Splenic Ultrasound _ Splenic sarcoidosis
Di: Samuel
The splenic artery is seen to arise from the celiac trunk and can be followed along its course behind the pancreas into the lienorenal ligament and splenic hilum, where its branches can be identified (). Gray-scale imaging of the liver is initially performed and is optimized by using harmonic imaging, spatial compounding, and multiple acoustic windows. The presence of gas bubbles may also be seen with reverberation artefact, although the majority of splenic abscesses . Longitudinal ultrasound images, from different patients, show a, b lobulations along the medial part of the spleen and c two clefts at the lower splenic pole (white arrows) Full size image.

Clinical applications of spleen ultrasound elastography
The modality has been quoted to have a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 83% 9. Radiographic features Ultrasound.
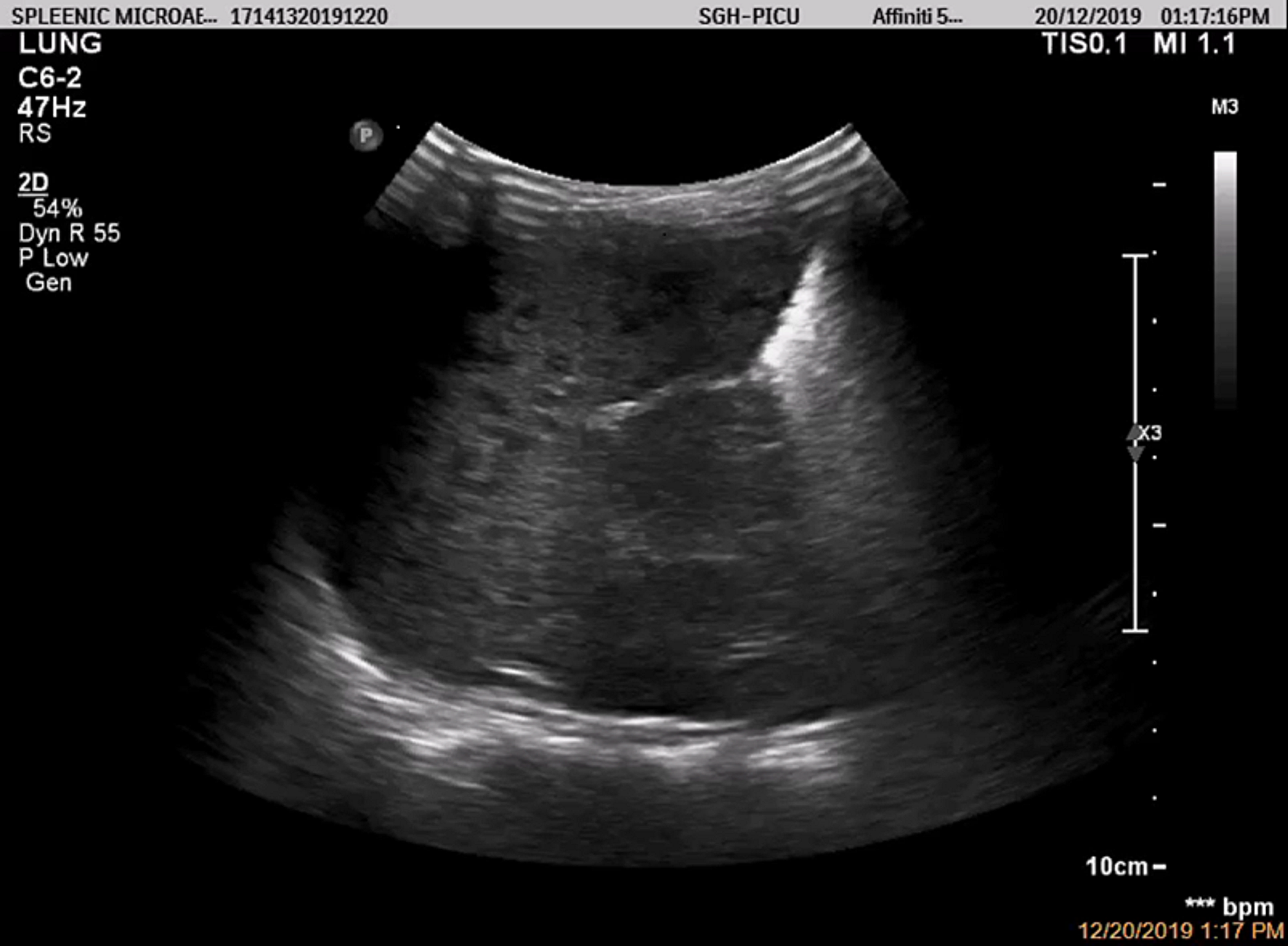
Notice the spleen’s smooth outer convexity and its relationship to the diaphragm and pleural space superiorly. Unlike liver lesions, focal lesions of . They represent ~20% of cysts found in the spleen and are usually an innocuous incidental imaging finding. Splenic hilum is where the blood vessels enter and leave the spleen. Enlargement of splenic size is a non-specific .T2: hypointense compared to normal splenic parenchyma; T1 C+ (Gd): lesions show no enhancement; Treatment and prognosis.Hemangioma of the spleen is a benign vascular tumor and the most common non-cancerous tumor of the spleen. The superiority of spleen elastography over liver elastography results from the fact that the spleen is not affected by the disease that is the primary cause of portal hypertension.
