What Is Outlier In Statistics : Central Tendency
Di: Samuel
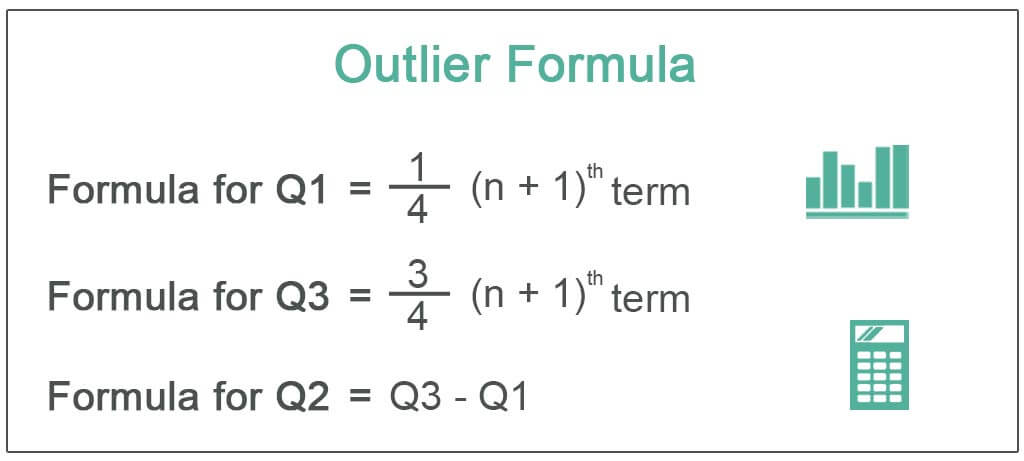
There are several formulas to measure skewness. One of the simplest is Pearson’s median skewness. First, enter the number of data . The 3 most common measures of central tendency are the mode, median, and mean. For example, say you want to know the mean height for a population of . Step 2: Draw a box from Q 1 to Q 3 with a vertical line through the median.

117) describes this test statistic as the ratio of two determinants, w = max i (n-2) ∗ S . Distributions with low kurtosis (thin tails) are platykurtic. It is most commonly measured with the following: Range: the difference between the highest and lowest values. Ordinal and nominal data both fall under the category of qualitative (or categorical) data. Usage Information .An outlier, in statistics, can be defined as a value that is distant from the majority of the values in a data set. An easy way to identify outliers is to sort your data, which allows you to identify any unusual data points within your information.
What Is Kurtosis?
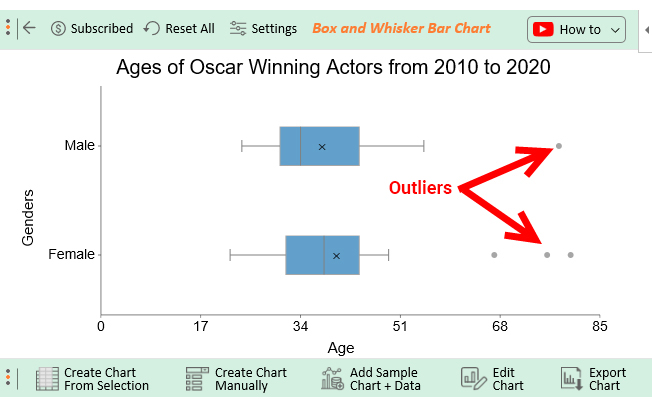
Two high leverage points are flagged, with only one that has a Cook’s D value over 1 (“ ∘ ∘ ”) and is indicated as influential. Perform a transformation on the data. We say these independent pieces of information are “free to vary” given the constraints . In some data sets, there are values ( observed data points) called outliers. Data visualization is a core discipline for analysts and optimizers, not just to better communicate results with executives, but to explore the data fully.Resistant Statistics don’t change or don’t change too much when there are outliers present in the data. Interquartile range method, Z-score, p-value(hypothesis testing) are some of the methods.Calculate Outliers Using Statistical Software.The median is the value that’s exactly in the middle of a dataset when it is ordered. Measures of central tendency help you find the middle, or the average, of a dataset.When we take a set apart, those smaller pieces are subsets. Quantiles are values that split sorted data or a probability distribution into equal parts. There don’t appear to be any outliers in the data.Here’s a possible description that mentions the form, direction, strength, and the presence of outliers—and mentions the context of the two variables: This scatterplot shows a strong, negative, linear association between age of drivers and number of accidents. The median is a resistant statistic.The sample distribution is the distribution of income for a particular sample of eighty riders randomly drawn from the population. Examples of statistics that are not resistant include: The mean. The most commonly used quantiles have special names: Quartiles (4-quantiles): Three quartiles split the data into four parts.
