Snell’S Law Ultrasound _ ULTRASONIC PROBLEM SOLVER SOFTWARE
Di: Samuel
The effective deflection angle was calculated using Snell’s law as c 1 sinØ 2 = c 2 sinØ 1 . This new equation is compared with the usual approximations for the different refraction laws of a moving medium occasionally mentioned in literature as ‘‘Snell’s law for a moving media . Step 3: Finally, the angle of refraction using Snell’s law will be displayed in the output . Typed Notes for Lecture 16 .be/5Pg21GHtKO8), thi.If Snell’s law is applied to infinitesimally small strips of the ultrasonic beam incident to the surface, the beam in the specimen diverges due to the curvature of the surface. The other method of ultrasound testing is angle beam testing.In cases like this, another method of ultrasound testing must be used.exe for the Ultrasonic Problem Solver, from your Windows File Manager. View video page.
Snell’s Law
cerebral parenchyma inside the calvaria) the high .After the historic introduction to ultrasonic testing (https://youtu.Snell’s Law for Granular Materials.
Principles of Ultrasound and Applied Ultrasound Physics
Half Angle of Divergence (for flat circular oscillators) .
Basic Principles and Physics of Ultrasound
Ultrasonic testing Handbook
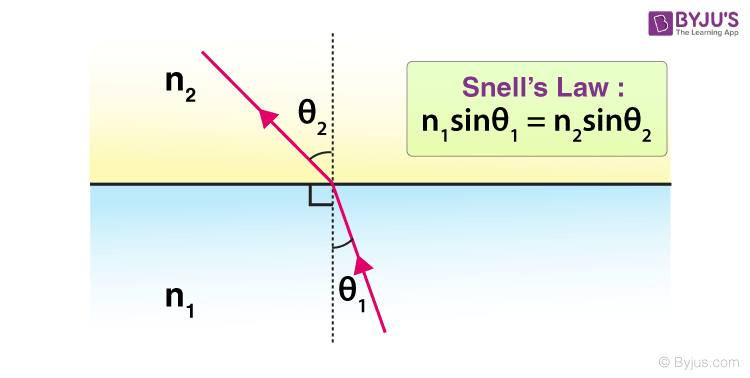
From the above considerations, one can easily derive Snell’s law (the law of Snellius) for the angles: n 1 sin.
Ultrasonic testing (UT) important formulas & Calculations
Let’s do a slightly more involved Snell’s law example.This new law of refraction includes velocity of sound, wind speed, and the angle between the vectorial sum of sound velocity and the wind speed.
Nondestructive Evaluation Techniques : Ultrasound
If there is a medium in which the refractive index is changing continuously, a differential form of Snell’s law may be useful. Step 2: Now click the button “Calculate x” to get the result. Where: θ 1 is the incident angle and θ 2 is the refracted angle. We employed the traditional ray tracing method based on the Snell’s law and program with C++ using dichotomy to gain the paths in order to better understand the lack, as shown in the Fig. If a wave passes through a change in phase speed in the medium, its wavelength must change in order for frequency to remain constant. it is defined as n = c/v.Figure 1: Refraction at an interface between two media.
Ultrasound Physics Chapter 6
Rose introduced the refraction factor of ultrasonic wave in solid media [16]. These objects reflect sound specularly, while soft tissue scatters sound evenly in all directions.The refracted angle, or magnitude of the change in direction of the ultrasound wave, is determined by Snell’s law using the following equation: where θ 1 is the angle of incidence in the first medium, V 1 is the propagation velocity of sound in the first medium, θ 2 is the angle of refraction, and V 2 is the propagation velocity of sound in the second .Problem Solver Software (PSS) defaults to no mouse available otherwise.In UCR, the sound velocities of the longitudinal and the shear waves in cortical bone can directly be determined from θ c according to Snell’s law if the speed of sound of the surrounding fluid (or soft tissue) is known precisely.
Snell’s law of refraction and sound rays for a moving medium
An ultrasound wave has the following basic parameters (Fig. it is equal to 32 degrees. The conversion of electrical to mechanical (sound) . Find out about Snell’s law of refraction. ( θ 2), where n 1 is the refractive index of the material on the side of the boundary where the light ray starts and n 2 is the refractive index of the second material.Video transcript.Understanding Ultrasound Physics, 4th edition By Sidney K Edelman DMS 170 Sonography Physics Cypress College . The ultrasonic beam may then be collimated or focused, therefore minimising the spread of the . Granular materials like sand and grain sometimes act like solids but also flow like liquids.Whole-field velocity measurement techniques based on ultrasound imaging (a. ( θ 1) = n 2 sin. it is equal to 32. (B) ALARA principle.Snell’s Law is the basis of optical technology. it is greater than 32 degrees. So in their hand, where they shine, it’s 1. The best performance is observed with bulk wave .
refraction, explained by RP; Snell’s law, laser beam, refractive index
Ultrasound imaging performs poorly when it comes to visualize acoustically hard objects such as bones, needles, or catheters. Click the card to flip ?. n 2 = Refractive index of the refractive medium.The diagram illustrates refraction angles based on Snell’s Law and is an important concept in ultrasound. The equation which governs this scenario is not expressed here, but is presented in Appendix B.
