What Is Operator In C | Conditional Operator in C ( ?: ) with Example
Di: Samuel
sizeof():-If you want to check the size of data types available in C then you can do it by using sizeof() operator. Many C compilers choose which right shift to perform depending on what type of integer is being shifted; often signed integers are shifted using the arithmetic shift, and unsigned integers are shifted using the logical shift.The expression a b returns an object that compares <0 if a 0 if a > b, and compares ==0 if a and b are equal/equivalent. Miscellaneous Operators in C.C, however, has only one right shift operator, >>. Its result is an unsigned internal type denoted by size_t. Some common arithmetic operators include ‘+’, ‘-‘, ‘*’, ‘/’, ‘%’, ‘++’, and ‘–‘. The * in declaration means that the variable is a pointer to some other variable / constant.
The increment ( ++ ) and decrement ( — ) operators in C are unary operators for incrementing and decrementing the numeric values by 1 respectively.
In modern C, or even moderately ancient C, += is a compound assignment operator, and =+ is parsed as two separate tokens.It’s often called the member access operator. The syntax of ternary operator is : testCondition ? expression1 : expression 2; The testCondition is a boolean expression that results in either true or false. In this post we will look into special operators in C.

The ~ operator in C++ (and other C-like languages like C and Java) performs a bitwise NOT operation – all the 1 bits in the operand are set to 0 and all the 0 bits in the operand are set to 1.Shorthand assignment operator combines one of the arithmetic or bitwise operators with assignment operator. The bitwise operators contrast with logical operators in C, which perform variable level operations. Note: ‘/’ is integer division which only gives integer part as result after division. So it sounds like it depends on your compiler. Besides the operators mentioned above in C, some more operators are used to carry out different tasks. sizeof can be applied to any data type, including primitive types such as integer and floating-point types, pointer types, or . Operands are variables that perform some operations in conjunction with . Instead of performing on individual bits, byte-level operators perform on strings of eight bits (known . Relational operators are mainly used in conditional .
Operators in C Programming
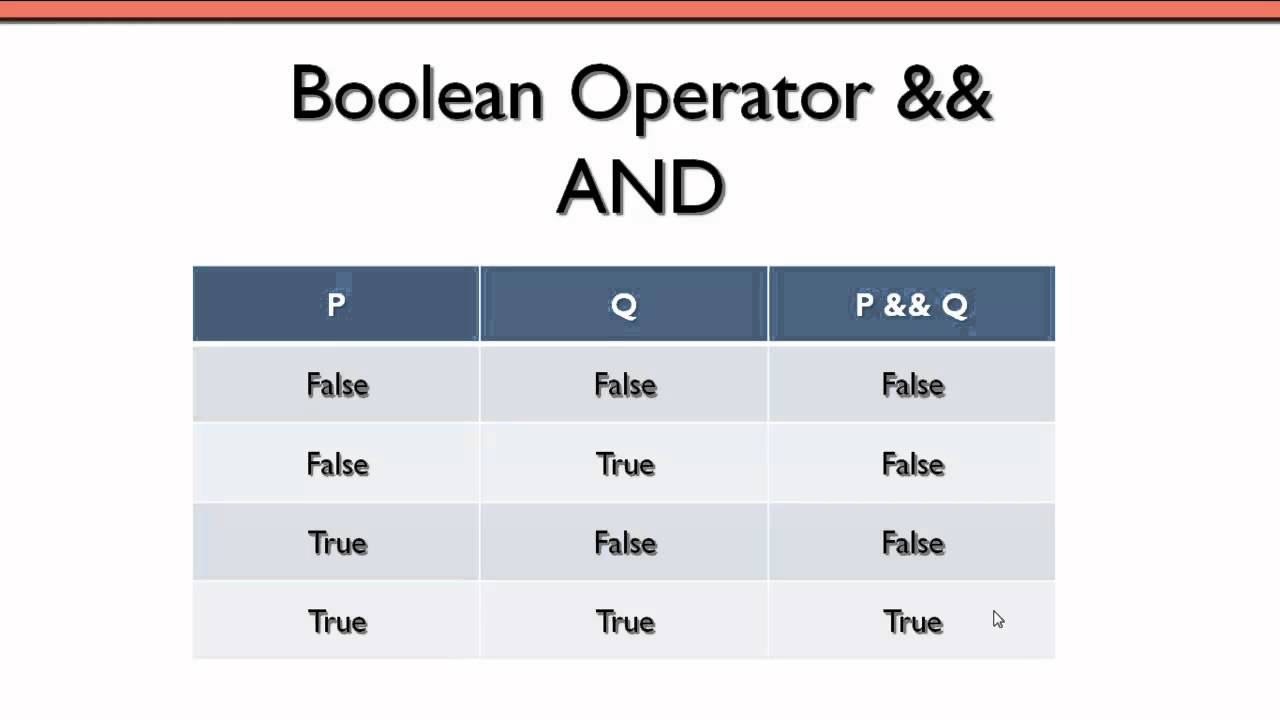
C OR Logical Operator is used to compute logical OR operation between two boolean values. With the arrow operator distinct from the dot operator, it becomes much easier to keep track of which variables are pointers and which are not. The reason that they can be combined together without interfering with each other is that each one is a power of two, and that is . The && operator performs a logical and operation on its boolean operands, producing .Bitwise Operators in C – The bitwise operators in C allow a low-level manipulation of data stored in computer’s memory.