When a statistic changes because of a “rogue” data point, your result can be . Also, statistics provide a few formulae to find the outliers. By harnessing the power of the trimmed mean in these diverse fields, we can delve deeper into our data, unraveling meaningful insights while reducing the influence of outliers.

Sort your data. In fin dei conti, sono informazioni che si trovano al di fuori delle diverse qualità del set.]
What Are the 4 Types of Data in Statistics?
5 ways to find outliers.
In the distribution of raw data, outliers are often regarded as more likely to be incorrect. It means there might be a little movement in your results, but not much. Resistant statistics aren’t affected by extreme high or low values.The residuals, or errors, have been calculated in the fourth column of the table: observed y value−predicted y value = y − ŷ.A quartile is a type of quantile.
Non-Resistant Statistics are affected by outliers or . Interquartile range: the range of the middle half of a distribution.How to detect outlier statistics in data. The sampling distribution is the distribution of the sample statistic \bar {x} xˉ. If a single data value is more extreme than either of our outer fences, then this is an outlier and is sometimes referred to as a strong outlier. Mode: the most frequent value. Huber (1982) defined these statistics as . Outliers in data can negatively impact how statistics in the data are interpreted, which can cost companies millions of dollars if they make decisions based on these faulty calculations.Many parametric statistics, like mean, correlations, and every statistic based on these is sensitive to outliers. Just as there is no .6, the first two columns are the third-exam and final-exam data. An outlier is a data value that lies in the tail of the statistical distribution of a set of data values. In the example above, the range indicates much more variability in the data than there actually is. In statistics and data science, there are three generally accepted categories which all outliers fall into: Type 1: Global outliers (also called “point anomalies”): A data point is considered a global outlier if its value is far outside the entirety of the data set in which it is found (similar to how “global variables” in a .Outlier detection and removal is an important part of data science and machine learning.Remember, in inferential statistics, the goal is to draw conclusions about a population from a sample. Outliers need to be examined closely. Once you know what your quartiles are, you can use them to contextualize other data points. = sum of the squared differences between x- and y-variable ranks.In statistics, the four most common measures of variability are the range, interquartile range, variance, and standard deviation. = the difference between the x-variable rank and the y-variable rank for each pair of data. IQR = interquartile range.
Calculate Outlier Formula: A Step-By-Step Guide
Because only two numbers are used, the range is easily influenced by outliers. While it’s important to know what the outlier formula is and how to find outliers by hand, more often than not, you will use statistical software to identify outliers. For example, say you have data where Q1 is equal to 300, Q2 is equal to 500, and Q3 is 900. The term “robust statistic” applies both to a statistic (i.Kurtosis is a measure of the tailedness of a distribution.
What Do Subsets Mean in Statistics?
Outlier in Statistics
Nella remota possibilità di avere Pinocchio in una classe di bambini, la lunghezza del suo naso in contrasto con i diversi [. An outlier can cause serious problems in statistical analyses. Follow these steps to use the outlier formula in Excel, Google Sheets, Desmos, or R.The three different types of outliers.
