Types Of Diabetes In Europe | Chronic diabetes affects millions of people in the EU
Di: Samuel
0% annual increase in .6 % of the market share of insulins prescribed in primary care practices was also reported in Germany .

The study evaluated more than 7000 patients with Type II diabetes in eight countries – Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden and . Authors M Massi-Benedetti 1 , CODE-2 Advisory Board. This is expected to increase to 643 million by 2030 and to 783 million by 2045.The narrow view relates to the enormous burden that type 2 diabetes represents in Europe, in individual and in societal terms. The cost of diabetes Type II in Europe: the CODE-2 Study Diabetologia. These micro level indicators describe measurements, which should be used if evaluation, reporting, and . Epub 2002 May 24.
Diabetes prevention
Totally, 22 quality indicators were generated. A further 296 500 children and adolescents under the age of 20 live with type 1 diabetes. This report is based on 24,423 children, registered by 36 centres, .
Texts adopted
8% of total deaths (21. Emerging data in literature continuously confirm the improvement of glycemic control thanks to the technological evolution taking . In 2021, Switzerland had the highest health expenditure per person with diabetes in Europe, with it costing over 12. Tea consumption was associated inversely with incidence of type 2 diabetes; the HR was 0. This indicates that people in low-middle, middle, and high-middle SDI countries could more be prone to type 2 diabetes because . For example, in the moderate-risk region, the estimated 10-year CVD risk was 11% for a 60-year-old man, non-smoker, with type 2 diabetes, average conventional risk factors, HbA1c of 50 mmol/mol, eGFR of 90 .History in the Making.0% annual increase in type 1 diabetes 1,20. Lindström J, Neumann A, Sheppard K, Gilis-Januszewska A, Greaves C, Handke U, Pajunen P, Puhl S, Pölönen A, Rissanen A, Roden M, et al. Dietary protein intake and incidence of type 2 diabetes in europe: the EPIC-InterAct case-cohort study.1007/s00125-002-0860-3. Registries provide valid information on incidence of type 1 diabetes with more complete data available for children than for adults.The literature has already shown that Sweden has a relatively high use of insulin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes compared to other European countries .Diabetes remains a substantial public health issue.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus in European children and adolescents
The burden of both types of diabetes was notably higher in males than females in Europe, and it escalated with age increment.1 million in 2040. It lists the following: the newest and most recently updated medicines authorised for diabetes in the European Union. Grants are offered for basic and clinical studies.Third, while the recalibration applied accounts for substantial variation in whole population levels of risk across Europe, SCORE2-Diabetes also shows good ability to discriminate and provide individual risk estimates for individuals with type 2 diabetes, taking into account their specific risk factors such as age of diabetes diagnosis, HbA1c .6 million people in the Europe IDF region are estimated to have impaired glucose tolerance and thus a risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life (IDF 2019).3% in 2019, potentially affecting 2 million live births in the IDF European region ( IDF 2019 ).Objective: The aim of this study was to analyze socioeconomic position (SEP) inequalities in the prevalence and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in people aged 50 years and over in Europe and to describe the contribution of body mass index (BMI) and other possible mediators.

