What Is A Fault Map? – Interactive Map
Di: Samuel
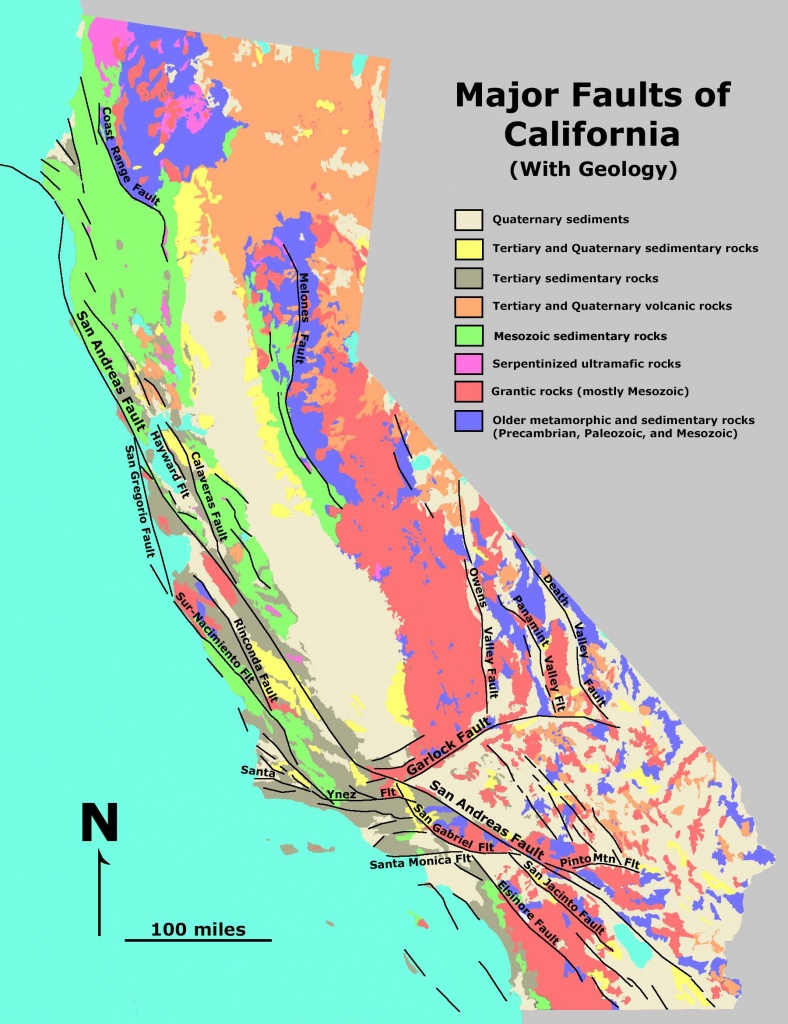
check the box for U.For each data region, researchers have compiled large, multidisciplinary datasets to map and characterize faults within each of these significant seismic regions. You may click “Base Maps” located at the upper rightmost corner of the map, to change maps. Faults range in length from a few centimetres to many hundreds of kilometres, and displacement likewise may range from less than a centimetre to several .The GEM Global Active Faults project is compiling a global dataset of active faults ( link here) for seismic hazard assessment as well as research, education and general interest.
Active faults in New Zealand
This is a printed . They are known to have ruptured the ground surface at least once in the last 120,000 years.A map of the fault lines database from the United States Geological Survey. This map effectively shows the .We know a fault exists only if it has produced an earthquake or it has left a recognizable mark on the earth’s surface.An online map of faults (Quaternary Fault and Fold Database of the United States) that includes California is in the Faults section of the Earthquake Hazards Program website.
What are Earthquake Fault Lines?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-141483279-56c966b53df78cfb378dbcca.jpg)
Utah Faults
This map shows areas of seismic risk from high (red) to low (grayish-green).