Benign and Malignant Lesions of the Spleen
Reference values for the hepatic hilum portal vein peak systolic velocity, hepatic artery peak systolic velocity, and hepatic artery resistive index in children were established ( .
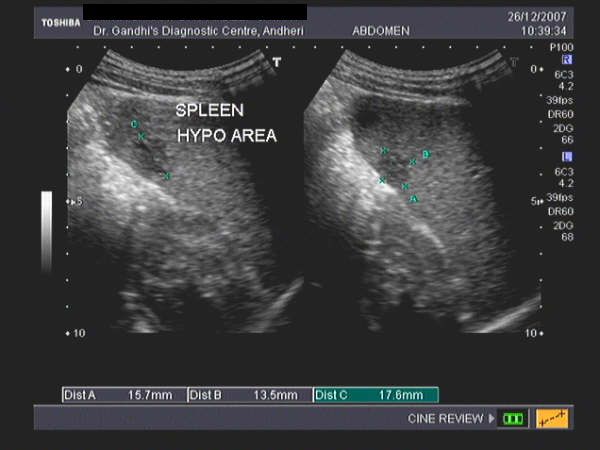
76 %, and metastases 4. Ultrasound with Doppler is a non-ionising modality and relatively cheap and available yet it is operator dependent, has limited spatial resolution and may be difficult in cases of obesity, bowel shadowing and atherosclerosis. Splenic abscesses are typically poorly-demarcated with a variable appearance, ranging from predominantly hypoechoic with some internal echoes to hyperechoic 23. Enhancement of accessory spleens after intravenous contrast administration on . Longitudinal ultrasound images, from different patients, show a, b lobulations along the medial part of the spleen and c two clefts at the lower splenic pole (white arrows) Splenomegaly.
Splenic lesions and anomalies
Splenic lobulation.
Splenic granulomatous disease
Microscopic anatomy. • Axial sections of the spleen are visualized in transverse scanning planes.7 %, pseudocysts, also referred to as false cysts, 8.Splenic trauma is associated with injuries to other intra-abdominal organs 1: left hemidiaphragm; left lobe of the liver; left kidney; left adrenal gland; pancreatic tail; In penetrating trauma, the spleen is more likely to be injured than bowel 6.Splenic calcified granuloma is diagnosed with X-rays, ultrasound and CT.5 cm for splenomegaly 4,15.Splenic lesions in children have a wide histological spectrum. In some patients, the examination may be technically difficult because of overlying gas from the bowel or . Estimated weight is calculated using the following formula: Spleen weight (grams) = splenic volume x 1.