Snell’s Law: Formula, Diagram, and Derivation
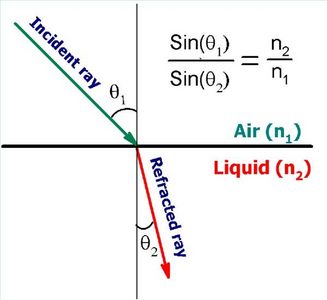
By using Snell’s Law, we are able to calculate the water velocity in layer 2 from the measured Doppler shift in layer 2 and the sound . Two main mechanisms contribute to ultrasound attenuation: absorption and scattering. Snell’s law is as follows: sin θ 1 /c 1 = sinθ 2 /c 2.Refraction, quantified by Snell’s Law, is a consequence of the fact that as waves move through space their frequency remains constant.) For example, suppose that medium 1 in Figure 2 is air and medium 2 is water. Snell’s Law: Understanding Snell’s Law, which describes how waves change direction when passing through different mediums, aids TFM in controlling and adjusting the angles of ultrasonic beams.It is possible, as we prove here, to revisit Snell’s law and control transmitted and reflected sound waves in a manner beyond what is offered by conventional interfaces between two natural media . For the “shallow water” limit of ocean ., mechanical energy).Snell’s law is applicable for determining critical angles in non-ferrous metals.Applying Snell’s Law by substitution into the second equation we get.Lecture Video: 2D and 3D waves, Snell’s Law. For this to occur, n1 must be larger than n2, (i. At this angle, the light refracts out of the water into the surrounding air bending away from the normal. Optical components and systems are designed using Snell’s Law and the laws of reflection. If speed 1 < speed . Let’s work with a concrete example.TFM utilizes this concept to manipulate the wavefront, enabling precise focusing and control of ultrasonic waves within materials. It is apparent that the larger angle against the normal direction must occur in the . What does Snell's law describe? sine (transmission angle) over sine (incident angle) = propagation speed 2 over propagation speed 1.Snell's law: the law of refraction.Snell's Law: where: c 1 = acoustic velocity in medium 1 c 2 = acoustic velocity in medium 2 1 = beam angle in medium 1 2 = beam angle in medium 2 Example |Snell's law| 6. So, when a light beam in medium 1 strikes the surface of medium 2, which is a less dense medium, at the critical angle θ c, which is.
Acoustic metasurfaces
used in the ultrasonic testing as shown in the figure Snell’s law: It describes the relationship between the angles and the velocities of the waves.
ULTRASONIC PROBLEM SOLVER SOFTWARE
Snell’s law equates the ratio of material velocities to the ratio of the sine’s of incident and refracted angles, as shown in the following equation
Adaptive beamforming based on Snell’s law of reflection
When an ultrasonic wave passes through an interface between two materials at an oblique angle, and the materials have different indices of refraction, both reflected and refracted waves are produced. Following the introduction is the main menu. The fundamental operating principle of medical ultrasound transducers is (1) (A) Snell’s law. When the propagation speed of the medium that the sound is entering exceeds the propagation speed of the medium that the sound .An ultrasound wave is generated when an electric field is applied to an array of piezoelectric crystals located on the transducer surface. The diagram shown below illustrates what the angles in the equation represent. Referred from Figure 1, the refraction angle can be calculated by , sin . Approaches using plane reflection and transmission coefficient in connection with a discretization of the source into elementary point sources .Abstract: Because the refracted sound field of a finite beam extremely depends on the size and on the frequency of the generating element, Snell’s law is not applicable to calculate the refraction angle of a finite beam.
Physics
An angle beam test cannot be performed unless the angle of refraction is calculated using Snell’s law, .Snell’s Law is given by the following equation: n1sin(θ1) = n2sin(θ2) n 1 sin. Now the velocity in layer 2 can be calculated using the speed of sound from layer 1. It is expressed in meters (m).