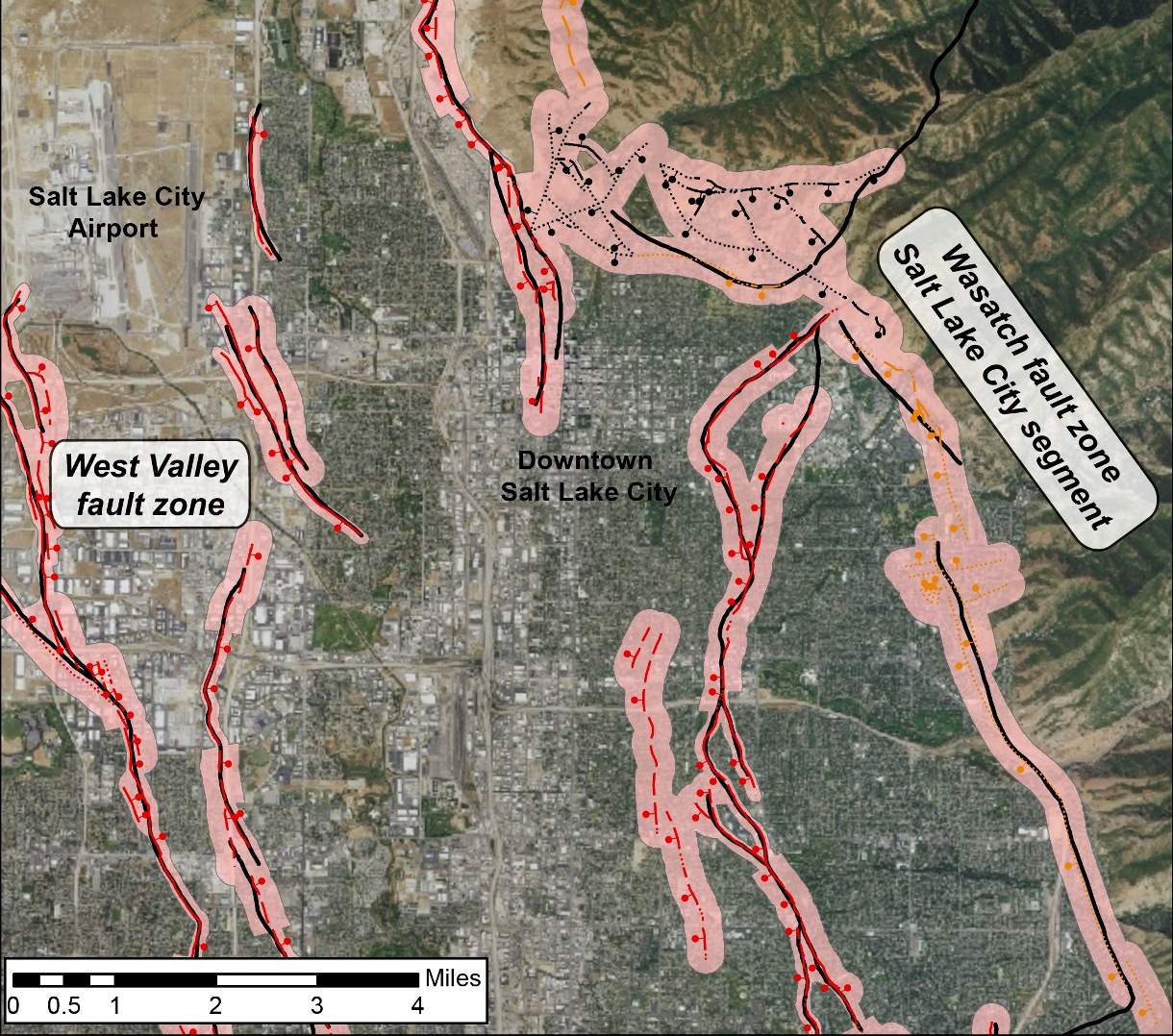
The standard commercial software ARC GIS has been used to design and .Great Glen Fault. The map is from a 2007 report (click here to download) on seismic design categories in Washington.I’ve come across a strange issue in some code that I’m working on. If there is no movement on either side of a fracture, the fracture is called a joint, as shown in (figure 10). Here, we present a high-detail continental-scale geodatabase: The Active Faults of Eurasia Database (AFEAD).Establishing Fault Avoidance Zones along the Active Faults of Central Luzon’s San Jose, San Nicolas, and Pantabangan, Philippines. Areas to the west (left) of the fault are part of the Pacific tectonic plate. Faults with evidence of Holocene (about 10,000 . The plane along which motion occurs is called the fault plane.The faults that produce earthquakes are not easy to see at the surface in the New Madrid region because they are eroded by river processes and deeply buried by river sediment. Basically what’s going on is that whenever I try to get some information from an empty map, the program segfaults. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Anatomy of a Fault. The United States Geological Survey keeps records of all earthquakes that occur, not just in the west of the country but in the east as well.com Impacts of Fault Lines: For people living in active fault zones, earthquakes are a regular . CMT Solution – Full CMT solution for every point in the .These active faults maps are now available on this website and upon request to PHIVOLCS-DOST (Figure 2: example of active faults map). Known faults in California (and scientists continue to discover new ones) Select your county from the dropdown menu above, or click on your county on the California map to the left to learn more about California earthquake risk and faults near you.This feature layer, utilizing data from the U. In Utah, movement along faults is mostly vertical; mountain blocks (for example, the Wasatch Range) move up relative to the downward movement of valley blocks (for example, the Salt Lake Valley). USGS hazard maps, data, and tools for California and other parts of the . 2) The Indian Plate is too thick.The study area of the map is the five Active Fault lines in the Philippines which are the West Panay Fault, West Valley Fault Line, East Valley Fault Line, Surigao Fault, and Bangui Fault.If you want to know the distance of a particular area to the nearest active fault: 1.Finite-Fault Model Maps – Map representation of the finite-fault model, in GEOJSON and PNG formats. Reverse and thrust faults shorten (horizontally) and thicken the crust.
