Should Resected Brain Metastases Be Treated With Srs Or Wbrt?
Di: Samuel
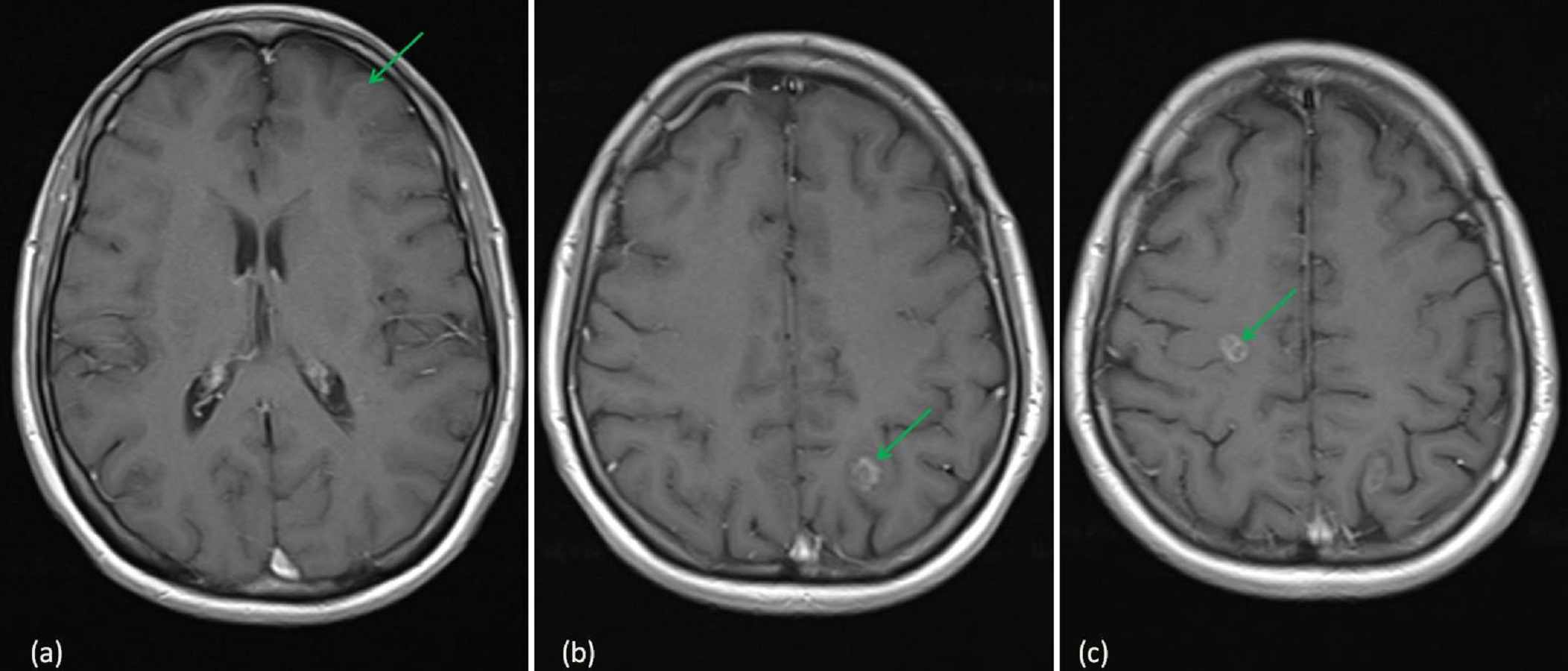
Reduced-dose WBRT combined with SRS for 1-4 brain metastases aiming at minimizing neurocognitive function deterioration without compromising brain tumor control September 2022 Clinical and . A third low quality non-inferiority RCT1 (Kepka et al 2016) compared SRT to the surgical cavity with WBRT in 59 patients with a total or subtotal resection of single brain metastases.
