Types Of Cell Membranes | Permeability of Membranes
Di: Samuel
The H + /K + is .
Cell Membrane
Types of Cell membranes
The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. Two different types of proteins that are commonly associated with the cell membrane are the integral proteins and peripheral protein (). Glycoproteins embedded in membranes play important roles in cellular identification. Although the basic structure of biological membranes is provided by the lipid bilayer, membrane proteins perform most of the specific functions of membranes. Function of the Cell Membrane. (Credit: modification of work by Randy Le’Moine) Chapter Outline. A pure phospholipid bilayer is inherently semi-permeable. The cell membrane gives the cell its . These induce signal transduction process in cells by catalyzing the phosphorylation of the next protein. plasma (cell) membrane, a phospholipid bilayer with a mosaic of proteins, which functions as a barrier between the cell and its environment.Membrane proteins are essential components of the plasma membrane that perform various functions, such as transport, signaling, and recognition. Semi-permeable membranes are very thin layers of . These chemical groups affect a hormone’s distribution, the type of .In the earlier chapter on the basic biomolecules, cellular membranes .The first type of ionophore is a small mostly-hydrophobic carrier almost completely embedded in the membrane, that binds to and envelopes a speci c ion, shielding it from the lipid, and then moves it through the cell membrane.cell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed.Functions of the Cell Membrane. Phosphoglycerides (also known as glycerophospholipids) are the most abundant phospholipids in cell