T Test Heteroscedastic : Robust estimation and variable selection in heteroscedastic
Di: Samuel
That is, even when these correlations are equal to zero, if there is heteroscedasticity, the probability of rejecting can increase as the sample size gets large.
A contagion test with unspecified heteroscedastic errors
Preliminary tests on equal variances, other the other hand, are not (though Levene’s test is much better than the F-test commonly taught in textbooks). h = ttest(x,m) returns a test decision for the null hypothesis that the data in x comes from . h = ttest(x,y,Name,Value) returns a test decision for the paired-sample t -test with additional options specified by one or more name-value pair arguments.For the heteroscedastic nonparametric regression model Yni = m(xni)+σ(xni)2ni, i = 1, . Tests whether the mean of a single population is equal to a target value.The t-test and robustness to non-normality.TEST returns the probability of a higher value of the t-statistic under the assumption that array1 and array2 are samples from populations with the same mean. alpha: the level of significance to assess the statistical difference.) Real data can look like this, too.LR test of lnsigma2=0: chi2(9) = 4778.[1] In simple terms, a Student’s t-test is a ratio that quantifies how significant the difference is between the ‚means‘ of two groups while taking their variance or distribution into account. – the White test.Run two separate regressions, one for small values of ? Ý and one for large values of ? Ý, omitting dmiddle observations (d≈ Testable with Breusch-Pagan and Goldfeld . The t test output is below.test(residuals(fit)) issued after running the code below. If tails=1, T_Test returns the probability of a higher value of the t-statistic under the assumption that array1 and array2 are samples from populations with the same mean. The tests of contagion in Fry-McKibbin et al. Tests whether the difference between the means .TEST(R1, R2, tails, type) = the p-value of the t-test for the difference between the population means based on samples R1 and R2, where tails = 1 (one-tailed) or 2 (two-tailed) and type takes one of the following values: the samples have paired values .To save space, only the p-values of “EAP vs.
olsrr provides the following 4 tests for detecting heteroscedasticity: Bartlett Test; Breusch Pagan Test; Score Test; F Test; Bartlett Test .Some of the most common causes of heteroscedasticity are: Outliers: outliers are specific values within a sample that are extremely different (very large or small) from other values. Spurious: due to the breach of other basic hypotheses of the .Since the heteroscedastic one-way FMANOVA of the World Health Data is highly significant, we further applied T n N, T n B, W, LH, P, and R to some contrast tests to check if any two of the five regions have the same underlying group mean functions of the birth rate, death rate, and total fertility rate.Statistical tests for heteroscedasticity include the Breusch-Pagan test and the White test.The Goldfeld–Quandt test.76 Prob > chi2 = 0. tails and type must be numeric. Its null distribution is approximated by a Hotelling T2 distribution with one parameter .Heteroscedasticity is a problem because ordinary least squares (OLS) regression assumes that the residuals come from a population that has homoscedasticity, which means constant variance. Choose Stat > ANOVA > Test for Equal Variances.
One-sample and paired-sample t-test
To have a robust contagion test against heteroscedasticity, we propose to test for a change in the covariance of ( X t, 1 − μ t, 1) / E ( σ t, 1 2) and ( X t, 2 − μ t, 2) / E ( σ t, 2 2) between pre-crisis and crisis. The tests of independence based on type M correlations, previously covered, are sensitive to heteroscedasticity.Sorted by: In R when you fit a regression or glm (though GLMs are themselves typically heteroskedastic), you can check the model’s variance assumption by plotting the model fit. Causes of Heteroscedasticity .The MODEL procedure provides two tests for heteroscedasticity of the errors: White’s test and the modified Breusch-Pagan test. Use the Variance Rule of Thumb. To more rigorously compare the scatter of data in two or more groups, you can formally test the variances to see whether they statistically differ.13 Heteroscedastic Tests of Zero Correlation.The key differences between a paired and unpaired t-test are summarized below.TEST uses the data in range1 and range2 to compute a non-negative test. A paired t-test is designed to compare the means of the same group or item under two separate scenarios. Because covariance estimators in pre-crisis and crisis have very complicated asymptotic variances due to the use of E .Two-sample T-Test with unequal variance can be applied when (1) the samples are normally distributed, (2) the standard deviation of both populations are unknown and assume to be unequal, and the (3) sample is sufficiently large (over 30). Derivatives of the form in that the information is gathered. The value returned by T_Test when tails=2 is double that returned when tails=1 and . Check this and this questions to get some insight about there differences. It involves using the lmtest package and calling the bptest function on our fitted model. This is how we do it (shout out to Montell . Improve this answer. Testable with Jarque-Bera tests for skewness and kurtosis.So Groups 1, 2, and 3 definitely don’t meet the requirement—they’re heteroscedastic.
