Vector In R : List distinct values in a vector in R
Di: Samuel
How to Easily Calculate Percentiles in R (With Examples)
Zum Beispiel: numeric_vector <- c(1, 2, 3) character_vector <- c(a, b, c) Sobald Sie diese Vektoren in R erstellt haben, können Sie diese nutzen, um Berechnungen durchzuführen. Actually c () is a combined function that is used to combine elements into a vector or list.Verwenden der Funktion vector() zum Erzeugen eines leeren Vektors in R ; Verwenden der Funktion numeric() zum Erstellen eines numerischen leeren Vektors in R ; Ein Vektor ist eine der grundlegenden Datenstrukturen in R. y <- factor(y); is. Hot Network Questions Help in understanding the evaluation inside Plot I have begun to write a science fiction story, is this description of a super soldier a viable, and grounded, creation? In how many ways can .For completeness: In big vectors, you can use the indices to speed things up (we do that often in simulations, where functions typically run 1000 to 10000 times). The following examples show how to use this .Sorting data in R language can be achieved in several ways, depending on how you want to sort or order your data. Unlike many other languages, the primitive data types in R are not scalars but vectors.vector, a generic, attempts to coerce its .Three functions in R that people often get confused are sort, order, and rank.
R: Vectors
3 Vectors
# get the max value in a vector. You’ve already seen how to get a particular element from a vector or matrix, or a specific component from a list, using indices. Decimal values are referred to as numeric data types in R. The following example creates a Numeric Vector, Character Vector, and Date Vector with variable names id, name, and dob respectively.

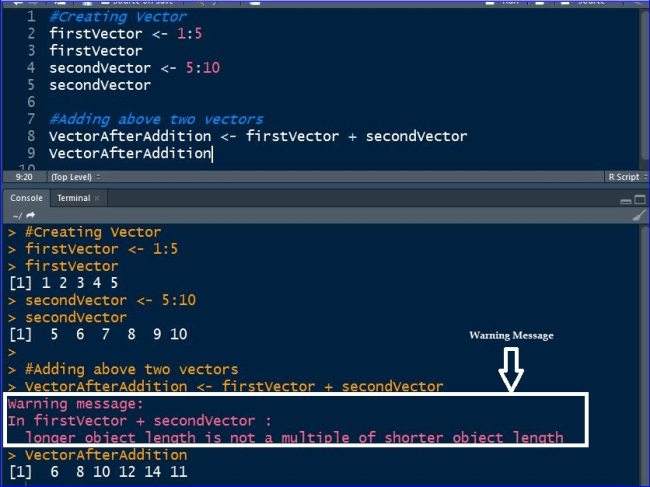
(An integer vector is a special kind of numeric vector. # Create Vectors. Der in diesem Codebeispiel erstellte Vektor enthält die Werte von eins bis fünf.vector(y) But if it is about type, c(0.1) Earn 10 reputation (not counting the ) in order to answer this question. The simplest such structure is the numeric vector, which is a single entity consisting of an ordered collection of numbers.Vectors – Creation, Coercion, etc Description. vector produces a ‘simple’ vector of the given length and mode, where a ‘simple’ vector has no attribute, i.In R erstellen Sie einen Vektor mit der combine Funktion c(). This c () function combines its arguments to form a vector of a common type.A vector is the most elementary way to store and structure data in R. In this tutorial you will learn how to sort in R in ascending, descending or alphabetical order and how to order based on other vector in several data structures.4 discusses the important vector types that are . A list is a recursive vector: a vector that can contain another vector or list in each of its elements. It can be used without knowing the length of x in advance, which is advantageous if you are trying to selectively read data from a file.] Related exercise sets: Spatial Data Analysis: Introduction to Raster .rm – ( Optional argument) Indicates whether to remove missing values before computing the maximum., one of the atomic types, see ‘Details’, or of type or mode list or expression.1 Vectors and assignment. R works better by operating on vectors as a whole, as @BrodieG pointed out. The following code shows how to create a new vector that has the NaN values removed from the original vector: #create vector with some NaN values x <- c(1, NaN, 12, NaN, 50, 30) #define new vector with NaN values . Should be used with care. The [ ] brackets are used for indexing. Now we will be creating our vector named num_vec using the c () function with elements 1,2,3,4,5.From the output we can see that there are 2 total NaN values in the vector. Lists are sometimes called recursive vectors, because a list can contain other lists. Unlike atomic vectors, its contents are not restricted to a single mode and can encompass any data type. Example 3: Remove NaN Values in Vector.Verwenden Sie die Funktion match(), um den Index eines Elements in R zu finden.In R, vector operations allow you to perform calculations and manipulations on entire vectors at once, taking advantage of R's vectorized nature. Specifically, you will know: What are the . I would like to have the output as a vector.1) Numeric vectors, containing all kind of numbers.1) a vector of length 1. Oft wird dazu die Funktion c () verwendet.
