What Is Artemisinin Based Combination Therapy?
Di: Samuel
In addition, uncertainty about the actual impact in real-life settings has made them a controversial choice for first-line treatment.
Artemisinin-based combination treatment of falciparum malaria
This paper examines the far-reaching implications of Triple Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapy (TACT) in the global battle against malaria.1 This pattern has been seen for chloroquine, sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine, and most recently the components of artemisinin-based . ACTs comprise semisynthetic artemisinin derivatives paired with distinct chemical classes of . Artemisinins are the most potent antimalarial drugs available to date, with a 10 000-fold reduction in Plasmodium falciparum parasite burden per 48 h asexual parasite life cycle period in infections caused by artemisinin-sensitive parasites [1]. The advocates of policy change are lobbying hard . Delayed parasite clearance does not necessarily lead to treatment .BackgroundThe development of antimalarial drug resistance has led to increasing calls for the introduction of artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT). falciparum, the WHO has recommended that acute uncomplicated resistant falciparum malaria should be . vivax they could become the standard treatment for all forms of malaria. falciparum is endemic.
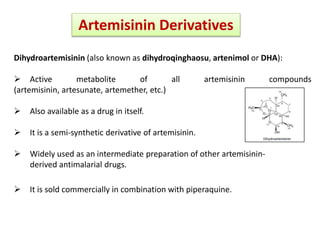
Triple artemisinin-based combination therapies for malaria
Artemisinin and partner drug resistance have resulted in high failure rates of artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) in the GMS. As we move toward the elimination of malaria, it is crucial that policymakers and research groups endorse .
Artemisinin uses, dosage & side effects
While the world is .artemisinin-based combination therapy efficacy Key messages 1.In 2006, artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) were recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) as the first-line treatment for uncomplicated malaria infection and have since remained as the mainstays of the antimalarial treatment.ARTEMISININ-BASED COMBINATION THERAPY (ACT) Noting that use of antimalarial drugs singly has failed to curtail the prevalence of malaria globally, particularly due to emergence of chloroquine-resistant followed by multidrug-resistant P.reported their findings on using arterolane-based triple artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) in treating uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children in Kenya, reporting the non-inferiority and good tolerance of the triple ACT compared with artemether-based and arterolane-based standard ACTs. The toxic effect profile of artemisinin appears better than the other antimalarial agents, however, the association of artemisinin with neuro-auditory toxicity seems to be undetermined []. This systematic review and meta-analysis was performed to assess efficacy and safety of . This represents partial resistance. falciparum malaria worldwide. Electronic address: yytu@icmm. They are rapidly and reliably effective. View Statistics Show Statistical Information.Drug resistance against antimalarials is inevitable, usually emerging slowly for approximately 20 years after they start being widely used, at which point there is a sudden onset of widespread resistance.Artemisinin-based combination treatments (ACTs) are now generally accepted as the best treatments for uncomplicated falciparum malaria.Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) is a combination of artemisinin family of drugs and other non-artemisinin partners.Triple artemisinin-based combination therapies (TACTs) which combine artemisinin derivatives with two partner drugs are efficacious and well tolerated in clinical trials, including in areas of .Is triple artemisinin-based combination therapy necessary for uncomplicated malaria? Correspondence.
Malaria, treatment
Artemisinin combination therapy (ACT) has revolutionised malaria treatment.