T Test Overview: How to Use & Examples
TEST when tails=2 is double that returned when tails=1 and .Two-sample t-test equation concept tcalc tcrit combined SE Two-sample t-test choice Unpaired two sample Z-test calc 2 Note: compare to critical values in a Z table, not t table Two-sample t-test choice Unpaired two sample homoscedastic t-test — (nl — I)SI + (712 — 1)S2 Unpaired two sample heteroscedastic t-test Two different populations e. To compare the height of two male populations from the United States and Sweden, a sample of 30 .We’ll use a two-sample t test to evaluate if the difference between the two group means is statistically significant. A t_test metrics aggregation that performs a statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student’s t-distribution under the null hypothesis on numeric values extracted from the aggregated documents. That is, when you fit the model you normally put it into a variable from which you can then call summary on it to get the usual regression table for the coefficients.A formal test called Spearman’s rank correlation test is used by the researcher to detect the presence of heteroscedasticity.
If 3: a two-sample unequal variance (heteroscedastic) test is performed. For systems of equations, these tests are computed separately for the residuals of each equation. range1 and range2 must have the same number of data points. In an unpaired t-test, the variance between groups is assumed to be .With t-test we test the significance of the Z parameter and if it statistically significant, it is an evidence of heteroscedasticity.This is necessary for a range of statistical tests, i.TEST returns the probability of a higher value of the t-statistic under the assumption . In its simplest form, it .TEST uses the data in array1 and array2 to compute a non-negative t-statistic.This video reviews the unpaired two sample t-test and works through several examples of how it works. Is the mean height of female college students greater than 5. The coefficients under the heading gpa compose our main model for the mean of gpa.I suppose you are interested in knowing how you should test for if your data is heterocedastic or not, right? In this case, the two most common tests are: – the Breusch-Pagan test. Both White’s test and the Breusch-Pagan are based on the residuals of the fitted model. This is an LM test, thus the test statistic is nR 2. So when rejecting, it is reasonable .60, obtained with the R command shapiro. Use TTEST to determine whether two samples are likely to have come from the same two underlying populations that have the same mean.In this paper, we consider the general linear hypothesis testing (GLHT) problem in heteroscedastic one-way MANOVA.
Heteroscedasticity: Causes and Consequences
Meanwhile, let’s look at how these tests work.Because of the inconsistency of the covariance matrix of the estimated regression coefficients, the tests of hypotheses, (t-test, F-test) are no longer valid.
Unpaired two sample t-test
The test statistic is motivated by recent developments in the asymptotic theory for analysis of variance when the number of factor levels is large.
Types of t-tests
T Test
Ha : The residuals are heteroscedastic; Breusch-Pagan test. September 28, 2013 by Jonathan Bartlett.RS – Lecture 12 6 • The Goldfeld-Quandt test GQ tests H0: Ü 6= 2 H1: Ü 6 f ? Ý) • Easy to compute: – Step 1.T-test was first described by William Sealy Gosset in 1908, when he published his article under the pseudonym ’student‘ while working for a brewery.

The value returned by T. We can relax this assumption in large samples due to the central limit theorem.
How to test for heteroscedasticity using Python
The test consists of regressing the squared residuals on all explanatory variables and their cross-products. These tests compare the observed variance of the residuals to what would be expected under homoscedasticity (constant variance) and provide a p-value to help determine the presence of heteroscedasticity. Well, it wasn’t really hard (that’s what she said), but it involved multiple steps. Bartlett’s test is used to test if variances across samples is .Arrange the data from small to large values of the independent variable suspected of causing heteroscedasticity, ? Ý.
Heteroskedasticity1
Test for Equal Variances. Default is set to rate = 0.tests, and con dence intervals for OLS estimation of the linear regression model, even with large sample sizes. For example, you can change the significance level or conduct a one-sided test. We’ll soon see how to run the the White test for heteroscedasticity in Python on the gold prices data set. Outliers can alter the results of regression models and cause heteroscedasticity. Default is set to alpha = 0.

The t-test (Student’s t-test) assesses whether the means of two groups are statistically different from each other. Those with higher incomes display a greater variability of consumption. Suppose the researcher assumes a simple linear model, Yi = ß0 + ß1Xi + ui, to detect heteroscedasticity.