In 2019, both types of diabetes caused 995 (95% UI 780-1240) crude DALYs per 100,000 people across Europe, with type 2 diabetes accounting for 93. The study evaluated more than 7000 patients with Type II diabetes in eight countries — Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden and . However, the share of people reporting chronic diabetes clearly varies between age groups. more
The cost of diabetes Type II in Europe: the CODE-2 Study
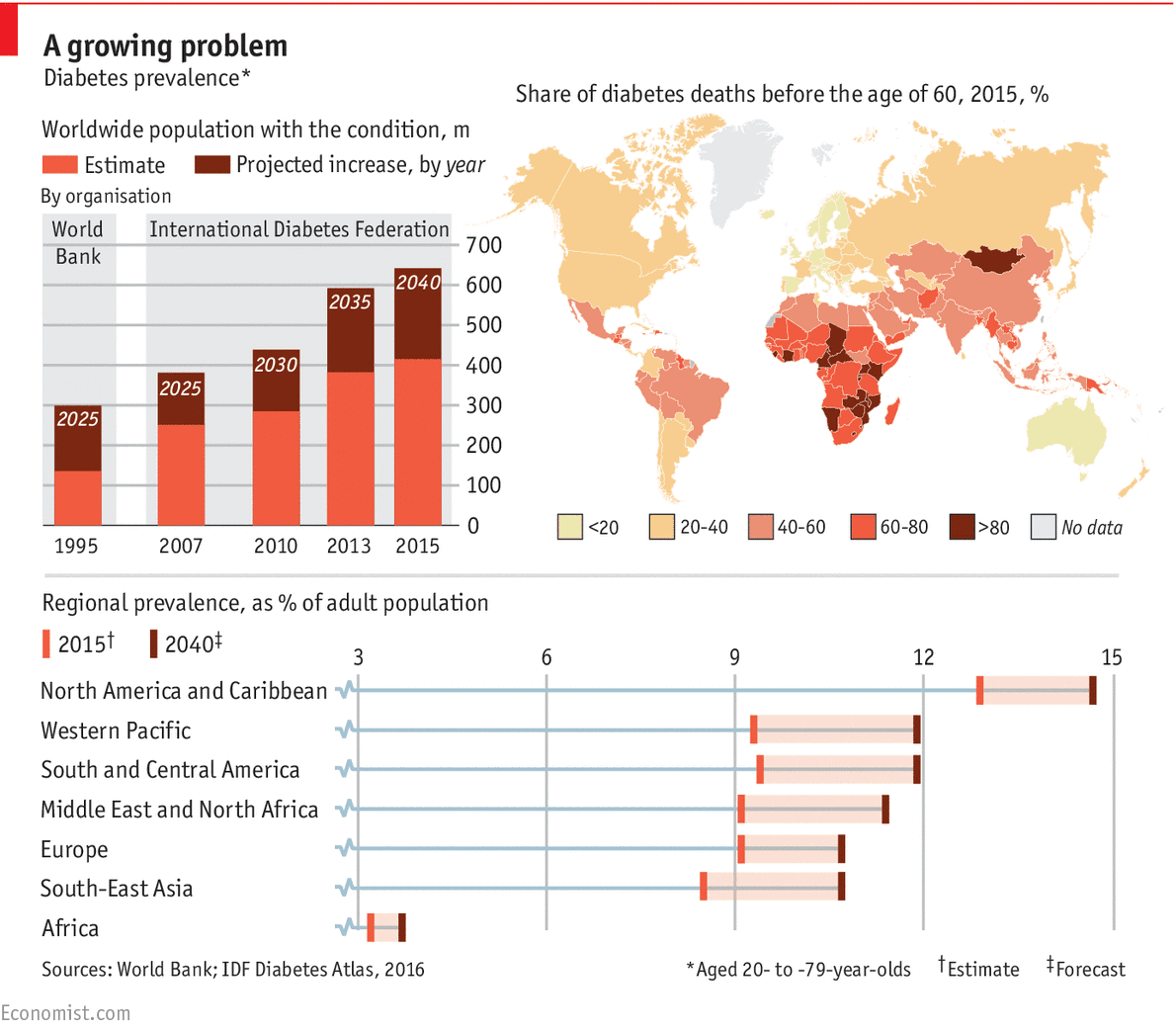
Aims/hypothesis Data on type 1 diabetes incidence and prevalence are limited, particularly for adults.9 billion for the eight .Aim: The aim of the study was to review the published and unpublished data on type 2 diabetes in European children in order to determine how common this problem is in the dominantly Caucasian population. As a specific task of the EU Bridge Health project, we carried out a survey of diabetes-related data sources in Europe. In the new millennium, pancreatic transplantation, first performed in 1966, 25, 26 exists as a radical therapy for especially intractable Type I diabetes with advanced complications. What’s more, an estimated 240 million of those who have diabetes are currently undiagnosed. 1 Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for CVD.BackgroundRegistries and data sources contain information that can be used on an ongoing basis to improve quality of care and outcomes of people with diabetes.According to the most recent IDF data, 537 million people—approximately 10% of all people aged 20-79 in the world—were living with diabetes as of 2021. Of these costs, hospitalisations accounted for the greatest proportion (55%, range 30-65%) totalling EUR 15. The older the age .This programme on autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes is intended to stimulate and accelerate European research aimed at improving understanding of any aspect of autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes, its pathogenesis, screening and monitoring, its clinical course and its interventions. Type 2 diabetes, which makes up the bulk of diabetes cases, is largely preventable and, in some cases, potentially reversible if identified and managed early in the disease course.Representatives from the nine project partners discussed the start of the research activities and the path towards what has the potential to be a real breakthrough towards a cure for type 1 diabetes. This study protocol provides a standardised and transparent methodology to assess TD1 trends .Country specific medians of tea consumption ranged from 0 cups/day in Spain to 4 cups/day in United Kingdom.
In addition, 20 scientific evaluation indicators with measurement standards were produced. Methods: This was a cross-sectional and longitudinal study including . Registries and information systems for diabetes care in the WHO European Region: preliminary findings for consultation 6 WHO.Almost 30 million people in the European Union (EU) report suffering from chronic diabetes. whereas some forms of type 2 diabetes, diabetes in pregnancy, diabetes-related complications and other consequences of diabetes may be prevented through policies addressing the condition’s modifiable risk factors, such as promoting active and tobacco-free living and access to healthy foods as well as policies tackling the .
