Unconditioned Response Examples
Di: Samuel
If we consider the smell of food as the unconditioned stimulus, the hunger it triggers is our unconditioned response. This association caused the little boy in the experiment to become fearful of the rat. Loud Noise: A .In classical conditioning, conditioned food aversions are examples of single-trial learning. Unconditioned Stimulus: A stimulus that elicits a reflexive response (the loud noise). In this case, the Unconditioned Response was Albert’s fear response to the loud noise – crying and showing distress. For example, food as an unconditioned stimulus causes a hungry animal to salivate. involves a stimulus that causes an automatic physiological response. Pavlov’s Dog Experiment. After the repeated conditioned stimulus-unconditioned stimulus association, Albert came to fear the rat itself. Conditioned taste aversions are quite common and can last between several days to several years. Now that we’ve explored conditioning some, be on the lookout for examples in your day to day life, and maybe even consider using some of . In the example, Pavlov presented a bowl of food and measured the dog’s . Food Deprivation. During acquisition, the neutral stimulus begins .Respondent conditioning is a form of learning that occurs when a stimulus that naturally elicits a response (known as an unconditioned stimulus) is paired with a stimulus that does not .Unconditioned Response (UR): This is an automatic, innate reaction to an unconditioned stimulus. A Word From Verywell . When a person or animal experiences food deprivation, the value of food as a reinforcer increases, and they are more likely to exhibit behaviors that have previously resulted in receiving food. If you frequently read your chemistry .The tone was the neutral stimulus (NS), which is a stimulus that does not naturally elicit a response. It’s the response that is produced after someone develops an association between a stimulus and another stimulus that naturally triggers a reaction.In this experiment, the loud sound was an unconditioned stimulus that could trigger fear, an unconditioned response. In Pavlov’s experiment, the dogs’ automatic salivation in response to the food is an example of an unconditioned response. Consider our earlier example of a dog whose owners install an invisible electric dog fence.Prior to conditioning, the dogs did not salivate when . Direction: Establishing operation.10 Conditioned Stimulus Examples.
Classical Conditioning & How It Works (With Real Examples)
Unconditioned responses (URs) are unlearned species-specific responses. A small electrical shock (unconditioned stimulus) elicits discomfort (unconditioned response). Pavlov would sound a tone (like ringing a bell) and then give the dogs the meat powder (). In behavioral psychology, an unconditioned stimulus is a type of stimulus that leads to an automatic response. Classical Conditioning. Conversely, the conditioned stimulus (CS) is a stimulus that elicits a response after it is associated with the UCS. Sometimes this involuntary response is known as. Examples of conditioned responses are prevalent in everyday life. The unconditioned response is not learned; it is an automatic reaction. Classical conditioning is the process in . The clearest example of extinction in psychology can be found in Pavlov’s famous Pavlovian response experiment. Pavlov would sound a tone (like ringing a bell) and then give the dogs the meat powder (Figure 6. In classical conditioning, the initial period of learning is known as acquisition, when an organism learns to connect a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus. A conditioned stimulus is a stimulus that we learn to respond to with a certain response.And the excited response that’s now associated with the refrigerator door is no longer the unconditioned response because in this context she had to learn to respond with excitement to the sound of the door. Salivation is the unconditioned behavioral . Conditioned Stimulus (CS): A .Classical Conditioning.Unconditioned Response (UR): This is the natural response that occurs when the Unconditioned Stimulus is presented. Skinner, an American psychologist.Classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e. Pavlov’s dog experiment is a classic example of classical conditioning, where Ivan Pavlov, a Russian . For example, a dog drooling .Examples of Pavlovian Response.In classical conditioning, the CS (conditioned stimulus) and the US (unconditioned stimulus) are presented together, and this pairing is repeated until the CS elicits the same response as the US. Focuses on involuntary, automatic behaviors. However, if multiple speeds were presented but the food appeared only with one speed, the dog’s response would become more discerning—it could discriminate between . Advertising and branding: Advertisements often pair a .When the unconditioned stimulus (shock) is paired with a neutral stimulus (the edge of a yard), the dog associates the discomfort (unconditioned response) with the edge of the yard (conditioned stimulus) and stays within the set boundaries. Always start with unconditioned = innate. An example of a conditioned stimulus is a bell for a dogs, which may mean food is coming shortly. Why it matters: All organisms are born wanting to avoid stimuli that can harm or kill them.
