Types Of Hemolytic Diseases – 4 Types of Hypersensitivity Reactions
Di: Samuel
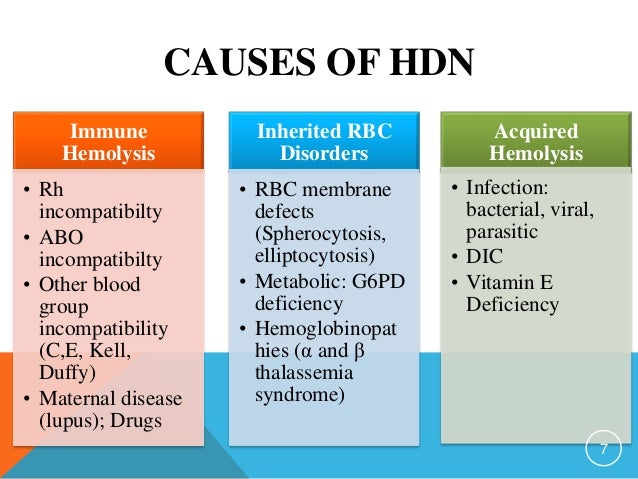
ABO Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn. In hemolytic anemias, the low red blood cell count is caused by the destruction — rather than the underproduction — of red blood cells. For instance, the overall prognosis of hemolytic disease of the newborn is good if identified and treated promptly. HDN is relatively uncommon in the United States due to advances in early detection and treatment, limiting it to approximately 4,000 cases a year. In the past, an HDN (clinically known as erythroblastosis fetalis) could put a baby’s health at serious . If you’re Rh negative and have not been sensitized, you’ll get a medicine called Rh immunoglobulin (RhoGAM). It is associated with the development of maternal Rh sensitization and hemolytic disease of the neonate (HDN).Hemolytic disease of newborns is another type II hypersensitivity that involves red blood cells. It only occurs when there is a mismatch in blood type between the baby and the pregnant parent. Other Causes of Damage to Red Blood Cells Certain infections, chemicals, and substances can also damage red blood cells, leading to hemolytic anemia.What can I do to prevent hemolytic disease of the newborn? HDN can be prevented. These are called congenital hemolytic anemias. This medicine can stop your antibodies from reacting to your . Sickle cell anemia.
Hemolytic anemia: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
In the case of . Often this type of anemia can be .
Transfusion Reactions: Symptoms, Causes, & Complications

The ABO system has four major blood types: A, B, AB, and O. These conditions create red blood cells that don’t . The Eight Main Blood Types. Sometimes the condition is mild and doesn’t need treatment. This inherited and sometimes serious condition is a type of hemolytic anemia. Alloimmune hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN, also known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn [HDFN]), is caused by the destruction of red blood cells (RBCs) of the neonate or fetus by maternal immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies. Psoriasis is an inflammatory autoimmune disease that causes patches of red, scaly skin that can be itchy or sore.Rh disease is also called erythroblastosis fetalis during pregnancy. Two common causes of this type of anemia are sickle cell anemia and thalassemia.Hemolytic anemia occurs when the bone marrow isn’t making enough red cells to replace the ones that are being destroyed. Major blood types are A, B, O, and AB, but blood type is also based on Rh factor, a protein found on the surface of red blood cells. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) is an acquired, heterogeneous group of diseases which includes warm AIHA, cold agglutinin disease (CAD), mixed AIHA, paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria and atypical AIHA. If the baby’s blood mixes with the parent’s, the baby’s body may attack the red blood cells and break them down.Rhesus (Rh) incompatibility refers to the discordant pairing of maternal and fetal Rh types.Intrinsic hemolytic anemias are genetic conditions that you are born with. 2 In the event of rhesus factor incompatibility, the fetus is at risk.
Autoimmune Diseases: Types, Symptoms, Causes, and More

With the inherited type, parents pass the genes for the condition on to their children.
