What Is Molar Entropy? : Entropy
Di: Samuel
The molar entropy, in contrast, is given by
What is the precise definition of standard molar entropy?
That is, an element in its standard state has .

In statistical mechanics, configuration entropy is the portion of a system’s entropy that is related to discrete representative positions of its constituent particles. The standard molar entropy is usually given the symbol S o, and the units J mol −1 K −1 (joules per mole kelvin). Chemical, physical and thermal properties of ethylene, also called ethene, acetene and olefiant gas.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.
Entropy of Mixing
This can be seen in Figure 18.The standard free-energy change can be calculated from the definition of free energy, if the standard enthalpy and entropy changes are known, using Equation 13. where: s = specific entropy (J/kg) S = entropy (J) m = mass (kg) Entropy quantifies the energy of a substance that is no longer available to perform useful work. I understand the first one, but I can’t grasp the second one.
Appendix 5 lists S° values for many chemicals.In chemistry, the standard molar entropy is the entropy content of one mole of substance, under conditions of standard temperature and pressure (STP).The standard molar entropy of a substance is its molar entropy (units: J K-1 mol-1) when it is in its standard state at the specified temperature. For any element in its standard state, the value of entropy has a definite, non-zero value.14: ΔG° = ΔH° − TΔS°. constant pressure. One way of calculating ΔS for a reaction is to use tabulated values of the standard molar entropy (S°) The entropy of 1 mol of a substance at a standard temperature of 298 K.
What is the use of standard molar entropy?
The molar enthalpy of fusion is actually smaller for lead, because of smaller bonding energies between particles.34 Formula State of Matter Enthalpy (kJ/mol) Entropy (J mol/K) Gibbs Free Energy (kJ/mol) Ba 2TiO 4 (s) -2243. The enthalpy of fusion for water is 6. You might find the pressure quoted as 1 atmosphere rather than 1 bar in older sources. Unlike enthalpy or internal energy, it is possible to obtain absolute entropy values by measuring the entropy change that . This equation is also commonly written with the total number of moles: ΔmixS = −nR(χA lnχA +χB lnχB) (1) (1) Δ m i x S = − n R ( χ A ln.8 J K-1 mol-1}$ and $\pu{29.This partial molar entropy contribution (R ln X i) is what will influence phase stability and does not depend on the number of other components already existing in the solution under the ideal mixing assumption. ΔS° reaction = (4 S° NO + 6 S° H2O) – (4 S° NH3 + 5 S° O2)
15 Thermochemistry II Spontaneity, Entropy and Gibbs Energy
Entropy of gas at standard conditions (1 bar) Data from NIST Standard Reference Database 69: NIST Chemistry WebBook The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) uses its best efforts to deliver a high quality copy of the Database and to verify that the data contained therein have been selected on the basis of sound scientific .5144 BaCl 2 (s) -858. To convert heat values to joules per mole values, multiply by 44.The molar enthalpy and entropy of vaporisation and the boiling temperature of some simple liquids are presented in Table 18.What is the change in molar entropy of helium in the following process . (3) Δ μ i = RT ln a i Eq. Because entropy tells so much about . χ A + χ B ln.m is equal to ratio between the molar enthalpy of vaporisation and the boiling temperature, which leads to Eq. If ΔS° and ΔH° for a reaction have the same sign, then the sign of ΔGo depends on the relative magnitudes of the ΔH° and TΔS° terms.
Hydrogen
, 1984: CODATA Review value: S° gas,1 bar: 213.The standard molar entropy of any substance increases as the temperature increases. ΔS = q T = ΔHphase T.One way of calculating ΔS for a reaction is to use tabulated values of the standard molar entropy (S°), which is the entropy of 1 mol of a substance at a standard temperature of 298 K; the units of S° are J/(mol·K).Entropy changes during physical changes. When solids, liquids or gases are combined, the thermodynamic quantities of the system experience a change as a result of the mixing.Calculating ΔS from Standard Molar Entropy Values. Reason(R ) : The larger the complexity of mole.Unlike standard enthalpies of formation, the value of S o is an absolute.4408 BaCl 2 (l) -832. ΔS° reaction = Σn p S° products – Σn r S° reactants. The exercises cover topics such as calculating entropy changes, predicting spontaneity of reactions, and applying Gibbs energy to equilibrium. Because naturally you would think that $\ce{H2}$ would have a higher entropy than $\ce{Ne}$ because one mole of it is generally lighter. I have seen the equation that associates the heat capacity .0 J K-1 mol-1}$) is significantly larger than that of hydrogen ($\pu{130.
