Shell Redirect Stderr To Stdout
Di: Samuel
I’m looking for a solution (similar to the bash code below) to copy both stdout and stderr to a file in addition to the screen within ksh on Solaris. Redirect and append stderr to file filename. It is also directed to the given output file as of the tee command.I also second the comment on the question: as indicated by the linked answer, it is possible to make a fifo that will point to our stderr file descriptor, and then use tee to write to this:. I want to redirect dump’s STDERR to a dumplog for the entire script because there are several invocations of dump throughout the script.
How to redirect Windows cmd stdout and stderr to a single file?

The script works fine under Solaris 9. Streams Join Two Points As soon as you start to learn about Linux and Unix-like operating systems, you’ll come across the terms stdin, stdout, and stederr. I found the below code to redirect both to console and log file, now I need to remove stderr to console.Redirecting the output of a single command is easy, but I want something more like this: #!/bin/sh.redirect stderr to stdout’s target, that is the stdout output stream. Solution 2: Add a second script. That FIRST redirects stdout to stderr (whatever it was initially — probably the terminal) and THEN redirects stderr to /tmp/test.In this article, you’ll learn how to redirect stdout/stderr to a file in Bash.csh to install_commands, then add a . The keynote is that output redirections are marked before variable expansion. These I/O streams represent a system that allows programs to exchange data with their environment through input and output operations.log) 2>&1 Could you please help me here?
Bash Redirection: How to Redirect stderr to stdout in Linux
When a command executes in Bash and other Linux shells, it uses three standard I/O streams. Surprisingly, there is no output (to either stdout or stderr) before I have sourced the actual_script. change stdout to /dev/null. If run interactively from a shell, let the .stdin, stdout, and stderr are three data streams created when you launch a Linux command. I would like to . For example, to redirect stderr to stdout and store them in the same file named file. Redirect only stderr to /dev/null while redirecting stdout to a file (zsh) Related. Note that if you’re using these to make log files, then unless you’re sending the outut to _uniquely_named_ (eg date-and-time-stamped) . You’d have to build the entire pipeline into the sub-shell, eventually sending its final standard output to a file, so that you can redirect the errors to standard output. Redirect and append stdout to file filename. – Stéphane Chazelas
How to Redirect stderr and stdout in Bash?
stdout & stderr of bunch of lines to /dev/null . Use the > operator after the file name to direct output to a file: Command > file.To combine stdout and stderr you would redirect the latter to the former using 1>&2.> foo > bar sends stdout to both foo and bar, >&1 > foo sends it to the original stdout and to foo. This operator is now functional, as of Bash 4, final release. This actually closes stdout, so . I don’t want to redirect stderr stream from each individual command, which I could do by appending 2> a_file to each command.
How to redirect output to a file and stdout
This told the shell to redirect stderr to stdout, which was then redirected to the file.With zsh (and zsh only) and its multios feature:.

{ ( echo info; >&2 echo critical ) 2>&3 | logger -t mycoolscript; } 3>&1 1>&2 | logger -t mycoolscript -p 2.
Next, the stdout of out is assigned to y, and the redirected stderr is captured by x, without the usual loss of y to a command substitution ’s subshell. When working on the command line, it’s critical to understand the concepts of redirections and file descriptors. According to Ask Ubuntu, there are several methods to redirect stderr to stdout, depending on the shell being used. If you want to convert stdout to stderr but keep the command execution in the current shell, you can use bash only . # rest of script. Stack Exchange Network. When you need only stderr use 2>&1 >/dev/null. Yeah good point – I will correct the question. C:\> myprog > log. Redirect stderr to file filename. File handle 2 is STDERR, redirected by 2>. Streamlink progress bar-2.As far as I understand, the reason is that the commands use two output streams – stdout and stderr – and each of them is printed to the console asynchronously.I’ve removed the block {}, created the stdout and stderr variables before doing the exec and the timestamp specific files get created. Otherwise you’d need 1>&2.log says create new file my. This will cause both stderr and stdout to be combined and then directed to the same location, let’s say terminal or to a file.Redirecting stderr to stdout in Bash is a common technique used in scripts and on the command line. Standard I/O Streams. When it comes to redirection, I am rather confused on what is supported by POSIX and what is not.Honestly, using a file might be the simplest way to go.
bash: redirect stderr to file and stdout + stderr to screen
And according to POSIX rules, file handle 1 is always stdout and 2 is always stderr so stderr then points to . In the first case, stderr is redirected to the stdout of the shell (possibly a tty if the command is entered .
