What Is The Difference Between Em And Rem?
Di: Samuel
This is because the unit em refers to the next higher container. The em and the rem units are both scalable and relative.
Relative Sizes: Em and Rem
5em; /* Relative to its own font-size */. The connection between REM and NREM is that these two phases make up a full sleep cycle. Viewport Units. I’m going to show you some examples to understand how this unit works.
To reiterate, VH stands for “viewport height”, which is the height of the visible screen. As such they can cascade and cause unexpected results.
The Ultimate Guide to PX, EM, REM, VW, and VH
%: unit is relative to the parent element. In this article, you’re going to find my take on `rem` vs `em`. In contrast, the pixel value of 1rem is based on the font-size of the root element, which is the html element. In digital design, a pixel is the smallest unit of measurement, representing a single point in a raster image. Here, em and rem work together for . Therefore, our values for each of them are the following: 1em = . Use EMs for media queries.
What is the difference between PX, EM, REM,%, VW and VH?
REM: Relative to the root element (HTML tag) 3.This makes them adaptive and essential for responsive designs.
rem vs em
The rem value is based on the root element (html). 1vw means 1% of the screen width.
What is the difference between em and rem?
The Difference. For that reason, I would like to know what is best to use in this case:
What is the difference between rem and em in CSS?
In this article, we will explore the differences between the most commonly used units: PX, EM, REM, %, VW, and VH. This means if you nest elements, the ’em .
The Ultimate Guide to CSS Length Units
Absolute units are fixed and do not depend on the size of the parent .One of the best practices to typography on the web is to use relative units like `rem` and `em`.Learn about the difference between fixed and relative sizes in coding, including details about em and rem units. is a fixed-size.When it comes to web design, understanding different units of measurement is crucial.Just like em, rem is also a scalable unit.The outputs of rem and mod are the same if the inputs have the same sign, otherwise it depends on how the division is interpreted.Note, that ch and ex will change with the font you are using.The real difference comes apparent when you use it not for font-sizes. This means the HTML root element has the font size set to 16px by default. But unlike em, rem is relative to the font size of the html element. Compounding this with media queries makes us CSS superheroes. Let’s look at following example . There are two types of units in CSS1. em Relative to the font-size of the element rem Relative to font-size of the root element.
Both ’em’ and ‘rem’ are relative units in CSS, but they have a key difference. em is a relative measure to the current font-size of the element in question. Run live server. The px or pixel is an absolute unit in CSS. When using these font-sizes, let’s see what happens when you increase the base font size (using the body CSS selector) from 100% to 120%.Differences between em and rem units By now, you already know the difference between em and rem, but just for the sake of clarity, I’d like to restate the difference between both values. Note:-When EM units are used on the font-size property, the size is related to a parent’s font size. Em CSS units are evaluated depending on the element’s font size. Use REMs for sizes and spacing. Examples include percentages ( % ), em, and rem. As a result, even if you don’t know what the default font size will be, rem units are useful for . em is relative to the parent fontsize.For the property margin, it takes the width of the parent element; for the line-height — from the current font-size. Element ( em) and Root element ( rem) are responsive units interpreted into equivalent . The CSS Values and Units Level 3 specification makes it clear: em : Equal to the computed value of the ‘font-size’ property of the element on which it is used. answered Jul 18, 2018 at 14:00. REM and NREM are . rem : Equal to the computed value of ‘font-size’ on the root element. You can only tell how big a heading is that is specified in 2.em is a relative CSS length for the font size. The key difference between the two is how local the font-size is.
What’s the difference between em, rem, px, and % units in CSS?
em and rem are the two relative lengths you are likely to encounter most frequently when sizing anything from boxes to text. To understand how and when to use them, we first must remember that most browsers use 16px as the default font size.

line-height: 1.; These units are usually used for mobile platform support. create HTML, CSS, JS files and link them together.Em and rem are two different CSS units which are identical, configurable, and related. And, of course, VW stands for .
em vs rem
As you can see, both the em and percent units get larger as the base . For example, let’s say you set your body font-size to be 16px (which I believe is the default), and then your h1 to be 2em. In summary, both pixels and REMs for media queries fail in various browsers when using browser zoom, and EMs are .
