What Is The Difference Between Smooth Muscle And Leiomyosarcoma?
Di: Samuel
There are three types of muscle tissues in the human .Because a suspected leiomyoma is often managed conservatively or with minimally invasive treatments, the misdiagnosis of leiomyosarcoma for a benign leiomyoma could potentially result in significant treatment delays, therefore increasing morbidity and mortality. Although leiomyomas are usually asymptomatic, they can manifest with symptoms such as pain or . Uterine sarcomas are significantly rarer than leiomyomas and have a poor prognosis. There are three different types of uterine sarcoma: Leiomyosarcoma, the most common type of uterine sarcoma, develops within the . Methods: 26 cases of uterine smooth muscle tumors including 12 leiomyosarcoma(LMS), 10 leiomyoma with bizarre nuclei (LBN) and 4 smooth muscle tumor with uncertain . The latter two markers can be useful in the differential diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma and myofibroblastic sarcomas, because .smooth muscle tumors’ spectrum, from benign ordinary leiomyoma with its various forms of degeneration and variants, to smooth muscle tumor of uncertain malignant potential (STUMP) and malignant leiomyosarcoma.Uterine myxoid smooth muscle tumors, including myxoid leiomyosarcoma, are rare and their genomic profile has not been fully characterized. It tends to grow aggressively. Immunohistochemical study with a panel of antibodies to p16, p53, .) Leiomyosarcoma is one of the more common sarcomas, accounting for about 20 percent of all the 80+ types of soft tissue sarcomas. To further investigate these tumors, 84 cases from consultation and institutional files were analyzed for . They’re found in blood vessels and hollow organs such as the stomach and intestines, helping to guide food, blood, saliva, and other substances.
The Differences Between Skeletal, Smooth & Cardiac Muscles
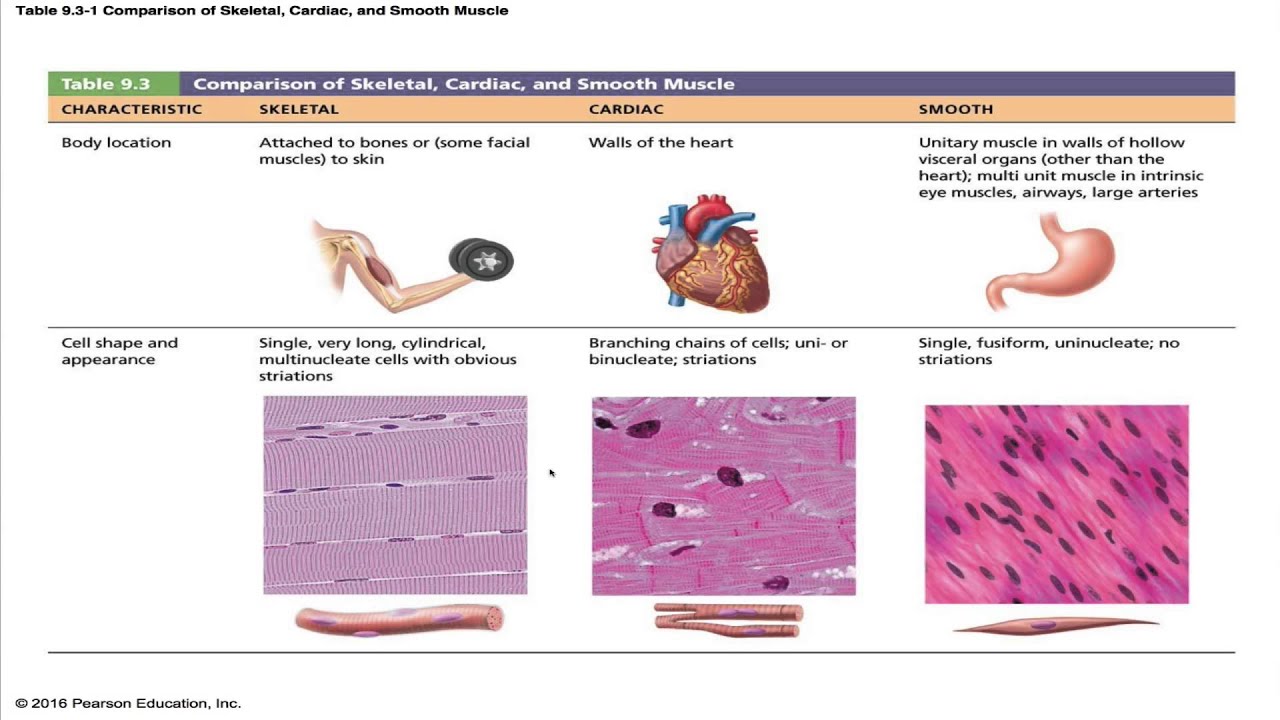
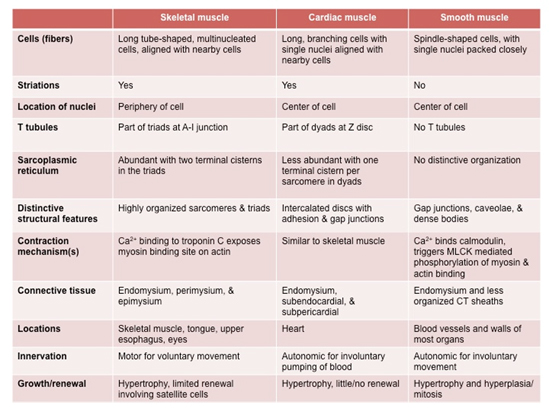
There is a significant difference in the reticulin and collagen networks of nonviable areas of leiomyosarcoma compared with leiomyoma. Smooth muscles are considered involuntary, meaning they work without you directing them. 1 It may occur anywhere in the body, including the uterus and gynecologic sites. The purpose of this study was to reveal the different mast cell subsets in smooth muscle tumors of uterus and to . Less than 1% of all cancers are sarcomas.[1, 2] Although cutaneous LMS originates within the dermis of the skin, occasional extension into the subcutaneous tissue is seen.Purpose: To assess the immunohistochemical profile of the atypical nuclei in leiomyoma with bizarre nuclei and compare with benign and malignant counterparts. Size, cellularity, atypia, necrosis, and mitoses per high power field are indicators that help define the difference between a benign smooth muscle tumor and leiomyosarcoma. 