Standard Molar Entropy
2: Entropy Change for Melting Ice.
What is use of standard molar entropy?
This includes solid to liquid, liquid to gas and solid to aqueous solution. When a system receives an amount of energy q q at a constant temperature, T T, the entropy increase ΔS Δ S is defined by the following equation.For a given temperature, more states are available to be occupied, increasing the number of available microstates the system may occupy, and hence the entropy of the system.

Entropy is a measure of disorder. It is easily ignited and a flame can easily flash back to the source of the leak.You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Phase diagram included.The entropy change for a phase change at constant pressure is given by.-We will now discuss the uses or application of standard molar entropy: 1) . The table below shows the molar entropies for the noble gases. This is often because these liquids have .The molar heat capacity of hydrogen gas and deuterium gas are nearly the same, $\pu{28. Statistical thermodynamics defines the entropy of a system in the following way: S = k l n ( W) S = k\ ln (W) S = k ln(W) where: k – Boltzman’s constant, W – the number of ways in which the macroscopic thermodynamic state of the system can be realized through microscopic states.represents the equation for the entropy change of mixing. ΔG can predict the direction of the chemical reaction under two conditions: constant temperature and.) Definitions of standard states: For a gas, the standard state is as a . Ethylene, C2H 4 , is a highly flammable, colorless and noncorrosive gas with a sweet odor.2 J K-1 mol-1}$, respectively, but the absolute entropy of deuterium ($\pu{145. Standard molar entropies are listed for a reference temperature (like 298 K) and 1 atm pressure (i. Hence, the magnitude of ΔS Δ S for a reversible process such as a phase change is calculated.792 BaBr 2•2H 2O (s) -1366. In the general case of mixing non-ideal materials, however, the total final common volume may be different from the sum of the separate initial volumes, and there may occur transfer of work or heat, to or from the . There are 2 steps to solve . asked Apr 19, 2022 in Chemistry by aryam (122k points) class-12 ; chemical-thermodynamics-and-chemical .7 J K-1 mol-1}$).The specific entropy (s) of a substance is its entropy per unit mass. These large increases occur due to sudden increased molecular mobility and larger available .Up to a temperature of 0. Note that the use of 1 atm in this context is obsolete. For example, it may refer to the number of ways that atoms or molecules pack together in a mixture, alloy or glass, the number of conformations of a . In other words, it is a measure of how disordered a system is; When a system becomes more disordered, its