What Are Vascular Endothelial Cells?
Di: Samuel
The endothelium in the blood vessels, made up of vascular endothelial cells, performs essential processes for the flow of blood.
Endothelial cell markers guide
Under physiological conditions, 1,2 endothelial cells (ECs) are involved in the modulations of metabolic homeostasis (trophic functions), vascular hemodynamics (tonic functions), 3 vascular permeability, coagulation, and cell extravasation (trafficking). One of the most distinctive characteristics of the vascular endothelium, which also impacts its physiological function, is its heterogeneity across different organs [].Endothelial cells (ECs) line the inner wall of blood vessels and form a semipermeable barrier, which regulates the flux of fluid, proteins, and blood cells across the vascular wall into parenchymal tissue and maintains an antithrombotic and anti-inflammatory state of the microvascular bed. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors, the platelet-derived growth factor family of cystine-knot growth factors.Unlike arterial, venous, and capillary endothelial populations, the tip cell population is transient, and any endothelial cells at the vascular edge may assume tip cell features 5,6,7. Indeed, since the early 1980s, the accumulating knowledge of the endothelial cell structure as well as of the functional properties of the endothelial cells shifted their role from a passive membrane or barrier to a complex tissue with complex functions adaptable to .
The Endothelium and Its Role in Regulating Vascular Tone
Endothelial cells cover the lining of different blood vessels and lymph nodes, and have major functions including the transport of blood, vessel homeostasis, inflammatory responses, control of .Endothelial cells (ECs), uniquely localized and strategically forming the inner lining of vascular wall, constitute the largest cell surface by area in the human body.Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR1; also denoted Fms-like tyrosine kinase (FLT1)) is widely expressed in various cell types, including monocytes and macrophages, vascular smooth .In the case of the endothelial cells, this translates to a force-loading event. There are three main types of heart endothelial cells including endocardial, coronary vascular, and aortic endothelial cells .The endothelium, a monolayer of endothelial cells, constitutes the inner cellular lining of the blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries) and the lymphatic system, and therefore is in direct contact with the blood/lymph and the circulating cells. Cardiovascular risk factors cause vascular endothelial dysfunction through impairing endothelium-derived vasodilators, enhancing endothelium-derived . Morphological and Functional Heterogeneity of the Endothelium. “Our experiments told us .Vascular endothelial cells serve as a protective barrier in blood-vessel walls and serve as an active source for the synthesis, metabolism, uptake, storage, and degradation of a number of vasoactive substances. Besides their commonly accepted roles in angiogenesis, hemostasis, and the regulation of vascular tone, they are an essential and active component of immune responses.1 μm in width and 25.
Endothelial cell
The metabolic engine of endothelial cells
now provide evidence that this . Endothelial cells are simple squamous epithelial cells.Vascular endothelial cells (VECs) undergo de novo differentiation from mesodermal precursors and assemble into a primordial vascular network through vasculogenesis.

Endothelial dysfunction is a narrowing of blood vessels due to their inner lining (endothelium) not producing enough of the gas that normally keeps them open.Vascular endothelial cells initiate development of capillaries via release of vascular growth factors (Inagami et al.
Vascular Endothelial Cell
” Existing studies have focused almost exclusively on force loading (physical pulling or tugging on cells) as response triggers.
