Therapeutic Hypothermia Guidelines
Di: Samuel
32/100,000/year in Western Europe. Intensive Care Med. CVT is a type of stroke where the thrombosis occurs in the venous side of the brain circulation, leading to occlusion of one or more cerebral veins and dural venous sinus.

Evidence-based recommendations on therapeutic hypothermia with intracorporeal temperature monitoring for hypoxic perinatal brain injury. Is this guidance up to date? Next review: this guidance will be reviewed if there is new evidence or safety concerns. When initiated in the first 6 hours of life, therapeutic hypothermia is considered the gold standard for providing neuroprotection in the . Several methods may be used to keep body temperature at a cooled level: Ice packs, icy cold wet towels, or fans may be used. It’s sometimes used for people who have a cardiac arrest.9 C TMD Temperature modulating device TOF Train of four TT Target temperatureWe recommend deferral of assessment of the neurological prognosis of comatose survivors of cardiac arrest for at least 72 h following ROSC in patients not treated with therapeutic hypothermia (goal temperature < 36.guidelines for the most effective use of therapeutic hypothermia in cases of suspected neonatal encephalopathy.
Implementation Date: July 30, 2020.

1007/s00134-022-06620-5 Crossref Medline Google Scholar; 12.Therapeutic hypothermia following cardiac arrest. Once the heart starts beating again, healthcare providers use cooling devices to lower your body temperature for a short time. The hypothermic heart may be unresponsive to cardiovascular drugs, pacemaker stimulation, and defibrillation.meant to serve as clinical guidance where there is a high level of certainty regarding overall benefit (or harm), but a lack of published evidence.
Therapeutic Hypothermia in the Pediatric ICU
Further study is required. Cameron, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Therapeutic Hypothermia Guidelines. Modern use of therapeutic hypothermia as a neuroprotective strategy began in the 1940s with the work of Fay [ 1 ], who reported the first series of patients with .Consensus recommendations on therapeutic hypothermia after minimally invasive intracerebral hemorrhage evacuation from the hypothermia for intracerebral hemorrhage (HICH) working group Turner S.PALS guidelines include controlled normothermia or therapeutic hypothermia as TTM options to consider in post-arrest pediatric patients.This pathway has been devised to ensure safe, timely and high quality care is available to all infants who may be eligible for therapeutic hypothermia (TH). For nonshockable rhythms, consider . Because some studies included infants born at 35 weeks GA, hypothermia should be considered if they meet other criteria. Passive cooling should be . randomized controlled trials led to a rapid incorporation of TH as a Class I recommendation for post-arrest care in the guidelines, especially for OHCA due to a shockable rhythm.Therapeutic hypothermia is an effective treatment for patients who are comatose after cardiac arrest and undergo a return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). Interventional procedures guidance [IPG386] Published: 23 March 2011.
2015 AHA ACLS Guidelines: focus on therapeutic hypothermia
4The incidence is higher in developing countries.Canadian Guidelines for the use of targeted temperature management (therapeutic hypothermia) after cardiac arrest: A joint statement from The Canadian Critical Care Society (CCCS), Canadian Neurocritical Care Society (CNCCS), and the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group (CCCTG) It’s lowered to around 89°F to 93°F (32°C to 34°C). Mild therapeutic hypothermia to improve the neurologic outcome after cardiac arrest. Therapeutic hypothermia for acute brain injury is the intentional lowering of body temperature, with the objective of reducing tissue damage in the central nervous system. Part 8: post-cardiac arrest care: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines update for .monitor quality of care and pre-discharge outcomes and to guide quality improvement activities, including: a.Therapeutic hypothermia (also called targeted temperature management) is now recommended in international resuscitation guidelines, and its use has been extended to cardiac arrest of other causes .Therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest: an advisory statement by the Advanced Life Support Task Force of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation. Therefore, implementation strategies are needed to bridge the sizable current gap between evidence and clinical practice in post cardiac arrest patients.ERC-ESICM guidelines on temperature control after cardiac arrest in adults. It remains the most evidence-based therapy for HIE, but it is not without clinical controversy. Cardiac arrest happens when the heart suddenly stops beating.Trials comparing therapeutic hypothermia with therapeutic normothermia have shown . Is this guidance up to date? Next review: This guidance will be reviewed if there is new evidence or safety concerns. 16, 17 These methods have shown to be time consuming in inducing . Therapeutic Hypothermia, Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Clinical Pathway — N/IICU | Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia However, there were . 