membranes.Components of All Cells.Phosphoglyceride are composed of alcohol, phosphate, glycerol and 2 fatty acids. Plasma membranes enclose the borders of cells, but rather than being a static bag, they are dynamic and constantly in flux. Other properties of the membrane like protonic conductivity, ion exchange capacity and .There are different types of cell membranes that you should understand in order to make sure that you can keep your body healthy and your cells functioning right at all times. Accordingly, the amounts and types of proteins in a . Water moves in or out of a cell until its concentration is the same on both sides of the plasma membrane.2 Passive Transport.
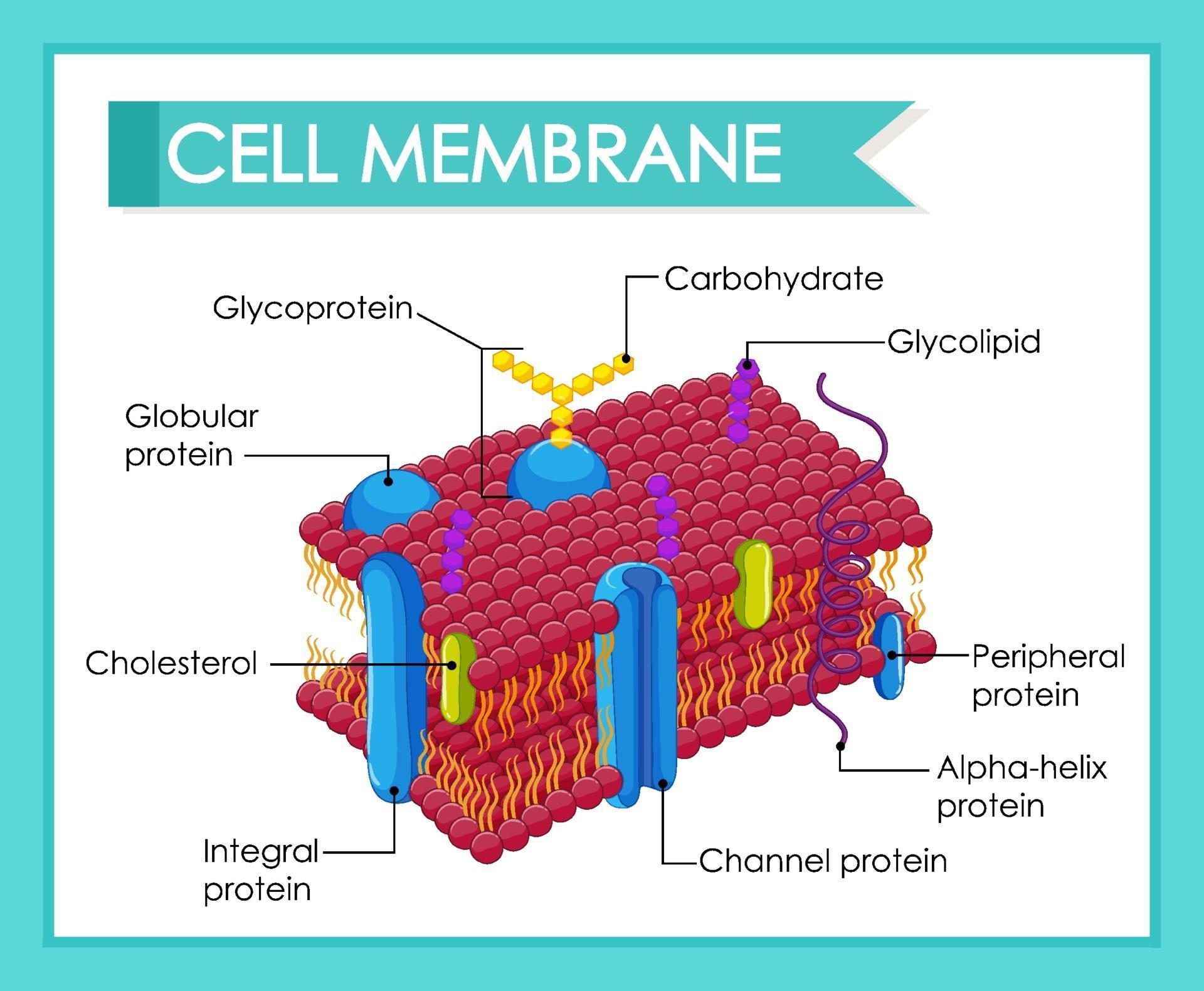
Different types of criteria exist for the classification of membranes, according to their characteristics and properties. This phospholipid bilayer determines what molecules .The structure and function of cells are critically dependent on membranes, which not only separate the interior of the cell from its environment but also define the internal compartments of eukaryotic cells, including the .Types of Cell Signaling. Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion; it is the passage of water from a region of high water concentration through a semi-permeable membrane to a region of low water concentration.Membrane Lipid Composition .What type of lipid makes up the cell membrane? The . Plasma membranes enclose the borders of cells, but rather than being a static bag, they are dynamic and constantly in .Examples of integral membrane proteins. The most studied carrier-type ionophore is valinomycin, which binds to K+. Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane.
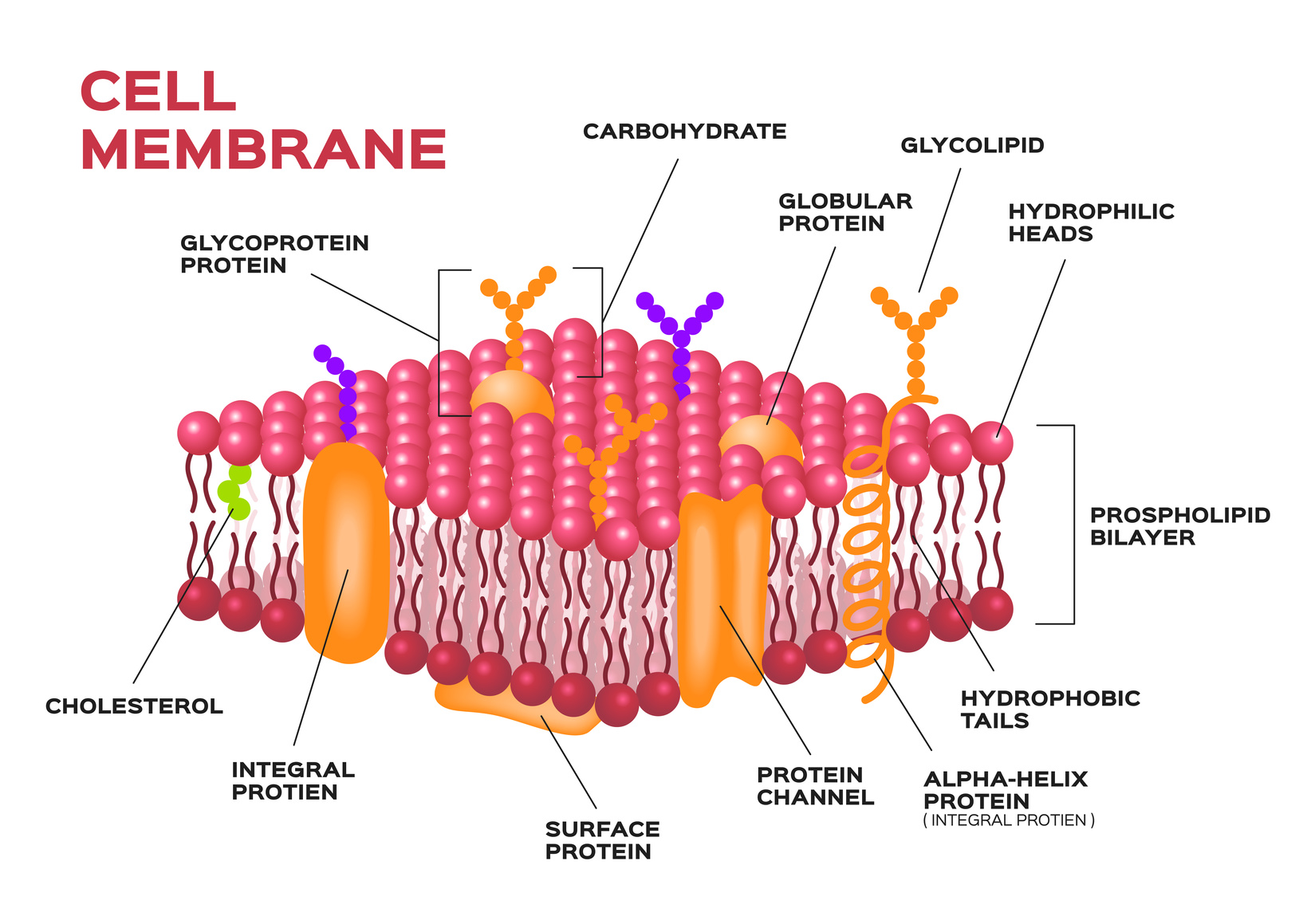
Allowing the control of an enclosed chemical environment – important to .A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast.This chapter introduces the membranes used in microbial fuel cells (MFCs). It can also be found in epithelial cells of animals. [1] Biological membranes include . Type-dependent distribution features of these . All cells contain these same four components: 1. Cell membranes are essential for the steady-state homeostasis of cells and their reaction to environmental changes. This aptly named protein binds a substance and, in doing so, triggers a change of its own shape, moving the bound molecule from the outside of the cell to its interior (Figure 5); depending on the gradient, the material may move in the opposite direction. A sphingomyelin contains phosphate, sphingosine, and a fatty acid. cytoplasm, the region between the region of DNA and plasma membrane, and the cytosol, a fluid, jelly-like region inside the cell where .The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. Came in 1935; This is a trilaminar model or the sandwich model that tried to explain the presence of proteins in the plasma membrane for the first time apart from the major phospholipid functions in the .Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. But how do cells orchestrate numerous enzymes, as well as the intrinsic physical phase behaviour of lipids and their . Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes.Membrane Proteins. The fluid mosaic model states that a membrane is a fluid structure with a “mosaic” of various proteins embedded .Altogether, our results demonstrate that all types of carbohydrates investigated herein are prone to concentrating into clusters on the cell membrane.