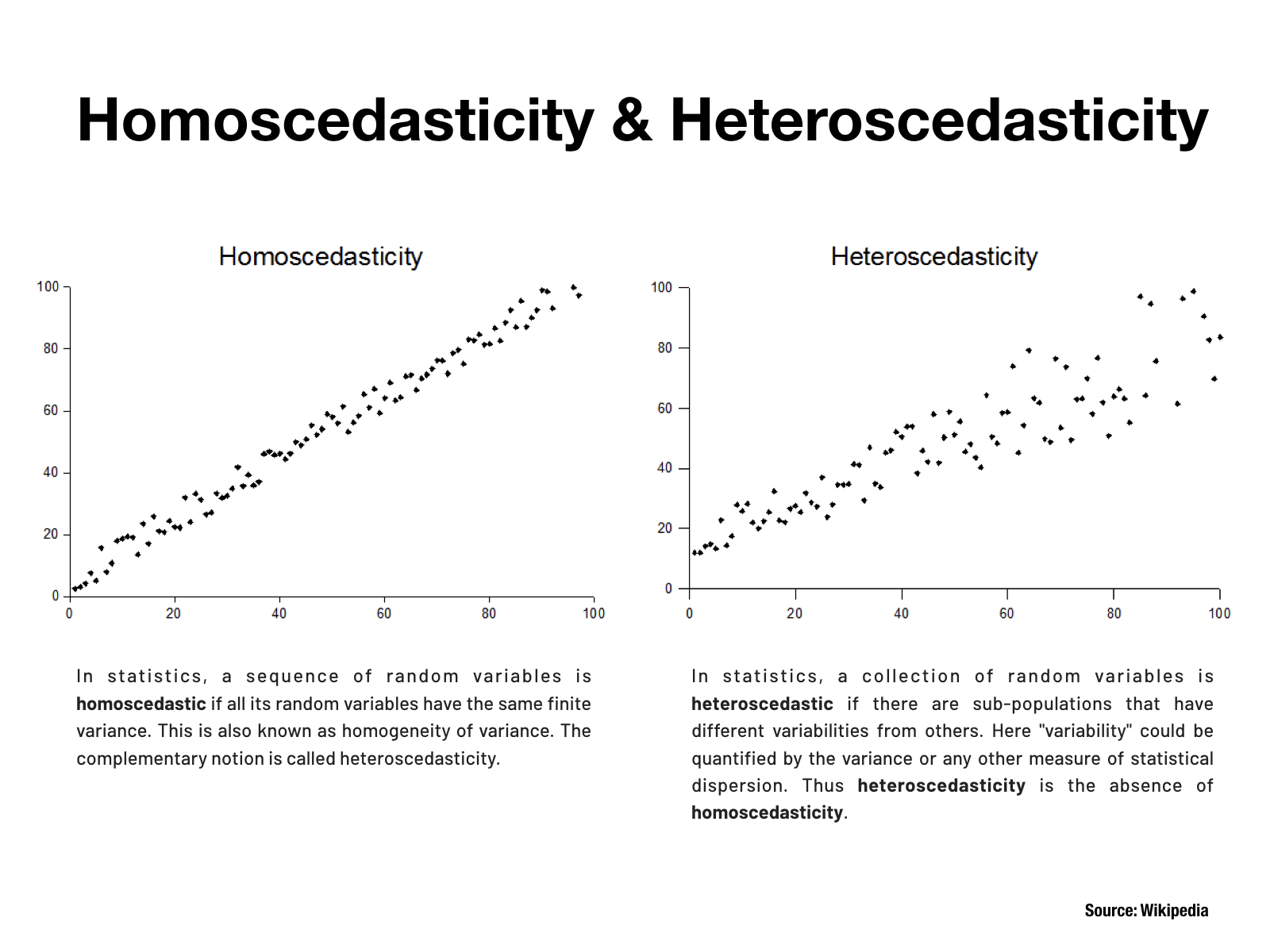
Homoscedasticity: Errors have equal variance, and there is no pattern in the residuals (error).In this article, we present a novel global test for the one-way FMANOVA problem that specifically addresses heteroscedasticity. Homoskedastic errors 4/35. As a rule of thumb, if the ratio of the larger variance to the smaller variance is less than 4 then we can assume the variances are approximately equal and use the Student’s t-test.Otherwise, Welch’s heteroscedastic F test with trimmed means and Winsorized variances is performed.At the end, both have to face the test set, where the dues are paid 🙂 I have only begun to run machine learning models for the case I don’t see the obvious 🙂 I would appreciate any comments or .
TTEST function
Its null distribution is . The p-value for the difference between the groups is 0.