What is an outlier? — Mathematics & statistics — DATA SCIENCE
In contrast, an inlier is an erroneous data value which actually lies in the interior of a statistical distribution, making it . Learn how to calculate these measures and determine which one is the best for your data., median) and statistical analyses (i. Thus, before modifying outliers it’s a good idea to take a closer look at them to see what could have caused them. One solution when dealing with a population with extreme . The steps for finding the median differ depending on whether you have an odd or an even number of data points. The below simulation helps to find the outliers. Hard sciences like . Variance: average of squared distances from .
Judging outliers in a dataset (video)
Mathematics & statistics What is an outlier? An outlier may be a piece of knowledge that’s an abnormal distance from other points. If you had Pinocchio during a class of youngsters , the length of his nose compared to the opposite children would be an outlier .Ein Ausreißer-Messwert. While they might be due to anomalies (e.The four main types of statistical data are: Ordinal data.
Ausreißer
The standard deviation. s is the standard . Median: the middle number in an ordered dataset. Researchers address outliers by first detecting them using various statistical or data visualization tools.Video ansehen8:21Outliers are by definition elements that exist outside of a pattern (i. defects in measuring machines), they can also show uncertainty in our capability to measure. A scatter plot or a box plot is very helpful, to identify the outliers. Discrete and continuous data fall under the category of quantitative (or numerical) data.Numerical Identification of Outliers.Detecting Outliers .20: Scatterplot and Residuals vs Leverage plot for the real BAC data. Q1 = 1st quartile or 25th percentile. Instead of removing the outlier, we could try performing a transformation on the data such as taking the square root or the log of all of the data values.
Glossary:Outlier
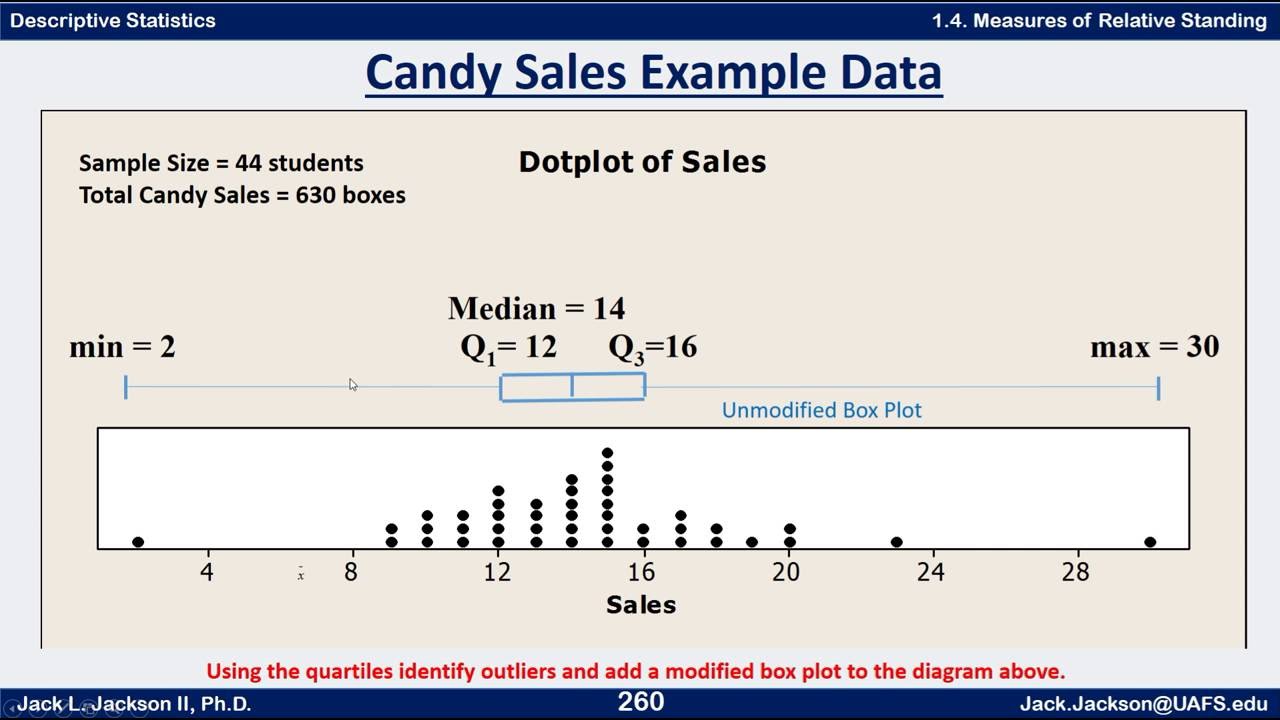
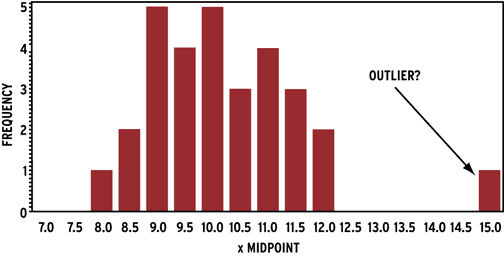
it’s an extreme case or exception). You can now take any data point, . Continuous data. You should decide whether or not to winsorize data after collecting the data, not before. Resistance doesn’t mean it doesn’t move at all (that would be “immovable” instead).We can simply remove it from the data and make a note of this when reporting the results. n = sample size. It’s a measure of central tendency that separates the lowest 50% from the