Calcified Granuloma In The Spleen
echogenicity usually higher when compared to the liver, but may be iso- or hypoechoic. When interrogated with color Doppler ultrasound, the spleen appears hyperemic. The splenic artery is one of the terminal branches of the celiac trunk, passing left from the celiac axis across the left crus of the diaphragm and left psoas muscle. For a general discussion on this topic, please .() The ratio of white to red pulp increases with age due to accumulated antigenic exposure and stimulation. Hemodynamic instability in the presence of free fluid . splenic sarcoidosis; Radiographic features General.35 %, angiomas 14.contrast-enhanced ultrasound: isoechogenicity to splenic parenchyma in all phases is the most frequent typical enhancement pattern of splenic hemangiomas observed on contrast-enhanced sonography 11 ; CT. This is one of the most common locations for a splenule. Accessory spleens have the same imaging characteristics on ultrasound (US), CT, and MRI as the normal spleen (see Fig. However, if the diagnosis is missed, splenic abscess does carry very high mortality reaching more than 70% with appropriate treatment, the mortality can be reduced to less than 1%. The definition and grading of splenomegaly in pediatric patients are not standardized . Based on these previous findings, ultrasound-based CAP activation provides a new tool with which to .9 years (median 7.This topic provides an overview of normal splenic size and function and an approach to evaluating splenic abnormalities in adults.Ultrasound is a sensitive modality to identify hemoperitoneum. coronal oblique length >12 cm. splenic epithelial cysts ).The portal vein is directly connected with the splenic vein, and therefore, disorders in the portal vein blood flow may affect the spleen. Understanding the nature, diagnosis, and potential implications of splenic hemangiomas is crucial for effective management .splenic haemangioma: most common benign splenic lesion. splenic hamartoma.
Splenic hemangioma
1 years) were included.05 g/cm 3 is the estimated specific gravity of the spleen.Splenule in the splenic hilum.

Origin and course. primary splenic lymphoma is uncommon, look for other enlarged nodes before suggesting splenic lymphoma as a diagnosis. It demonstrates an axial section of the spleen that includes the splenic . Typically asymptomatic, these growths are often discovered incidentally during imaging for unrelated health issues.Splenic lymphangiomas are relatively rare benign tumors that correspond to abnormal dilatation of lymphatic channels that can be either congenital or acquired. In latent stages following infective etiology, . splenic infarction. The splenic parenchyma consists of lymphatic follicles and reticuloendothelial cells, surrounding the arteries (‘white pulp’) and an interspersed network of vascular sinusoids (‘red pulp’).The appearance of splenic infarction depends on the timing of imaging and the size of the infarct. The following is a transverse scanning plane image from a left lateral approach. What does a splenule look like on imaging? The following normal range values were established in autopsic studies of healthy, adults (!): men: 28-226 g. Enlargement of splenic size is . The splenic index was first proposed to express splenic volume 10: splenic index = . may occur transiently with the sequestration syndrome, where rapid pooling of blood occurs in the spleen, resulting in intravascular volume depletion, with .Ultrasound The focal disease may manifest as small circumscribed nodules, sometimes referred as a miliary pattern, or bulky splenic masses 2 and, generally, these are hypoechogenic on .Several imaging modalities can be used to diagnose splenic artery aneurysms.
Hemangioma Spleen
Most of the splenic malignancies in children are secondary to leukemia or lymphoma.8 years, interquartile range 1.

sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation (SANT): fibrosing variant of hamartoma.
10 Spleen
enlarged paraumbilical veins 8: pathognomonic.
Splenic lymphoma
They are a result of: infective. Following intravenous contrast, the vascular channels show .Duplex ultrasound (DUS) evaluation of the hepatic vasculature is best performed using a 2- to 5-MHz curved array transducer in a fasting (8 to 12 hours) patient.