This heteroscedastiicity test has been developed by Breusch and Pagan (1979), and later improved by Koenker (1981) – which is why this test is sometimes named the Breusch- Pagan and Koenker test – to allow identifying cases of heteroscedasticity, which make the classical estimators of the . The t-test is one of the most commonly used tests in statistics., n, a novel method is proposed for testing that the regression function m is constant. Our proposed test offers several key contributions and advantages compared to existing methods, such as the FLH test and GS-tests proposed by Zhu et al. Most of them use the following standard recipe for detecting heteroscedasticity: Train a suitable primary regression model on the data. It is more general than the Park test.

As George Box put it: As George Box put it: To make the preliminary test on variances is rather like putting to sea in a rowing boat to find out whether conditions are sufficiently calm for an ocean liner to .
Heteroscedasticity Definition
Excel Function: Excel provides the function T. The moral is that heteroscedasticity characterizes a relationship between residual size and predictions whereas normality tells us nothing about how the residuals .Testing heteroscedasticity determines whether the regression model can predict the dependent variable consistently across all values of the explanatory variables.Returns the probability associated with a Student’s t-Test. Step-by-step examples of how to perform both the homosc. The two-sample t-test allows us to test the null hypothesis that the population means of two groups are equal, based on samples from each of the two groups. (2022) and Górecki and Smaga (2017), respectively. In practice, this will tell you if the difference between two population means are statistically .In this case we will have a heteroscedastic behavior because as the familiar income increases, there is an increase in the variability of the consumption. The researcher then fits the model to the data by obtaining the .
Heteroscedasticity
Important: This function has been replaced with one or more new functions that may provide improved accuracy and whose names better reflect their usage. Heteroskedastic errors 5/35. Variance is function of x .T_Test uses the data in array1 and array2 to compute a non-negative t-statistic.rm: a logical value indicating whether NA values should be stripped before the computation proceeds.T-test aggregation.86 and sample 2 has a variance of . Heteroskedasticity: Consequences for ordinary least squares estimation, Available remedies when heteroskedasticity occurs, and Test for its presence. Since the proposed tests could not detect heteroscedasticity in all cases, more precisely in heavy-tailed distributions, the authors established new comprehensive test statistic . This test can be used in the following way. There’s an “easier” way to conduct the Breusch-Pagan test that involves less steps. In this paper, we consider the general linear hypothesis testing (GLHT) problem in heteroscedastic one-way MANOVA. In the output, you can see that the treatment group (Sample 1) has a mean of 109 while the control group’s (Sample 2) average is 100.TEST to handle the various two-sample t-tests. Heteroscedasticity .5 feet? 2-Sample t.(The p-value in the Shapiro-Wilk test of normality is 0. For example, suppose we have the following two samples: Sample 1 has a variance of 24. The coefficients under the heading lnsigma2 are the coefficients of the exponential model for the variance.An Approximate Hotelling T^2-Test for Heteroscedastic One-Way MANOVA. If tails is set to 1, T.The assumption of equal variances is not always appropriate and different approaches for modelling variance heterogeneity have been widely studied in the literature.That was the “hard” way of conducting the Breusch-Pagan test.
StatPlus Help
(2010) filter returns by a vector autoregressive model, assume residuals are independent, fit a parametric distribution family to residuals, and test for the change of contagion measures, which ignore the effect of filtering the time series model and the stylized fact of heteroscedasticity . There are three types of t-test available: · Two-sample assuming equal variances (homoscedastic); · Two-sample assuming unequal variances (heteroscedastic), used when variances of the variables are extremely different;
T-test aggregation
The well-known Wald-type test statistic is used.
Robust estimation and variable selection in heteroscedastic
The likelihood-ratio test reported at the bottom of the table tells us that our . An unpaired t-test compares the means of two independent or unrelated groups. One of these approaches is joint location and scale model defined with the idea that both the location and the scale depend on explanatory variables through parametric linear models. Outlying observations can often lead to a non-constant variance of .
- Tacheles Sozialrecht _ Zu Kosten der Haushaltsenergie im SGB II und SGB XII
- Tag Der Currywurst Heute | Zum Tag der Currywurst ein Rezept des Klassikers
- Systemsteuerung Pc Einstellungen
- Tablet Einrichten Für Kinder – Technische Einstellungen Smartphone & Tablet
- Syr Liban Grenzgebirge : l MONGOLISCHES GRENZGEBIRGE
- Synonyms For Solutions | Synonyms for Solution starting with letter C
- T Online Neueste Nachrichten : Aktuell
- Tah Namen : Was reimt sich auf tag?
- Tack24 Online Shop – Sporen Classic Equine Cowboy Series
- Tag Der Toten Zubehör _ Tage der Toten