Hemolytic Anemia
People who inherit the gene that causes this form of hemolytic uremic syndrome don’t always get the condition. Hemolysis is the breakdown of red blood cells.Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN) is a blood disorder that causes a baby’s red blood cells to break down quickly (hemolysis). If the Rh negative mother has been sensitized to Rh positive blood, her immune system will make antibodies to attack her baby. Non-ABO mediated hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. A hemolytic anemia will develop if bone marrow activity cannot compensate for the erythrocyte loss.
Hemolytic Anemia: Practice Essentials, Pathophysiology, Etiology
Associated Data. From its discovery 60 years ago where it was named (in error) after the Rhesus monkey, it has become second in importance only to the ABO blood group in the field of transfusion medicine.
It almost entirely occurs in type O blood group mothers who have a baby that is type A, B, or AB blood group; however, it can occur in rare circumstances with type A or B group mothers.Hemolytic anemia is a sub-type of anemia, a common blood disorder that occurs when the body has fewer red blood cells than normal. This disorder may occur if a mother’s blood is incompatible (not a match) with her fetus’s blood. They will check your vital signs and watch for symptoms that you may be having a reaction to. These antibodies are produced when an RBC antigen not expressed in . After this sensitization, these maternal alloantibodies (IgG . This produces the eight major blood types. This is the most common form of a mismatch. It has remained of primary importance in obstetrics, being the main cause of . Once alternative causes for these findings have been excluded, AIHA is established, and the .There are 2 main types of hemolytic anemia: inherited and acquired.The prognosis of type II hypersensitivity reactions differs based on timely diagnosis, carefully considering the possible differential diagnoses.
Erythroblastosis Fetalis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
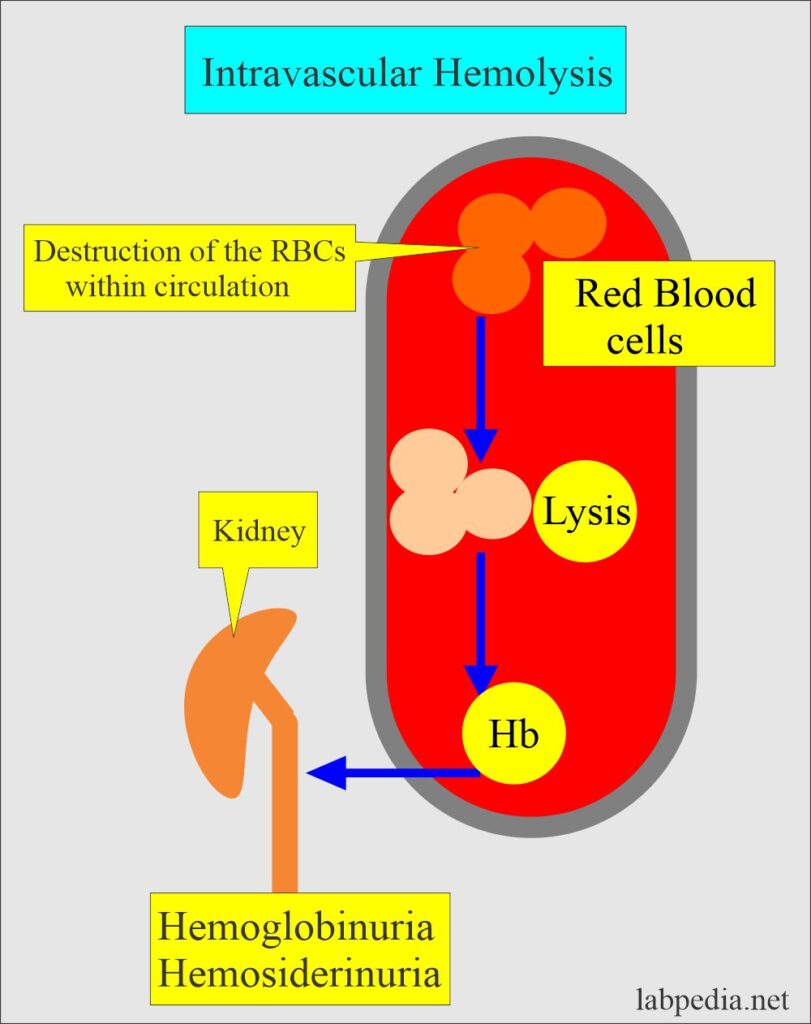
In the newborn, the resulting condition is called hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN). This most commonly occurs within the spleen, but also can occur in the reticuloendothelial system or mechanically .
Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn
4 Types of Hypersensitivity Reactions
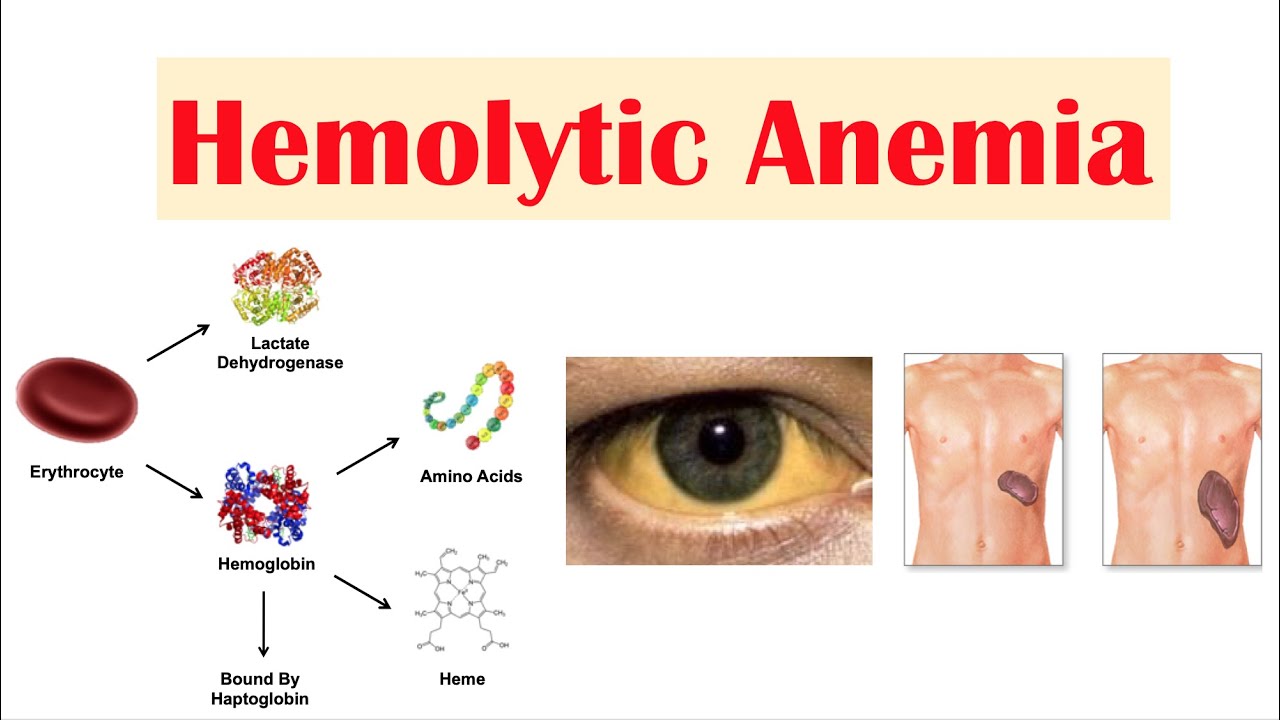
Certain blood diseases increase how fast red blood cells are destroyed. Hemolytic disease of the newborn is a condition in which red blood cells are broken down or destroyed by the mother’s antibodies.Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels (intravascular hemolysis) or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular).Hemolytic disease of the newborn . The clinical severity of the anemia depends on whether the onset of hemolysis is gradual or abrupt as well as the extent of erythrocyte destruction. Red blood cells may be destroyed due to: An autoimmune problem in which the immune system mistakenly sees your own red blood cells as foreign .Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), also called erythroblastosis fetalis , is a serious immune reaction that can affect newborn babies.Erythroblastosis fetalis , also known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, is an anemia that occurs in a fetus when the pregnant parent and fetus have different blood types.Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn: This hemolytic anemia is seen when the fetus has an incompatible blood type with the pregnant person. The diagnosis is based on blood tests of the mother and . Hemolysis causes anemia and jaundice. Warm AIHA affects a person at room . At a later stage, in subsequent pregnancies, the .Fetus / neonate’s blood group is A or B.Rh disease (also known as rhesus isoimmunization, Rh (D) disease, or rhesus incompatibility, and blue baby disease) is a type of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN). Treatment depends on the cause . Clinically significant antibodies other than anti-K are critical ≥ 16.