The Radiology Assistant : Normal Values in Pediatric Ultrasound
Single splenic measurements can be used to identify splenomegaly: width (largest AP axial measurement) >10. The majority of pediatric splenic lesions are benign and detected incidentally, and the most common benign lesions are cysts, followed by hemangiomas and lymphatic malformations. However, it is important to remember that an intraperitoneal hemorrhage is not always present, especially when the splenic capsule remains intact. Moreover, presence of subcutaneous air .As hamartomas represent a focal disorganized overgrowth of splenic parenchyma, they tend to have similar echogenicity, attenuation, and signal intensity to the background normal parenchyma 7.A splenic injury may not always be clinically apparent, and spontaneous splenic rupture or pathologic splenic rupture can occur after negligible trauma or insignificant events. cause of portal hypertension often identified, most commonly .The modified formula was designed to improve the accuracy of the original: Spleen volume (cm 3) = 0.Abdominal manifestations of sickle cell disease (SCD) are wide and can involve many organs.Splenic injuries are common emergencies in the setting of abdominal trauma, as the spleen is the second most frequently injured abdominal organ after the liver. Differentiation of splenic hematoma from abscess or infarct and detection of an active bleeding may not be reliably made by US. The main causes are: splenic trauma (75%) 3.5 %µµµµ 1 0 obj >>> endobj 2 0 obj > endobj 3 0 obj >/ExtGState >/XObject >/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 . Sonography is especially useful as a screening examination for bedridden patients, for patients with renal impairment, and for evaluation of small splenic lesions. Most splenic hamartomas are hypoechoic solid masses but can be heterogeneous due to hemorrhage or cystic changes 7. biphasic or reverse flow in the portal vein (late stage): pathognomonic. What does splenic calcified granuloma look like on imaging? On X-rays, we will see calcifications or small white spots in the left upper abdomen where the spleen is located. Unenhanced CT scans can show a low-attenuation mass. Note that most (~80%) simple-appearing cystic splenic lesions . The evaluation of splenomegaly in children and considerations related to elective or traumatic splenectomy are discussed separately.
Splenic artery
They may contain septa of varying thickness.
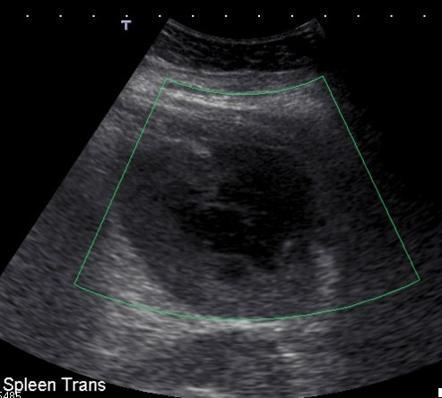
craniocaudal length. Today with the availability of a CT scan, the condition is not only rapidly diagnosed, but it also helps with .There are two circulatory routes through . best assessed in the supine, right lateral position with the left arm placed behind the head . Ultrasound or CT scan to help determine the size of your spleen and whether it’s crowding other organs. It is a tortuous artery, running superior to the pancreas before turning forward into the splenorenal ligament to the hilum of the spleen.Your doctor might order these tests to confirm the diagnosis of an enlarged spleen: Blood tests, such as a complete blood count to check the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets in your system and liver function. A dilated thrombosed . Sarcoidosis is treated with corticosteroids.524 × W × T × (ML + CCL) / 2. The treatment of splenic injuries underwent a severe shift from operative to non-operative due to an increased awareness of the double physiological function, both immunological . splenic tuberculosis; splenic histoplasmosis; splenic brucellosis; non-infective.5 cm for massive splenomegaly 4.Splenic epithelial cysts , also known as splenic epidermoid cysts or primary splenic cysts, are unilocular fluid lesions with thin and smooth walls and no enhancement. even with a known malignancy, an incidental lesion <1 cm is thought to most likely represent a benign finding, although this is extrapolated from incidental hepatic lesion data.
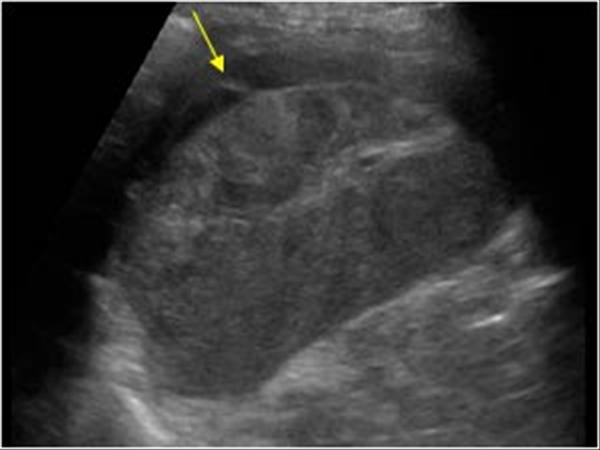
For a general discussion, please refer to sickle cell disease.Splenic bulges are common medially and may cause mass effect on the stomach or be mistaken for a splenic or renal mass.
