What Is Wavenumber In Spectroscopy?
Di: Samuel
That is, first overtone \(v = 1 \rightarrow 2\) is (approximately) twice the energy of the fundamental, \(v = 0 \rightarrow 1\).0 ppm region of a 1 H NMR spectra.A wavenumber is the reciprocal of the wavelength of the wave.77 µm, the upper wavelength limit of visible light) to 4000 cm –1 (a wavelength of 2,500 nm or 2.The commonly used region for infrared spectroscopy is 4000 ~ 400 cm -1 because the absorption radiation of most organic compounds and inorganic ions is within this region. none, wavenumber is a dimensionless quantity Q. 1: Pictured above is the Harmonic Oscillator approximation (green parabola) superimposed on the anharmonic oscillator (blue curve) on a potential energy diagram.3 Show how to obtain the number of electron volts in 1 hartree .When an atom in a molecule is changed to an isotope, the mass number will be changed, so µ µ will be affected, but k k will not (mostly). 1 for the CO C O molecule. (Known as a ‘background’.
Infrared spectroscopy correlation table
The most common wavelength units are the nanometer (nm), the Ångström (1 = 10 -1 nm) and the micrometer (µm).25 × 10 − 4 cm or 6. In the case of UV-Visible spectroscopy, at 200 nm (shorter wavelength) the energy and frequency of UV-Visible radiation are high as compared to 800 nm (Longer wavelength).1 Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy. A diverse range of materials containing the covalent bond absorbed electromagnetic radiation in the IR region.Infrared spectroscopy is a powerful technique for identifying the functional groups and structures of organic and inorganic molecules. These are the conventions that spectroscopists are expected to follow so they can communicate . This article outlines the main concepts of atomic structure, with some emphasis on terminology and notation. Absolute wavenumbers: Example: 500 nm corresponds to 20000 cm-1. Spectroscopy generally is defined as the area of science concerned with the absorption, emission, and scattering of electromagnetic radiation by atoms and molecules, which may be in the gas, liquid, or solid phase.62608 ×10−34 6.
What is a wave number?
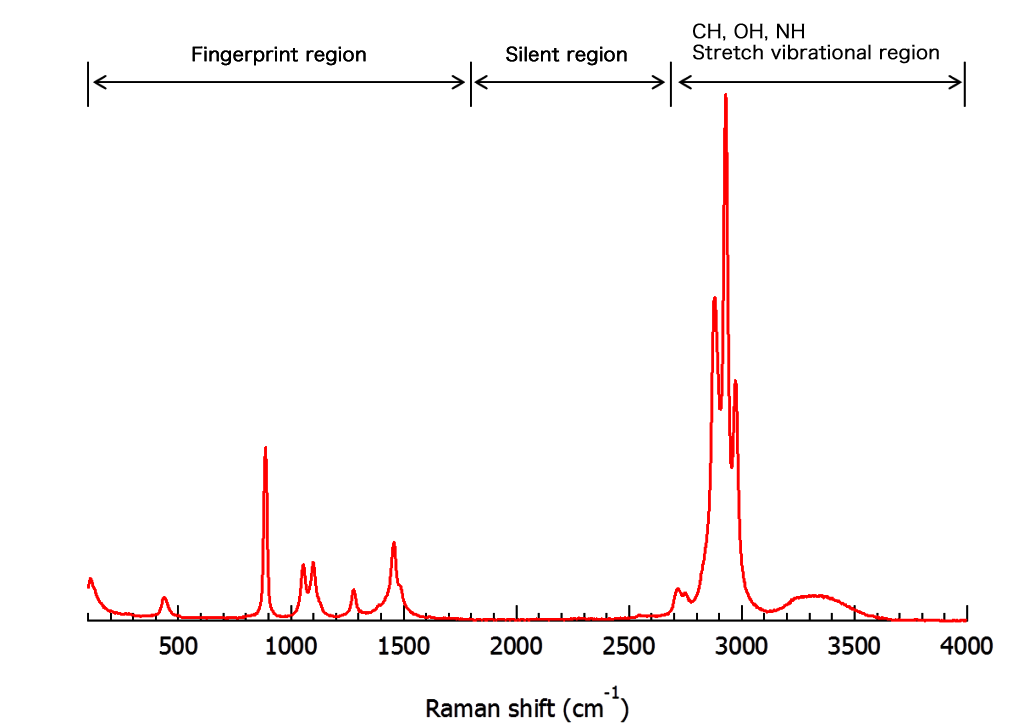
1 shows a portion of the Raman spectrum for carbon tetrachloride and illustrates several important features. Which of the following bonds undergoes stretching at the highest frequency? a. Due to historical reasons however, we typically discuss IR light in . A diatomic molecule consists of two masses bound together.A typical rovibrational spectrum is reported in figure 29.This transformation is accomplished by applying the Fourier transform to the interferogram. Excitation Laser. Vibrational Modes. For Raman selection rules it can simply explained by electromagnetic field interactions within the molecule’s .