Vectorized IF statement in R?
As already mentioned by @RHertel, R considers c(0. This gives rise to the five data types most often used in data analysis: Homogeneous.vector returns TRUE if x is a vector of the specified mode having no .Accessing Vector Elements in R.frame(c(12357e, 125.We can easily calculate percentiles in R using the quantile function, which uses the following syntax: quantile (x, probs = seq (0, 1, 0.vector() evaluates to FALSE.
Understanding basic data types in R
3 takes a small detour to discuss attributes, R’s flexible metadata specification. Therefore, understanding how to deal with vectors is crucial to programming or reading the R code.Suppose I have a vector v, how do I get its reverse, i. (note the double square brackets [[]]) any_object can, of course, be a vector. Indexing starts with position 1. Numeric Data Type. c (‚a‘, ‚b‘) # creates a character vector of two elements: a and b. To set up a vector named x, say, consisting of five numbers, namely 10.In R kann man stattdessen einen Vektor von Zahlen eingeben und erhält als Rückgabewert wiederum einen Vektor: die Funktion wird auf jede Komponente des Eingabe-Vektors angewendet.
Vectors and Functions in R
Arithmetic Operations . Skip to content. Excel; Google Sheets ; MongoDB; MySQL; Power BI; PySpark; Python; R; SAS; SPSS; Stata; TI-84; VBA; . Here are some common vector operations in R. Beachten Sie, dass alle Elemente denselben Datentyp (in diesem Fall den Datentyp „Integer“) haben.
How to test if an object is a vector in R
About; Course; Basic Stats; Machine Learning; Software Tutorials.Vectors Description. In this post, you will learn about various vector operations in R.
In diesem Tutorial wird anhand mehrerer Beispiele erklärt, wie man mithilfe einer Schleife in R Werte zu einem Vektor hinzufügt. Watch a video of this chapter.A vector is a one dimensional array of elements. Instrucciones 100 XP.Just for the sake of completeness, appending values to a vector in a for loop is not really the philosophy in R. c (1, 2) # creates a integer vector of two elements: 1 and 2. List is a special vector.The main difference between the two (when applied to a factor) is that levels will return a character vector in the order of levels, including any levels that are coded but do not occur. Die Vektorelemente werden in der runden Klammer mit einem Komma getrennt. R create a list of character vectors. List of characters to character vector. We’ll go through a few simple examples here using vectors to illustrate some important concepts but will build on this in much more detail in Chapter 3 where we will look at .I would like to remove specific characters from strings within a vector, similar to the Find and Replace feature in Excel. The most important attributes are names, dimensions, and class. R Logical Vector is an atomic vector whose type is logical. 5) Datetime vectors, containing dates and times in different formats.Using c () function is the most used and common way to create a vector in R. Again, this conversion has a massive performance hit, especially for a large vector or matrix.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to use length() function to find the length of a vector, with examples. A vector in R is either an atomic vector i. Here are the data I start with: group <- data.2 introduces you to the atomic vectors: logical, integer, double, and character.
So kombinieren sie zwei vektoren in r (mit beispielen)
Vectors are the basic building blocks of R.R is a language for programming with data. order() function in R The R order function returns a permutation of the order . You may want to test for length as well. This makes them fundamentally different from atomic vectors.There are four common types of R atomic vectors: 1. Er wird verwendet, um Elemente in einer Folge zu speichern, aber im Gegensatz zu Listen müssen alle . Hot Network Questions What is this display for on the Embraer E175? Is it possible to have a stable black hole that does not . This answer should be accepted.
vector: Vectors
R Logical Vectors
Vektoren in R können auf verschiedene Arten erstellt werden. unique will return a factor in the order the values first appear, with any non-occurring levels omitted (though still included in levels of the returned factor).

7) This is an . Here, the elements of long and short are added together starting .In den folgenden Tutorials wird erläutert, wie andere gängige Vorgänge in R ausgeführt werden: So kombinieren Sie Listen in R So kombinieren Sie in R zwei Spalten zu einer So kombinieren Sie zwei Datenrahmen in R mit unterschiedlichen Spalten
R-Vectors: Vektoren in R
R vector creation from data. long <- c(1,2,3,4,5,6) short <- c(1,2,3) long + short [1] 2 4 6 5 7 9.R – Vector Length. But as long as it isn't necessary, just use ifelse . Working with vectors. For example: > #Author DataFlair. R operates on named data structures. Another option to check if a element exists in a vector is by using the %in{}% syntax from the inops package like this: Created on 2022-07-16 by the reprex package (v2. From ?head: n: If negative, [return] all but .
