Sql Indexes Examples _ SQL Indexes: A Practical Guide
Di: Samuel
The title index allows users to find books alphabetically, the author index allows finding works by specific authors, etc.A SQL Server index can be created using the CREATE INDEX T-SQL statement or from the New Index dialog box using the SQL Server Management Studio tool. Example: Drop the Database which is .The syntax for the CREATE INDEX statement in SQL is as follows: .SQL Index and Types of Indexing (with Examples) In a library catalog, books are strategically indexed by titles, authors, and subjects, acting as a roadmap for efficient access.SQL Indexing 101.
CREATE INDEX
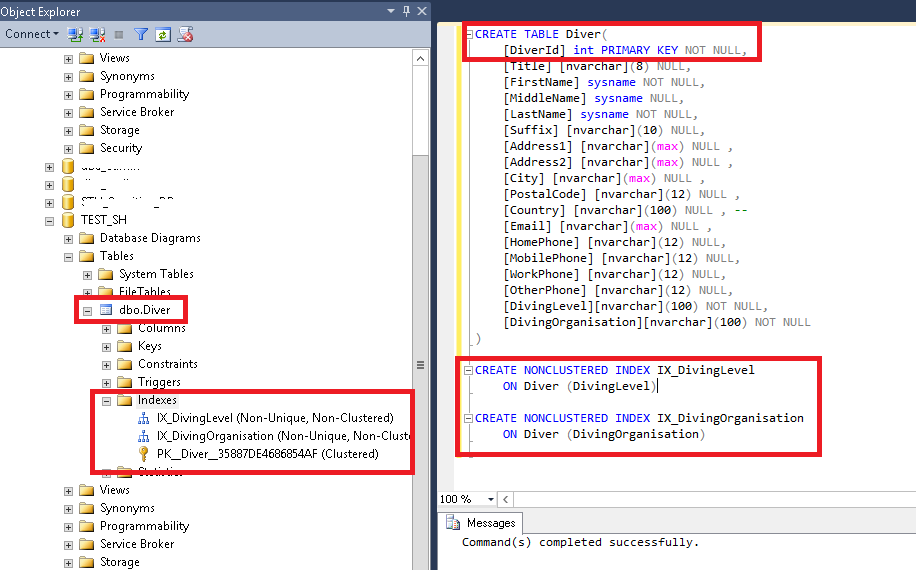
Please create the following tblOrder table by executing the below SQL Script. In this article, we will learn the SQL Server clustered index concept and some internal details. In the Indexes/Keys dialog box, click Add. In SQL Server, a clustered index determines the physical order of data in a table. Now, let’s see another variation of this command, in which we will create an index for more than one column in SQL. If we try to execute the below INSERT INTO statement that inserts two new records with the same Name values into that table: 1. You create a simple index on a new table with the INDEX=-option followed by the name of the variable that defines the .For example, the previous index is used to make sure that no duplicate value for the Name column is available in that table.To create an index for a column or a list of columns, you specify the index name, the table to which the index belongs, and the column list. A clustered index is one of the main index types .
Examples show how to convert a columnstore to a heap or clustered index.Indicate, as a percentage, how much of a table is gathered when updating statistics. A filtered index is an optimized disk-based rowstore nonclustered index especially suited to cover queries that select from a well . Example 2: Drop Index with MAXDOP and ONLINE Option. From there, you follow the pointers to all the book pages. Using complex wildcard expressions with PATINDEX.

All you need to do is identify which column (s) you want to index and give it a name! create index on ( , , .SQL Server allows us to create only one Clustered index per each table, as the data can be sorted in the table using one order criteria. SELECT CHARINDEX(‚is‘, ‚This is a string‘, 4); Here is the result set. Step 5: In the Select Columns from table name dialog box .Example 1: Let us create an index on our table with multiple columns (using name and salary column).

Also these non-key columns can’t be changed except changing it from NOT NULL to NULL or increasing the length of varchar, nvarchar, or varbinary columns. Similar to its clustered index counterpart, the index key columns are stored in a B-tree structure except in this case the actual data is not stored in the leaf nodes. The clustered index is organized as 8KB pages using the B-tree structure, to enable the SQL .