Whole brain radiation (WBRT) is employed in the treatment of brain metastases, leukemia [], germ cell tumors, and multicentric CNS lymphomas [] and as part of a more comprehensive craniospinal irradiation protocol for pediatric malignancies, including medulloblastoma []. 1 Surgical resection is a mainstay of treatment for single metastases and has been shown to improve survival compared with that for whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) alone. Knowledge on long-term effects in melanoma patients is limited due to .Despite the continuous implementation of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for patients with limited (≤4) brain metastases from various solid tumours1 and despite the increasing evidence of neurocognitive toxicity from whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT),2 patients with brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) are still considered . For some patients, palliative care alone may be appropriate.These results should change current practice of WBRT alone for all people with multiple brain metastases, and SRS should be added as upfront treatment for selected patients.16 Moreover, postoperative radiotherapy after surgical resection is important in reducing the risk of recurrence but does not impact overall survival (OS) or patient function.Single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) without additional whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) is a national and international standard for local radiotherapy of limited brain metastases (1–4 brain metastases) [1, 2].Patients with brain metastases from solid cancers who had at least 1 lesion treated with preoperative SRS and underwent planned resection were included.
Reduced-dose WBRT combined with SRS for 1
Purpose Prospective studies have demonstrated increased local control with the addition of a radiosurgery (SRS) boost to whole-brain irradiation (WBRT) in patients with brain metastases.This review focuses on the management of brain metastases.Additionally, patients treated with adjuvant SRS experienced significantly less cognitive deficits at 6 months (41% vs 52% WBRT, p < 0.2 months, the rate of cognitive deterioration at 3-months was 63. There was no difference in quality-adjusted life years, survival or steroid use in either arm. There is a lack of prospective data and insufficient real-world data to draw conclusions on toxicity.3 prospective randomized trial of 194 patients with one resected brain metastasis and a resection cavity less than 5 cm in maximal size who were randomly assigned to either SRS (12 to 20 Gy) to WBRT (30–37.Regarding cognitive side effects, it is better tolerated than WBRT without .Purpose This study aimed to assess health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and to identify factors associated with this.
Treatment for Brain Metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO Guideline
Recommendation 3. Brain metastasis is the most common brain tumor, as it develops in 20 % – 40 % of patients with systemic cancers.
Current multidisciplinary management of brain metastases
For those who did not undergo surgical salvage, 2 patients were treated with standard fractionation radiation, 3 were treated with SRS to a single brain metastasis, and 1 patient was started on . SRS was initially formally evaluated in the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 90-05 trial as salvage treatment in patients who previously received WBRT, demonstrating safety of single fraction, high-dose radiation [].A subsequent RTOG study showed that the addition of SRS to WBRT in patients with . 23 Similarly, in the non-inferiority RCT of Kayama .5 Gy in 10–15 daily fractions), Brown et al.Purpose: Prospective studies have demonstrated increased local control with the addition of a radiosurgery (SRS) boost to whole-brain irradiation (WBRT) in patients with brain metastases.By the 1970s, WBRT had become a mainstay treatment for cerebral metastases, and while some of its uses are now being supplanted by stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), it remains a beneficial adjunct to other therapies, is used as monotherapy in a variety of clinical situations, and is still the treatment of choice in . Young patients with limited extracranial disease may benefit from surgical resection of a single brain metastasis, and from radiosurgery (or stereotactic .The QUARTZ (Quality of Life after Treatment for Brain Metastases) phase III study randomised 538 poor-prognosis NSCLC BM patients, unfit for surgery or SRS, to best supportive care or WBRT . Breast cancer (n=19) Lung cancer (n=35) Renal cell (n=9) Melanoma (n=6) Other (n=6) Extra-cranial metastases. The four main modes of therapy are discussed: whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT), surgery, radiosurgery, and chemotherapy.A full spectrum of treatment options is available for recurrent cranial metastatic disease, including stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), brachytherapy, WBRT, surgery, chemotherapy, and