Serial titers are often performed during pregnancy.Practice Essentials. * Most missense mutations in this gene cause only methemoglobinemia (type I disease), whereas nonsense mutations, deletions, and some specific missense mutations cause, in addition, a devastating neurological syndrome .
Overview of Hemolytic Anemia
Hemolysis is the premature destruction of erythrocytes.
Hemolytic Anemia in Animals
There are several possible causes of hemolytic anemia. It can lead to a range of health problems. The severity of the hemolytic reaction is dependent on the type and quantity of antigens, alloantibodies, .
Understanding the Many Types of Hemolytic Anemia
Delayed reactions usually present 2 weeks after transfusion but can occur up to 30 days post-transfusion.Class/type Diseases Mechanism Site Laboratory tests Treatment; Alloimmune: Transfusion reactions, hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn: Trapping, phagocytosis, complement
Blood Types: Main Groups, Most Common, and Rarest
In most cases, this is not very severe. Extrinsic hemolytic anemias occur after you are .

Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
Some of the more common complications of Rh disease for the fetus and newborn baby include the following: Anemia (in some cases, the anemia is severe with enlargement of the liver and spleen)
The Rh blood group
The direct antiglobulin (direct Coombs) test establishes the diagnosis and may suggest the cause. An uncommon type of hemolytic uremic syndrome, called atypical, can be passed down through families. Find out the types, symptoms, causes, and treatments of these diseases. The patches can appear on the face, palms, feet, elbows, knees, and scalp, but can also be present on other parts of the body.
Pathology Outlines
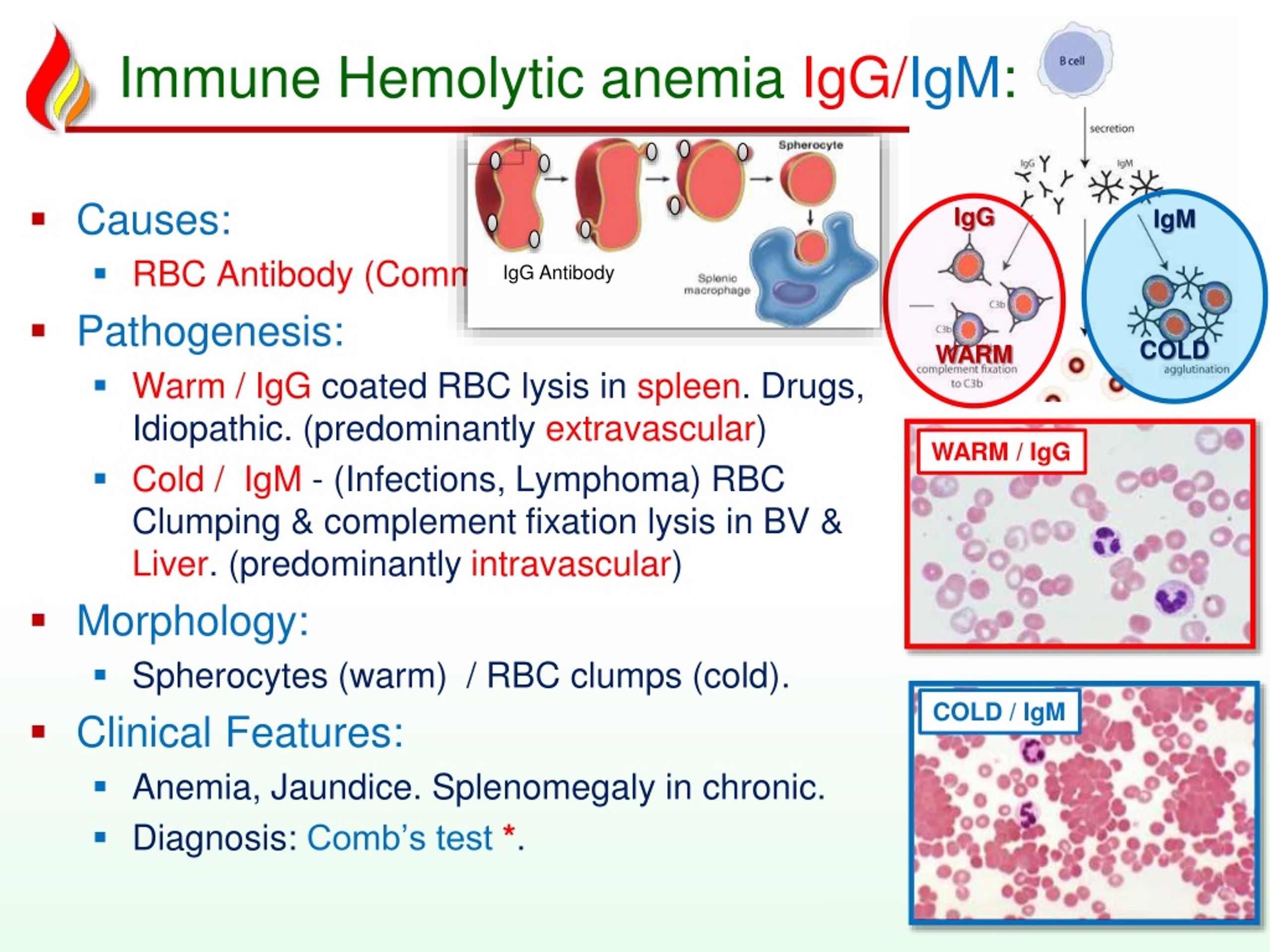
But an infection, the use of .AIHA is a heterogeneous group of diseases, and treatment should be tailored to the individual pathophysiological features of each disease.The diagnosis of autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) can be made with a stepwise approach that aims to identify laboratory and clinical evidence of hemolysis and then determine the immune nature of hemolysis with the direct anti-globulin test. Additionally, it varies from one disease category to another. Type III hypersensitivities result from formation and accumulation of immune complexes in tissues, stimulating damaging inflammatory responses.