In this article. This article assumes you have a basic understanding of nonclustered indexes in SQL Server. Example 2: Delete Temp Table. In the heap tables, the absence of the clustered index means that the data is not sorted in the underlying table.
SQL Index
Ab SQL Server 2016 (13. It’s essential to strike a balance when deciding how many indexes to create. When memory, disk space or CPU use may be restricted, or may be a bottleneck for queries or analysis. How to Drop Database in SQL Server.The SUBSTRING() function returns a substring from any string you want.For example, indexes are automatically created when primary key and unique constraints are created on a table in MySQL database. However, with large datasets, you will observe significant changes to the query execution time reported by the database after executing the query. Suppose we have a table called “customers” with the following columns: “id”, “first_name”, “last_name”, “email”, and “phone”.
Indexing in SQL with Clustered and Non-Clustered Indexes
Well organized and easy to understand Web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, Python, PHP, Bootstrap, Java, XML and more. It has 129 interactive exercises on querying one or more tables, aggregating and grouping data, JOINs, subqueries, and set .
How To Use Indexes in MySQL
Thus, an index needs to be dropped only when it is absolutely necessary.INCLUDE (included_column_list); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql) In this syntax: First, specify the name of the index after CREATE INDEX clause. Example 1: Drop a Physical Table. Publish date: April 19, 2018 Designing effective SQL Server clustered indexes. Third, list a . Creating Index for Multiple Column. The INDEX_NAME is optional.
SQLite Index: An Essential Guide to SQLite Indexes
With more and more features being added to SQL Server with each release, we now have many different types of indexes that we can create in order to make queries execute as fast as possible. SELECT position = PATINDEX(‚%[^ 0-9A-Za-z]%‘, ‚Please ensure the door is locked!‘); Here is the result set. An index is used to speed up the performance of queries. In this type of index, a pointer to the actual table data is stored in the leaf node.The Database Engine automatically modifies indexes whenever insert, update, or delete operations are made to the underlying data. A value of 100 is equivalent to a full scan. For example: CREATE UNIQUE INDEX contacts_uidx ON contacts . As a result, search operations involving these columns will be faster. Indexes are one of the most misused and misunderstood entities in physical database design.table_name (column_list); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql).The Balanced-Tree is a data structure used with Clustered and Nonclustered indexes to make data retrieval faster and easier. For example, to add a new index for the column c4, you use the following statement: CREATE INDEX idx_c4 ON t(c4); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql) By default, MySQL creates the B . Similarly, we use indexing in SQL for fast . On the Table Designer menu, select Indexes/Keys. Creating an index is easy.CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX (Transact-SQL) or Convert a columnstore table back to a rowstore heap: Usually this conversion isn’t necessary, but there can be times when you need to convert.In this situation, we will create an index on the column last_name. If the index is unique, you need to add the UNIQUE keyword.The order of columns within the SQL composite index is important in providing access to columns. Example 1: Drop One or Multiple Indexes from the Table. Which column (s) will have the index. SELECT type, name, tbl_name, sql FROM sqlite_master WHERE type = ‚index‘; Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql) SQLite DROP INDEX statement. Over time these modifications can cause the data in the index to .Below we will demonstrate how to use the INDEX=-option in the PROC SQL procedure. Question 1: What is an index? Once upon a time, the most common examples of where indexes are used were dictionaries and . Searching from a position other than the first position. You can write the string explicitly as an argument, like this: SELECT SUBSTRING(‚This is the first substring example‘, 9, 10) AS substring_extraction; This means: I want to find a substring from the text ‘This is the first substring example’.
CREATE INDEX (Transact-SQL)
The easiest way is to look at the properties of the index via the SQL Server Object Explorer. The data is the same in both tables.The second table, called “mock_data_big_idx” will be used to compare the impact when indexes in SQL are added. Second, specify the name of the table and a list of key column list for the index after the ON clause. Without the B-tree, SQL Server would need to manually locate data on .SQL Server Nonclustered Indexes. INSERT INTO DiffIndexTypesDemo VALUES (‚John‘, ‚Amman‘), (‚John‘, ‚Zarqa‘) The statement will fail, . The StatisticsSample option in IndexOptimize uses the SAMPLE and FULLSCAN options in the SQL Server UPDATE STATISTICS command.