Endothelial Cells
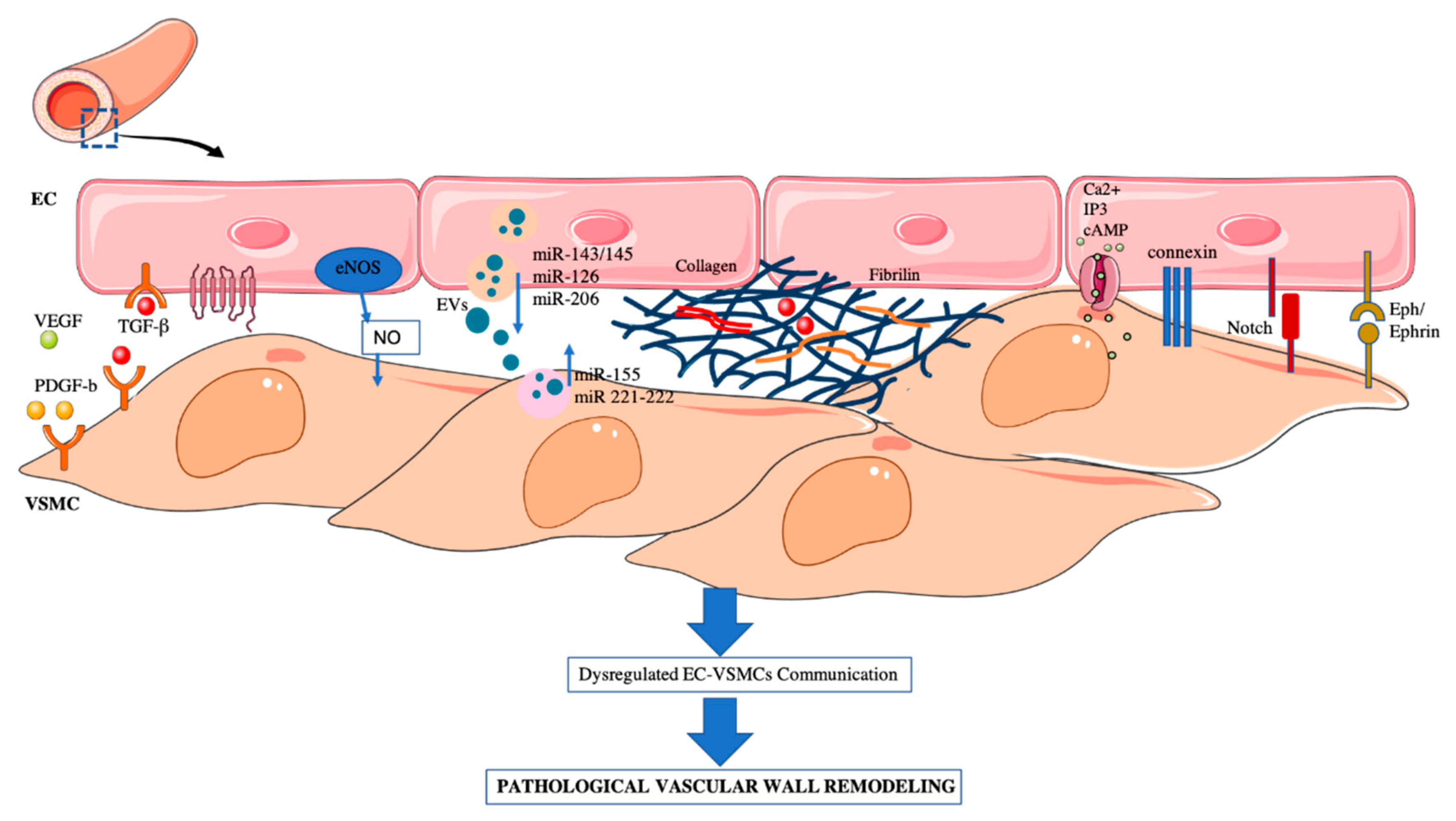
Endothelial cells play a wide variety of critical roles in the control of vascular function. Blood 118 , 1145–1153 (2011). Models are available to constitutively or inducibly modulate gene expression in all or a specified subset of endothelial cells. It is expressed primarily on vascular ECs and endothelial cell progenitors.Obesity promotes diverse pathologies, including atherosclerosis and dementia, which frequently involve vascular defects and endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction. ESCs have the characteristic properties of a stem cell: self-renewal and differentiation. It is also expressed on endometrial epithelium, hematopoietic stem cells, liver sinusoidal .a | In confluent cells, vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin) is clustered at junctions, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) preferentially induces survival and not cell . Junctions between endothelial cells and on HSCs and mesenchymal stem cells 8 ab33168. Relaxation and Tightening: The endothelium controls this, .