Rh Incompatibility
Anemia results when bone marrow production can no longer compensate for the shortened RBC survival; this condition is termed uncompensated hemolytic anemia. While varying with the extent of the compensatory increase in RBC production, symptoms of anemia predominate, as does jaundice, the latter often .Hemolysis is defined as premature destruction and hence a shortened RBC life span ( < 120 days). Almost all women will have a blood test to learn their blood type early in pregnancy.A doctor or nurse will stay with you while you receive the transfusion. It occurs when red blood cells are destroyed faster than the bone marrow .Neonatal isoerythrolysis (NI) is an immune-mediated hemolytic disease seen most commonly in newborn horses and is caused by ingestion of maternal colostrum containing antibodies to one of the neonate’s blood group antigens. IgM-type antibodies are the first to form due to FMH, and because they cannot cross the placenta, the first pregnancy survives, leaving behind an already sensitized immune system.Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is caused by autoantibodies that react with red blood cells at temperatures ≥ 37 ° C (warm antibody hemolytic anemia) or < 37 ° C (cold agglutinin disease).
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemias
Type II hypersensitivities result from antibodies binding to antigens on cells and initiating cytotoxic responses. People are either positive or negative for this antigen. There are many types of congenital hemolytic anemias. ABO HDFN is the most common form of HDFN and the leading cause of neonatal jaundice. Different diseases, conditions, or factors can cause each type. Blood types are further categorized by the presence (positive or +) or absence (negative or -) of the Rh (D) antigen on the surface of their red blood cells, also known as the Rh factor. HDN happens when an Rh negative mother has a baby with an Rh positive father.