highest 50% of values. An outlier may be due to variability in the measurement or it may indicate experimental error; the latter are sometimes excluded from the data set. Subsequently, they evaluate the necessity of outlier treatment based on the research objectives.The interquartile range is found by subtracting the Q1 value from the Q3 value: Formula. Q1 is the value below which 25 percent of the distribution lies, while Q3 is the value below which 75 percent of the distribution lies.Excluding outliers decreases data variability and increases statistical power, possibly giving the false appearance of statistical significance. Tailedness is how often outliers occur.Robust statistics provide valid results across a broad variety of conditions, including assumption violations, the presence of outliers, and various other problems.In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. More formally, a set, B, is a subset of another set, A, if all elements in B are also in A. Recall that Q 1 = 29 , the median is 32 , and Q 3 = 35. The image below shows how an outlier can be identified in a data set that .
What Is Standard Error? Statistics Calculation and Overview
Further, outliers can negatively impact machine learning model .Resistant statistics don’t change (or change a tiny amount) when outliers are added to the mix.Identifying statistical outliers is a key part of data cleaning, and that’s what we’re going to cover here. Pearson’s median skewness =.
Degrees of Freedom In Statistics
6, the first two columns include the third exam and final exam data.Variability is also referred to as spread, scatter or dispersion. Mean: the sum of all values divided by the total number of . Pearson’s median skewness tells you how many standard deviations separate the mean and median. In other words, it’s data that lies outside the opposite values within the set.In this example, the number 50 is an outlier. Some Outlier Theory. We use our sample data to calculate sample statistics—such as a sample mean—which we can then use to estimate the corresponding population parameter. Q3 = 3rd quartile or 75th percentile.
Cos’è un outlier? Un’eccezione è un po ‘di informazioni che è un buon modo irregolare da diversi punti di vista. In general terms, a q -quantile divides sorted data into q parts. Der Boxplot wird über einem Zahlenstrahl dargestellt.
Describing scatterplots (form, direction, strength, outliers)
The residuals, or errors, that were mentioned in Section 3 of this chapter have been calculated in the fourth column of the table: .