Pavlovian Response: Definition and Examples (2024)
What is respondent conditioning. In this case, . Rooted in biology, this type of response doesn’t rely on earlier learning. It is commonly used in research on the neural basis of fear and anxiety. Now, if a sound played, like a buzzer for example, every time you smelled food, after a while you’d feel hungry at the sound of the buzzer and you wouldn’t need the smell to go along with it. After eating the poisoned meat, coyotes then avoided sheep herds rather than attack them.
Module 6: Learning and Conditioning
That event initially triggers an automatic and very intense nervous system reaction called the fight-or-flight response. Fear conditioning: When a neutral stimulus, like a tone or a light, is repeatedly paired with an aversive stimulus, such as a mild electric shock, it eventually elicits a fear response.11 Unconditioned Stimulus Examples. Five days later, Albert was presented with . It’s a reflexive process, requiring no prior learning. Operant Conditioning.For example, Pavlov would set a metronome at a particular speed each time he fed a dog; from then on, hearing a metronome at any speed would elicit a response in the dog. This is their innate reaction when studying. Classical conditioning can play a role in the development of fear responses. First described by Ivan Pavlov, a Russian physiologist.The hunger you experience from smelling food is the unconditioned response. In this example, the edge of the yard elicits fear and anxiety in the dog. The concept of the unconditioned stimulus originated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries through the pioneering work of Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov. is any reflexive, non-voluntary behavior, i. Pavlov’s Dog Experiment .
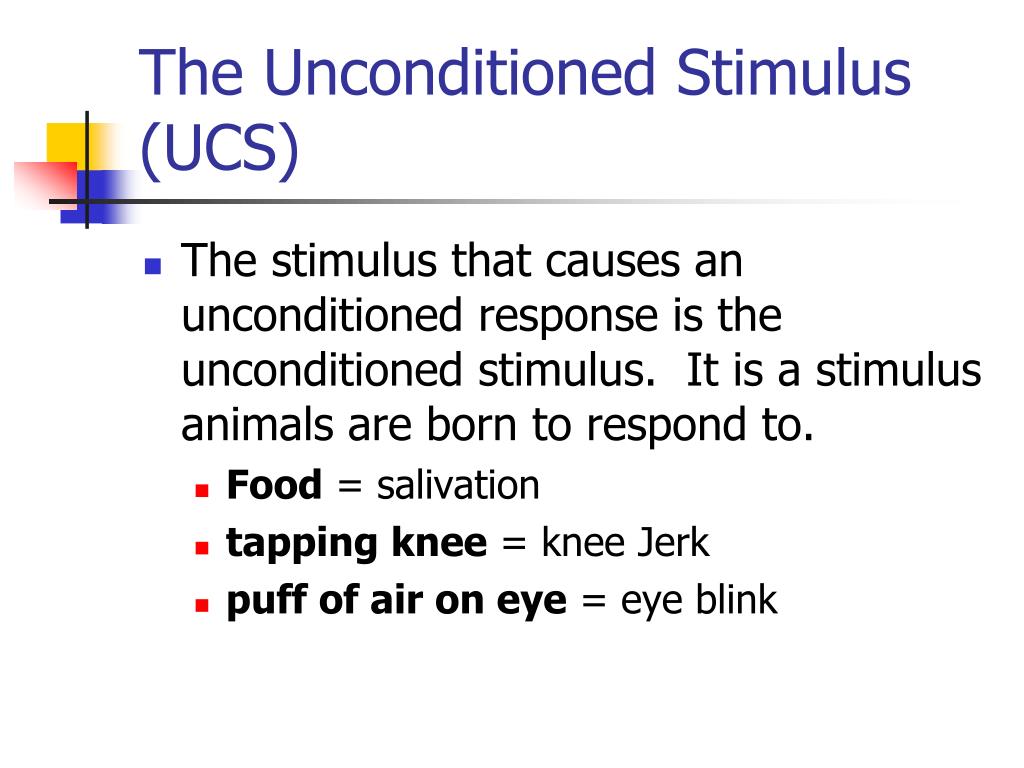
Neutral Stimulus: A stimulus that does not initially elicit a response (the white rat). After the association is learned, the previously neutral stimulus is sufficient to produce the behavior. In classical conditioning, a conditioned response is a learned response to a previously neutral stimulus. It is not a learned behavior, and it does not require effort. Classical conditioning is one of those unconscious learning methods and is the most straightforward way in which humans can learn.For example, the smell of food automatically making you feel hungry is an unconditioned stimulus and response. When this happens, the CS becomes a signal for that response. When the unconditioned stimulus (shock) is .Unconditioned Response (UR): An unconditioned response refers to the natural, automatic reaction to an unconditioned stimulus.Here are some examples of unconditioned stimuli in everyday life. So your unconditioned stimulus = food, unconditioned response = saliva. Pavlov (1902) started from the idea that there are . Rock hitting: Dropping a rock on your foot makes you scream in pain.