entropy will increase; An increase in entropy means that the system becomes energetically more stable; For example, .0032 BaBr 2 (s) -757. (4) RT ln a i = RT ln γ i + .edu/echem1aCurriculum and ChemQuizzes dev. At the triple point, ice can exist together with both liquid water and vapor.) We can always determine the absolute value for S° (J K-1 mol-1) since we know the absolute zero of entropy (third law). The webpage also includes answers and explanations for the exercises, as well as links to . ΔS = qrev T (18.8024 BaBr 2 (g) -439.The term standard state is used to describe a reference state for substances, and is a help in thermodynamical calculations (as enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energy calculations). The change in the standard molar entropy of a reaction can be found by the difference between the sum of the molar entropies of the products and the sum of the molar entropies of the reactants.3 “Entropy vs.7 kJ/mol? O 86. Heat content data, heat of vaporization, and entropy values are relative to the liquid state at 0 °C temperature and 3483 kPa pressure.The table below gives thermodynamic data of liquid CO 2 in equilibrium with its vapor at various temperatures. Entropy is given the symbol S, and standard entropy (measured at 298 K and a pressure of 1 bar) is given the symbol S°.Configuration entropy.The molar volume of a mixture can be found from the sum of the excess volumes of the components of a mixture: = (+ ¯).The entropy (S) of a given system is the number of possible arrangements of the particles and their energy in a given system. (3) The chemical potential of component i in terms of the activity of component i. χ B) where the total number of moles is .The law of thermodynamics states that the molar entropy of a pure crystal at 0K is For enthalpy, absolute values (such as absolute zoro) bo determined, and thus it necastary to define a standard state for the scale For entropy, absolute values be determined, and therefore at necersary to define a standard sate. The temperature is not a part of the definition of . Solve any question of Chemical Thermodynamics with:-
Thermodynamics of Mixing
Standard Molar Entropy, S 0 The entropy of a substance has an absolute value of 0 entropy at 0 K.Increasing the molar mass of that specific element increases the entropy.Gibbs free energy, denoted G, combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value.Ethylene – Thermophysical Properties.Thermodynamics of Mixing is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.标准摩尔熵(standard molar entropy)是一个热力学和化学名词,指在标准状态下,1摩尔纯物质的规定熵。通常会用So的符号来表示。0K时,纯固体和纯液体的熵值等于零,仅仅是热力学中的规定,它没有涉及原子核内微观粒子状态的变化。在标准状态下,1mol物质的熵称为该物质的标准摩尔熵。
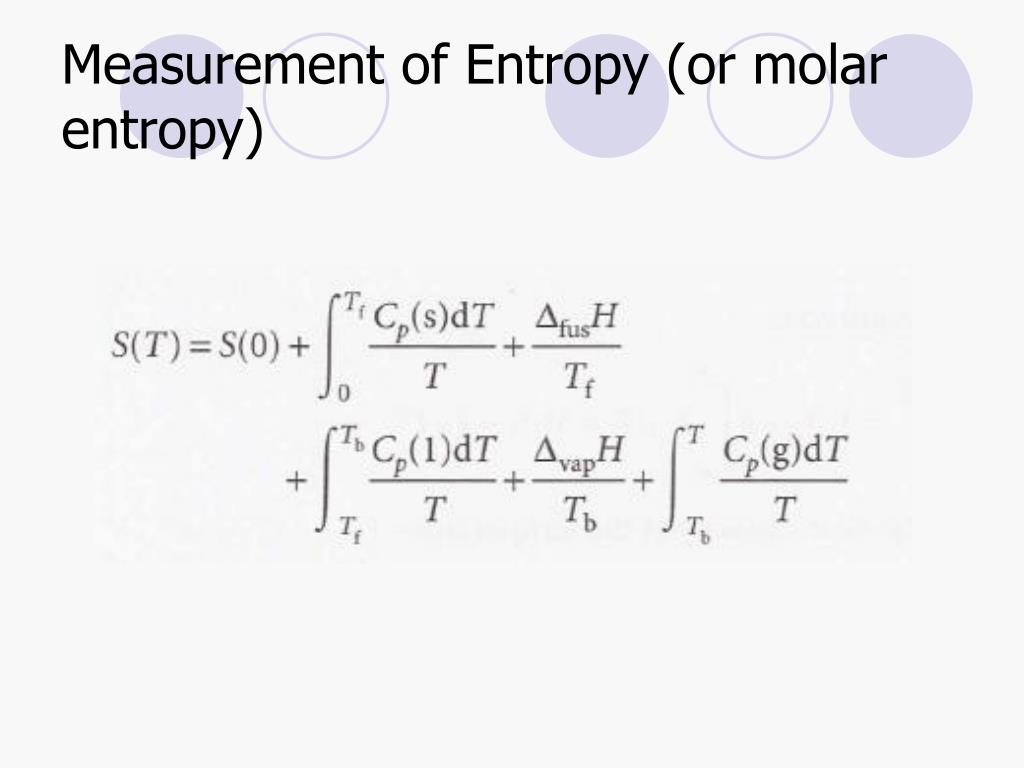
Measuring Entropy and Entropy Changes
1) Δ S = q r e v T.