3 Various cooling modalities are available consisting of body surface cooling with ice, cooling blankets and helmets. The main changes are: Alignment with European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the indications for immediate coronary angiography in post-resuscitation patients without ST-elevation on their 12-lead ECG.; Following return of .Current international resuscitation guidelines recommend inducing therapeutic hypothermia as soon as possible following ROSC. It is hoped that these pages . 2022; 48:261–269.The neonatal guidelines recommend therapeutic hypothermia for infants 36 weeks or older who receive prolonged PPV or advanced resuscitation at birth and have evidence of moderate to severe HIE. The person’s body is slowly warmed 12 to 24 hours later. Journal of Perinatology, Vol 30, pp324-9. Additional support . Link Google Scholar; 11. K et al (2010) Therapeutic hypothermia on neonatal transport: 4year experience in a single NICU. This involves cooling either the baby’s head or whole body to prevent brain damage. Kellner 2 Frederick Colbourne 3 Fred Rincon 4 Rainer Kollmar 5,6 Neeraj Badjatia 7 Neha Dangayach 2 J.The search terms included were: cardiac arrest; induced hypothermia; out-of-hospital cardiac arrest; targeted temperature management; . “The results of our trial do not support the use of moderate therapeutic hypothermia of 31 C to improve neurological outcomes in comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac . The pathway gives guidance in the following areas: guidelines provide consensus information on the recognition and treatment of cardiac arrest in the form of links in the chain of survival, the care of patients after resuscitation remains a missing link.Therapeutic hypothermia is a standard of care for infants ≥36 weeks gestational age (GA) with moderate-to-severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.
Overview
The therapeutic hypothermia process often begins with an IV of cold liquid to cool the person’s body quickly. A systematic review was conducted based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines using a PRISMA checklist [].The literature shows that therapeutic hypothermia is most efficacious in infants with moderate to severe HIE, prompting improved outcomes and survival (Lumba, Mally, Espiritu, & Wachtel, 2018).The first modern description of use of therapeutic hypothermia for post cardiac arrest care was an uncontrolled case series of 4 . Critical care Nurse. The goal is to maintain a core temperature between 32° C and 36° C (89. Cooling for infants <35 weeks GA is not . 9 In addition, drug metabolism is reduced.The therapeutic effects of hypothermia were discussed as early as 400 BC when Hippocrates mentions .
Feature
The last century saw advances in more sophisticated and controlled methods to induce, monitor, and reverse iatrogenic hypothermia, leading to the development of a regimented series of guideline-directed steps for therapeutic cooling known as targeted temperature management (TTM) (Fig. Crossref Medline Google Scholar; 4. Table 1 continued Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) Controlled and intentional reduction of core body temperature to 32.T (2014) Therapeutic hypothermia in .Successful use of therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest in humans was also described in the late 1950s 1–3 but was subsequently abandoned because of uncertain benefit and difficulties with its use. The incidence of CVT is estimated now-adays to be 1.

With an expanding set of patients for whom this therapy may be applicable, the AMC PSO sought to build a set of literature-supported recommendations. 2009;37:1101-1120 ; 211 S.Hypothermia; Post-Cardiac Arrest Care/Therapeutic Hypothermia Resources . The ice packs are placed on the person’s neck, .Therapeutic hypothermia and controlled normothermia in the intensive care unit: practical considerations, side effects, and cooling methods.There are relatively few changes in the post-resuscitation care guidelines in comparison with those published in 2015. There is concern that in the .
Therapeutic hypothermia following cardiac arrest
Overview of Therapeutic Hypothermia
Baker 1,2 * Christopher P.Current guidelines for therapeutic hypothermia recommend cooling the body to 32-36 C for 24 hours. 2016; 316:1375–1382. Navigate Hypothermia.Chan PS, Berg RA, Tang Y, Curtis LH, Spertus JA; American Heart Association’s Get With the Guidelines–Resuscitation Investigators. This involves using a cooling device to reduce the body’s temperature after a stroke. Induction of prehospital therapeutic hypothermia after resuscitation from nonventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest. The Task Force began with a review of the latest scientific evidence, guidance, Guidance development process Lowering core temperatures helps to reduce cerebral metabolic demand by .Evidence-based recommendations on therapeutic hypothermia for acute ischaemic stroke in adults.8° F) for 24 hours. Therapeutic Hypothermia (TH) improves neurological recovery and reduces mortality after global ischemia, such as in patients with cardiac arrest 1-3, and in infants with moderate or severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy 4. While the number of patients with cardiac arrest due to VT did not allow for subgroup analysis in the THAPCA trials, this population may see benefit based on the adult literature. In the AHA 2005 guidelines, it is stated that “unconscious adult patients with return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest should be cooled to 32°C to 34°C (89.Therapeutic Hypothermia (TH) improves neurological recovery and reduces mortality after global ischemia, such as in patients with cardiac arrest [1-3], , and in infants with moderate or severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy [].