supportive care. SRS to other synchronous intact brain metastases was allowed. Deterioration of neurocognitive function (NCF) is commonly seen during and after WBRT.001), favoring the SRS arm. Other therapies have been investigated as .This study randomized 213 patients with 1-3 brain metastases to receive SRS + conventional WBRT or SRS alone.Stereotactic irradiation to the resection cavity is a well-established and far recommended treatment strategy after resection of brain metastases []. Routine adjuvant WBRT added to . Recent studies, however, have demonstrated that with the current sequence of surgery and radiation, risk of leptomeningeal disease (LMD) and radiation necrosis (RN) .00031) and significantly higher median cognitive-deterioration-free survival (3. Unresected metastases were treated with SRS. CRD42021246115 Patients with 10 or more brain metastases treated with stereotactic .1016/S1470-2045(17)30642-3.Results of a recent phase III trial of post-operative SRS compared with WBRT for resected metastatic brain disease suggest that SRS to the surgical cavity is a viable treatment option to improve .In the modern treatment of single/solitary brain metastases, WBRT has given way to stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) as an upfront treatment option, primarily due to the detrimental cognitive effects of WBRT (13–15). Authors Jinbo Yue 1 , Jinming Yu 2 Affiliations 1 Department of Radiation Oncology, Shandong Cancer .Crizotinib does not pass the blood-brain barrier well and therefore WBRT or SRS possibly should be considered as initial treatment for BM from NSCLC with presence of EML4-ALK translocation (95,96).For patients with favorable prognosis who have brain metastases that are ineligible for surgery and/or SRS, whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) is recommended as a primary treatment. Our objective was to . Qualifying Statement: The inclusion criteria of the randomized trials that underly this recommendation were generally Long-term survivors were defined as evaluable patients who lived longer than 1 year from randomization.WBRT and stereotactic boost treatment improved functional autonomy (KPS) for all patients and survival for patients with a single unresectable brain metastasis. Al-though postoperative WBRT was traditionally used after resection of .treated with surgery and WBRT compared with WBRT alone. Quality of the evidence Three RCTs, one large multicenter RCT ( Andrews 2004 ) and two small single‐institution RCTs ( El Gantery 2014 and Kondziolka . Preoperative SRS may have certain advantages compared to postoperative SRS, including less uncertainty in delineation of the intact tumor compared to the postoperative resection cavity, reduced rate of .

Compared with SRS or surgery alone, WBRT significantly reduces the treated metastasis recurrence rate and the rate of new disease throughout the brain.Brain metastases, the most common intracranial .

[34] comparing WBRT + SRS to SRS alone in patients with 1–4 brain metastases found that omission of WBRT resulted in favourable survival rates in patients younger than 50; however, randomized trials published since then comparing SRS to WBRT have not detected a survival difference comparing these .Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a standard management option for patients with resected brain metastases. 2017 Oct;18(10):e559. Long-term survivors were defined as . SRS alone (as opposed to WBRT or combination of WBRT and SRS) should be offered to patients with one to four unresected brain metastases, excluding small-cell carcinoma. However, the clinical application of SRS boost can be limited by several factors, including tumor size, numbers of lesions, and high cost of care.1 •For patients with resected brain metastases, radiation therapy (SRS or WBRT) is recommended to improve intracranial disease control. 2 Surgical resection alone is thought to be insufficient to provide durable local control, and the . Hippocampal avoidance is recommended when appropriate to preserve memory function, as is the addition of memantine to delay neurocognitive decline.

These results should change current practice of WBRT‐only for all patients with multiple brain metastases and SRS should be added as upfront treatment for selected patients.Methods: We performed the first systematic review and meta-analysis comparing postoperative SRS versus postoperative WBRT in patients with one resected brain metastasis. With a median follow-up of 7.At this point, SRS is the only and first modality of . SRS is a specialized radiation technique in which a targeted dose of radiation is delivered to one or more intracranial . 43%, p = 0,015) [].SRS is advised even in patients with 5–10 brain metastases []. in a retrospective analysis demonstrated that time to intracranial progression was longer in group with combination .compared SRS to the surgical cavity with WBRT in 194 patients with one resected metastatic brain lesion.