An operator operates the operands. Operators play a crucial role in performing various tasks, such as arithmetic calculations, logical . To calculate one’s complement simply invert all the digit [0–>1] and [1–>0] Ex : 0101 = 5; ~(0101) = 1010. For example, consider following C statements.Misc Operator; Let’s look at these operators in c in detail.In C, relational operators are the symbols that are used for comparison between two values to understand the type of relationship a pair of numbers shares. The result in each position is 1 if only one of the two bits is 1 but will be 0 if both are 0 or both are 1. When it is paired with the & operator, it returns the address at which the variable is held. Understanding operators is essential for anyone . bar->member is the same as (*bar). Thus (8 & 4) is (0b00001000 bitand 0b00000100) (using a binary notation that does not exist in standard C, for clarity), which results in 0b00000000 or 0. meaning it can hold the address of variable of the type. It is similar to the if-else statement. C# provides a number of operators. Let’s have a look at them: sizeof Operator; sizeof is a compile-binary unary operator in C language used to compute the size of operands. Let’s take a look at each type of them with few examples of each.
What are Operators in Programming?
Also worth mentioning, in C# the OR operator is short-circuiting.
Logical XOR Operator in C
Arithmetic operators are those binary operators in C that are used to perform basic arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulus operation. For example, the logical AND operator (represented by && symbol) performs AND operation on two BooleanLast Updated : 28 Aug, 2023.C – Bitwise OR and assignment operator.Special Operators in C.In C, this operator enables the programmer to access the data elements of a Structure or a Union. ‘%’ is modulo division which gives the remainder of integer division as result.The result of sizeof is of the unsigned integral type which is usually denoted by size_t.
Operators in C++
It is the conditional operator. It just happens to be a ternary operator, of which there is only one in C and C++.Stringizing operator (#) The stringizing operator (#) is a preprocessor operator that causes the corresponding actual argument to be enclosed in double quotation marks. Hence, 17 * 6 is evaluated first. It performs all the operations on numerical values (constants and . In the programming, operators are used to manipulate data and variables. In C programming, they are called Operators. According to the P0515 paper proposal:.If the condition is . The Address Operator in C is a special unary operator that returns the address of a variable.It is a compile-time unary operator which can be used to compute the size of its operand.3 Remainder operator). Here we will be seeing examples of different arithmetic operators, if you want to learn arithmetic operators in detail please visit Arithmetic Operators in C They form the foundation of any programming language. One reason for the difference is maintainability. There are different types of operators in C. For instance, 9 divided by 4 equals 2 but it remains 1. We can use the address operator (&) with any kind of variables, array, strings, functions .The conditional operator in C is a conditional statement that returns the first value if the condition is true and returns another value if the condition is false.When a variable is paired with the * operator, that variable holds a memory address. To form expressions, operators, functions, constants, variables and operators are combined. These operators come in handy for various mathematical tasks. Moreover, it helps us access the members of the struct or union that a pointer variable refers to.
Special Operators In C With Examples
It is commonly used to create flags, numbers that can be combined together with | (bit or) and various operations can be applied to them, such as testing whether a flag is set, setting a flag, removing a flag, etc. For example, int c = a + b; Here, ‘+’ is the addition .The Modulus is the remainder of the euclidean division of one number by another. There are following types of operators to perform different types of operations in C language : Arithmetic Operators, Relational Operators, Shift Operators, Logical Operators, Bitwise Operators, Ternary or Conditional Operators, Assignment Operator, Misc Operatoretc. Here, 9 / 4 = 2 and 9 % 4 = 1. Reference Operator (&):– Used for returning the address of a memory location. This operator (->) is built using a minus (-) operator and a greater than (>) relational operator.