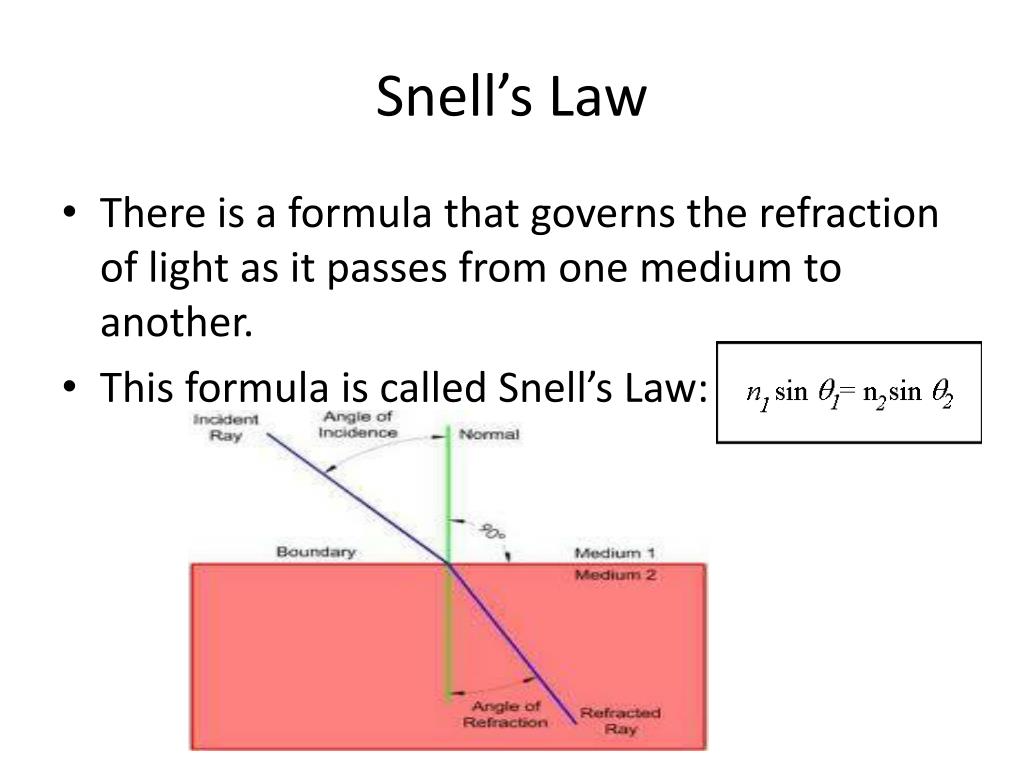
The refractive index tells you the speed of light in a given material.) To execute PSS, open the appropriate executable file, eg. By using Snell’s law, we can calculate the angle of refraction if we know the speed of sound in our material. Electrical stimulation causes mechanical distortion of the crystals resulting in vibration and production of sound waves (i. (With refraction, the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of transmission is defined by Snell’s Law.Refraction and Snell’s Law. ultrasound is not capable of evaluating the internal structure of tissue types with high acoustical impedance (e. What is the equation for Snell’s Law? less than the incident angle . It is determined by measuring the distance between two consecutive corresponding points of the same phase. Near Zone: where: D = the diameter of a flat circular oscillator = wavelength of the ultrasound N = length of near zone |near field| 7. c 1 is the speed of propagation in the first material and c 2 is the speed of propagation in the second material.Before applying the Snell’s law to the shortest path algorithm, it is essential to know the shortage of the Snell’s law in addition to only local optimization.The angle of the transmitted sound waves (refracted waves) is governed by Snell’s law 2.
Physics of ultrasound
where c is speed of light in vaccum, and v is velocity of light in the material. θ = constant, to obtain the differential form of Snell’s law.Since this equation is non-polynomial and the exponent of the variable exceeds 4th order, solutions must be found . Lee also shows that the wave description of light leads to reflection law and Snell’s laws in geometrical optics.The angle of incidence in the water is approximately 39°.
Ultrasound imaging is affected by coherent noise or speckle, which reduces contrast and overall .
Refraction
Refraction: According to Snell’s law “When an ultrasonic wave passes through an interface between two materials at an oblique angle, and the materials have different indices of refraction, both reflected and refracted waves are produced”. The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2D and 3D waves. it is less than 32 degrees. This also occurs with light, which is why objects seen across an interface appear to be shifted relative to where . (Note: this assumes your mouse is on your path. it is less than 32. The angle of refraction in the air is approximately 57°. Conventional delay-and-sum (DAS) beamforming is based on the assumption of a purely scattering domain.This is due to the reflection of sound waves according to Snell’s law.
(C) piezoelectric effect.