Standard Molar Entropy and the Third Law Pt 5
, 1984: CODATA Review value: Δ f H° gas-393. It equals to the total entropy (S) divided by the total mass (m). One way of calculating ΔS for a reaction is to use tabulated values of the standard molar entropy (S°), which is the entropy of 1 mol of a substance at a standard temperature of 298 K; the units of S° are J/(mol•K). The ’standard state‘ is the state for the pure substance at 1 bar (1 bar = 10 5 Pa). Calculate the entropy change for . This module will discuss the effect that mixing has on a solution&.In chemistry, the standard molar entropy is the entropy content of one mole of substance, under standard conditions (NOT STP). My recollection from a long time ago is that it goes roughly like this: for each element, assume that its entropy goes to zero at 0 kelvin when it’s in some standard state
Entropy
Unlike enthalpy or internal energy, it is possible to obtain absolute .65°C given that AH vap = 28.

Question: Question 7 (1 point) What is the molar change in entropy of tetrachlorosilane when it boils at 57.
标准摩尔熵
I understand what the standard molar entropy is, and how to use it in calculations, but I’m interested in understanding exactly how it’s defined and measured. The change in free energy, ΔG, is equal to the sum of the enthalpy plus the product of the temperature and entropy of the system.kJ/mol: Review: Cox, Wagman, et al. Shields explains the Third Law of Thermodynamics and how to use standard molar entropy values in calculating entropy changes for chemical reactions.The entropy of mixing is entirely accounted for by the diffusive expansion of each material into a final volume not initially accessible to it., which is the entropy of 1 mol of a substance at a standard temperature of 298 K; the units of S° are J/(mol·K).1 J/mol-K O 104 J/mol-K O 98. the entropy of a pure substance at 298 K and 1 atm pressure).2 Some liquids deviate sharply from the rule.010: J/mol*K: Review: Cox, Wagman, et al.
79: J/mol*K: Review: .01 °C, the triple point of water, water normally exists as ice, except for supercooled water, for which one data point is tabulated here.3 Standard Molar Entropies. A table of standard molar entropies at 0K would be pretty useless because it would be 0 .3: Entropy of Substances is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4. (ΔH°, ΔG°, S°. At higher temperatures, the data are for water vapor only. Changes of state. Temperature of a Single Substance. with the temperature in Kelvin. This formula holds because there is no change in volume upon mixing for an ideal mixture.
” Large jumps in entropy occur at the phase changes: solid to liquid and liquid to gas. Assertion(A) : Helium has lower entropy than `CO_(2)` gas which has lower entropy than gaseous benzene. The standard molar entropy of a substance is the entropy of one mole of that substance at Thermodynamic standard conditions (25°C, 1 bar, 1M conc, .The standard molar entropy is the total (minimal) amount of entropy gained by 1 mole of a substance when its temperature is increased from 0K to the standard conditions. The greater the molecular motion of a system, the greater the number of possible microstates and the higher the entropy. These forms of motion are ways in which the molecule can store energy.eCHEM 1A: Online General ChemistryCollege of Chemistry, University of California, Berkeleyhttp://chemistry.52: kJ/mol: Review: Chase, 1998: Data last reviewed in September, 1965: Quantity Value Units Method Reference Comment; S° gas,1 bar: 213.Standard molar entropy → The total (minimal) amount of entropy that 1 mole of a substance gains, as it is brought from 0 K to the standard conditions is known as Standard molar entropy. The molar enthalpy of vaporization of lead is larger than that of water, but this problem reminds us that in some cases a mass-based result can be of practical value, showing that less heat is required to vaporize an equal mass of lead.The partial molar entropy, can be obtained by potentiometric methods via determination of the temperature dependence of the OCV (cell-TD-OCV), or with calorimetric methods via measuring the reversible heat, For calorimetric measurements, however, large cell formats are necessary to reach the required accuracy.This webpage provides a set of exercises on entropy and Gibbs energy, two key concepts in thermodynamics. The superscript degree symbol (°) indicates that substances are in their standard states.