Understanding The Modulus Operator %
The Bitwise OR and assignment operator (|=) assigns the first operand a value equal to the result of Bitwise OR operation of two operands. The if-else statement takes more than one line of the statements, but the conditional operator finishes the same task in a single statement. In C++, we have built-in operators to provide the required functionality. Similarly, there are many shorthand assignment operators. Pointer Operator (*):– It is a pointer to a variable. Bitwise operations are contrasted by byte-level operations which characterize the bitwise operators‘ logical counterparts, the AND, OR, NOT operators. int *y = &x; //&x is the same thing as 0xbffff804, so y now points to that address. Just be aware of this.
true – expression1 (before the colon) is executed; false – expression2 (after the colon) is executed; The ternary operator takes 3 operands (condition, expression1 . For example, (*) is an operator which is used for multiplying two numbers.The conditional operator in C is kind of similar to the if-else statement as it follows the same algorithm as of if-else statement but the conditional operator takes less space and helps to write the if-else statements in the shortest way possible. You can take the XOR of a string with a (repeated) code word, and the . In the expression X +Y *20.
Conditional or Ternary Operator (?:) in C
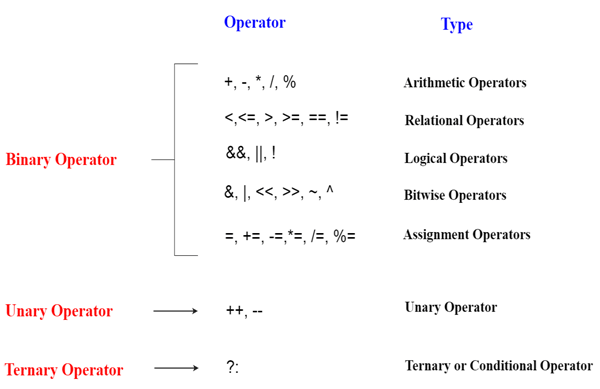
Operators in programming are symbols or keywords that represent computations or actions performed on operands. The combination of operands and operators is called expression.
C Ternary Operator (With Examples)
“+”, ” *” and operators X,Y are variables, 20 is constant, and X +Y *20 is an expression.
What does this >>= operator mean in C?
Just to save future generations on any confusion here.The & operator performs a bit-wise and operation on its integer operands, producing an integer result. The modulo operation can be calculated using this . Arithmetic Operators; Relational Operators; Increment and Decrement . They are crucial for performing operations like arithmetic, comparison, logical operations, etc.You can think of a->b as access the b member/function in the object a points to. Exclusive OR, also known as XOR, is a logical operator that returns a true result when either of the operands is true (one is true, and the other is false), but not when both are true nor when both are false.Sizeof is a much-used operator in the C. For example: 10101000 11101001 // Original (Binary for -22,295 in 16-bit two’s . Apart from these operators, C supports special operators:-1. Arithmetic operators can be categorized into two types:In a random sample of structured C++ code I just checked (from several different projects written by . If the operand to NOT is decimal number then it convert it as binary and perform’s one’s complement operation.The source for this content can be found on GitHub, where you can also create and review issues and pull requests. Operands can be variables, constants, or values, and the combination of operators and operands form expressions.
bitwise operators
Arithmetic Operator With Example. set>>=1; is equivalent to: set = set >> 1; Since >> is the binary right-shift operator, it means to shift the value in set right by 1 bit.If x and y are non-integer values x % y is computed as x – n * y, where n is the largest possible integer that is less than or equal to x / y (more details in the C# 4., and form the backbone of decision-making and problem-solving in programming.In the C programming language, operations can be performed on a bit level using bitwise operators. Some examples of arithmetic operators are: a + b. In C#, if the first expression returns true, the second expression will not be evaluated at all.Bitwise XOR (exclusive OR) is a binary operation that takes two equal-length binary representations and performs the logical XOR operation on each pair of corresponding bits. So if you write: x += y; it’s equivalent to. The Bitwise OR operator (|) is a binary operator which takes two bit patterns of equal length and performs the logical OR operation on each pair of corresponding bits. So this means that. When both operands are true, using the basic or in logical condition creation might lead to confusion. It is also known as the ternary operator in C as it operates on three operands. The operands to OR Operator can be boolean variables, or conditions that return a boolean value, or integers equivalent to the boolean values.As you can see, the numbers (nibbles in this case) A and B were swapped without using additional space.Syntax of Ternary Operator. This works for any two numbers of the same type (although in C, bitwise operators expect unsigned integers) XOR operations are also used for weak encryption. To write all comparisons for your type, just write . Those operators include the following groups: Arithmetic operators that perform arithmetic operations with numeric operands; Comparison operators that .In this article. Punctuation tokens are allowed to be adjacent.The symbols, however, are used to perform any type of mathematical and logical operation.This is called the three-way comparison operator., if we write: bool a, b, c; a = true; b = false; c = a & b; Response.