Infrared spectroscopy
3: Some Subtle Points of IR Spectroscopy is shared under a CC BY-NC 3. 2 2 The intensity of the signals is—once again—proportional to the initial population of the levels. Earlier we noted that absorption bands in the region that extends from 1500 cm –1 to 4000 cm –1 are called group frequencies. Equation (1) shows the Fourier transform. The energy equation is E = hν. f˜(ν) = ∫x −x f(x)e−2iπνxdx (14. Infrared light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum between visible light and microwaves, with wavelengths ranging from 780 nm to 1 mm.Popular answers (1) If bond length decreases the peak wave number shift to higher values. See how the hybridization state of carbon affects the wavenumber in a carbon-hydrogen bond stretch. The far IR requires the use of specialized optical materials and sources.Rotational spectroscopy is therefore referred to as microwave spectroscopy. Bond length changes may occur due to the change in .Learn how to interpret IR spectra of hydrocarbons containing single, double, and triple carbon-carbon bonds.1 H Nuclear Magnetic Spectroscopy.The wavenumber (cm-1) scale represents an energy form and we know that frequency = (1/wavelength) and there is a direct relation bet. A vibration that absorbs light at 1020 cm‐1 absorbs light in the infrared at a .The technique is therefore very useful as a means of identifying which functional groups are present in a molecule of interest.
You will conduct the following measurements. This tells you how many wavelengths fit into a unit of distance. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms.You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and . UV-VIS (ultraviolet-visible) spectroscopy of electronic states. Vibration modes for the same functional groups are observed at the same wavenumber. Vibrational energy levels, νe ν e, are affected by both k and µ, and is given by.The power of infrared spectroscopy arises from the observation that the covalent bonds characterizing different functional groups have different characteristic absorption frequencies (in wavenumber, Table 6. The wavenumber has units of 1/distance, or distance − 1.

Alpha protons of carboxylic acid derivatives, due to the presence of a carbonyl, resonate in the 2. Their spectra are important in such fields as geochemistry and mineralogy. Fluorescence spectroscopy of electronic states. What are the units of wavenumber, 7, in infrared spectroscopy? a.An infrared spectroscopy measured the absorption of IR radiation made by each bond in the molecule and as a result gives spectrum which is commonly designated as % transmittance versus wavenumber (cm −1).2 Identify why 1 hertz is said to equal 6.A wavenumber is the reciprocal of a wavelength (1/λ); thus, a wavenumber of 1600 cm −1 corresponds to a wavelength of. Raman spectroscopy is based on scattering of incident light at an energy shifted by the vibrational energy ( hν) of the molecule.98645 × 10 − 23 J.e) Covalent O-H shows up at higher wavenumber, because a covalent bond is stronger than a hydrogen bond This page titled 3.A measurement of any one of the entities frequency, wavenumber, or wavelength (in vacuum) is an equally accurate determination of the others since the speed of light is exactly defined. STEP 3 Record a second spectrum and interpret the data. Hydrogens on carbons in and epoxide appear in the region of 2.1) f ~ ( ν) = ∫ − x x f ( x) e − 2 i π ν x d x. If it decreases the bond length increases. A wave number is related to but different from frequency, which is temporal in nature. The carbonyl stretching peak is perhaps the perfect example of a group .The peak size and shape should be similar, but not necessarily identical due to minor differences in sample preparation.5–50 µm 50–1,000 µm This chapter focuses on the most frequently used mid IR region, between 4000 and 400 cm –1 (2. Rigid Rotor Model. Here, we typically refer to light . This change in reduced mass will affect the vibrational modes of the molecule, which will affect the vibrational spectrum. Blue shift means that frequency or wavenumber of phonons interacting with the incident photon increased, red shift means that it decreased. When looking at an .0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Chris Schaller