Chronic diabetes affects millions of people in the EU
The size of the study is comparable with the meta-analyses reported to date on this topic [6] , [11] and provides the opportunity to explore a potential non-linear association .8 million adults in 2015 to 71. Hyperglycemia in pregnancy affects about one in every six pregnancies worldwide ().Therefore, we investigated the association between tea consumption and incidence of type 2 diabetes in European citizens who were part of the EPIC-InterAct project. Insulin treatment is usually started after the oral therapy is already . The VANGUARD project is funded by the European research and innovation program Horizon 2020 (project number 874700), under the .Aims/hypothesis: ‚The Cost of Diabetes in Europe – Type II study‘ is the first coordinated attempt to measure total healthcare costs of Type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in Europe.4 per 100 000 population) .the European Region had diabetes in 2019 (1). Individuals with diabetes from high-income countries have, on average, a 2-fold greater risk of developing CVD .ObjectivesWe aimed to report on the organization of different .
Diabetes in Europe: an update
Except for genetic conditions or special types of diabetes (like type-1 diabetes), it is often a preventable chronic disease through a healthy lifestyle starting in childhood. dollars for every person living with diabetes in .The increasing trend of type 1 diabetes has principally occurred in high income regions including Europe and the United States, in which there has been a reported 2. Still in experiment mode, gene therapy with molecules like leptin and insulin may one day be a reality. No systematic difference can be observed between men and women.Egg ingestion in adults with type 2 diabetes: effects on glycemic control, anthropometry, and diet quality—a randomized, controlled, crossover trial.Aims/hypothesis: ‚The Cost of Diabetes in Europe-Type II study‘ is the first coordinated attempt to measure total healthcare costs of Type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in Europe. Diabetes Care 2014;37:1854-1862.The cost of diabetes Type II in Europe: the CODE-2 Study. The most common is type 2 diabetes, usually in adults, which occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or .This has been the widely used definition of GDM for many years, but it presents limitations in terms of the non . Arch Intern Med 159:1873–1880.Aims/hypothesis: To study the epidemiology of childhood-onset (Type I) insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Europe, the EURODIAB collaborative group in 1988 established prospective, geographically-defined registers of all children diagnosed with Type I diabetes under 15 years of age. The age-adjusted prevalence of hyperglycaemia in pregnancy was 6.According to IDF (International Diabetes Federation) data, the absolute number of diabetics in the EU will rise from approximately 33 million in 2010 to 38 million in 2030. EMA’s latest diabetes-related news announcements.Keywords Type II diabetes, pharmacoeconomics, Eu rope. As recently as 1995, an es timated 135 million peop1e worldwide were affected by diabetes and by the year 2025, this figure is projected to
Diabetes cost per person in Europe in 2021
In 2016, diabetes mellitus accounted for 2. ADA and EASD Cosensus Report (2019) Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: ADA and EASD Consensus Report (2018) 2016 European Guidelines on CVD Prevention in .
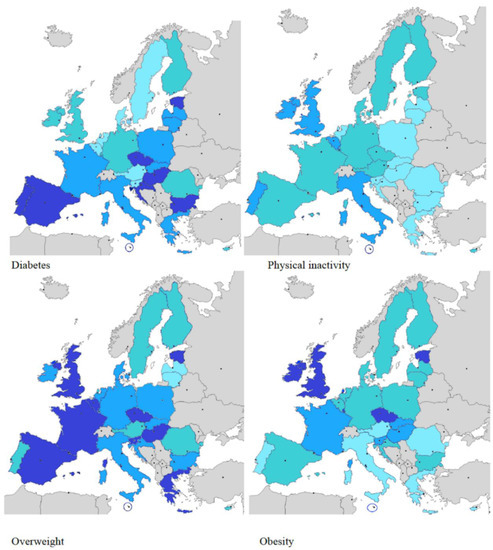
Revealing the cost of Type 11 diabetes in Europe
Introduction: Monitoring type 1 diabetes (T1D) trends across most European countries using objectively measured data and how this incidence has evolved over the past three decades should be considered a public health priority. Methods Incidence rates of type 1 diabetes in children (available .The prevalence of obesity is increasing rapidly in all age groups in most EU-countries and is one of the fastest growing epidemics, now affecting 10-40% of the adult population. (2010) Hormone and Metabolic Research 42 (S 01): S37-S55. Methods: The MEDLINE database was searched and a questionnaire was distributed among European Childhood Obesity Group (ECOG) . However, all evidence indicates that diabetes prevalence is increasing worldwide, primarily due to a rise in .EASD and ADA Diabetes Technology Working Group Consensus Report (2019) 2019 update to: Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018.