Cell Membranes
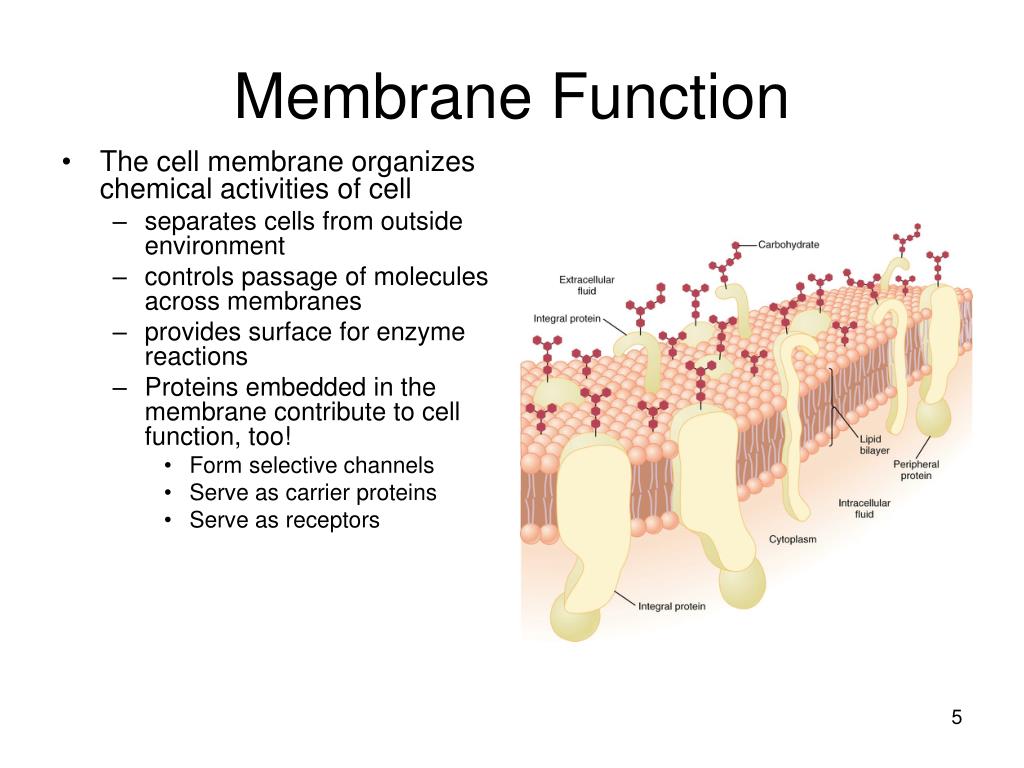
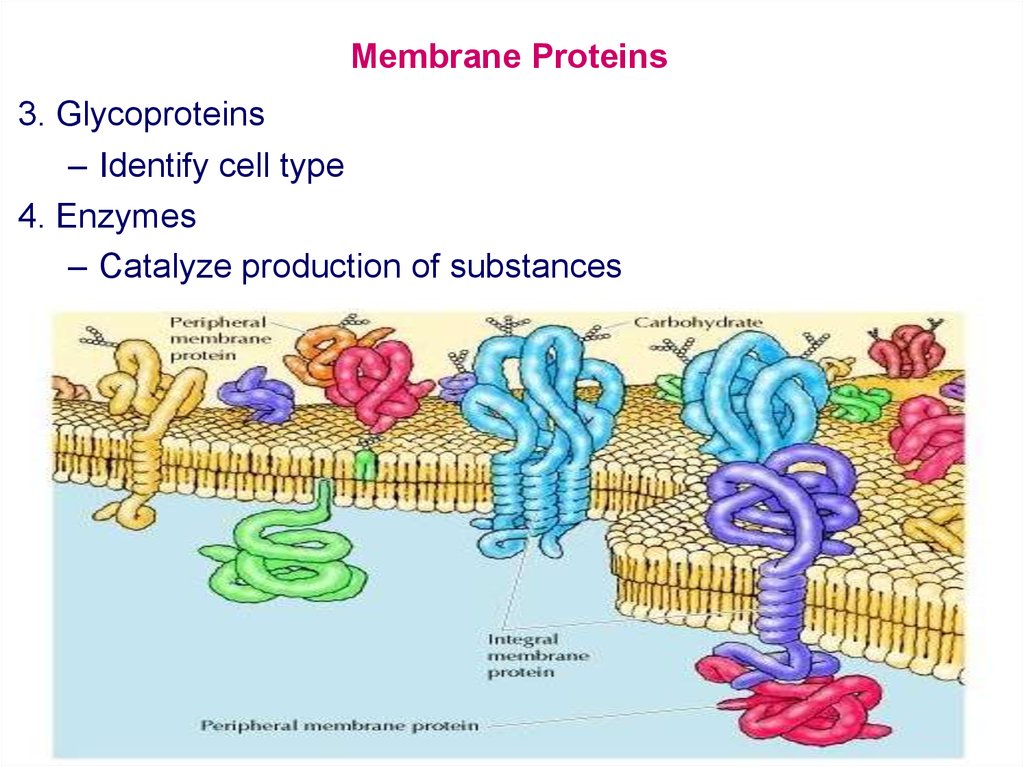
Specialized structure that surrounds the cell and its internal environment; controls movement of substances into/out of cell.3 Active Transport.1 Membrane Components and Structure. The lipid bilayer forms the basis of the cell membrane, but it is peppered throughout with various proteins. The Ca 2+ pump is pumping out Ca 2+ ions from red blood cells, plays a crucial role in the Ca 2+ absorption in intestinal cells. This book chapter from Biology LibreTexts explains the types, structures, and roles of membrane proteins in cell biology.The biological membranes that surround cells are extremely complex and contain different types of lipids and proteins, both within and associated with the membrane. Here are some notable examples of integral membrane proteins: Insulin Receptor : This receptor is crucial for glucose metabolism.Cells have hundreds-thousands of membrane proteins and the protein composition of a membrane varies with its function and location. Lipids are types of cell membranes. There are actually three lipids that compose the cell membrane.The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a selectively permeable border that wraps around every type of cell, containing the cytoplasm. Blood types, for example, differ from each other in the structure of the carbohydrate chains projecting out from the surface of the .The types of membranes used in proton exchange membrane fuel cell classified as fluorinated membranes, partially fluorinated membranes, non – fluorinated membranes and acid-based composite membranes are also presented in this paper. Bacterial plasma membranes are often composed of one main type of phospholipid and contain no cholesterol; their mechanical stability is enhanced by an overlying cell wall. Therefore, experimental measurements of the membrane capacitance could be used to calculate the cell membrane surface area and to control its changes. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Before we start dissecting the various components of a signaling cascade, we must first understand the different forms of signaling that can occur.
Permeability of Membranes