via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts . Hydrogens on carbon adjacent to the ether show up in the region of 3.Use our Raman shift / wavelength calculator tools below to convert instantly, or download our apps for Apple or Android for easy access. This area is sometimes referred to as the carbonyl stretching region as a result.Infrared, or IR, spectroscopy is a chemical analysis technique that takes advantage of the interaction between infrared light and matter. As the molecule rotates it does so .Video ansehen15:25e.1 ) the sample to be analyzed is held in front of an infrared laser beam, in order to do this, the sample must be contained in something, consequently this means that the very container the sample is in will absorb some of the infrared beam. The Raman Shift Calculator allows you to convert a known absolute wavelength to a Raman .Simply, detectors used in Raman spectroscopy have varying pixel size, and the smaller the pixel size the higher the spectral resolution.62608 × 10 − 34 J and 1 wavenumber is said to equal 1. The SI wavenumber unit is the inverse meter .Vibrational Raman spectroscopy is not limited to intramolecular vibrations.
1: Spectroscopy
Atomic radiation is discussed, in particular the wavelengths, intensities, and shapes of spectral lines, and a few remarks are made regarding continuous spectra. The derivative of the wavenumber . example: the first orden phonon of . The downfield shift occurs from deshielding due to higher electronegativity of the sp 2 hybridized carbonyl carbon relative to the sp 3 hybridized alpha carbons.Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. 1 1600 cm − 1 = 6. 1 An example of a modern benchtop FT-IR spectrometer (Varian Corp.
14: Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
98645 ×10−23 1. Organic chemists find it more convenient to .

1 H NMR Spectroscopy.1 List three reasons why spectroscopy is used as the stepping stone to Quantum Mechanics. The IR region is .Atomic Spectroscopy – Introduction.There are three quick, simple steps involved in obtaining a spectrum of a sample: STEP 1Record a spectrum with no sample present. The region between 400 cm -1 and 1500 cm -1 is known as the fingerprint region, so called because it’s difficult to assign all the absorption bands, and because of . Notice that the scale at the bottom of the infrared spectrum for 2-hexanone shown is calibrated in wavenumbers (cm −1). The wave number is measured either in cycles per unit distance or in radians per unit distance, depending on the context.
Atomic Spectroscopy
This module is designed to introduce the basic concepts of spectroscopy and to provide a survey of several of the most common types of spectroscopic measurement. For wavelengths expressed in meters, this is m − 1, and if the wavelength is expressed in cm, the units of the wavenumber are cm − 1.4 : An exaggerated view of .Nanometers, wavenumbers and relative wavenumbers. Sometimes you may be using FTIR to identify an unknown.
Infrared Radiation
The ladder of vibrational levels shown in Figure .However, the Raman spectrum is plotted as a function of wavenumber (ṽ) shift relative to the absolute wavenumber of the laser, which is equal to the reciprocal of the wavelength 1/λ. Notice how the signals in the spectrum are divided among two sides, the P-branch to the left, and the R-branch to the right. where: f(x) f ( x) is the signal measured at the detector which is a function of the mirror position, x x . Therefore, the spectral dispersion in wavenumber and not wavelength is relevant and important to the Raman spectroscopist. The frequency, wavelength, and wavenumber are related to each other via the following equation(1): (1) These equations show that light waves may be described by their frequency, wavelength or wavenumber.
Isotope Effects in Vibrational Spectroscopy
Hydrogens on carbons adjacent to the sulfur in sulfides and thiols appear in the .Carbonyl stretching peaks generally fall between 1900 and 1600 cm-1 (assume all peak positions hereafter are in wavenumber units), a relatively unique part of the IR spectrum. Learn how infrared radiation interacts with different vibrational modes, how to interpret the IR spectrum and characteristic absorption bands, and how to apply IR spectroscopy to various fields of chemistry.