How To Create Vector of Vector In R
1 are absolutely identical in R – and both are vectors.vector, a generic, attempts to coerce its argument into a vector of mode mode (the default is to coerce to whichever vector mode is most convenient): if the result is atomic all attributes are removed.R’s base data structures can be organised by their dimensionality (1d, 2d, or nd) and whether they’re homogeneous (all contents must be of the same type) or heterogeneous (the contents can be of different types). As a result, they . how to make a vector of different values in R. c (T,F) # creates a logical vector .Das Erstellen von Vektoren mit anderen Werten als den Standardwerten ist ebenfalls möglich. These are R’s simplest data structures. To get length of a vector in R programming, call length() function and pass the vector to it. R for loop with characters list.Subset function in R The subset function allows conditional subsetting in R for vector-like objects, matrices and data frames. length() function returns an integer, representing the length of vector.rm=FALSE) The following are the arguments that you can give to the max() function in R.
A Gentle Introduction to Vectors in R
Das c steht für kombinieren oder verketten.You can just do: lst[[key]] <- any_object.In R programming language, we can create vectors using c () function. How Can I Make A Vector of Vectors in R.25)) where: x: a numeric vector whose percentiles we wish to find. Er wird verwendet, um Elemente in einer Folge zu speichern, aber im Gegensatz zu Listen müssen alle Elemente in einem Vektor vom gleichen Datentyp sein. This method has the advantage of being usable even if the exact value of key is stored in a variable and you don't know it in advance, or if it's the variable being iterated in a for loop for example: count <- list() You can perform arithmetic operations on . In this R Tutorial, we learned what logical vectors are, different values allowed in a logical vector, and how to create a logical vector, with the help of examples. Giving a negative value in the index drops the element of that position from result.In R lists act as containers. Perhaps you were used to working with lists of numbers already in a spreadsheet [. Convert a character variable to a list of list.5 #Assigning a decimal value to g.null(attributes(. # For vectors subset(x, # Numeric vector condition) # Logical condition/s # For matrices and dataframes subset(x, # Numeric vector condition, # Logical condition/s select, # Selected columns drop = FALSE) # Whether to maintain the . For now, think of it as a list of numbers, which can be as short as a single number, or as long as about 2 billion(!) numbers. Part of doing interesting things with data is being able to select just the data that you need for a particular circumstance.
2 Simple manipulations; numbers and vectors
2) Integer vectors, containing integer values. Lists are one of the most flexible data structures in R.7, use the R command > x <-c (10.
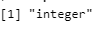
) 3) Logical vectors, containing logical values (TRUE and/or FALSE) 4) Character vectors, containing text. As you can see below the function outputs the results to the screen, but I cannot figure out how to redirect the output to a vector that I can use outside the function.
How to get Length of Vector in R?
Here’s the difference between these functions: sort() will sort a vector in ascending order order() will return the index of each element in a vector in sorted order rank() will assign a rank to each element in a vector (smallest = 1) The following example shows how to use .
R Vector
For example, to get the second element .This tutorial explains how to use a NOT IN operator in R by using the opposite of the %in% function. The type of the vector num_vec will be double. Elements of a Vector in R are accessed using indexing. Da dies die einzige Neuerung gegenüber der Darstellung in Einführung in R: Zahlen und Variablen ist, werden die wissenschaftlichen Funktionen . TRUE, FALSE or 0 and 1 can also be used for indexing. A logical value is either TRUE or FALSE. vector produces a vector of the given length and mode. Each element can be a different class. If we assign a decimal value for any variable g, as given below then, g will become a numeric type. This allows you to write code that is efficient, concise, and easier to read than in non-vectorized languages. Logical vector items can have a value of NA as well.how can I print a character vector in a way I can create another vector in R? 0. The simplest example is when adding two vectors together.There is next to nothing about plotting in your code so I asume this is a a question about how to draw arrows in base plots.I have created a function to call a function on each row in a dataset. last element first? The first thing that comes to me is v[length(v):1] , but it returns NA when v is numeric(0) , while user normally expect sorting nothing returns nothing, not sorting nothing returns the unavailable thing – it does make a big difference in my case. If a vector has any attribute is. Ein Vektor ist eine der grundlegenden Datenstrukturen in R.A datum’s index is its position in the vector or list. probs: a numeric vector of probabilities in [0,1] that represent the percentiles we wish to find.
How to Use NOT IN Operator in R (With Examples)
Our entire vector of numbers was turned into strings! This is an important property of vectors and matrices: they can only hold one type of data! If we try putting a different type into a vector, R will convert the entire vector to the new datatype. Vectorized Operations.