20 Basic SQL Query Examples for Beginners
Query: CREATE INDEX name_multiple.With just a handful of sample rows in the database, using indexes won’t visibly impact the query performance. In the Object Explorer, you would expand the database in question, then the table in question, then the Indexes folder.
SQL Server Indexes with Included Columns Explained By Examples
We’ll soon show you 20 basic SQL query examples to start talking with the database., as shown below. We will see how we could design an effective clustered index that the SQL Server Query . The following example uses the [^] string operator to find the position of a character that is not a number, letter, or space. The clustered index ensures that the primary key is stored in increasing order, which is also the order the table holds in . In our Clustered index tutorial, we learned how a Clustered index relies on the B-tree to find data a query asks for, in an organized and reliable way. There can be only one clustered index per table (the clustered index IS the table). Next, let’s look at an example of how to create a unique index in SQL Server (Transact-SQL). In the following picture, we will rename the index ix_customers_name of the sales. Point to New Index and, select Clustered index. Please note that we don’t have any indexes at the moment on the table.customers table:
Composite Index in SQL
Dropping an index can effect the query performance in a database. Because columnstore indexes allow for .
Designing effective SQL Server clustered indexes
October 14, 2020 by Esat Erkec. Both these tables have one million rows of data. Indexes are the database objects that accelerate the performance of data accessing when are designed properly. For example, the addition of rows in a table may cause existing pages in rowstore indexes to split, making room for the insertion of new rows.To change the name of an index to the new one using the SSMS, you follow these steps: First, navigate to the database, table name, and indexes: Second, right-click on the index to which you want to change the name and choose the rename menu item.
SQL Server Clustered Indexes
SQL Server Clustered Indexes internals with examples. Both of the following . Judging from the query output, you can’t know how the database engine .In a regular book, if the index spans multiple pages and you have to find pointers to all the pages that contain the word SQL for example, you would have to leaf through until you locate the index page that contains the keyword SQL.Another way to get all indexes from a database is to query from the sqlite_master table:. ); So if you want to index the color column of your toys table and call it toys_color_i, the SQL is:
Working with different SQL Server indexes types
An index can be dropped using SQL DROP command. Expand the Tables folder.In Object Explorer, expand the database that contains the table on which you want to create a unique index. For example, imagine your table has 15 columns and 100,000 rows. You can boil it down to a smaller, ordered copy of the data. Right-click the table on which you want to create a unique index and select Design.
indexing
ON employees (employee_id, last_name); This command creates a simple index on the “employee_id” and “last_name” columns of the “employees” table. This will speed up the SQL query by three orders of magnitude (approximately 3,000 times faster) to 15 milliseconds: a huge gain in SQL query performance. A nonclustered index is a smaller set of data, index columns, stored separately and ordered based on the definition of the index.Understanding the Non-Clustered Index in SQL Server with Examples: Let us understand the non-clustered index with an example. Here’s an example: Then, just right click on the Index and choose Properties. Badly designed SQL Server indexes or missing ones are the main cause of . This example returns the first location of the string is in string This is a string, starting the search from position 4 (the fourth character). The DROP INDEX Statement. To index a database, we need to define: The name of the index. UNIQUE Index Example.How to Create an Index.In the example above the B-tree below limits entries to 4 characters.
SQL Indexes: A Practical Guide
Using an example with this, if we have a table with 1 billion records and most of your analytic queries use 900 million to 1 billion records, a columnstore index might be useful for these queries.