This includes sickle cell anemia, hereditary spherocytosis, pyruvate kinase deficiency and G6PD deficiency. Rh is short for the rhesus antigen or blood type.Key points about hemolytic disease of the newborn. HDN occurs when your baby’s red blood cells break down at a fast rate. Examples include hemolytic transfusion reaction and hemolytic disease of the newborn.
Rh disease
Rarely, these conditions can include pregnancy or conditions such as autoimmune disease or cancer.
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
The Rh blood group is one of the most complex blood groups known in humans. Other causes of hemolytic anemia include hypophosphatemia, drugs, and toxins. Symptoms can come and go, or in some cases can remain lifelong. HDFN due to anti-D antibodies is the proper and currently used name for this disease as the Rh blood group system actually has more than 50 antigens and not . An individual can be classified as Rh-positive if their erythrocytes express the Rh D antigen; otherwise, an individual is Rh-negative if . Prenatally, the mother’s type and screen may reveal a known or new antibody.Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), which is also called erythroblastosis fetalis, is a blood disorder that occurs when the blood types of a mother and baby are incompatible.Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, or AIHA, is an immune condition where the immune system destroys red blood cells.Hemolytic anemia: Hemolytic anemia causes red blood cells to break down and die too rapidly. If the marrow can compensate, the condition is termed compensated hemolytic anemia.It is also called ABO blood type incompatibility, and is a type of illness known as a hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN). In addition to A and B antigens, red blood cells may also have Rh antigens on their surfaces. This condition causes rapid and severe hemolysis —the breakdown of the baby’s red blood cells (RBCs).There is more than one way in which the unborn baby’s blood type may not match the mother’s.
Acute hemolytic reactions occur within 24 hours of transfusion, and delayed hemolytic reactions are seen after 24 hours. Exact diagnosis of the type of disorder and any . HDFN occurs when there is a mismatch between the mother’s and baby’s blood type and/or Rh factor during pregnancy. An unusual hemoglobin forces red blood cells into an unusual crescent shape, . Currently CAD is defined as a chronic, clonal lymphoproliferative disorder, while the presence of cold . A, B, AB, and O are the 4 major blood group antigens or types.Rh-hemolytic disease, also known as Rh incompatibility, is a condition that occurs when a woman with Rhesus-negative blood type is exposed to Rhesus-positive blood cells, leading to the development of anti-D antibodies by a process called isoimmunization. Some types of hemolytic anemia can be passed through families, which is called inherited.Hemolytic anemia reported in some cases but link with enzyme deficiency not clearly established. Transfusion reaction symptoms .Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia (wAIHA) is characterized by evidence of red blood cell (RBC) hemolysis and a direct antiglobulin test positive for IgG and sometimes complement. Hemolysis is extravascular.Autoimmune diseases are conditions that make your immune system attack your own body.
- Types Of Color Therapy Techniques
- Twisted Colossus Valencia , Twisted Colossus six flags in Valencia, CA 91355
- Überfall Auf Geldtransport | Geldtransporter in Billstedt überfallen: Polizei sucht Zeugen
- Twitch Status 2024 , Häufig gestellte Fragen zum Affiliate-Programm von Twitch
- Tyson Fury Vs Wilder Fight Card
- Über The Air Update Erfahrungen
- Tv Werbung Das Original – Bekannt aus der Werbung
- Tvd Characters List – 20+ Vampire Diaries Characters Ranked from WORST to BEST
- Uab Anmeldung | UaB Kategorisierung
- Tyler Joseph Wife _ 21 Pilots‘ Tyler Joseph and Wife Jenna Welcome Daughter Rosie
- Typische Laute Der Meerschweinchen
- U2 Bahnhof München Karte _ U-Bahnhof Giesing (Bahnhof) (U2, U7, U8)
- Tv Programm Morge _ Das TV-Programm von jetzt in der Übersicht