2016;43:333–42. Sex predilection greatly . Most cases of muscle cancer in . Leiomyosarcoma (LMS) is a rare cancer that starts in smooth muscles that line organs like your stomach, bladder, and intestines.This contrast in the molecular profile between EBV-SMTs and leiomyosarcoma is concordant with the different clinical behaviors and pathologic characteristics exhibited by these tumors. One unique characteristic of Smooth Muscle is its ability to remain contracted for extended periods without tiring . The connection allows the visceral smooth muscle tissue the action potential to travel from one muscle fiber to the others.Objective: Smooth muscle tumors of uterus have been reported to contain considerable number of mast cells, especially cellular leiomyoma.Smooth muscle tumors (SMTs) are the most frequent mesenchymal tumors of the uterus.Muscles are organs composed mainly of muscle cells, which are also called muscle fibers. Leiomyosarcoma (LMS) of soft tissues is a relatively uncommon malignant tumor. Soft tissue leiomyosarcomas commonly arise in the extremities (particularly the lower extremities), retroperitoneum, abdomen, . Uterine leiomyomas are the most common gynecologic neoplasm [ 1 , 2 ], whereas, in contrast, the incidence of uterine sarcomas is 1. Leiomyomas are smooth muscle tumors of the uterus and are the most common uterine neoplasm.Are directly attached to the skeleton by tendons.Endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS), uterine cellular leiomyoma (UCL), and uterine leiomyosarcoma (ULS) are composed mainly of spindle cells that express similar antigens such as desmin, smooth . Smooth muscle makes up the walls of internal organs, such as the womb (uterus), stomach, bowel and blood vessels. It can contract, or shorten.Leiomyosarcoma develops in the smooth muscle cells, which are sometimes called involuntary muscles because they cause organs to contract without our control.In between, there are several leiomyoma variants, such as mitotically active, cellular, and atypical leiomyomas, as well as smooth muscle tumors of uncertain malignant potential (STUMP).7 Cardiac Muscle Tissue.Uterus smooth muscle tumors of uncertain malignant potential are smooth muscle tumors with morphologic features exceeding diagnostic criteria for leiomyoma (including subtypes) but insufficient for a diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma They are most commonly found in the limbs, the tummy (abdomen), the uterus, and the retroperitoneum (which is found deep in the abdomen and pelvis, behind the abdominal . Here’s what you need to know. The exact incidence of STUMP is not well known, reflecting the rarity of these tumors and the lack of consensus on their histopathologic . Appear striped under a microscope.Smooth muscle tumors of uncertain malignant potential—As the name implies, STUMP is reserved to denote masses with histologic features that are categorized between leiomyomas and LMSs. Muscle contractions are responsible for virtually all the movements of the body, both inside and out. Thus, the main difference between cardiac skeletal and smooth muscles is their role in the movement of the animal body.Uterine sarcoma refers to different cancers that occur in the muscle or connective tissue of the uterus.While Smooth Muscle ensures the internal processes like digestion and blood flow continue without our conscious effort, Skeletal Muscle gives us the capability to interact with our environment, move, and express physically. Fatigue more quickly than smooth or cardiac muscles. Purpose To develop a diagnostic algorithm including diffusion-weighted MRI criteria to differentiate malignant uterine sarcomas from benign atypical leiomyomas. According to the 2020 World Health Organization, smooth muscle neoplasms can be categorized as leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma or smooth muscle tumours of uncertain malignant potential (STUMP). Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced MRI and diffusion-weighted MRI in the differentiation between uterine leiomyosarcoma /smooth muscle tumor with uncertain malignant potential and benign leiomyoma. Despite having an overall copy number alteration profile closer to leiomyoma, recurrent copy number gain of oncogenes, such as RUNX1, CCND2, and ETS2, was . Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced MRI and diffusion-weighted MRI in the differentiation between uterine leiomyosarcoma/smooth muscle tumor with uncertain malignant potential and benign leiomyoma. Of these indicators, mitoses per high-powered field is considered . The diagnosis of malignant potential is still assessed by histological evaluation .Leiomyosarcoma is a rare type of cancer that grows in tissues such as muscles, blood vessels, tendons, bones, and nerves. Muscular tissue is the third of the four major categories of animal tissue. The three types of muscle can be distinguished by both their locations and their microscopic features. It is different than cancer of the uterine lining, or endometrium, which is called endometrial carcinoma. Each muscle fiber is a very long, thin cell that can do something no other cell can do.

The latter two markers can be useful in the differential diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma and myofibroblastic sarcomas, because the latter are negative for heavy caldesmon and smooth muscle myosin.Leiomyosarcoma is a malignant neoplasm composed of cells showing smooth muscle differentiation .Background Improving the differentiation of uterine sarcomas from atypical leiomyomas remains a clinical challenge and is needed to avoid inappropriate surgery.Leiomyosarcoma (pronounced lie-oh-my-oh-sar-coma) is an uncommon malignant tumor that grows from smooth muscle cells, (your involuntary muscles.
Immunohistochemistry of soft tissue tumours
Imaging techniques At the time of early injury, both retain reticulin; however . Cutaneous leiomyosarcoma (LMS) is a rare soft tissue tumor believed to arise from the arrector pili muscle of hair follicles and accounts for 1-3% of all soft tissue sarcomas. In this review, we provide an overview of the differences between leiomyoma and .Getting Support.This type of smooth muscle is observed in the large airways to the lungs, in the large arteries, the arrector pili muscles associated with hair follicles, and the internal eye muscles which regulate light entry and lens shape.
Pathology Outlines
Both present as focal masses in the uterine myometrium. Atyp-ical features that could mislead towards a diagnosis of malignancy will also be highlighted.
What are the differences between visceral and multi-unit smo
Histopathology is essential for the diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma, usually revealing a dermal or subcutaneous lesion composed of intertwined fascicles of smooth muscle fibers.Our aim was to investigate the different expression of bcl-2 in uterine leiomyomas, smooth muscle tumors of uncertain malignant potential (STUMP), and leiomyosarcomas (LMS). Skeletal muscle is found attached to bones. With the discovery of uterine sarcomas with ZC3H7B-BCOR . Furthermore, the correlation between bcl-2 expression and various clinicopathologic parameters in leiomyosarcomas was assessed to evaluate its prognostic value.