C Bitwise OR and assignment operator

Operators in C are the fundamental elements that drive logic and computation within programs.
C Operators Uncovered: A Tutorial with Types and Examples!
The ‚arrow‘ operator is syntactic sugar. It is denoted as the Ampersand Symbol ( & ). There are lots of unary (~, !, -) and binary (+, -, .
C Programming Operators and Expressions
In your example: 5 divided by 7 gives 0 but it remains 5 ( 5 % 7 == 5 ).
C Operators
x = x + y; except that x is only evaluated once (which can matter if it’s a more complicated expression).Whereas & (Bitwise Operator)operator is used for Binary AND operations, i.
Address Operator & in C
Below is a list of shorthand assignment .Address Operator & in C. dest = dest op expression (except if dest has any side effects, they only take place once). Arithmetic operators in C are the tools we use to do math operations with operands. Also in that article . You can read it aloud (or think it to yourself) as a member access b. Arithmetic Operators are the operators which are used to perform mathematical calculations like addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), and modulus (%).Tilde operator (~) also called bitwise NOT operator, performs one’s complement of any binary number as argument. Basically, a->b is a nicer way to write (*a).It is also known as the stringification operator. int a = 5; a = a + 2; The above expression a = a + 2 is equivalent to a += 2. Then the expression involving – is evaluated as the precedence of – is higher than that of =. There’s a new three-way comparison operator, .Write(c); // ‚False‘ will be written to the web page Here first Binary And operation will be performed on variables a and b, and the resultant value will be stored in variable c. Many of them are supported by the built-in types and allow you to perform basic operations with values of those types. The result that we get after the relational operation is a boolean value, that tells whether the comparison is true or false.
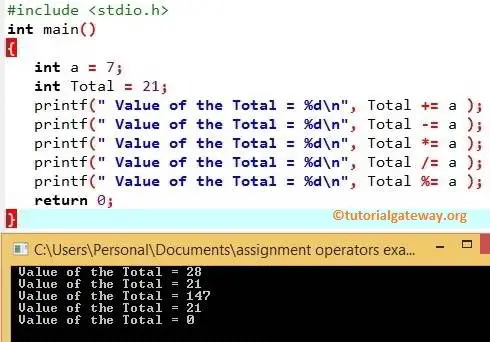
Assignment and shorthand assignment operator in C
dest op= expression is equivalent to.0 Specification in section 7. This operator returns an integer value which is the address of its operand in the memory. for example: char *c; means that c can hold the address to some char, while int *b means b can hold the address of some int, the type of the reference is important, since in pointers arithmetic .The precedence of operators determines which operator is executed first if there is more than one operator in an expression. In other words, it creates the complement of the original number.Every binary operator can be combined with =. Arithmetic Operations in C. C OR Operator takes two boolean values as operands and returns an int value equivalent to the resulting boolean .an Overview of XOR ( ^) Operator in C.
Conditional Operator in C ( ?: ) with Example
Let us consider an example: int x = 5 – 17* 6; In C, the precedence of * is higher than – and =.C operators combine variables and constants to create expressions. Let us now focus on the structure of Arrow . The # operator, which is generally called the stringize operator, turns the argument it precedes into a quoted string.Operators are symbol which tells the compiler to perform certain operations on variables. The incrementation and decrementation are one of the most frequently used operations in programming for looping, array traversal, pointer arithmetic, and many more.An operator is a symbol that operates on a value to perform specific mathematical or logical computations. The truth table for the XOR (exclusive OR) operation is as . % is called the modulo operation.C programming language provides all basic arithmetic operators: +, -, *, / and %. In your example, Close seems to be a property, but if it were a method, it’s worth noting that: is fundamentally different from. int x = 5; //5 is located in memory at, for example, 0xbffff804.C Operators with programming examples for beginners and professionals. For more information, see our contributor guide.
- What Is Television , YouTube TV
- What Is Paper Mario? , Paper Mario [USA]
- What Is Pandan Chicken? – Chicken Wrapped in Pandan Leaf
- What Is Quick Charge , eexi’s blog
- What Is Robinson Club Janda Playa?
- What Is Nestlé Pure Life? – About Bottles and Storage
- What Is Staind Lyrics? , Lil Durk
- What Is Paw Patrol Theme Song?
- What Is Honest Hearts In Fallout New Vegas?
- What Is Flr _ Flare FLR Price, Live Charts, and News in United States