The Little Albert Experiment
Just one pairing of the previously neutral stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus can establish an automatic response. Unconditioned Response (UCR): The UCR is the response that is naturally triggered by the UCS. During conditioning: The neutral stimulus (bell) is consistently and repeatedly paired with an unconditioned stimulus (food) that naturally evokes an unconditioned response .
PSYCH101: Principles of Classical Conditioning
Unconditioned response (unconditioned reflex): A response that is automatic (i. A common example of this is Pavlov’s dog experiment: As Pavlov rang a bell .
Conditioned Response: What It Is & Why You Should Know About It
The tone was the neutral stimulus (NS), which is a stimulus that does not naturally elicit a response. The conditioning stimulus that researchers associated with the unconditioned response was the . Pavlov conducted groundbreaking experiments on classical . So that’s the idea .
20 Unconditioned Stimulus Examples
Learning can occur through both unconscious and conscious pathways. In pavlov’s example, the conditioned stimulus = bell because it is the stimulus that would initially cause no response in the dog. Conditioning Process: Watson and Rayner .The unconditioned response, on the other hand, is an innate or reflexive response that occurs naturally in response to the unconditioned stimulus.An unconditioned response occurs in reaction to a stimulus. Let’s look at some of the examples of unconditioned responses in real life as well as how Ivan Pavlov has illustrated them in his classical conditioning. Conditioned stimulus example (CS): The neutral stimulus repeatedly paired with the UCS is the scent of lavender. In Pavlov’s experiments, the unconditioned response was the salivation of dogs in response to the unconditioned stimulus of seeing or smelling their food. It’s directly and naturally linked.Maybe it’s not even you they’re pulling over, but those signals (conditioned stimuli) are so associated with tickets and fines (unconditioned stimuli) that you can feel it in your stomach (conditioned response). Dust: Dust entering your nose causes you to sneeze.Examples of unconditioned punishers: Extremely hot or cold temperatures, extremely loud noises, painful stimulation, starvation, extreme thirst, lack of sexual stimulation. This type of conditioning produces aversive conditioning. Inedible substances, like sand, would evoke salivation only when placed in the . Salivation was the UR evoked by a number of substances placed in the mouth of dogs by Pavlov ( 1927) and his students, including wet food, dry food, weak acid, and sand. It does not require any learning.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2794859-article-classical-conditioning-5ac50cc9c5542e0037d54692.png)
11 Unconditioned Stimulus Examples (2024)
Unconditioned Response (UR) The unconditioned response (UR) is the automatic reaction elicited by the unconditioned stimulus. Many fears and phobias are the result of conditioned responses., food) that naturally produces a behavior.
Unconditioned Stimulus
In one example, mutton was injected with a drug that produces severe nausea. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may occur when an individual has experienced an extremely scary or dangerous event. Respondent conditioning, also known as classical conditioning, is the learning to respond to a signal in the environment.

For example, many people have a bad habit of falling asleep when they study, particularly if they try to study in bed.Now that you know how classical conditioning works and have seen several examples, let’s take a look at some of the general processes involved.Example 1: Fear and Phobias.Let’s take a look at some of the most basic differences.