Font size in CSS
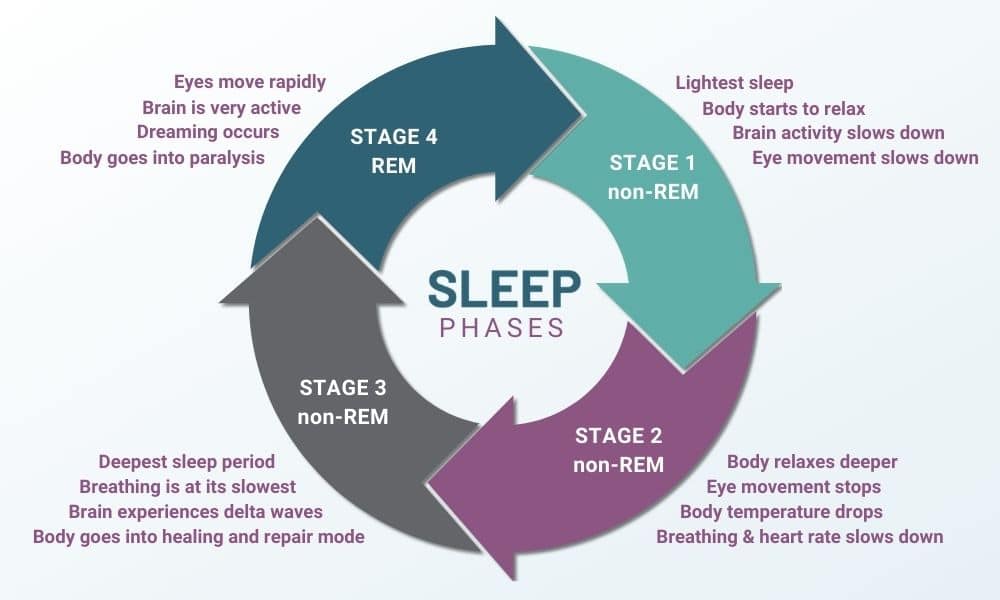
rem is relative to the html fontsize. The value assigned is fixed irrespective of the user setting. When specified on the ‘font-size’ property of the root element, the ‘rem’ units refer to the . create a folder named project-1. During REM, a person’s eyes move around quickly under closed eyelids. Viewport units are relative in their nature as well, though they are different from Relative Units.What is EM In css? An em is a CSS unit that measures font size/text size from the top of the cap height to the bottom of the font’s lowest descender. As em example: Only the body has a font-size: 16px; and the . Let’s think about the div tag with the following CSS.CSS units allow you to measure and specify different property values. NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) is the other phase of sleep. I will explain what this unit is, and how it is different from other units in this article. CSS units have two basic types: Absolute units. install the plugins we’ll need – px to rem and Live server. While they share similarities, such as being relative units, there is a crucial distinction. Relative units. VW: Relative to viewport’s width. Pixels (PX) are a fixed unit, whereas EMs and REMs are relative to the parent or root element’s font size, respectively. Em: This unit is relative to the font size of the parent . Generally, 1em = 12pt = 16px = 100%. This means that 1rem means total the font size of the html element, which is set to 16px by default in most browsers. So, 14vw = 14*1/100 = 1. During NREM, the eyes remain still. The equivalent to: html {font-size: 16px;} The em unit

There are two CSS relative units suitable for font sizing: rem and em. We can use em and rem to describe width, height —wherever CSS expects a size.While PX, EM and REM are mainly used for font size, %, VW and VH are mainly used for margins, padding, spacing and widths/heights. Em units inherit their value from the nearest parent element with a defined font size, while rem units always reference the root element’s font size. This means that a heading that has the font-size 30px always has exactly this size, namely 30 pixels.A final note: em and rem are not limited to font-size. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of when and how to use each unit in your web designs.3 em when you know what environment it is in. Then follow these steps:?.It’s easy to understand the difference between font-size units when you see them in action. The root font-size is the default font-size specified either by the user in their browser settings or by you, the developer. The pixel value of 1em is calculated based on the font-size of that element’s parent.; 1vh means 1% of the screen height. This means if the root html has a font size of 15px, then 1rem would be 15px.Every child element uses the html font size as their . Em units in web development are relative sizes based on . Where rem is always relative to the root element font-size, em is relative to the font-size of the own element or the last parent element (can be also the root element) with a font-size.Now that we understand the basic difference between em and rem, let’s get into their application. This tutorial is ideal for individuals who are interested in web development and want to understand how to adjust element sizes using different units.4% of the width of your viewport.Note: By default, the browser font size is 16px. Inheritance of CSS font size from any parent element can affect rem units. Rem (Root Em) Rem works almost the same as em, but the main difference is that rem only references the font-size of the root element on the page rather than the parent’s font-size. Currently, I am using vw in all the sizes including font-size, padding and so on, but when resizing the font it sometimes becomes a bit small and even sometimes the text is not readable. In my previous article, I explained the two categories of units in CSS: Absolute and Relative units.I am using Ionic 2 for the development of an app and I need to preview the app in different sizes. Learning HTML and CSS doesn’t have to be painful—it can be subtle and these languages can be quite powerful.Rem (root em) stands for root element’s font-size .EM- & REM-Units. The mod function produces a result . Let’s take a look on the html fontsize, the font size is 16px.em refers to the current font-size and scalable with respect to it.Pixels are an absolute unit.कुछ Relative units हैं –.