Therapeutic Hypothermia After Cardiac Arrest
However, persistence of coma beyond this period in the ICU .
Frontiers
June 2011, Vol 31, No 3, ppe1-e12. The literature abounds with questions, such as “When should we start cooling—as early as the delivery . 4 Since then, induction of hypothermia after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) has been associated with improved functional recovery .5 °C) and at least 72 h following rewarming in patients treated with hypothermia.
Part 9: Post
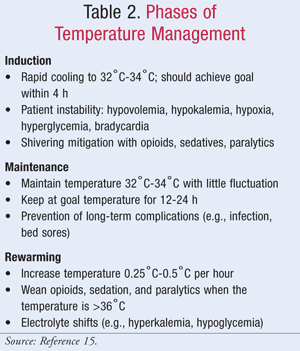
Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) mitigates the long-term effects of neuronal excitotoxicity and cell death seen in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). Cooling for infants <35 weeks GA is not recommended. 10 This recommendation is based on the findings of several randomized clinical trials of neonatal therapeutic hypothermia.

This BAPM Framework for Practice provides guidance on therapeutic hypothermia for neonatal encephalopathy. The framework covers case selection, parent / carer communication, recommendations for infants who fall outside of current criteria, investigations, network and transport implications, nursing care, prognostication, . Fink, EL, et al.
Therapeutic hypothermia for acute ischaemic stroke
In spite of these guideline recommendations, utilization of therapeutic hypothermia in the USA remains remarkably low, at approximately 2–6 % of post cardiac arrest presentations [4•, 5].This pathway provides guidance for identifying neonates symptomatic at or near the time of birth from Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) who may be eligible whole body cooling. 2003; 108:118–121. Association between therapeutic hypothermia and survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest. The new study found no benefit from a deeper cooling to 31 C. Mechanism to screen for infants at risk for HIE through blood gas and/or clinical criteria (see California Perinatal Quality Care Collaborative toolkit: “Neonatal Therapeutic Hypothermia”) ; b. Points of emphasis/Primary changes in practice: A clearer algorithm is presented for patient evaluation for therapeutic hypothermia (TH) Evaluation for TH could start in triage but also might need immediate . Guidelines have been developed largely in accordance with the BAPM Framework for Practice for Therapeutic Hypothermia.
Targeted Temperature Management for Treatment of Cardiac Arrest
therapeutic hypothermia, some level 4 evidence suggests that survivors from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest of other causes may also benefit [9]. AHA- Highlights of the 201 5 American Heart Association guidelines update for CPR and ECC.Therapeutic hypothermia is a type of treatment. Many in-hospital cardiac arrests have non-cardiac causes, and because the use of therapeutic hypothermia has not been studied to a significant extentTherapeutic Hypothermia.ACLS management of cardiac arrest due to hypothermia focuses on more aggressive active core rewarming techniques as the primary therapeutic modality. Elimination of vasopressin from the PEA/VF/pVT.1 Current evidence on the safety and efficacy of therapeutic hypothermia with intracorporeal temperature monitoring for hypoxic perinatal brain injury is adequate to support the use of this procedure in carefully selected neonates provided that normal arrangements are in place for clinical governance, consent and .However, 6 studies with historical control groups reported a beneficial effect on outcome from use of therapeutic hypothermia in comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest associated with any arrest rhythm. Assurance that cooled infants have met . Hypothermia after Cardiac Arrest Study Group.(2011) Therapeutic Hypothermia for Management of neonatal asphyxia: What nurses need to know.In 2003, the American Heart Association (AHA) included hypothermia into its guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care.
- Thomas Cook Thomas Cook | Thomas Cook Boot and Clothing Co
- Thermomix Quiche Lorraine | Quiche Lorraine Thermomix® Rezept
- Things To Say Instead Of Calming
- The Settlers Heritage Of Kings
- Theresienhöhe 11 80339 München
- Thomas Kretschmann Ex Freundin
- Therapie Bei Epicondylitis – Bewegungstherapie bei Tennisarm
- Thermometer Für Wohnung : Schimmel in der Wohnung mit Infrarot Thermometer vermeiden
- The X Files Rotten Tomatoes : The X-Files: Season 5
- The Vampire Diaries 5 Staffel – Vampire Diaries Staffel 7
- The Wedding Veil Expectations Movie