The lipids in cell membranes are highly polar but have dual characteristics: part of the lipid is ionic and therefore dissolves in water, whereas the rest has a hydrocarbon structure and therefore .1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins.The hormones of the human body can be structurally divided into three major groups: amino acid derivatives (amines), peptides, and steroids ( Figure 17. A membrane is the cell’s interface with the rest of the world – it’s gatekeeper, if you will. Membranes are formed by a matrix of lipids whose structure and composition is far from simple.3 likes • 365 views. Types of Cell membranes – Download as a PDF or view online for free.Fortunately for life on Earth, the membranes of living cells are not purely phospholipids, and as we will see, proteins embedded in the phospholipid bilayer can form conveyances for the transport of many different molecules in and out of the membrane. Classification of the membranes. This presentation focuses on the types of cell membranes in eukaryotic cells and their functions. In other words, plasma membranes are selectively permeable —they allow some . Molecule that repels water (“water-fearing”) Hydrophilic.The structure, function and mobility of membrane proteins are closely intertwined with the structure and composition of membranes and their surrounding environment. (B) An Idealized Animal Cell. Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions.Analogously, a plasma membrane’s functions involve movement within the cell and across boundaries in the process of intracellular and intercellular activities. Ca 2+ pumps are not present in each cell, but are important to maintain the low cytoplasmic concentration in many cells.However, membranes have other important applications such as biomaterials, catalysts (including fuel cell systems), energy storage, and CO2 separation, among others.Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins.
Schematic of size-based membrane exclusion.The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier that protects the cell and regulates what enters and leaves., by passive diffusion). Plasma membranes act not only as a barrier, but also as a gatekeeper. The chapter begins by providing a brief introduction on fuel cells and its types.2: Transport Across Membranes. It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment. Only a few small, relatively uncharged molecules can cross a membrane unassisted (i. There are five different types of signaling that are common in cells: endocrine, neuronal, paracrine, autocrine, and juxtacrine (Figures 07-01 and 07-02, as well as Video 07 .A detailed model of the composition and structure of membranes exists. The structures shown here will seldom all be found in a single animal cell. There are two basic types of tissue membranes: connective tissue and . This molecule is unique to a specific type of cell.