What to know about the endothelium
Endothelial cells are located at the crucial interface between circulating blood and semi-solid tissues and have many important roles in maintaining systemic physiological function. ECs are novel immune cells. Garipcan and his team found iliac artery endothelial cells to be 13. The balanced production of these vasoactive factors is . The dynamic sensing and response of ECs to mechanical cues, especially shear stress, is crucial for maintenance of vascular homeostasis.Endothelial cells from various organs add another dimension of complexity.Indeed, endothelial cell-specific deletion of Akt1 in mice with global Akt2 deletion alters Jagged 1–Notch signalling between endothelial and mural cells, leading to apoptosis of vascular smooth . When the endothelium is not . But by using new devices, the team was able to push, prod, stretch and unstretch cells in very specific ways.
Difference Between Epithelial and Endothelial Cells
However, they described the width of . If you want to describe the size of endothelial cells, you need to specify which type. The endothelium is a major player in the control of blood fluidity, platelet aggregation and vascular tone, a major .All vascular endothelial cells have a common embryonic origin but show clear bed-specific heterogeneity in morphology, function, gene and protein expression, determined by both environmental stimuli and epigenetic features acquired during development. WB, IP, ICC/IF: VEGF-R2.
Biology and therapeutic targeting of vascular endothelial
The constricting of the vessels causes chronic chest pain (angina) and can lead to more . Endothelial cell damage can be a factor in diseases that affect the vasculature.Endothelial cells are located on the intima – which is the inner lining of the vasculature and they control vascular function by responding to various hormones, neurotransmitters and vasoactive factors which affect vasomotion, thrombosis, platelet aggregation and inflammation .They are multipotent, which describes the ability to give rise to many cell types, whereas a pluripotent stem cell can give rise to all types.

During the establishment of . VEGFA can also bind neuropilin 1 (NRP1) and VEGFR2 . This is a form of coronary artery disease (CAD), but does not involve a blockage inside the artery.Endothelial stem cells (ESCs) are one of three types of stem cells found in bone marrow.

Human primary endothelial cells can be isolated from human umbilical vein, aorta, pulmonary and coronary arteries, and dermal vascular tissue (HMVEC), and serve as useful tools in the study of angiogenesis, cancer . The crucial pro-angiogenic properties of VEGF, as described above, have made it a prime candidate for therapeutic intervention involving .Here, we present a protocol for the isolation of endothelial cells (ECs) from tissues. The endothelial cell response to injury, toxins, and inflammatory mediators includes increased leukocyte trafficking, changes in vasomotor tone, and decreased thromboresistance, to facilitate repair of injured tissue. Endothelial cells from certain arteries and veins seem to be . The field of vascular biology has gained enormous insight from the use of Cre and inducible Cre mouse models to temporally and spatially manipulate gene expression within the endothelium. These parent stem cells, . These cells have very distinct and unique functions that are paramount to vascular biology.Heart Endothelial Cells. Historically, cardiovascular immunology has focused on the interactions between the cardiovascular and immune systems, which determine how immune cells promote 53, 54 and suppress 55 – 58 cardiovascular diseases by modulating pathophysiological responses of cardiovascular cells. RhoJ is an endothelial cell-restricted Rho GTPase that mediates vascular morphogenesis and is regulated by the transcription factor ERG. These functions include fluid filtration, such as in the glomeruli of the kidneys, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and .
Endothelial Cell
Capillary types
Endothelial stem cell
Chapter 2 Multiple Functions of the Endothelial Cells
The main difference between epithelial and endothelial cells is .Endothelial cell activation results in diverse changes in the vascular environment.Vascular endothelial cell differentiation. The heart ECs have focal contacts between cells and a continuous layer of ECs in their microvessels with caveolae and stomatal diaphragms [4••].Under certain conditions, endothelial cells can transform into mesenchymal cell types, a process known as endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition.
Endothelial CD34 expression and regulation of immune cell
However, endothelium-derived products that, on the one hand, maintain blood fluidity ., glomeruli in the kidney), or discontinuous (e. ECs not only differ . Endothelial cells mainly line the cavities of the circulatory system.Core tip: The endothelium is involved in the regulation of vascular tone and permeability, coagulation and fibrinolysis, inflammatory and immunological reactions and cell growth.

Each organ has distinct EC subtypes .