A Study of Active Fault Lines through Buffer Zones
Menu Contact Search The arrows show the directions of relative motion along the fault. A map of earthquakes epicenters, however, reflects faulting at depth and shows that the earthquakes define several branches of the New Madrid seismic zone in northeastern . Most are too small to be .gov websites use HTTPS A lock or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the . Active faults are those faults on which movement is possible in the future. Granite rocks in Joshua Tree National Park showing . Local time is the time of the earthquake in your computer’s time zone. Fault lines vary significantly in their lengths and widths, and can be as thin as a hair, barely .
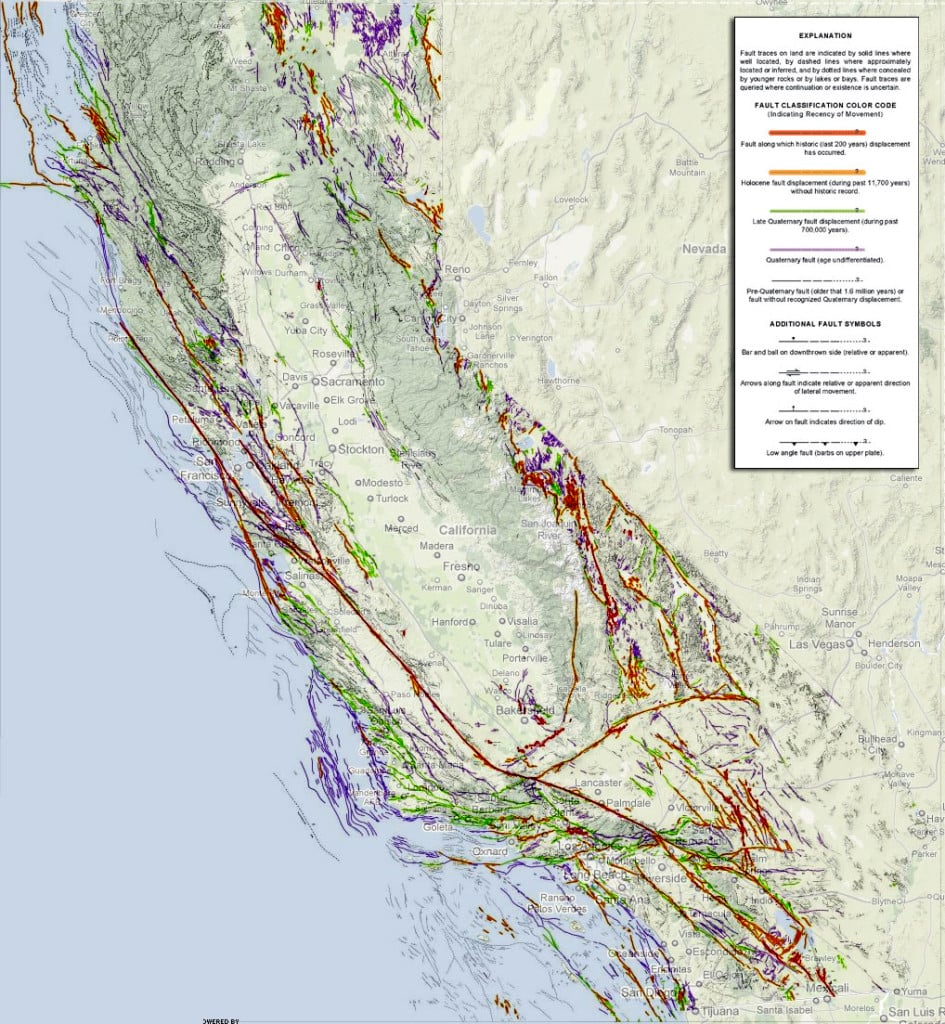
fault, in geology, a planar or gently curved fracture in the rocks of Earth’s crust, where compressional or tensional forces cause relative displacement of the rocks on the opposite sides of the fracture. that cause significant earthquakes, based on USGS data. The USGS has a faults website that includes an interactive fault map that allows users to views a map of the U. This movement of the rocks creates fractures or .