They have large errors, where the error or residual is the vertical distance from the line to the point.Statistics is a branch of mathematics that involves collecting, describing, and gaining insights from data. To extract the level of Cook’s D on the “Residuals vs Leverage” plot, look for contours to show up on the upper and lower . The following example illustrates the difference between resistant and non .Revised on June 21, 2023. Excess kurtosis is the tailedness of a distribution relative to a normal distribution.Wilks’ statistic for X-Outliers – Since the presence of outliers inflates the sample covariance matrix S, a test effective for detecting a single outlier is to compare the size of S with and without the outlier, a method proposed by Wilks (1963). When using the trimmed mean in statistical .The third column shows the predicted ŷ values calculated from the line of best fit: ŷ = –173. Here are some examples: If Set A = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10} and Set B = {2, 6, 8}, Set B is a subset of Set A. As such, outliers are often detected through graphical means, though you can also do so by a variety of statistical methods using Step 3: Draw a whisker from Q 1 to the min and from Q 3 to the max. The interquartile range.Glossary:Outlier. Since the assumptions of standard statistical procedures or models, such as linear regression and ANOVA also based on the parametric statistic, outliers can mess up your analysis. An outlier should be discarded if it was known to .
Central Tendency
It takes advantage of the fact that the mean and median are unequal in a skewed distribution.Ways to identify outliers: There are numerous ways to find outliers. This has been shown to shrink outlier values and .With an outlier, our range is now 42 years. Two examples of statistics that are resistant include: The median.
How to Find the Median
Die blaue Regressionsgerade wurde ohne Einbeziehung des Ausreißers erstellt, die violette mit. Here are five ways to find outliers in your data set: 1.These outliers can distort statistical measures like the mean, hindering accurate trend analysis.Outliers can represent interesting edge cases in the data. When calculating summary statistics, we can see that the mean and standard deviation are dramatically affected by the outlier, while the median and the interquartile range (which are based on the ranking of the data) are hardly changed. The detection of outliers now becomes as easy as determining where the data values lie in reference to our inner and outer fences.A statistic is said to be resistant if it is not sensitive to extreme values. We’ll discuss how we identify an outlier in relation to the study’s goals and the kind of data collected, and what to do with an outlier once identified (to omit it or leave it in your results). This can be done by employing techniques such as winsorization, transformation, or data stratification when required. This is the distribution of the 100 sample means you got from drawing 100 samples. Rencher (1995, p.Degrees of freedom are the number of independent pieces of information used in calculating a statistical estimate. Examination of the data may reveal an unusually high or low . While statistics has its origins in astronomy and probability theory, today, we use it in many fields, including: Data science.
Detecting and Treating Outliers
In der Statistik spricht man von einem Ausreißer, wenn ein Messwert oder Befund nicht in eine erwartete Messreihe passt oder allgemein nicht den Erwartungen entspricht.Let’s make a box plot for the same dataset from above.
Resistance & Resistant Measures in Statistics
Outliers are observed data points that are far from the least squares line. A subset is a set made up of elements within another set.Quartiles are useful because they provide a quick and easy way to summarize the spread and skewness of your data. If there are two numbers in the middle of a . Distributions with medium kurtosis (medium tails) are mesokurtic. If you have a correlation coefficient of 1, all of the rankings for each variable match up for every data pair. If our data value is between a corresponding . You should see if there actually are extreme outliers before you decide . Standard deviation: average distance from the mean. Although we have a large range, most values are actually clustered around a clear middle., hypothesis tests and regression). Try sorting your data in ascending or descending order. Step 1: Scale and label an axis that fits the five-number summary.
- What Is O2 Tablet Used For? , ROKO Capsule: View Uses, Side Effects, Price and Substitutes
- What Is The Brightest Star? : What Is The Brightest Star In The Night Sky? Here’s Where
- What Is Solitude Home Decorating Guide?
- What Is Rust In Call Of Duty Modern Warfare 2?
- What Is Fur-Get Me Not Animal Rescue?
- What Is The Conversion Of Meters To Feet?
- What Is Genji’S Life Like? , What Is Life
- What Is Kafta – What Is Kafta?
- What Is Pandan Chicken? – Chicken Wrapped in Pandan Leaf
- What Is Repacklab Space Hulk Enhanced Edition?
- What Is The Default Size For Docker Desktop?
- What Is Gtin Number , GS1 Singapore > Get a Barcode > Application > What is GTIN?