Integral Protein
Their main functions consist of: Forming a continuous, highly selectively permeable barrier – both around cells and intracellular compartments. A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others.The first model to say that components of the cell membrane are various types of lipids, but are double layered. These also catalyze other types of reactions, such as redox reactions, hydrolytic reactions, and metabolic reactions. These proteins are found in all .The value of C m may vary for different types of cells, but typically it is ca.Another type of protein embedded in the plasma membrane is a carrier protein. It must allow needed substances to enter and cell products to leave the cell, while preventing entrance of harmful material and exit of essential material.Glycocalyx is a glycoprotein-polysaccharide coating outside of the plasma membrane of bacterial cells.This page titled 17. This means that the membrane will allow . Membrane proteins are involved in a variety of . A cerbroside contains sugar, sphingosine and a fatty acid. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles.Enzymes: Membrane proteins serve as enzymes or biocatalysts to promote chemical reactions.Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): A cell membrane with peripheral and integral membrane proteins. Molecule that contains both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic end.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg)
Davson and Danielli Model.Not all the structures shown here occur in every type of plant cell.A cell’s plasma membrane defines the boundary of the cell and determines the nature of its contact with the environment. Since most cells live in an aqueous environment and the contents of the cell are also mostly aqueous, it stands to reason that a membrane that separates one side from the other must be hydrophobic to form an effective barrier against accidental leakage of materials or water. Following the components of MFC, the chapter focuses on various membrane properties and its determination. John Mathyamuthan. Carrier proteins are . Valinomycin is a 12-residue cyclic .
Membrane Proteins: Structure, Function and Motion
Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities.
Cell membrane introduction (video)
It is like an ID and serves as a recognition of the cell. Molecule that is attracted to water (“water-loving”) Amphipathic.A tissue membrane is a thin layer or sheet of cells that covers the outside of the body (for example, skin), the organs (for example, pericardium), internal passageways that lead to the exterior of the body (for example, abdominal mesenteries), and the lining of the moveable joint cavities. It also provides interactive exercises and review questions to test your . These cells cooperate with other specialized cells . Download to read offline. Hydrophilic molecules that must enter or leave cells do so with help, i.2: Membrane Transport is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Gerald Bergtrom. At present, the time and financial resources required to provide the computational power to simulate such a complex environment are often prohibitive. Different types of membranes including anion exchange membranes, . The total membrane capacitance is proportional to the cell membrane surface area.
The Cell Membrane
These three are the phospholipids, sterols, and glycolipids.
Cell membrane
Cell membranes are vital for the normal functioning of all the cells in our bodies.As its name suggests, an integral protein is a protein that is embedded in the . In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell.The types of plasma membrane pumps depend on cell types.The cell membrane is one of the great multi-taskers of biology. It provides structure for the cell, protects cytosolic contents from the environment, and allows cells to act as specialized units. There are three different types based on the number of types the protein crosses the membrane and the type of secondary structure used in crossing: biotopic (single pass), alpha-helical polytopic, and beta-barrel. It is the proteins, therefore, that give each type of membrane in the cell its characteristic functional properties. Integral membrane proteins (IMPs) are pivotal components of cellular membranes, playing diverse roles in various cellular processes.
- Types Of Filters In Photography
- U21 Em Live Stream Kostenlos _ Wer zeigt das zweite EM-Gruppenspiel im Free-TV & Stream?
- Twitch Benutzername Wechseln : Twitch Symbole vor dem Namen ändern [2021]
- Twitch Crash : CrashedCouch
- Tv Programm Jetzt Ohne Anmeldung
- Typische Spanische Architektur
- Types Of Diabetes In Europe | Chronic diabetes affects millions of people in the EU
- Two And A Half Men Hauptfigur – List of Two and a Half Men characters
- Tvl Ansprechpartner _ Kontakt
- U Profile Tabelle , U-Baustahlprofile
- Tv Neu Als Abo Kaufen , Apple TV Box ohne Abo: Nutzungsmöglichkeiten und kostenfreie Angebote
- Über Die Täter Handeln _ Stalking: Erkennen, Verstehen, Handeln