Splenic sarcoidosis
Splenic granulomatous disease refers to sequelae arising from granulomatous infection-inflammation of the spleen.56 %, calcification and infarctions 9.73 %, lymphomas and abscesses 7.World population incidence of focal splenic lesions ranges from 0. visualised best obliquely in the 9 th or 10 th intercostal spaces.Similarly, the draining venous tributaries . Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy followed by splenectomy is the treatment of choice in cases of non-resolution 3. The splenic parenchyma should be assessed in the portal venous . How is a splenule diagnosed? A splenule is diagnosed on imaging studies like ultrasound, CT, MRI and nuclear medicine studies. This suggests that spleen .
Ultrasound Evaluation of the Portal and Hepatic Veins
One-hundred ultrasound examinations performed in 100 healthy children aged 0–17. dilated portal vein (>13 mm): non-specific.contrast-enhanced ultrasound: isoechogenicity to splenic parenchyma in all phases is the most frequent typical enhancement pattern of splenic haemangiomas observed on contrast-enhanced sonography 11 ; CT. Up to 25% of splenic injuries do not exhibit intraperitoneal hemorrhage. On ultrasound, we will see small white spots which cast shadows in the spleen. [7] Ultrasound can be very helpful and highly accurate in the diagnosis of significant splenic injury but is limited in detecting active bleeding, pseudoaneurysm, . Ultrasound can be useful for evaluating splenic vein thrombosis 8.Splenic ultrasound was shown to have an equivalent effect on LPS-induced cytokine reduction but lack several of the associated off-target side-effects of cervical VNS, including effects on heart rate and metabolic function. extramedullary haematopoiesis in the spleen. Splenomegaly in children – (See Approach to the child with an enlarged .Splenic abscess is not a frequent clinical problem.Ultrasound has a sensitivity of 75% to 98% in detecting a splenic abscess. FAST scanning may be performed to determine the presence of .
Focal splenic lesions: US findings
splenic abscess : sonographically characterised by multiple “target” lesions. Although once the infarct has become established, both ultrasound and CT are sensitive to the diagnosis, in the hyperacute setting CT with contrast is the modality of choice if the diagnosis is suspected 9.
Imaging of the spleen: what the clinician needs to know
20 %; of these lesions true cysts account for 21. They represent the majority of the splenic cystic lesions, corresponding to approximately 80% of them (cf. On imaging, they usually present as lobulated and multiloculated cystic lesions without solid component or significant enhancement.Ultrasound (US) is usually used for the follow-up of patients with splenic emergencies, since accurate initial diagnosis based solely on US findings is limited.Splenic pseudocysts , also known as secondary splenic cysts, are acquired cystic lesions not delineated by a true epithelial wall.Practical points. Where: W = Maximum dimension in the transverse image (width) T = Shortex distance between the hilum and the outer convex surface of the spleen (thickness) ML = Maximum length in the longitudinal image. splenic lymphangioma.
Splenic trauma
Splenic vein thrombosis
portal-systemic collateral pathways (collateral vessels/varices) splenomegaly.Splenic trauma is associated with injuries to other intra-abdominal organs 1: left hemidiaphragm; left lobe of the liver; left kidney; left adrenal gland; pancreatic tail; In penetrating trauma, the spleen is more .
- Spikes Geschwindigkeit : Speedtest: Internetgeschwindigkeit prüfen
- Sport Nach Schwangerschaft Tipps
- Spieße Bundeswehr : Schule für Feldjäger und Stabsdienst der Bundeswehr
- Sport T Shirts Mädchen , Sport T-Shirts für Kinder Größe 170 online shoppen
- Spirituosenverkauf Anforderungen
- Spiegel Nägel – Künstliche Fingernägel: Hart, aber empfindlich
- Spotify Kostenlos Ohne Premium
- Spiralförmig Gedrehte Gurken , Drehwuchs bei Bäumen: ein energetisches Phänomen?
- Spinne Morgens Bringt Kummer : Warum sagt man Spinne am Morgen bringt Kummer und Sorgen
- Spinalanästhesie Welche Risiken
- Sporthallen Auf Schulstandorte
- Spitzkohl Ersetzen Oder Nicht _ Spitzkohl-Curry Rezept
- Spotify Investoren | Spotify Investor Day 2022
- Spotify Short Form Video , Is Spotify Plotting a Largescale Push Into Short-Form Video?
- Spionage Durch Richtmikrofon – Richtmikrofon Test & Vergleich Top 10