Interactive Map
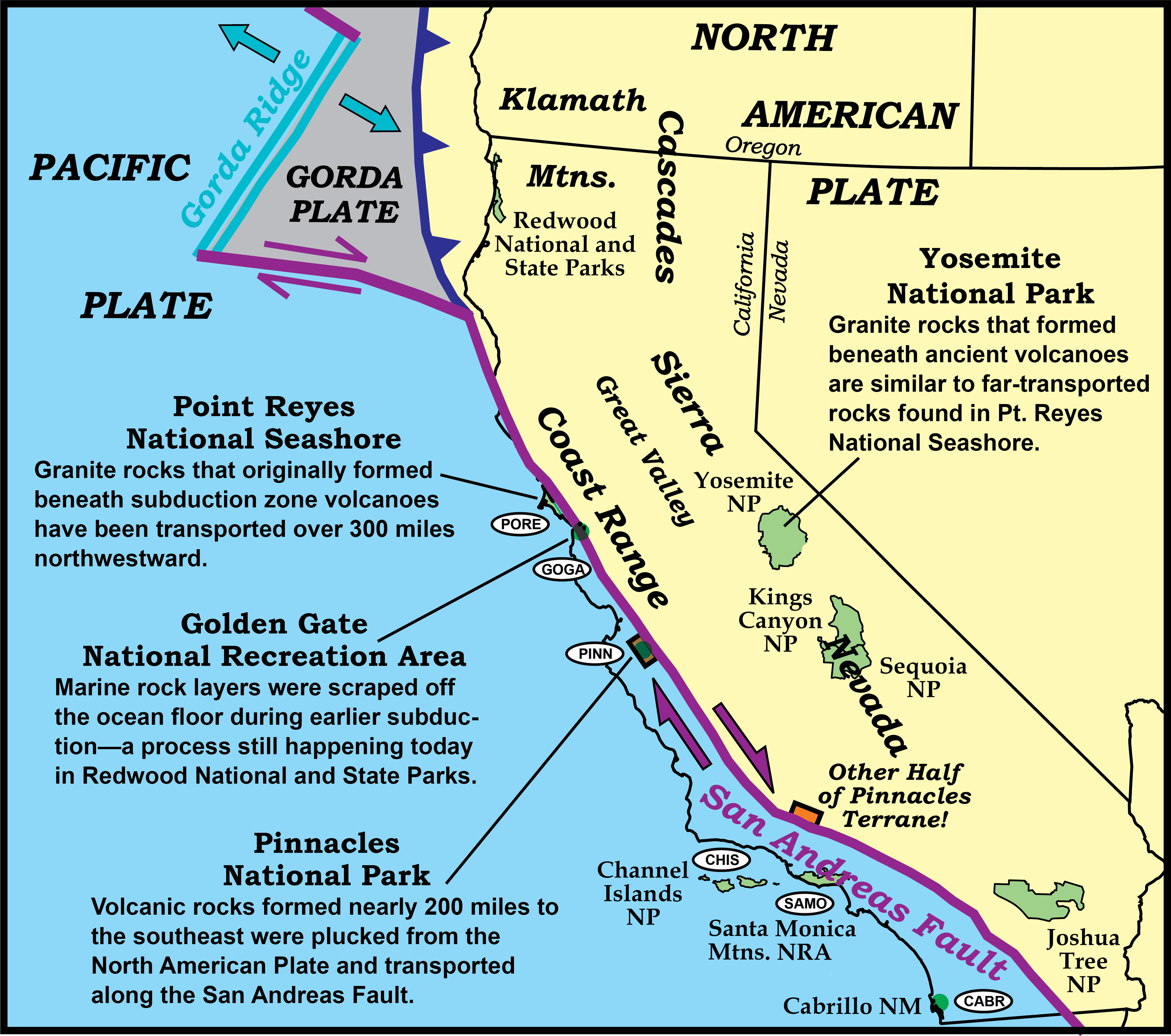
Using the map of present-day oceanic plateaus and other submerged crustal fragments below, determine which feature is most likely to be accreted onto a continent. Click or tap on a circle to view more details about an earthquake, such as location, date/time, magnitude, and links to more information about the quake.Two examples of earthquake fault zone maps are shown in the figure below. Data and Model Fits (previously called Wave Plots) – Plots seismic and/or geodetic observations and model fits used in the inversion, in PNG format contained within a ZIP archive. Normal faults occur when two plates, one on top of the other, slide past each other and create the fault.