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and
Crystal lattice vibrations and other motions of extended solids are Raman-active.In infrared spectroscopy, units called wavenumbers are normally used to denote different types of light.Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopy.
Understanding Raman Spectroscopy
Laser wavelength also affects spectral resolution. Similar peaks in epoxides are shifted to a slightly higher field than other ethers. Although the peak is intense, it carries no useful information as the absolute energy is just that for the source.Infrared Spectroscopy 251 Wavenumber 13,000–4,000 cm –1 4,000–200 cm –1 200–10 cm –1 Wavelength 0.
Quantities, Symbols, and Units in Spectroscopy
The distance between the masses, or the bond length, (l) can be considered fixed because the level of vibration in the bond is small compared to the bond length. This effect is reduced for . Commonly, the symbol ν is used .The first term is the wavenumber Raman shift in cm-1, λ (0) is the wavelength of the excitation laser in nm, and λ (1) is the wavelength of the Raman scatter in nm. The spectral resolution decreases as the excitation wavelength decreases since Raman spectra uses an energy related unit (wavenumber, cm-1 . energy and frequency. Enter the values you know, and the others will be automatically computed and updated (laser wavelength is required).

Energy is proportional to the frequency absorbed, which in turn is proportional to the wavenumber, the first overtone that appears in the spectrum will be twice the wavenumber of the fundamental. Uncover the relationship between bond strength, frequency, and wavenumber as you explore real-life examples, comparing alkanes, .Most recent answer. V (R) is the potential energy .
Visible electromagnetic radiation is called light, although the terms light, radiation, and electromagnetic radiation can . First, Rayleigh scattering produces an intense peak at Δν¯¯¯ = 0 Δ ν ¯ = 0. The key collection parameters are: • The number of scans (background and sample .
What is matching % acceptable in infrared spectroscopy?
The infrared (IR) range of the electromagnetic spectrum is usually divided into three regions: The far-infrared is always used for rotational spectroscopy, with wavenumber range 400 – . The absorption of infrared (IR) radiation causes excitation of vibrations of the atoms of a molecule or the crystal lattice and causes bands in the spectra which are generally presented in the unit wave number \( \tilde{\nu } \) in cm −1 (wavelength λ was used in the older literature). In physical and analytical chemistry, infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy) is a technique used to identify chemical .) STEP 2Insert the sample into the spectrometer. The near-IR extends from approximately 13,000 cm –1 (a wavelength of 770 nm or 0.An infrared spectroscopy correlation table (or table of infrared absorption frequencies) is a list of absorption peaks and frequencies, typically reported in wavenumber, for common types of molecular bonds and functional groups.A wave number, or wavenumber, refers to the spatial frequency of a wave over a specific unit distance.6 of that tome lists the various conventions for naming and symbolizing quantities involved in spectroscopy, as well as the recommended SI unit (although occasionally other units are more popular, like cm-1 for wavenumber). Relative wavenumbers: Example: A Raman band at 1020 cm‐1 and excited with a laser wavelength of 500 nm scatters light at a wavelength of 527 nm.
Guide to FT-IR Spectroscopy
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of Metal Ligand Complexes.Infrared spectroscopy is based on absorption of light energy corresponding to the vibrational energy of molecules. Figure 2 shows that Raman spectroscopy measures the energy gap between the vibrational levels of the molecule.
- What Makes ‚Hard Knock Life‘ Different From Other Annie Songs?
- What Was The First Book Banned In The New World?
- What Song Does Dthang Gzz Sing ‚I Got A Feeling‘?
- What Time Does Formula 1 Practice Start On Friday?
- What Is The Success Rate Of Venture Capital?
- What Song Is Beautiful By Christina Aguilera?
- What Is The Hunger Games Simulator?
- What Time Is Sunrise In Reykjavik 2024?
- What Is The Take This Lollipop App?
- What Is The National Color Of Austria?
- What Is The Meaning Of Conga By Miami Sound Machine?
- What Is The Movie Dorian Gray About?
- What Should I Do If I Have A Counterfeit Banknote?