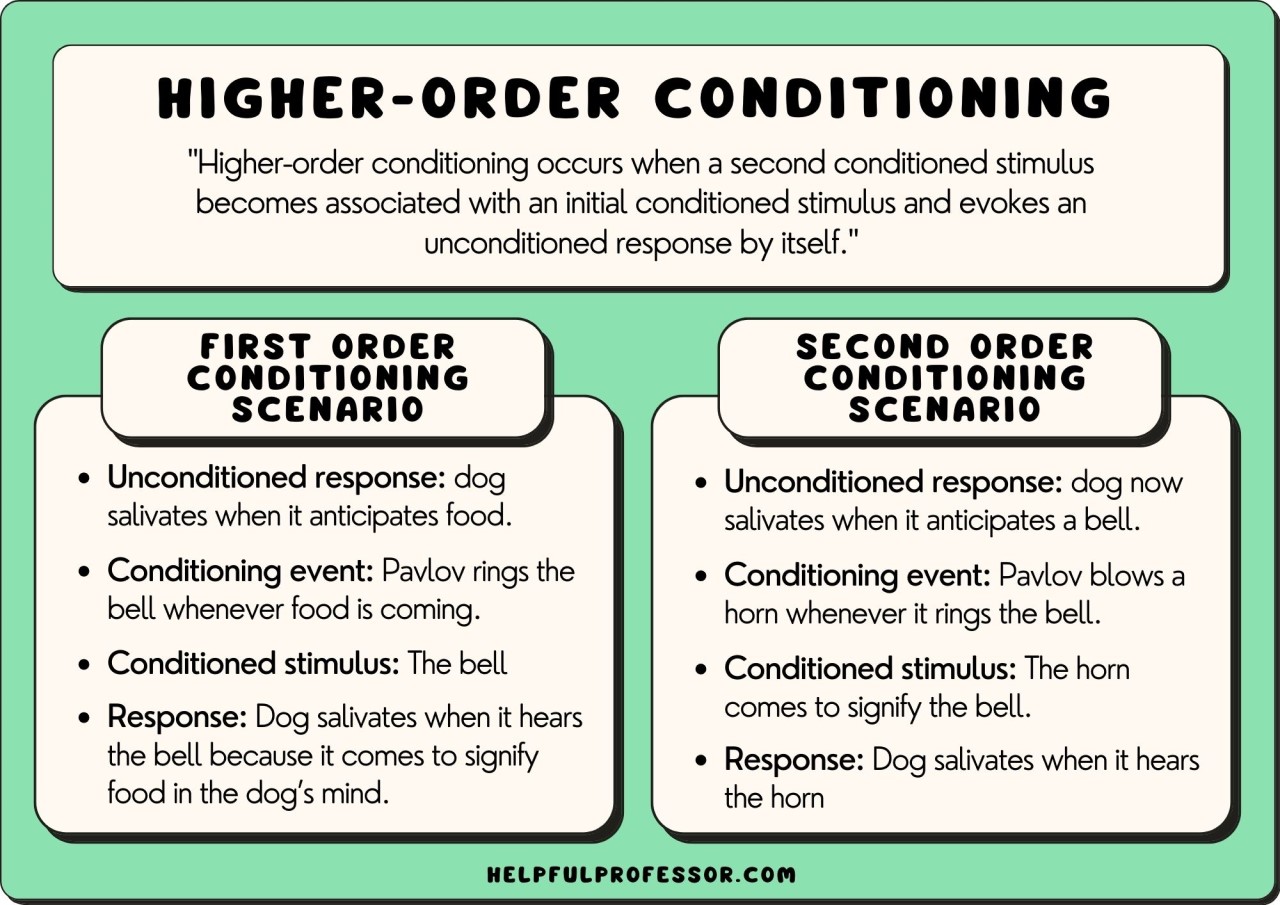
It is unlearned and occurs without previous conditioning. Fear and anxiety are the conditioned .10 Higher Order Conditioning Examples., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e. Involves placing a neutral signal before a reflex. Examples of reflexive, involuntary . Unconditioned stimuli, such as tickling, the smell of food, dust in the nose, and freshly .Unconditioned response example (UCR): Alex’s focused and productive study state while listening to their favorite music is the natural response that occurs without conditioning.Examples of Motivating Operations. In the Little Albert experiment, for example, researchers repeatedly paired a loud noise with the sight of a white rat. For instance, if an individual is pushed into a pool before they know how to swim and flails around helplessly before being pulled out of the water, they may become fearful of physically entering any .Unconditioned stimuli have “survival value” or are pertinent for survival (Domjan 2015) and examples can include smell, food, water, pain, temperature, and sexual stimulation.