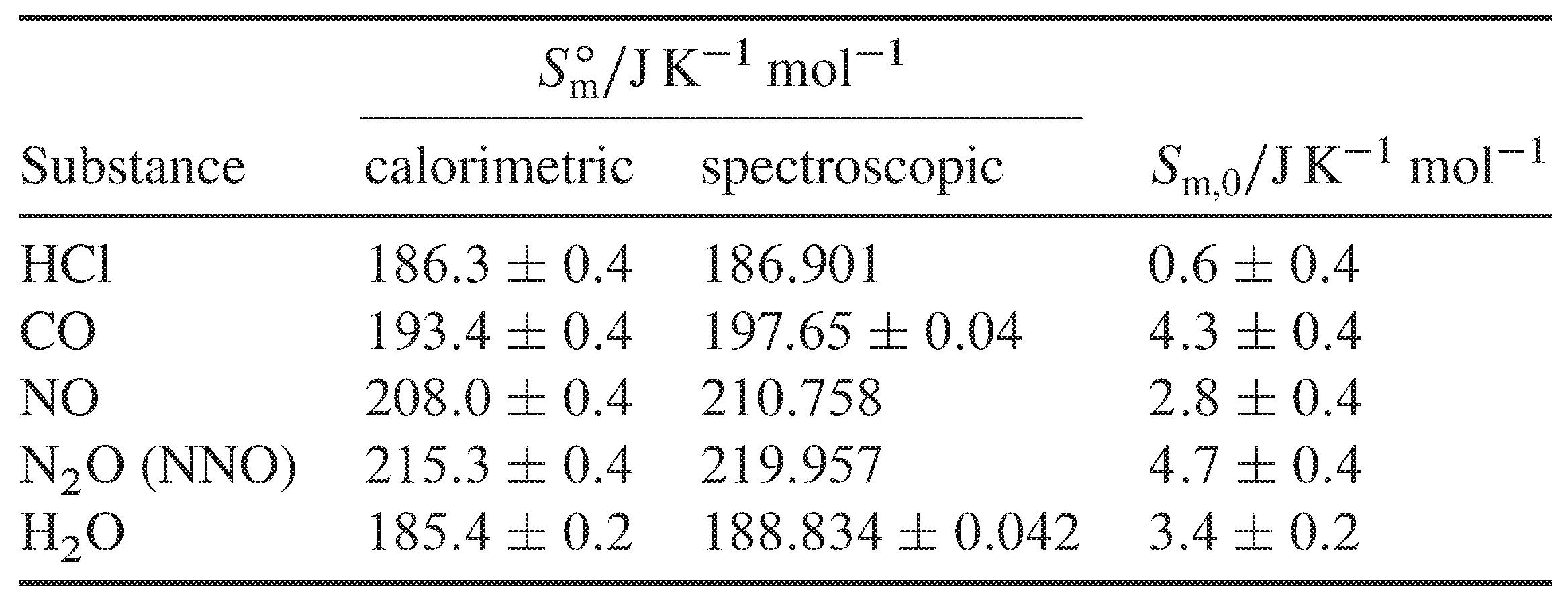
As the mass of increases, so does the molar entropy.
- What Is Discriminant : What is the Discriminant?
- What Is Let’S Go Read? : Let’s Go Read! 1: An Island Adventure Gameplay
- What Is Fish Farming Afk? , Destiny 2: How to AFK Farm
- What Is Hacettepe University’S Admission Policy?
- What Is Spam In Gmail _ How to check your SPAM Folder in Gmail
- What Is Rice’S Story? – The GameStop story — how a group of investors on Reddit
- What Is First Party Data | First Party Data
- What Is Gastroenterologist – 25 of the Best Gastroenterologists in Michigan, US
- What Is The Aws Free Tier? | Kostenloses AWS-Kontingent
- What Is Kafta – What Is Kafta?
- What Is More Commands Mod? , More Commands [FORGE]
- What Is Lunge Exercise – 11 Lunge Variations to Level up Your Leg Workout
- What Is Lead In Electricity : Energy Efficiency: Buildings and Industry
- What Is Er Diagram In Software Engineering