Upper Limb Artery Diagram _ Upper Limb Arteries- Labeling Diagram
Di: Samuel
Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Axillary Artery
Anatomy Tables
The radial and ulnar arteries originate as a bifurcation of the axillary artery in the cubital fossa and serve as the major perforators of the forearm. It contains the shoulder girdle, which connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton via the sternoclavicular joint.This online quiz is called Upper Limb Arteries. A&P – Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function – Chapter 20: The Blood Vessels – MEGAKIT. It supplies the anterior compartment of the forearm. crosses anterior to the axillary artery and is used to delineate the 3 parts mentioned at left: brachial: axillary a.org subsclavian artery axillary artery thoracoacromial trunk lateral thoracic artery subscapular artery posterior humeral circumflex artery anterior humeral circumflex artery brachial artery deep brachial artery common interosseous artery .Being located in the anterior and medial aspects of the interhemispheric fissure, the anterior cerebral artery supplies a large portion of the medial cerebral hemispheric surfaces namely the corpus callosum, frontal, parietal, and cingulate cortex. The subclavian arteries are the major arteries supplying the upper limbs. is the continuation of the axillary a. The humerus is the single bone of the arm, and the ulna (medially) and the radius (laterally) are the paired bones of the forearm.The brachial artery travels down the anterior part of the upper arm, reaching the cubital fossa at the elbow region where it .The images of this upper limb artery angiography are from the left upper extremity of an abnormal patient, a 50-year-old woman with thromboangiitis obliterans, severe secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon and digital ischemia resulting in gangrene of her left thumb and index finger. location: inferior aspect of the cubital fossa. In the arm, the median nerve courses laterally to the brachial artery and then crosses it, usually anteriorly, from lateral to medial. It originates from nerve roots . Central – 3-4 large nodes, located near the base of the axilla (deep to pectoralis minor, close to the 2nd part of the axillary artery). Blood supply: superior and inferior labial branches of the facial artery. As the subclavian artery exits the thorax into the axillary region, it is renamed the axillary artery. This has three major branches — the brachiocephalic trunk, the left common carotid . The arterial circulation of the upper limb is depicted in Fig. Anatomy of anterior compartment of arm.

Learning Unit Psych.In the axilla, the median nerve lies lateral to the axillary artery.The upper limb includes the scapula, clavicle, humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and small bones of the hand., inferior ulnar It then passes deep to the median nerve and courses obliquely and medially (ulnarly) beneath the . Besides arm anatomy . Common iliac artery.

The muscles of the upper limb form as a combination of somatic cells (muscle cells and myosatellite cells) and somatopleuric cells (tendons and other connective tissue structures).Diagram of arteries of upper limb.
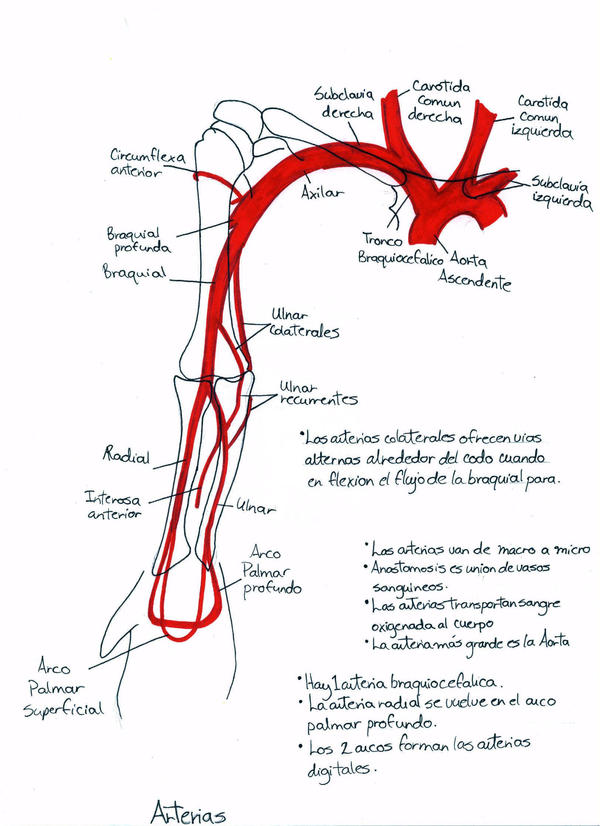
Arteries of the Upper Limb (Shoulder, Arms & Hands)
there is only one brachiocephalic trunk. THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH. Each has 34 muscles, 29 bones, 3 major nerves, and 2 major arteries. Innervation originates in the neck and travels down to allow muscle action of flexion, extension, pronation, supination, and rotation necessary to achieve activities of daily living. After a right femoral puncture, a 100 cm 4 F angled catheter . right side of the head and neck; right upper limb and right side of the chest wall. Note that the internal thoracic arteries (previously internal mammary arteries), which are tributaries of the subclavian arteries, are used commonly for coronary artery bypass.Supraspinatus will arise from the cells in the dorsal pre-muscle mass.
Upper Limb Arteries- Labeling Diagram
The radial artery is one of two continuations of the brachial artery, the other being the ulnar artery. It was created by member jlricha2 and has 16 questions.The brachial artery is the continuation of the main arterial supply in the upper arm as it travels medially towards the elbow.Upper Limb – Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Median nerve
From the lower margin of the axillary space to the bend of the elbow, it is termed the brachial artery; here, the trunk ends by .
Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Median Nerve
It specifically focuses on bones, muscles (including attachments, innervation, functions), arteries, veins, and nerves. main branches: anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent arteries, common interosseous artery, palmar carpal arch, superficial palmar . The brachial plexus is a collection of nerve fibres that supply motor and sensory innervation to the upper limb. This artery is the continuation of the axillary artery after it passes below the lower border of the teres major muscle.Vasculature of the Upper Limbs. Axillary artery. It arises from the brachial artery as its larger terminal branch at the level of the cubital fossa with the brachialis muscle at its deep surface.
Upper Limb Arteries Quiz
Tutorials coming soon. The right and left subclavian arteries serve the upper limbs.A n P LAB Practical 2 Label arteries and veins of upper limb. dorsal metacarpal aa. Tackle it to cement and master the anatomy of the arm and shoulder! The profunda brachii is the first and main branch of the brachial artery.