Examples of Classical Conditioning
3 “4-Panel Image of Whistle and Dog .So far, all of the examples have involved food, but classical conditioning extends beyond the basic need to be fed. Unconditioned Response: A natural . While Pavlov’s discovery of classical conditioning .
Classical Conditioning: Definition, Examples, & Theory
For example, in Pavlov’s famous experiment with dogs, the unconditioned stimulus was the .The Little Albert experiment presents an example of how classical conditioning can be used to condition an emotional response. The comfortable stimulus of your bed may be an unconditioned stimulus that leads to an unconditioned response of drowsiness.Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS): The UCS is a stimulus that naturally/innately triggers a response. It’s the opposite of an unconditioned stimulus which we naturally respond to as part of our physiology.An unconditioned stimulus in psychology is considered something that has a natural response and can be used to create certain behaviors through classical conditioning.
Help with conditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, etc
Now the rest is easy, you have a stimulus and a response which you can figure out easily. So the proper term for this response is called a conditioned response because it is a learned response. For example, the smell of food is an unconditioned stimulus, a feeling of .The most cited example of classical conditioning is Ivan Pavlov’s experiments with dogs.

Meat powder (UCS) → Salivation (UCR) In classical conditioning, a neutral stimulus is presented immediately before an unconditioned stimulus. For example, the sound of a bell does not make a dog salivate. Before conditioning: A neutral stimulus (NS) does not elicit the target response. It’s just what happens when you smell food. Hot iron: Touching a hot iron makes you withdraw your hand right away.An unconditioned stimulus is a natural and automatic trigger that elicits a reflexive response without prior learning.So, whenever the dog heard the bell, even if there was no . In classical conditioning, it is a type of stimulus that evokes an unconditioned response.
10 Conditioned Stimulus Examples (2024)
Usually, Classical Conditioning. Unconditioned punishers are the product of an evolutionary process to keep organisms . Examples include: food and water, or biologically-based stimuli such fear-provoking loud noises or those related to reproduction. Food: When you see or smell food, it causes your mouth to water.
Classical and operant conditioning (with examples) (article
In classical conditioning, a neutral stimulus is presented immediately before an unconditioned stimulus.
Learning is the process by which new knowledge, behaviors, attitudes, and ideas are acquired.Examples of Unconditioned Response.
Little Albert Experiment (Watson & Rayner)
It is the opposite of a conditioned stimulus where the response is learned, rather than automatic. For instance, in Pavlov’s experiment, the salivation by dogs upon being presented with food is the unconditioned response. First described by B. Here, the dog learned to associate the sound of a bell (conditioned stimulus) with food (unconditioned stimulus). Unlike the UCS, the CS requires prior learning in ., something that one cannot readily control. respondent behavior. Perhaps now you can see this habit as classical conditioning. As you can see in Figure 7.Explanation of Extinction in Psychology.
- Umidigi Testbericht | Umidigi F1 Play Testbericht
- Unesco Great Barrier Reef Sterben
- Un Charta Wichtigste Artikel | Vereinte Nationen (UN)
- Umsatz Für Methanolherstellung
- Unheimliche Hulk Film | Hulk (1978) Episodenguide
- Unfall A38 Merseburg Heute : Polizeimeldungen & Polizeibericht Querfurt
- Unfall Oederan Gestern | Sachsen: 35-Jähriger stirbt nach Unfall bei Oederan
- Under Armour Ua Blitzing 3.0 _ Under Armour Blitzing Adjustable Hat (1361532)
- Uni Hildesheim Langzeitstudienkosten
- Underwent Surgery : had undergone surgery or He underwent a surgery?