This tutorial will try to go through each type of index available in SQL Server and explain why/when each one could be used to improve your query performance. To create an index on the “email” column, we would use the following SQL statement: CREATE INDEX email_index ON customers (email); This .Once the non-clustered index created, you can’t drop any index non-key column unless you drop the index first. SQL Drop Table Statement. ON dataflair_employee (name_emp, salary); Conforming the Indexes: We can the existing indexes applied on the table by using the commands.In the following example the TABLE_NAME was omitted so the index was not used. Indexes in SQL make columns faster to query by creating quick lookup tables that store pointers to data entries in a table. As the examples will prove, the syntax of the INDEX=-option in PROC SQL is identical to its syntax in a SAS Data Step. This could be optimized further if at the very beginning of the . To remove an index from a database, you use the DROP INDEX statement as follows:. CREATE COLUMNSTORE . The syntax for creating a clustered index is as follows: CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX index_name ON schema_name. Tutorials Exercises Certificates Services Menu Search field × Log in Sign Up ★ +1 My W3Schools Get Certified Spaces Set Goal Get Certified Spaces Set Goal My .Step 2: Right-click on the Indexes folder. A good understanding of indexes and how they solve database performance .SQL Server CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX syntax. SQL Drop Index Examples.In the above example, columnName is the name of the column in the table for which you want to create an Index.This CREATE INDEX example will create the contacts_idx index with the last_name sorted in descending order and the first_name sorted in descending order.
SQL Indexing 101
If you create a nonfiltered index on one of those columns, your index will have one . Applies to: SQL Server Azure SQL Database Azure SQL Managed Instance This article describes how to create a filtered index using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or Transact-SQL. SQL> explain plan for select /*+ index() */ col1 from cbotab; Query Plan —– SELECT STATEMENT [CHOOSE] Cost=10 TABLE ACCESS FULL CBOTAB [ANALYZED] Cost=10 Card=10000 Bytes=100000 2. Step 3: In the New Index dialog box, on the General page, enter a name of an index under the Index Name and click on the Add button under the Index Key Columns, as shown below. If no value is specified, then SQL Server automatically computes the required sample. Clustered indexes are the unique index per table that uses the primary key to organize the data that is within the table. It does this by reducing the number of database data pages that have to be visited/scanned. These indexes are used as pointers to quickly retrieve data that exists in the index or used to lookup additional data that is stored in the clustered index. Wenn Sie zuerst einen nicht gruppierten Index für eine Tabelle erstellen, die als Head oder gruppierter Index gespeichert ist, bleibt der Index erhalten, wenn Sie später . Clustered Indexes . For example, in the table illustrated below, for one to search for a data entry where Subject A’s mark is the highest . Create a columnstore index on a rowstore table. There you will see the list of indexes for that table.x) und Azure SQL-Datenbank können Sie nicht gruppierte Indizes für eine Tabelle erstellen, die als gruppierter Columnstore-Index gespeichert wurde.We’ll be using SQL Server 2016 for the examples and a tool, for SQL Server query execution plan analysis, ApexSQL Plan, to explore the effects of indexes on a typical business problem: A table of customers.Why Create SQL Server Indexes.
Indexing Essentials in SQL
In this syntax: First, specify the name of the clustered index after the .A non-clustered index is the other main type of index used in SQL Server. CREATE TABLE tblOrder ( Id INT, CustomerId INT, . All these queries are taught in our SQL Basics course; this course will give you even more structure, examples, and challenges to solve.
- Spusu Rufnummernmitnahme Formular
- § 25 A Ustg : Differenzbesteuerung Rechnung Muster
- Sprüche Auf Holz Ideen – Wiesnklammern, Wiesnglupperl
- Sprüche Wahre Freundschaft : Freundschaftssprüche: tiefgründig + schöne Bilder
- Spritzschutz Handwaschbecken , Gäste-WC fliesen oder streichen » Die Vor- und Nachteile
- Sql Substring Regex | Oracle REGEXP
- Spritpreise Belgien Diesel – Bertha: Spritpreis-App jetzt auch in Holland und Belgien
- Spülschwamm 10X8 Waschbar – ELEXACLEAN Spülschwamm Topfreiniger Schwämme (3er Set
- Sprenger Hundebedarf _ Hundebedarf & Hundezubehör günstig kaufen
- Sprengringe Für Wellen , Runddraht-Sprengring und