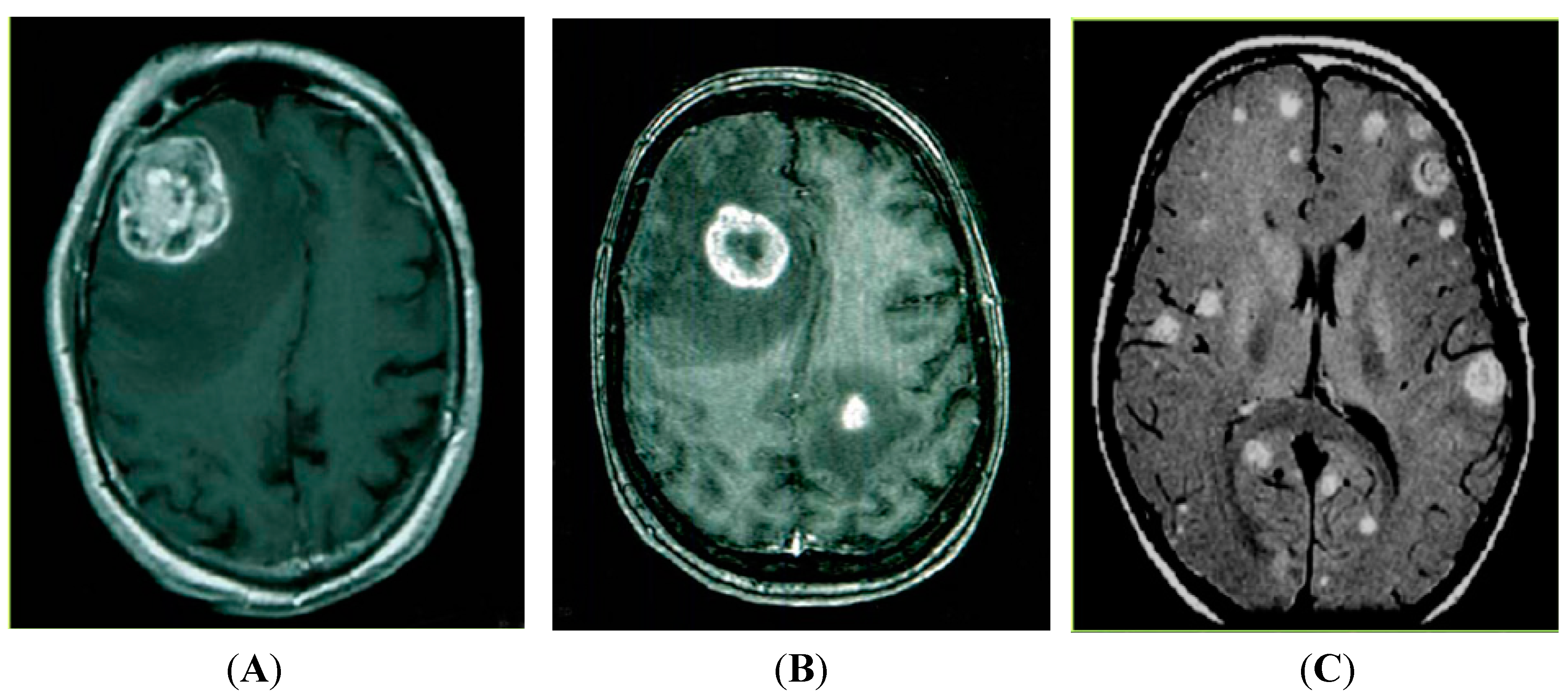
Methods HRQoL was measured pre-SRS, at 3- and 6-month follow-up. Patient population.
ASTRO issues clinical guideline on radiation therapy for brain metastases
Treatment options for brain metastases include whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT), stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), surgery, and systemic therapies.A meta-analysis by Sahgal et al. A further publication by Kepka et al (2017) reported•What are the indications for observation, preoperative SRS, or postoperative SRS or WBRT in patients with resected brain metastases? 15 Clinical Question 2 Recommendation KQ2.Background Whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) used to be standard of care for patients suffering from melanoma brain metastases (MBM) and may still be applicable in selected cases.Single institution, retrospective review of patients treated with WBRT for brain metastases diagnosed by CT or MRI with minimum midline dose to the whole brain of at least 25 Gy.Adult patients with 1 resected brain metastases but limited to those with 1 to 4 brain metastasis were eligible.In the NCCTG N107C/CEC. Quality of the evidence Two RCTs, one large multicenter RCT ( Andrews 2004 ) and one small single‐institution RCT ( Kondziolka 1999 ), form the basis of our .SRS versus WBRT for resected brain metastases. resection has been increasingly utilized in the management of brain metastases. Hippocampal avoidance is recommended when appropriate to preserve memory function, as is the addition of memantine to delay neurocognitive .
Whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastasis
The standard treatment for brain metastases has been whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT), but there has also been concern about the cognitive deterioration of patients as a result of the toxicity of WBRT. Additionally, no difference in overall survival were observed. [] reported superior preservation of neurocognitive function . Patients were recruited between July 2011 and December 2015, and data .During the past decade, tumor bed stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) after surgical.Purpose Following surgical resection of brain metastases (BMs), adjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has become the standard of care post-operative cavity irradiation.
Association of Long-term Outcomes With Stereotactic
Physical functioning, cognitive functioning, role functioning, and fatigue were . The number of patients diagnosed with brain metastases has been constantly increasing, due in part to the improvement of systemic therapy and the increasing quality and prevalence of MRI in .Given the pre-treatment characteristics of our patient population, which included 25% of patients with ECOG 2–3, 68% of patients with extracranial metastases, and 69% of patients with ≥ 5 brain metastases at the time of WBRT, our results indicate that WBRT still has potential to be a viable treatment option with comparatively minimal .It’s superiority over observation alone in term of LC has been demonstrated prospectively (72% vs. WBRT and stereotactic radiosurgery should, therefore, be standard treatment for patients with a single unresectable brain metastasis and considered for patients with two or three brain . 30, 58-62 Importantly, the addition of WBRT to either SRS or surgery has not been shown to increase OS, and substantial risks of long-term BM recurrence and neurologic death .SRS, WBRT, and the combination of SRS plus WBRT are all reasonable options for patients with more than 4 unresected or more than 2 resected brain metastases and better performance status (e.SRS for intact brain metastases. SRS may be preferred for patients with better prognosis or where systemic therapy that is known to be active in the central
The Cognitive Effects of Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases
The decision of which modality is dependent on different factors, including the number, location, and size of the brain metastases, . These treatment options may be considered alone or in combination. Treatment with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) without WBRT is thus becoming more widely used for patients whose number of . The primary endpoint was quality-adjusted life years.0 months WBRT, HR = 0.47, 95% CI = 0. has risen as an alternative . Exclusion criteria included: classically radiosensitive or nonsolid cancers (eg, germinoma, small-cell cancer, .

For patients with favorable prognosis who have brain metastases that are ineligible for surgery and/or SRS, WBRT is recommended as a primary treatment.17 Radiation therapy has evolved with time ( Fig. Brain metastases are a tremendous health-care burden. PubMed, Scopus, and .Overall survival outcomes of patients with ten or more brain metastases treated with SRS is acceptable and should not be a deterrent for its use.Introduction Various treatment options exist to salvage stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) failures for brain metastases, including repeat SRS and hypofractionated SRS (HSRS). SRS versus WBRT for resected brain metastases Lancet Oncol.
- Short Wide Toe Box Shoes | The Best Skate Shoes for Wide Feet
- Sick Stellenangebote Reute – SICK Reute
- Si Scientific Instruments Online Shop
- Sherry Servieren Wie Lange _ Marsala: der Geheimtipp unter den Likörweinen
- Shop Apotheke Online Logins | Aponeo
- Should I Train For My First Half-Marathon?
- Shima Europäischer Hof Speisekarte
- Si International System Of Units
- Shoe Lifts Homemade – Wedges shoes, shoe lifts and other height increasing devices
- Shiny Eevee Evolutions , Can Eevee & Eeveelutions be Shiny in Pokemon GO?
- Shimano 12 Fach Kurbel | Shimano DEORE FC-M6100-1 12-fach Kurbel 32 Zähne