The total direct medical costs of Type II diabetes in the eight European countries was estimated at EUR 29 billion a year (1999 values). This page brings together the European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) latest information on diabetes.52 The prevalence of diabetes in Europe is expected to increase from 59. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 2016; 4 : e000281. EMA’s upcoming events on diabetes-related topics. Building on an iterative six-step disease management process that leverages feedback loops and utilizes commodity digital tools, the PDM-ProValue study program demonstrated that integrated personalized diabetes management, or iPDM, . Diabetes Care 2014;37:1854-1862 Diabetes Care.

Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) is defined as the type of hyperglycemia diagnosed for the first time during pregnancy (2, 3). If not effectively .
Type 1 diabetes in 2017: global estimates of incident and
They constitute the minimum level of quality assurance recommended for diabetes prevention programs. Diabetes Factsheet 7 International .Dietary protein intake and incidence of type 2 diabetes in europe: the EPIC-InterAct case-cohort study. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. About Type 2 Diabetes. Nicolucci A, Cavalière D, Scorpiglione N et al.Prevalence of type 1 has also increased over the past 20 years in EUR and there was estimated to be 129,350 cases in children aged 0-14 years in 2013. There are large differences in distribution of risk factors . Unlike Type 1, which is an autoimmune disorder, T2 diabetes is a chronic and progressive condition developed over time and linked to a combination of lifestyle, environmental, genetic and other factors.Type 2 diabetes mellitus represents a multi-dimensional challenge for European and global societies alike. Diabetes is a chronic, metabolic disease characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose (or blood sugar), which leads over time to serious damage to the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys and nerves.Brown JB, Pedula KL, Bakst AW (1999) The progressive cost of complications in Type 2 diabetes mellitus.00] when participants who drank ≥ 4 cups of tea per day were compared with non-drinkers (p (linear trend) = 0. 2002 Jul;45(7):S1-4. Diabetes mellitus is a common disease and its preva lence is expected to increase in the future, especially in developing countries [1,2]. The estimated average yearly cost per patient was EUR 2834 a year.Take Action to Prevent Diabetes – The IMAGE Toolkit for the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes in Europe. As reflected by recent guidelines for the management of patients with type 2 diabetes,54 healthcare . Diabetes is also among the top-10 leading causes of noncommunicable disease-related deaths in the Region (2). We aimed to systematically review and meta . (1996) A comprehensive assessment of the avoidability of long term complications of diabetes . Obesity increases the risk of serious co-morbidities such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, certain cancers and . Affiliation 1 Dipartimento di Medicina .Type 1 diabetes (T1D) patients’ lifestyle and prognosis has remarkably changed over the years, especially after the introduction of insulin pumps, in particular advanced hybrid closed loop systems (AHCL). About Type 1 diabetes 5 Barbazza E, Raposo JF, et al.Background: Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) is defined as the type of hyperglycemia diagnosed for the first-time during pregnancy, presenting with intermediate glucose levels between normal levels for pregnancy and glucose levels diagnostic of diabetes in the non-pregnant state.Diabetes Atlas Factsheet: Diabetes in Europe in 2021 2 IDF. This study aims to estimate global numbers of incident and prevalent cases of type 1 diabetes in 2017 for all age groups, by country and areas defined by income and region.2337/dc15-er10b.Diabetes is a growing pandemic in Europe, and Type 2 (T2) diabetes accounts for around 90% of all cases. This represented 6.9% of the EU population aged 15 or over in 2014. 2015 Oct;38(10):1992. The age-standardized mortality rate and DALYs rate for type 1 .SCORE2-Diabetes risk predictions varied several-fold, depending on individuals‘ levels of diabetes-related factors.

Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) remain a major cause of morbidity and mortality in Europe with almost 13 million new cases recorded in 2019 alone.
- Tvöd Tabelle K – TVöD-K Krankenhäuser: § 15 Tabellenentgelt
- Tyler Skaggs Overdose – Jury finds ex-Angels staffer guilty in Skaggs‘ death
- Twe Vliesstoff _ Interior Applications
- Überbrückungsgeld Strafgefangene
- Twist And Shout Guitar Chords : Twist And Shout Chords
- U Bahn Karte Barcelona _ Barcelona: Tagestickets für Metro & Bus
- Types Of Hammers For Beginners
- Tz Bedarf Deutschland , Zeichenbrett / Zeichenplatte GRUNDAUSSTATTUNG
- Tw Audio Vera10 Test – TW AUDIO VERA10
- Two Letter Names For Boys | 100+ Three Letter Boy Names (Includes meanings and origins)