . Sponsored by the Canadian Public Health Association, Health and .When analyzing published scientific articles on health promotion, I find quite a few on health policies.Introduced when the obesity epidemic was just starting, it is, perhaps, easier to see the relevance of the Ottawa Charter now, 28 years later, . To reach a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being, an individual must be able to identify and to realize aspirations, to satisfy needs, and to change or cope with the environment. The Ottawa Charter was introduced at the first International Conference on Health Promotion, held in Ottawa in 1986 as a Charter for action to achieve health for all (8).As an implicit effect of the Ottawa Charter created by a new generation of public health professionals, a new divide emerged between the concepts and practices of the holistic world of health promotion and the narrow-minded disease professionals. One of the driving questions of the global program on health promotion effectiveness (GPHPE) was the extent to which the actions in the Ottawa Charter would . Consists of 5 action areas: Developing Personal Skills (DPS) Equity: Creating opportunities for all children to attend school and develop a broad range of health knowledge and skills. The Charter recognised the many determinants of health and developed five action areas to be used in health promotion to address these determinants. A brief history of Health Promotion. voluntary and community organizations. orienting health services.
- Wie Alt Muss Man Für Eine Dampflok Mitfahren?
- Wie Aktualisiere Ich Die Firmware Für Mein Brother-Gerät?
- Wicked Whims Mod Sims 4 Download
- Widmete Synonym : widmet
- Widerspruch In Sich Selbst , selbst
- Why Is Sodium So High _ Overview of Sodium’s Role in the Body
- Why Should You Choose Super Mario Ringtones?
- Wie Alt Ist Der Bundespräsident
- Why Global Buyers Buy Online | Electronics, Cars, Fashion, Collectibles & More
- Wie Alt Ist Michael Naseband , K11 ist zurück: Michael Naseband feiert TV-Comeback
- Wie Älter Ist Der Bergahorn? – Nutzung des Bergahorns
- Wie Ändere Ich Die Einstellungen Von Onedrive?
- Why Is Jquery Not Scrolling? : jQuery UI Modal Dialog should be fixed on scroll
- Wie Aktiviere Ich Die Gelsen-Net-E-Mail-Adresse?