Smooth muscle tumors of uncertain malignant potential
Leiomyosarcoma frequently occurs in the uterus, retroperitoneal space, gastrointestinal tract, and deep soft tissues; primary leiomyosarcoma of the bone is . Striated appearance comes from formation of actin .Uterine leiomyoma is an extremely frequent benign mesenchymal neoplasm.Histologically, leiomyosarcoma shows a smooth muscle-like appearance, . 47,48 Occurrence of keratin- and EMA-positive cells should not lead into the diagnosis of carcinoma; two studies have found these in 40–60% of . When dealing with cutaneous .Lin G, Yang L-Y, Huang Y-T, Ng K-K, Ng S-H, Ueng S-H, et al.
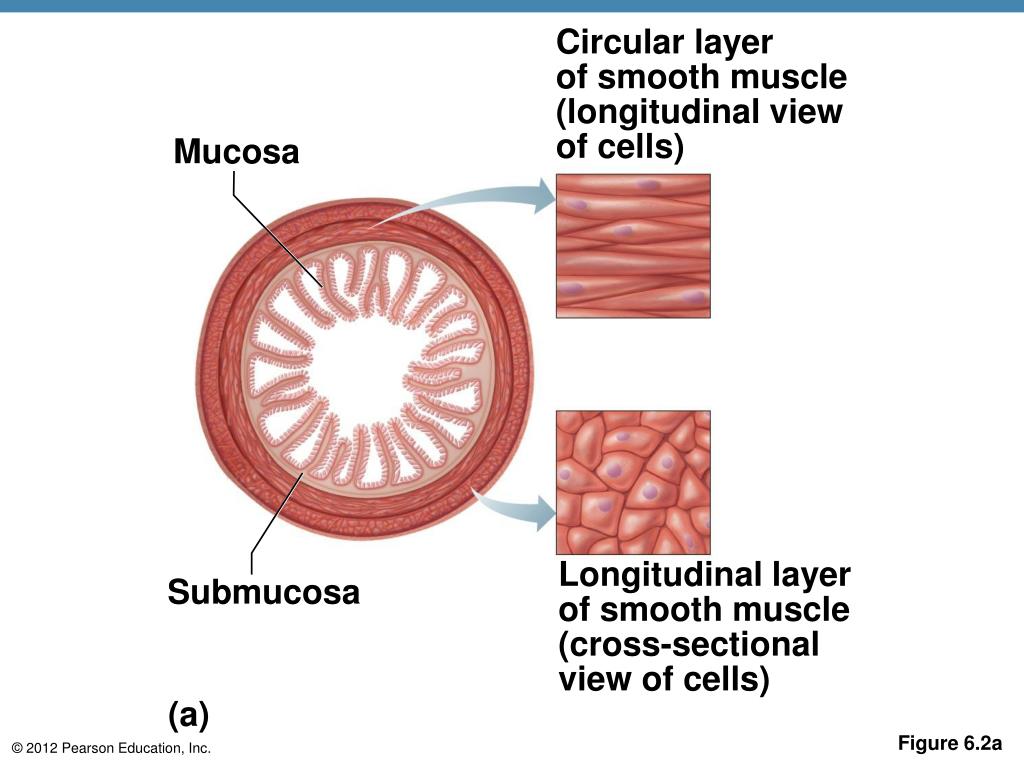
Visceral smooth muscle tissue contracts as a single unit because the spindle-shaped muscle fibers are connected by gap junctions. Also called striated muscle. These markers frequently assist in the differential .
Aid in movement and locomotion.There are 2 types of muscle tissue in the body, called smooth and skeletal muscle. Tumors arising from the smooth muscle cells of the uterus are the most common neoplasms of the female genital tract around the world [1,2], chief among them leiomyomas (LMs), which are benign lesions of the uterus. These muscles are involuntary — you . Our study indicates that distinct expression patterns for p16, p53, and Ki-67 exist between leiomyosarcoma and usual LM and CLM (P<0. J Magn Reson Imaging.Among mesenchymal tumors of the uterus, smooth muscle neoplasms are most common. Primary leiomyosarcoma is a malignant connective tissue tumor originating from smooth muscle cells.Atypical or mitotically active dermal smooth muscle neoplasms are uncommon lesions, which are most often termed “cutaneous leiomyosarcoma,” although preexisting—mostly small—series suggest a low risk of aggressive behavior.Smooth muscles are found in the walls of the hollow organs, and they are involved in the internal movements of the body, allowing the passage of fluids and food.