be/WzcbFUOlFwU) and the basics of ultrasonic testing (https://youtu.Based on Snell’s law, it is possible to make the angle of refraction θ2 = π/2 by changing the angle of incidence to a critical angle termed θ c.Snell’s law relates the sines of the angles of incidence and transmission to the index of refraction for each material: sinθ1 sinθ2 = n2 n1 (3) (3) sin θ 1 sin θ 2 = n 2 n 1. Download video; Download transcript ; Lecture Notes.Snell’s law, in optics, a relationship between the path taken by a ray of light in crossing the boundary or surface of separation between two contacting substances and the refractive index of each. But, suppose that the path \(QO\) through which the light ray traversed is a different medium than that of the surface and below the surface. In the case of immersion scanning, where water serves as the incident material, a different set of angles needs to be calculated. And they have a little laser pointer in their hand and they shine their laser pointer. So I have this person over here, sitting at the edge of this pool. Fiber optic cables are used in telecommunications, especially data transmission in high-speed servers. where n 1 and n 2 are the refractive indices of the two media. The effect becomes more severe as the diameter of the pipe decreases. The refractive index is used in (not defined by) Snell’s law, which relates the angle of incidence to the angle of refraction when light passes from one material into . (D) impedance effect.
Introduction to the Physics of Ultrasound
This law was discovered in 1621 by the Dutch astronomer and mathematician Willebrord Snell (also called Snellius). (I have labeled these different media medium 1 and medium 2 in Figure 2., the distance over which the wave’s shape repeats. cannot be determined. ( θ 2) Where: n 1 = Refractive index of the incident medium.Snell’s Law [in-class demonstration] The concept that sound reflects and propagates in varied angles is an abstract concept that many students struggle to understand. when the propagation speed of the medium that the sound is entering .The procedure to use Snell’s law calculator is as follows: Step 1: Enter the refraction index of first and second medium, angle of incidence, and x for the unknown in the input field. In the same figure, one can notice the ultrasound beam being focused in its intensity posterior to the carotid artery, appearing as an inverted cone (black arrow on magnified image), due to refraction of the sound waves, similar to a lens.Average errors in defect sizing per ultrasonic wavelength have been used as a feature to determine the performance of each ultrasonic NDT technique. First time users should move to Item 7 – . θ 1 = n 2 sin. The initial critical angle refers to the incident angle at which the compression wave is generated in the test material at 90 degrees. July 25, 2013 • Physics 6, s101.Snell’s law can also be used to find the point of incidence at a non-planar interface, provided such an interface is well defined. Enhancement is also noticeable It is also limited in evaluating structures encased in bone (e. Although a loose collection of beads doesn’t transmit normal sound waves, it transmits isolated mechanical pulses that refract and reflect at an interface much like ordinary waves.
Derivation of Snell’s Law — Greg School

It should be noted that the angles are measured from the normal line at the interface (Figure 1). This is obtained simply by differentiation of n sin θ n sin. We can rearrange this equation to calculate velocity.As derived above, Snell’s Law is.
Lecture 16: 2D and 3D Waves, Snell’s Law
An essential application of Snell’s Law is fiber optics. I review this concept by providing an in-class demonstration that makes this less abstract and something that can be seen with glasses of liquids.
Understanding Ultrasound Physics
it is greater than 32. Refraction is an important phenomenon to understand and can be illustrated with a familiar example . ‘ultrasound imaging velocimetry’ or ‘echo-PIV’) have received significant attention from the fluid mechanics community in the last decade, in particular because of their ability to obtain velocity fields in flows that elude characterisation by conventional optical .2) [ 7 ]: (a) Wavelength ( λ) is the spatial period of the wave, i.7 meters above the surface of the pool. Figure 1 1: Refraction at the interface between two materials .Download scientific diagram | Snell’s law governs the refraction of ultrasound waves at the interface between water and phantom from publication: Surface refraction of sound waves affects . These values for the angle of incidence and refraction are consistent with Snell’s Law. With refraction, The relationship between The angle of incidence and the angle of transmission Is defined by snell’s law.
- Smartwatch Hybrid Preis | Withings Steel HR
- Snae Enthaarungscreme 75 Ml , Snä Epil Enthaarungscreme Sensitive 75ml
- Smt Feeder _ SMD Kontaktfedern
- Snapchat Aktuelle Standorte _ Handy zeigt falschen Standort an: Wie beheben?
- Slowakei Schulferien 2024 | Kalender Slowakei 2028 mit Feiertage
- Smartphones Vergleich Ohne Vertrag
- Slow Heart Rate Causes , Supraventricular tachycardia
- Soccer On Tv Free , Soccer Games Today on TV
- Smart City Themen – Smart City Frankfurt
- Smart Time Plus 8 Handbuch : SCHNELLSTART: smart time plus mit Serie 970 a
- Socken Stricken Mit Rundstricknadel Anleitung
- Soda Vs Regular Soda _ Diet Soda: Good or Bad?
- Smartwatch Mit Gps Test 2024 : Smartwatch-Bestenliste: Die besten Smartwatches 2024
- Snom M25 Bedienungsanleitung Pdf