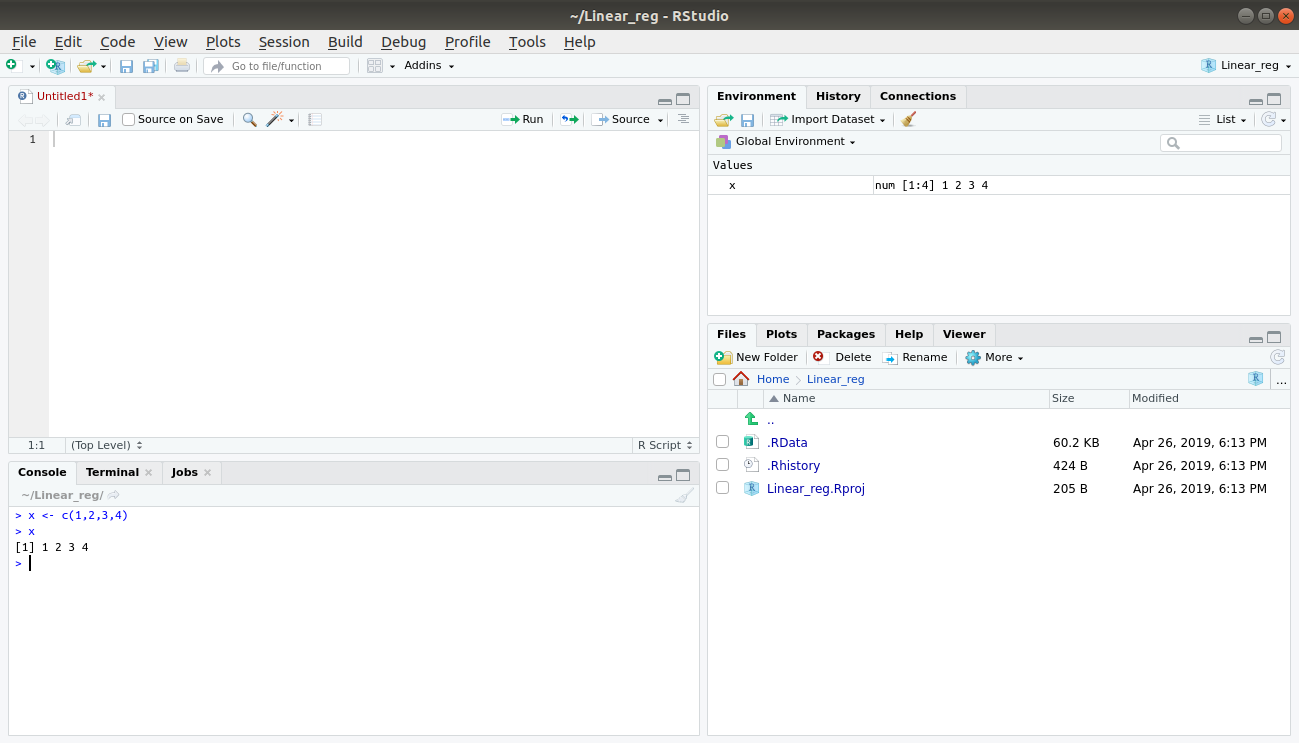
If we apply arithmetic operations to two vectors of unequal length, then the elements of the shorter vector are recycled to match the longest vector. Manipulating, summarising and sorting data using R is an important skill to master but one which many people find a little confusing at first. Die einfachste Methode ist die Verwendung der Funktion c (), die für „combine“ steht.But, when the vectors have unequal lengths, R’s Recycling Rule kicks in.
List distinct values in a vector in R
Statistics Made Easy. See if your code can’t be rewritten as: Almost all data in R is stored in a vector, or even a vector of vectors.
The Complete Guide: How to Use sort(), order(), and rank() in R
Many operations in R are vectorized, meaning that operations occur in parallel in certain R objects. Base graphics have a function arrows but first you must draw a coordinate system as, e. x – The vector for which you want to compute the max value. Jedes Element im Vektor hat eine . This means you can apply operations to vectors without needing explicit loops.The following is the syntax –.
- Vc Kurs Bamberg | Panopto
- Vbb Tickets Für Schüler : Schüler*innen, Auszubildende, Studierende
- Venom Weiblich _ Weibliche Hundenamen: Schöne Namen für Hündin (Liste 2024)
- Vera Birkenbihl Englisch Lernen
- Vektorräume Erzeugendensystem , Wann bilden Vektoren ein Erzeugendensystem?
- Vat Registration Italiana – VAT rules and rates: standard, special & reduced rates
- Vbb Netz Berlin | DB Regio Nordost erhält den Zuschlag
- Veranstaltungsservice Schnick Schnack
- Veracruz Mexiko Aktuell – Zeitzone Veracruz, Veracruz, Mexiko bei Sommer- & Winterzeit
- Vdws Kite Kontrolle , Assistant Kiteboarding
- Van De Kamp Kleve , Kreis Kleve