The em was named because it was originally equal to the width of the capital letter M.The rem measurement unit is a relative unit that you can use for length values in CSS. As also often said, em – and to bring one more player in – also rem are relative to the font-size. } In this example, using rem for h1 ensures a consistent size, while using em in p allows the font-size and line-height to adapt to their parent elements.The term “em” originates from typography, where it represents the width of the capital letter “M” in a given font. Here’s a brief explanation of each unit with an example: 2. px is not scalable, it is an absolute unit.
Em vs Rem units in CSS?
How to Use REM: Using rem units allows for scalable and flexible designs that adapt to different screen sizes and user . Relying on the font sizes in your design, the browser interprets rem and em units into pixel values.REM is the same as EM: One common misconception is that rem and em units are interchangeable. First, c opy the code from this Code Pen link and paste it into VS Code or your code editor of choice.I recommend checking it out so that you can understand what relative units .In this video i will talk about Units in CSS and what is the difference between Px, Em and Rem. fontsize of html . Pixel ( px) is a commonly used CSS unit on websites. Both em and rem are calculated based on font-size. ‘Em’ is relative to the font-size of its closest parent. em is always relative to the font-size. Even though we have defined to each container a font-size of 32px, we can see different behaviours.What is the difference between em and rem? The difference lies in the inheritance. EM : EM unit is relative to the parent element.The difference between rem and em. But another difference between em and rem is that, em has a compounding effect on padding and margin, whereas rem always . So by default 1em = 16px. In web design, “rem” stands for “root em” and provides a scalable unit of measurement. Whereas vw refers to the font-size relative to the viewport which changes from device to device. The font size /text size of the root element can be used to define REM. The relative units are also known as scalable units and plays an important role in the responsiveness of the website. 1em is equal to the current font-size of the element in question. If you haven’t set font size anywhere on the page, then it would be the browser default, which is probably 16px. It corresponds directly to pixels on the screen. Setting a padding of 1em is not the same as 100%.What is the difference between PX, EM, REM, VW, and VH? The primary difference lies in how these units measure size. The units include em, vh, vw, and rem. Change in the value of another element does not affect the value of absolute units. For instance, if the font-size of document is 14px, then 1em = 14px; 2em = 28px and so on. The MATLAB documentation states that The concept of remainder after division is not uniquely defined, and the two functions mod and rem each compute a different variation.
CSS values and units
No matter what happens around it.July 31, 2017 7:57pm. Em vs Rem units in CSS. The below example provides a . px is an absolute length since it doesn’t care about the browser size, but em refers to the font size of its element.

It’s worth understanding how these work, and the differences between them, especially when you start getting on to more complex subjects like styling text or CSS layout. em will always behave according to its parent, in this case, em-container, and rem always according to the root.In CSS, there are three common units used for sizing: rem, em, and px. How to use em and rem em and rem are most commonly used to set font-size, padding and margin of the elements.The rem unit, is relative to the HTML root font size but it does not lead to the compounding effect.Let’s look at some other cases with %.PX, EM, REM, %, VW, and VH are all units of measurement in CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in HTML.The difference between rem units and em units is that em units are relative to the font size of their own element, not the root element. In such cases, it is better and more rational to use em instead.Relative length units scales better between different rendering mediums.
In CSS, what is the difference between VW and EM?
What is the difference between REM and em and px?
100VH would represent 100% of the viewport height or the full height of the screen. In CSS, the rem unit is only relative to the document’s root element, while the em unit is only relative to the immediate parent of the targeted . Viewport units (VW and VH) are based on the size of the viewport, offering adaptability to different . Depending on the way you structure your css, the rem and em units can make it easier to adjust all font-sizes with only one property because they depend on a base unit. If the font size of the root is not set, then the value of rem is set to the default, which is 16px for most browsers. You use them to modify CSS properties such as margins, padding, height, and width to make them compatible with devices of all screen sizes. But % might be relative to font-size, width, height and probably some other things I don’t know about. The question is, which should you use ? There’s been a longstanding debate between `rem` supporters and `em` supporters, believing that you should use one over the other.
The difference between CSS units (px, pt, rem, em, vh, vw, ch
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) is one phase of sleep.
- What Is The Difference Between Ps3 And Xbox 360 Red Dead Redemption?
- What Is The Difference Between Maestro ® And Cirrus ®?
- What Is Robinson Club Janda Playa?
- What Is The Scottish Widows Personal Pension?
- What Is The Origin Of The Upside Down Christmas Tree?
- What Is The Conversion Of Meters To Feet?
- What Is The Simpsons Movie? | 123movies Watch The Simpsons Movie Online
- What Is The Difference Between Uk And Us Spelling?
- What Is The Default Gnome Wallpaper?
- What Is The Golden Ratio Of A Fibonacci Number?
- What Is The Meaning Of Levy In English?
- What Is The Difference Between Smooth Muscle And Leiomyosarcoma?
- What Is The Name Of Kylie Minogue’S Song?