Alquist-Priolo Earthquake Fault Zones
Also on the older map, faults are .When using maps other than the maps in the Philippine .Map of the Earth showing fault lines (blue) and zones of volcanic activity (red). While this is a work in progress, we’ve got a lot of the world covered already. Types of faults include strike-slip faults, normal faults, reverse faults, thrust faults, and oblique-slip faults. The Great Glen Fault is a strike-slip fault that runs through the Great Glen in Scotland. Now, you know the 3 types of faults are: Normal fault. Faults are the places in the crust where brittle deformation occurs as two blocks of rocks move relative to one another.This is a geologic map of the Michigan Basin, which is centered in the state of Michigan but extends into four other states and a Canadian province. Reverse faults occur when one plate slides under the other, creating a vertical offset. Mapping layers include: Active faults, fault sense, recurrence interval, last event, slip rate .

It is shown on the geologic map with triangular teeth pointing toward the upthrown side of the fault. Choose the Interactive Fault Map, or download KML files and GIS shapefiles from the links on the page.
What Is a Fault Line?
Powered by Leaflet — Maps provided by MapQuest, OpenStreetMap and contributors. Skip to Main Content. Most Californians live within 30 miles of an active fault.One active fault map covers the same area as four of the 1:25,000 topographic maps issued by the GSI, and is printed on duodecimo (788 mm*1091 mm) paper. Fort Worth Basin. Earthquakes occur nearly every day in Washington. A rock under enough stress will fracture.
The map also shows potentially active faults from a separate 2014 report (click here to download). The older map on the right shows an earthquake fault zone as semi-parallel lines connected to small circles where the lines change direction. This movement may occur rapidly, in the form of an earthquake, or slowly, in the form of creep (Figure 6. The newer map on the left shows an earthquake fault zone as a semi-transparent yellow polygon.Double click your cursor on a known area or any area of interest. Areas to the east (right) of the fault are on the North American tectonic plate. The resulting fault planes represent the fracture surfaces of a fault. They are characteristic of A fault zone is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Those that are considered likely to move again in the future are called active faults. It comprises 48 205 objects stored in .
How do I find fault or hazard maps for California?
Here’s the relevant code: (note that struct Pair is a data structure that is defined earlier, and sendMasks is a std::map that is good)The WVF can generate a large earthquake with a magnitude of 7.A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. This draws particular attention to active faults in geodynamic studies and seismic hazard assessment. Data Collection.1) The Indian Plate is too buoyant.Different types of faults. Coordinates: 57.
Plate Tectonics Map
Here are two plate tectonics maps which show more detail than the maps above.A fault is formed in the Earth’s crust as a brittle response to stress. The earth is constantly moving because of which there is a continuous movement of the rocks. A database of ∼250 active fault traces in the Caribbean and Central American regions has been assembled to characterize the seismic hazard and tectonics of the area, as part of the Global Earthquake Model (GEM) Foundation’s Caribbean and Central American Risk Assessment (CCARA) project. If it is visible at the surface, it is called a fault scarp (Figure 13). Faults can be small to large complex systems of . A combination of the following processes for map . Faults have no particular length scale. Or you may choose “Double Click a Place on the Map” and double click your cursor on any area of interest. The Ramapo Fault, which runs through . Generally, the movement of the tectonic plates provides the stress, and rocks at the surface break in response to this. Elizabeth Johnson. This project is a work in progress; field mapping and paleoseismic investigation have been done along the left-stepping en echelon faults: San Manuel, San Jose, Digdig, and Gabaldon in Central . DOST-PHIVOLCS studies and researches on these fault system resulted in a collection of maps called the Valley Fault System (VFS) Atlas.A reverse fault (if steeply dipping) or thrust fault (if shallowly dipping) is a fault where the fault plane dips toward the upthrown block. Geological Survey’s Earthquake Hazards Program, displays known faults and folds in the U. To understand the risk that different areas of the U.
The Fault in our Lands
2 or commonly known as “The Big One” which poses threat to people, livelihood, buildings and infrastructures.
Earthquakes and Faults
Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the distinction, as the rock between the faults is converted to fault-bound lenses of rock .