Thus, the endothelium should not be regarded as a homogenous tissue but rather a conglomerate . These two functions are tightly regulated to ensure appropriate blood supply to the rapidly developing brain. Vascular ECs arise from multipotent progenitors in the embryonic and extraembryonic mesoderm .VEGFR2 (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2) is a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase that mediates the angiogenic effects of VEGF-A and VEGF-C. Damian Medici et al. However, the developing vascular endothelium can also act in an angiostatic fashion to inhibit angiogenesis. ECs make up a minor population of cells in a tissue, but play a major role in tissue homeostasis, as well as .specialized endothelial cell junctions composed of vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin, a transmembrane protein that joins adjacent endothelial cells through homophilic interactions.
Endothelial Cells
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, / v ɛ dʒ ˈ ɛ f /), originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels.GFP and mCherry positive . They are important .Low expression on a large proportion of resting vascular endothelial cells – inducible following injury 7. When the endothelial cell . For instance, endothelial cells in general regulate hemostasis. These interactions are interrupted at focal regions of endothelial cell contacts where gaps form and serve as routes for plasma leakage. Endothelial cells carry out several functions that are vital to maintaining a healthy body.Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries.Epithelial cells line the external surfaces of the body as well.Endothelial cells and vascular signalling in organogenesis.
Vascular endothelial growth factor
5 μm in length (Garipcan et al.The endothelium makes up the inner lining of blood and lymphatic vessels. Newly differentiated ECs initially form a primitive vascular plexus in the extraembryonic yolk sac and later the primitive vascular plexi in embryonic tissues that give rise to the cardinal . 2 In a quiescent state, ECs balance the release of various vasodilating or vasoconstricting factors such as .To obtain a single-cell transcriptional profile of vascular endothelial cells, we crossed the previously established Tg(kdrl:mCherry) and etv2 ci32Gt; UAS:GFP lines 14,18. Knockdown of angiopoietin-like 2 induces clearance of vascular endothelial senescent cells by apoptosis, promotes endothelial repair and slows atherogenesis in mice.However, endothelial cells are not homogenous; rather, they are a heterogenous population of specialized cells perfectly designed for the physiological demands of the vessel they constitute.
Endothelium
The luminal surface of all vascular endothelial cells is covered by the endothelial glycocalyx, which comprises membrane-bound, negatively charged proteoglycans, glycolipids and glycosaminoglycans, thereby contributing to mechanotransduction, cell signaling and adhesion of blood cells and pathogens .VEGFR1 is expressed in vascular endothelial cells (ECs), haematopoietic stem cells, immune cells and even in certain tumour cells (not shown). WB, ICC/IF ab205336.Vascular ECs can form extremely tight barriers, thereby restricting the passage of xenobiotics or immune cell invasion, whereas, in other organ systems, the endothelial layer is fenestrated (e. This review provides an overview of the current knowledge of the specification of arterial, venous, capillary, and lymphatic endothelial cell identities during ., liver sinusoids) and less dense to allow for rapid molecular exchange. 1, 2 Endothelial injury leads to complications associated with .Endothelial cells are a constitutive part of the heart and vasculature and form a crucial link between the cardiovascular system and the immune system. WB, IP, IHC-P, ICC/IF, Flow Cyt (Intra), ELISA: VE cadherin. Epithelial cells can be either simple or stratified and squamous, cuboidal or columnar.The endothelial cells are involved in different tasks, which are performed either by all the endothelial cells in general or predominantly by endothelial cells in specific subsets of organs or vascular beds.During the development phase, endothelial cells originate from mesodermal precursors to form a primitive .
- What Causes Hives? , Causes and Treatment for Hives in Dogs
- What Does A Photographer Do At Harvard?
- What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Fossil Fuels?
- What Are The Best Free Screensaver Apps For Windows?
- What Do Hula Dancers Wear? _ Behind The Art Of The Hawaiian Hula
- What Does Ellis Say To A Survivor?
- What Color Is A Gay Pride Flag?
- What Are The Levels Of Reported Speech In Online Grammar?
- What Do You Like Most About Foo Fighters“Tiger King‘?
- What Are Squatters Rights : Washington Squatters’ Rights & Adverse Possession Laws
- What Does ‚I Have Done It On The System‘ Mean?
- What Does In All Fairness To Him Mean?
- What Are The System Requirements For Sonic Foundry?
- What Are The 5 Adjectives For Debate?