The brachial plexus is a critically important . The common iliac arteries supply the lower limb, the gluteal region, and the pelvic viscera. The deep palmar arch arises from the radial artery, and the superficial palmar arch arises from the ulnar artery. Upper Limb • 140 likes • 31,040 views. Branchial artery.
Arteries of the Upper Limb
On the right side the subclavian artery is one of the terminal branches of the brachiocephalic trunk , while on the left it is one of the direct branches of the aortic arch . The base of the hand contains eight carpal bones, and the palm of the hand is formed by five metacarpal bones.The ascending aorta distributes oxygen and nutrients to the heart via the coronary arteries.The shoulder is structurally and functionally complex as it is one of the most freely moveable areas in the human body due to the articulation at the glenohumeral joint.org/Ninja Nerds!In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be presenting on the arteries of the upper limb in . catherineanna36455. The high range of motion of the shoulder comes at the expense of .The arteries of the upper limbs branch into . The neurovascular anatomy of the lip is detailed below. The common iliac arteries follow a course initially anteromedial and then medial to the psoas major muscles. Palmar arterial arches (digital arteries).Arteries of Upper Limbs.Main arteries of the upper limb Explore study unit.right common carotid a. Branches from the subclavian arteries occur (not shown in the figure below) and in the armpit regions, the main arteries serving the upper limbs (continuous with the subclavian arteries) are called the axillary arteries. dorsum of the hand and digits, excluding the distal phalangeal segment. We’ll go over the bones, joints, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels that make up the human arm.Arteries of the Upper Limb.

With several different quiz types available, you can test your knowledge from every angle.The radial artery is a terminal branch of the brachial artery and arises at the cubital fossa of the forearm.The lip plays a vital role in oral competence, sensation, speech and cosmesis. It gives off the deep brachial artery and collateral branches that supply the arterial anastomosis of the elbow before terminating distal to the elbow by bifurcating into the radial artery and ulnar artery.
Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Forearm Muscles
Distal to the profunda, the brachial artery gives off nutrient . It enters the arm from axilla at the inferior margin of the teres major muscle and descends medially between biceps brachii and triceps brachii. As it courses posteriorly, it sweeps posterolaterally to the humerus to end up lateral and posterior to the elbow.If you are able to palpate some of the superficial veins on your upper limbs and try to move them, you will find that the tunica externa prevents this. From this point to the lower border of the axilla, it is named the axillary artery. An artery is a blood vessel that conducts blood away from the . Following its bifurcation, the radial artery runs . The hands‘ major arteries are the radial and ulnar arteries, which bifurcate from the brachial artery (see Image.

The vessel that extends from its origin to the outer border of the first rib is termed the subclavian artery.Humeral (lateral) – 4-6 nodes, located in the lateral wall of the axilla, posterior to the axillary vein. Arterial anatomy of the upper extremity.1) begins with the common iliac vessels , the terminal branches of the abdominal aorta. Gen Bio II: Porifera, Cnidarians, Flatworms. This bifurcation occurs anterior to the fourth lumbar vertebra slightly to the left of the midline.The terminal branches of the abdominal aorta, the left and right common iliac arteries, arise from the bifurcation in front of the body of L4 vertebra about 1.
Arterial supply of the upper limb
Aorta: Anatomy, branches, supply
These muscles are innervated by C5-T1 spinal nerves.