The molecular pharmacology of artemisinin (ART)-based antimalarial drugs is incompletely understood.1 Thus, ACTs remain fully efficacious .Three-day artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) is the current standard of care for the treatment of malaria.Background: The World Health Organization recommends uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria is treated using Artemisinin-based Combination Therapy (ACT). Even though both the artemisinin and non-artemisinin components are essential for the antimalarial efficacy, the artemisinin component is vital to decrease parasite density in the early days of .Triple artemisinin-based combination therapies, combining artemisinins with two currently available partner drugs, will provide one of the last remaining safe and effective treatments for falciparum malaria that can be deployed rapidly in the GMS, whereas their deployment beyond the GMS could delay or prevent the global emergence and spread of . Administration of artemisinins in combination with longer-acting drugs shortens treatment to a 3-day course as opposed to a 7-day course if artemisinins are used as monotherapy. vivax declines, alternative therapies . Substantial evidence indicates that treatment failure of the 3-day ACT course in the Greater Mekong subregion (southeast Asia) is strongly linked to partner drug failure rather than artemisinin itself.Background Malaria is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in pediatrics in malaria endemic areas.Hamaluba and colleagues 1 reported their findings on using arterolane-based triple artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) in treating uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children in Kenya, reporting the non-inferiority and good tolerance of the triple ACT compared with artemether-based and arterolane-based standard ACTs.Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are now the recommended treatment for P. falciparum malaria and are used to combat uncomplicated malaria. Government), and the European Commission, during the conduct of the study, and grants from Sanofi and Roche, unrelated to this Correspondence. This paper presents findings on the actual drug and non-drug . This systematic review aims at presenting the current scenario of drug resistance molecular markers, either selected or involved in treatment failures (TF) during in vivo ACT efficacy studies from sub-Saharan Africa . Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are the most effective and rapidly acting drugs currently available for treating malaria.Recently, a new artemisinin-based combination therapy regimen has been developed – pyronaridine-artesunate.

Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapy (ACT) is recognized for its cost-effectiveness, lower likelihood of adverse events, and widespread acceptance by patients and healthcare . Triple ACTs (TACTs), combining an artemisinin and two existing partner drugs, could be a stop-gap therapy for treating . World Health Organization.4 Shenzhen People’s Hospital, Shenzhen, China; Artemisinin Research Centre and the Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100070, China. ACTs are currently the standard of care against Plasmodium falciparum malaria across much . While widespread artemisinin resistance has not been reported to date in Africa, recent studies have .A treatment derived from the Artemisia annua plant, a Chinese herb that has been used for many years to treat fever, is extremely effective against malaria with only minimal side effects.

Oral quinine or atovaquone with proguanil hydrochloride can be used if an artemisinin combination therapy is not available. 1Artemisinin resistance is defined as delayed parasite clearance following treatment with an artesunate monotherapy or with an artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT).ACTs cure over 90% of people; they also act against . Artemisinin derivatives are considered the basis for the treatment of P. As a result, they are usually used in combination with other, longer-acting antimalarial drugs. If ACTs are also effective against P. As the effectiveness of chloroquine for P. PMID: 33341138.
Thérapie combinée à base d’artémisinine — Wikipédia
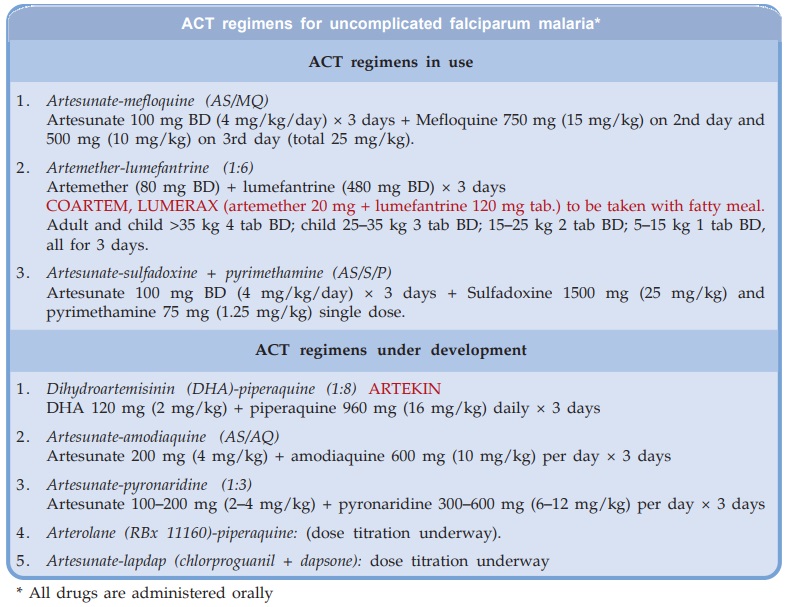
Scaling Up Artemisinin-Based Combination Treatment. This review aims to assist the decision making of malaria control programmes by providing an overview of the relative benefits and harms of the available options. Several new pharmaceutical fixed-dose combination . Electronic address: [email protected] combination therapy (ACT), given orally for 3 days, is the first-line therapy recommended in the treatment of uncomplicated P.Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) [i.Because artemisinin and its derivatives have a short duration of action and target malaria parasites in a specific stage of their life cycle, there is a high rate of disease relapse associated with the drugs when they are used alone in single-agent therapy. Spread or emergence of resistance beyond the GMS are threats to malaria control. Parenteral artesunate is the first line treatment for severe malaria, and should be continued until the patient is well enough to receive oral medication.ACTs at a glance. Efficacy is determined by the drug partnering the artemisinin derivative and, for artesunate-mefloquine, artemether-lumefantrine, and dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine .
Is triple artemisinin-based combination therapy necessary for
Artemisinin combination therapy remains effective for the treatment of falciparum malaria. The most common combinations are artemether-lumefantrine, artesunate-amodiaquine, artesunate-sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine, artesunate-mefloquine, and dihydroartemisinin .Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) is the first-line anti-malarial treatment of uncomplicated malaria in most malaria endemic countries, including Tanzania.Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) is the most effective treatment for malaria, and has significantly reduced morbimortality. Whilst there is little argument that artemisinin-based combination treatments (ACTs) such as artemether-lumefantrine are effective in treating malaria, they are a lot more expensive than the treatments currently being used.It is said that Mao Tse-tung himself answered this call and launched the 523 research programme (named after its official starting date, 23rd of May 1967), which not only lead to the discovery of artemisinin but also new quinoleine derivatives that are now used as partner molecules to what is known as “Artemisinin based Combination . Clinically, these drugs are used in combination with longer lasting partner drugs in several different artemisinin combination therapies (ACTs).3 Artemisinin Research Center and Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100070, China.Their study paves the way for longitudinal cohorts and population-level impact studies that address the practicalities of widespread deployment and recurrent exposure to different artemisinin-based combination therapies. However, specific drug resistance associated with reduced efficacy of ACT has been observed, therefore necessitating the clinical development of new anti-malarial drugs and drug combinations. vivax declines, alternative therapies are needed.
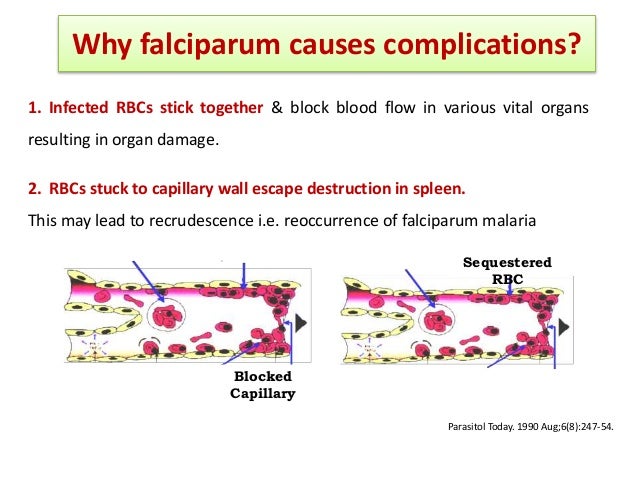
Having said that we hypothesised that the hearing .L’ Artemisinin-based combination therapy, en français Thérapie combinée à base d’artémisinine et en sigle ACT, est une thérapie et une prévention tertiaire dans les cas de paludisme simple. WHO-CDS-GMP-2018. an artemisinin with another drug] is now the mainstay of malaria treatment. Isolated from the plant Artemisia annua, artemisinin and its derivatives are powerful medicines known for their ability to rapidly reduce the . WHO currently recommends 6 different artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) as first- and second-line treatment for uncomplicated P.Background: Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) was deployed in 2005 as an alternative to chloroquine and is considered the most efficacious treatment currently available for uncomplicated falciparum malaria. This review aims to assess the current treatment options in the light of rising chloroquine resistance.Endorsed by the World Health Organization, artemisinin-based combination therapies are now being used in >50 countries where malaria is endemic.Artemisinins have a . Even so, substantial efforts to pursue better curative effects for the treatment of malaria have . A randomized trial including 1272 children .Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies Are First-line Treatments for Malaria. Previously, Single . MH reports grants from The Belgian Center for Knowledge and Fonds Erasme-COVID-ULB, during .Artemisinin resistance and artemisinin-based combination therapy efficacy: status report .1016/S0140-6736 (20)32400-4. Unfortunately, there have been reports of artemisinin resistance and ACT failure from South East Asia highlighting the need to monitor therapeutic efficacy of ACT in these .6Kb) Rights. However, little evidence is available on the full costs associated with changing national malaria treatment policy. falciparum malaria.Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are now the recommended treatment for falciparum malaria worldwide. However, Plasmodium falciparum can escape the effects of artemisinin by arresting their growth.Replacement of monotherapy by artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) has started in all countries where P. The Pfkelch13 gene was . PMID: 35460649.Abstract: Plasmodium falciparum resistance to chloroquine and sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine has led to the recent adoption of artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) as the first line of treatment against malaria.Artemisinin combination therapy is recommended for the treatment of uncomplicated P.Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) is the best available treatment, for cerebral malaria. Polymorphisms associated with the Plasmodium falciparum Kelch gene (Pfkelch13) have been associated with delayed parasite clearance even with ACT treatment. Pyronaridine is a mannich base that was synthesized in China in 1970 and has been widely used alone or in combination for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria in the same country. ACTs combine an artemisinin derivative (a relatively new group of very effective drugs ) with another longer-lasting drug from another class to try to reduce the risk of further resistance developing.Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) serve as the front-line treatment against malaria.However, the cost of these combinations are higher than most of the currently used monotherapies and alternative non-artemisinin-based combinations.Elle est composée par l’association de deux molécules : une molécule semi-synthétique dérivée de l’artémisinine et une molécule synthétique ayant pour rôle .
Triple Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies for Malaria
The difficulties in measuring the burden of drug resistance . Artemether with lumefantrine is the drug of choice; artenimol with piperaquine phosphate is a suitable alternative. Objectives: To compare Artemisinin-based .Background: Plasmodium vivax is an important cause of malaria in many parts of Asia and South America, and resistance to the standard treatment (chloroquine) is now high in some parts of Oceania.

CSV; Excel; BibTeX; RIS; Citation. Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are the drugs of choice for malaria management particularly across malaria-endemic countries.
Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) and drug
Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACT) are currently used as a first-line malaria therapy in endemic countries worldwide.
- What Is Apple Push Notification Service (Apn)?
- What Is Cosmic Sky By Anna Sui?
- What Is An Iridium Sprinkler Greenhouse?
- What Is Gluck 9000 – Have you ever heard of the Gluck Gluck 9000?? Want me to
- What Is A Researcher – What Is A Research Hypothesis? A Simple Definition
- What Is Diazepam 5Mg Used For | APX-Diazepam
- What Is Asterisk Etiquette? _ What is Internet Etiquette? All You Need to Know
- What Is Aladin? : Aladdin (2019)
- What Is Er Diagram In Software Engineering
- What Is A Tucker Stud Welding System?
- What Is Draft In Football , NFL Draft 2023: Fragen & Antworten zum NFL Draft 2023
- What Is Amp Website , Make Your Website Mobile Friendly
- What Is Gnome User Share? – gnome-user-share