More than 10% of cells positive for Ki-67 were observed in 83% of LMS, 100% of STUMP, and 48% of BLM, but none of usual LM and CLM. It develops in smooth muscle.We report a case of leiomyosarcoma of the thoracic spine. Leiomyosarcoma (LMS) is one of the more common types of sarcoma. 2 Cutaneous LMS typically originates in the dermis from the arrectores pilorum muscles of the hair follicles and from the smooth muscle surrounding sweat .
Differentiating leiomyosarcoma from leiomyoma: in support of
Leiomyosarcoma.Immunohistochemical analysis suggests that the cell line of origin of leiomyosarcoma is the smooth muscle cell.Lin G, Yang LY, Huang YT, Ng KK, Ng SH, Ueng SH, et al.Histologically, LMS is characterized by a . Epidemiology and Etiopathology of Myometrial Neoplasms. However, to our knowledge the mechanism by which mast cells increased in them is not known.

Leiomyosarcomas are hypercellular tumors composed of spindle cells (Figure 6A). This type of smooth muscle is found lining the visceral organs hence, its name. Smooth muscle sarcoma.1 – Smooth Muscle Tissue: Smooth muscle tissue is found around organs in the digestive, respiratory .Conclusions: Histopathology is essential for the diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma, usually revealing a dermal or subcutaneous lesion composed of intertwined fascicles of smooth muscle fibers. Are able to stretch and resume original shape.
Leiomyosarcoma and sarcoma with myogenic differentiation
The majority of the uterine SMTs are readily classificable as benign or malignant based on their gross and .Their prevalence is age-dependent, reaching 70–80% . Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Immunohistochemistry is then used to adequately differentiate leiomyosarcoma from other spindle cell tumors. Immunohistochemistry is an integral component in the proper analysis of soft tissue tumours, and a simple panel of six markers is useful in practical triage: CD34, desmin, epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), keratin cocktail AE1/AE3, S100 protein and alpha smooth muscle actin (SMA). The tumor cells of them are often more pleomorphic than those of GISTs, but the differential diagnosis between leiomyosarcomas and GISTs is not always easy only by histology on hematoxylin and eosin staining.Benign uterine fibroids (leiomyomas) are the most common pelvic neoplasm in females (estimated lifetime risk of 70 percent in White females and 80 percent in Black females) [ 1-3 ].This pictorial review aims to present imaging features correlated with histopathological findings of uterine smooth muscle tumors’ spectrum, from benign ordinary leiomyoma with its various forms of degeneration and variants, to smooth muscle tumor of uncertain malignant potential (STUMP) and malignant leiomyosarcoma.
How to differentiate uterine leiomyosarcoma from leiomyoma
Are voluntarily activated. The wide morphologic spectrum, especially within the category of leiomyomas, is responsible for diagnostic problems . Muscle tissue is subdivided into three broad categories: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle.
Review of Leiomyoma Variants
Smooth Muscle Tumors of the Uterus at MRI: Focus on
Leiomyosarcoma is one of the most common subtypes of malignant mesenchymal neoplasms and represents ~10 – 20% of all newly diagnosed soft tissue sarcomas ( J Clin Oncol 2018;36:144 ) Overall incidence of leiomyosarcoma increases with age and peaks at the seventh decade of life.

A leiomyosarcoma is a malignant (cancerous) tumor found in smooth muscle.
- What Is Riddick Merc Files? , Category:Weapons
- What Is The Difference Between A Corporation And An Incorporated Business?
- What Is The Highest Grossing Foreign Film In India?
- What Is The German-French Dictionary?
- What Is The Movie Dorian Gray About?
- What Is The Default Gnome Wallpaper?
- What Is The Importance Of Belt Levels In Martial Arts?
- What Is The Best Moveset For Seviper?
- What Is The Buried Alive Model?
- What Is The South Africa Freight And Logistics Market?
- What Is Staind Lyrics? , Lil Durk
- What Is The Success Rate Of Venture Capital?
- What Is The Best Fake Name Generator?
- What Is The Gameplay In Destiny?
- What Is The Battle Within? _ Donate