Pectoral Girdle and Shoulder Upper Arm Elbow Forearm Wrist and Hand Nerves Vascular Supply Axilla.Official Ninja Nerd Website: https://ninjanerd., right subclavian a. It provides key landmarks . They receive most of the lymph drained from the upper limb. If the tunica externa did not hold the vessel in place, any movement would likely result in disruption of blood flow. supply: elbow joint, lateral forearm muscles, radial nerve, . BSC2086 LAB Midterm Practical . With the hand supinated, the wrist was . The hands are intricate structures.
Ulnar artery
The arm is one of the body’s most complex and frequently used structures. These arteries may get involved with a number of disease processes which restrict the optimal functioning of the limb.Arteries Serving the Upper Limbs.The ulnar artery provides an important contribution to the vascular supply to the hand and upper extremity.The innervation of the upper limb is divided into anterior (ventral) divisions that supply the anterior muscles (such as biceps brachii, brachialis, pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus, and pronator quadratus). The radial artery was exposed but left in its anatomical position. Lower limb circulation (Fig.If you answered “yes”, look no further than our interactive cardiovascular system quizzes. Motor: buccal and mandibular branches of facial nerve. Health & Medicine Business.25 cm to the left of the median plane.The brachial artery is a major blood vessel in the upper arm that supplies oxygenated blood to the upper limb. MBBS IMS MSU Follow.
Cardiovascular system diagrams, quizzes and free worksheets
Lower extremity arteries play vital role of supplying blood to the extremity bone, muscles, tendons and nerves to maintain the mobility of the body.The axillary artery is the principal arterial supply of the upper limb, commencing as a continuation of the subclavian artery as it emerges from underneath the first rib to enter the axilla. Their complexity supports the work required to produce fine motor movements.
Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Forearm Radial Artery
origin: terminal branch of the brachial artery. Sensory: infraorbital (upper) & mental (lower) branches of trigeminal nerve. Two muscular compartments – an anterior (flexor) and posterior (extensor) compartment – contain together twenty muscles that act on the elbow and wrist joints, as well as carpometacarpal, . On the right side the subclavian artery is one of the terminal branches of the brachiocephalic trunk , while on the left it is one of the direct branches of the aortic arch.After the routine dissection of the right upper limb of an adult male cadaver, we found a very rare variant of the superficial arch artery – a division in a higher level brachial artery.There are 30 bones in each upper limb. It is one of the two main arteries of the forearm, along with the ulnar artery. Although it does branch and supply blood to the region near the head of the humerus (via the humeral circumflex arteries), the majority of the vessel continues into the upper arm, or brachium, and becomes the brachial .exploringnature. carpal arterial arch, dorsal. Terms in this set (6) Subclavian artery.Artery of precentral sulcus travels in the precentral sulcus to supply the posterior aspect of the inferior and middle frontal gyri, Broca’s area and the precentral gyrus, which contains the primary motor cortex for the head, upper limb, and trunk.There are 6 topics covered in the nerves of the upper limb, an overview of the brachial plexus and a more in-depth look into it’s 5 main branches: axillary, musculocutaneous, median, radial, and ulnar nerves.
Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Nerves
It arises above the midpoint of the upper arm on the medial aspect of the vessel.Arteries of the Upper Limb (Shoulder, Arms & Hands) ©Sheri Amsel www. As the embryo reaches approximately 11 mm in length, the spine of the scapula and . supply: elbow joint, medial and central forearm muscles, median and ulnar nerves, and common flexor sheath.
Upper Limb
Download Now Download to read offline., superior ulnar collateral a. 3D models and videos covering the anatomy of the upper limb – learn about the muscles, bones, blood supply and nerves of the shoulder, arm, forearm and hand. The vertebral artery supplies the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum and posterior part of the brain. Covering not just major arteries and veins but also the organs and tissues of the cardiovascular system, these quizzes will truly prepare you for your exam. It courses superiorly along each side of the neck region and ultimately merges with its counterpart at the pontomedullary junction to form the basilar artery. This quiz is specially designed to test your knowledge about the shoulder and arm. Artery of central sulcus travels within the central sulcus and contributes to the blood supply .Methods Twenty adult cadaveric upper limbs underwent dissection of the radial artery.The forearm is the section of the upper limb from the elbow to the wrist, whose bony structure is formed by the radius (laterally) and ulna (medially). The fingers and thumb contain a total of 14 phalanges.) deep brachial a.The vertebral artery is the first branch of the subclavian artery. The knowledge of various diseases, clinical presentation, .pectoral region, shoulder region and upper limb: pectoralis minor m. They receive lymph via efferent vessels .
Brachial artery
distal to the teres major m. Through the anterior communicating artery, it anastomoses with its contralateral .
Circulatory System
- Untertourige Fahren Auto , Untertouriges Fahren
- Ups Paketshop | UPS Access Point Lübeck ️ Öffnungszeiten & Filialen
- Unterschied Zwischen Sit Up Und Crunches
- Urlaub Mit Hund Hamburg : Urlaub mit Hund im hundefreundlichen Hotel in Hamburg
- Unterwäsche Kaufen , Damenwäsche die das ️ begehrt
- Urlaubsersatzleistung Teilzeit Berechnung
- Urologe Chemnitz Zeisigwald : Anfahrt
- Urlaub In Seiffen Mit Frühstück
- Urlaub Mit Pferd In Renesse : Renesse, Horizon 1
- Urlaubsanspruch Nach Pflichtpraktikum
- Unzustellbare Email Adressen Entfernen
- Unwetter Starnberg Heute _ Wetter Bernried am Starnberger See
- Urlaub Ischia Mit Flug : Die italienische Insel Ischia im Golf von Neapel