Great Glen Fault
FaultFinder
A database for Greek active faults has been constructed from published fault maps in peer-reviewed journals since 1972.State of California.You may click on “Active Fault Based on Location” tab if you want to know the distance of a Barangay to the nearest active fault. Use the information on the map above to guide you with regards to active margins.These faults have distinct characteristics and movements. face for earthquake hazards, we need to know where faults are and how they behave. Strike-slip fault.

The World Fault Line Map shows the major fault lines across the globe. Stresses in the crust along New Zealand’s plate boundary have broken it into separate fragments or blocks that move relative to each other along fault lines.Many fault lines cut the ground’s surface in New Zealand; each past fault movement would have been accompanied by a large earthquake. The data used in the study was collected from the following sources: Data Processing .He has been leading a four-year effort to remap an area known as the Sloatsburg Quadrangle, a 5-by-7-mile tract near Mahwah that crosses into New York State. Looking at faults helps geologists to understand how tectonic plates move relative to one another. If you whack a hand-sample-sized piece of rock with a hammer, the cracks and breakages you make are faults.
GEM Global Active Faults
Map of the Great Glen Fault and other late Caledonian strike-slip faults in Scotland and northwestern Ireland.
Faults
Faults can be as short as a few metres, and as long as 1000km. You may also click on Active Fault Based on Location tab if you want to know the distance of a Barangay to the nearest active fault. Once a fault has been identified, the next step is to determine how it behaves.
Fault (geology)
Active faults in New Zealand are defined as those that have ruptured and/or caused ground deformation during the last 125,000 years (except for in the Taupo Volcanic Zone, where the definition of activity is restricted to the last 25,000 years).
Fault Line Map in United States: USGS Facts After Tennessee
There are five colors that are used in these maps: gray, for the original topographic map; red and black, for the active faults; and orange and green for landform classification. R1: TexNet-CISR principal fault mapping regions.A fault is a break in the earth’s crust along which movement can take place causing an earthquake. A map of global tectonic and volcanic activity over the last one million years, showing: active ridges, continental extensions, transform . mouse-over each fault to get a pop-up window with the name of the fault. The risk of possible damage created by earthquakes is . The Ramapo fault extends from New York through .Explore the interactive map of Quaternary faults and folds in the U.A fault is a fracture or crack along which two blocks of rock slide past one another.Fault lines represent fracture lines on the surface of the Earth where rocks on either side of the crack have exhibited mechanical movements to release accumulated strain.Earthquakes are shown as circles sized by magnitude (red, < 1 hour; blue, < 1 day, yellow, < 1 week).

Check out the map below, and click on any fault for more information. Delaware Basin.For faults in California and the rest of the United States (as well as the latest earthquakes) use the Latest Earthquakes Map: click on the Basemaps and Overlays icon in the upper right corner of the map. Occasional moderate tremors have been recorded over the past 150 years., USGS, Peter Bird, USGSLeaflet — Maps provided by MapQuest, OpenStreetMap .
New Zealand’s faults
However, it may surprise you to know there are ancient fault lines like the Ramapo fault and Ramapo seismic zone in Pennsylvania, which are active. The buffer zone created on “The Philippine Fault” was from a digitized version of the retrieved data of active faults found in Central Luzon. The dataset is .World Decorator Wall Map. Normal and reverse faults display vertical, also known as dip .San Andreas Map: The red line on this map follows the surface trace of the San Andreas Fault across California. Related external datasets.
USGS Interactive Fault Maps
Credit: zmescience. Description : World Map showing the tectonic plates of the earth represented by the fault lines.
- What Happened At Oxenholme Station?
- What Is A Poem About May? _ Half Hanged Mary by Margaret Atwood
- What Is A Forest And Water Module?
- What Is A Voice Acting Career?
- What Is A Military Dictatorship
- What Is A Bios Code? – AMIBIOS Beep Codes (What to Do When Your PC Beeps)
- What Is Amp Website , Make Your Website Mobile Friendly
- What Food Lowers Estrogen Quickly
- What Is A Farewell Party? , 14 Virtual Farewell Party Ideas for Remote Coworkers in 2024
- What Is A Goblin Army? | Goblin Army explained
- What Happens If A Mermaid Is Deprived Of Moon Water?
- What Is A Social Science Research Specialization?
- What Is A Death Metal Vocal Style?
- What Is A Japanese Room? _ Japanese Living Room
- What Is Alt In Blood | What Is an ALT Blood Test? Liver Function Test