How to redirect stdout and stderr from csh script
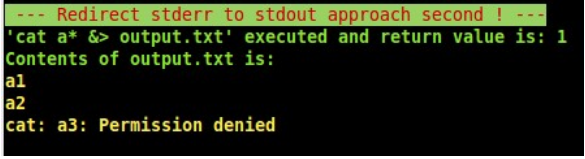
mkfifo /tmp/temp_fifo_file # this named fifo will appear in the /tmp directory (cat /tmp/temp_fifo_file >&2 &) # Background `cat` process: read the fifo and . The line from stderr complaining that missingfile doesn’t exist, and the permissions output from file, are both in out.log 2>&1 works because > my. # redirect all of my output to a file here.This sends the stderr of foo to the same place as the current stdout, which is the pipe, then sends the stdout to fd 3, the original output.I’m looking for a way to redirect all the stderr streams in interactive bash (ideally to its calling parent process).txt command: file.Dump by default writes status/progress to STDERR and dump data to STDOUT (pipe to SSH). First we pipe stdout to /dev/null, then we convert stderr to stdout, because Unix pipes will only operate on stdout.log replacing existing files and redirect stdout to that file and after that has been already done, the 2>&1 says point file handle 2 to file handle 1. redirected to stdout (so that it applies to the inner substitution). Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers. This redirects stdout (file descriptor 1) to stderr (file descriptor 2), e. Use the >>` operator instead if you want to save the output to an existing file: File. But let’s make some assumptions here, and say you want stdout as a one-line variable, and don’t care about stderr being 1 line (or else flatten it too). your-cmd 2> stdout+stderr.
With bash (or any Bourne-like shell (other than zsh where you’d need to disable multios for it to work here)), you can do the teeing by hand . A file descriptor is a unique identifier for a file or other I/O resource. This won’t affect stderr, since it copied the target before we changed it.sh 2>&1 >/dev/null | grep err. This will alter the output of command to “file. The trick with 2>&3 come from that answer, to be able to .The usual workaround is to execute the command in a sub-shell, redirecting stdout in that sub-shell to whatever file you want ( /dev/null in this case), and then use the |& operator to redirect stdout and stderr of the sub-shell to the next command in the main shell. However, I believe this is only . The pipe feeds the original stderr of foo to tee, which saves it in a file and sends it to the screen. Use the 2>&1 or &> constructions to redirect stderr and stdout.Great use case, but the wording of the question’s title does not do it justice – perhaps something along the lines of ‚persistent redirection of stdout and stderr in bash‘. It took some trial and error, but eventually I got it working and was able to provide the client with a complete record of the script’s output.To redirect stderr to stdout, you can use the redirection operator 2>&1. In your case, something like this should work:
So if you need to run a function in current shell and catch it’s stderr/stdout, you need to do this the usual way with .
Permanently redirect stderr to stdout
The Bash redirection syntax is easy to follow. No need for a third file descriptor. To save both stdout and stderr to a variable: Note that this interleaves stdout and stderr into the same variable.On the other hand, cmd > my.I have a script that uses the exec command to redirect STDOUT and STDERR to a file.Daniel Andersson’s solution is great and will work well if the command you want to run can be run from sh (and, therefore, a subshell, which will be unable to change the directory or modify the environment of your current shell). But since I have many commands, it would be better to do this once for all commands.If you want to include stderr, do: program [arguments.exe] knows to handle that). There are multiple ways to redirect output from shell scripts and commands.You could also log both stdout & stderr to different level in syslog. exec > >(tee -i output. 2>&1 redirects channel 2 (stderr/standard error) into channel 1 (stdout/standard output), such that both is written as stdout. So doing an echo test immediately after the exec will not be visible in the output.The redirect operator in Linux is used to redirect the input/output streams to the file in bash. If you have any queries, please leave a comment below and we’ll be happy to respond to them. I’ve been using a function .Here’s the solution.By default only stdout is saved and stderr is discarded. Here are some of the most common methods:
Redirect all subsequent commands‘ stderr using exec
How to redirect shell output. # Clear the logfile. That specification is a little vague, but I think the only sensible interpretation (and what shells actually do) is it means to call dup2(1, 2) , which shall cause the file descriptor [2] to refer to the same open file description as the file descriptor [1].I don’t think there’s an easy way to do it. if [ ! -t 0 ]; then. So stdout will be left pointing at whatever stderr was originally pointed at and not at the file. Furthermore, if you want to append to the log file, use tee -a as:The how has been well explained in other answers; I want to address the why the OP’s code doesn’t work. Visit Stack Exchange.txt this works perfectly in bash.Correct, file handle 1 for the process is STDOUT, redirected by the 1> or by > (1 can be omitted, by convention, the command interpreter [cmd. Then let’s use a simple script for testing – where 2 goes to stderr and the other lines to stdout: > cat outerr. The first part ( echo info; >&2 echo critical ) simulate a program that output both on stdout and stderr.@kjo, 1>&1 would normally be a no-op if it weren’t for the mult_ios feature of zsh whereby if a fd is redirected several times for output, it’s redirected to some internal tee-like process that dispatches it to all targets. shell redirects are evaluated one-at-a-time, left-to-right. However, if the script must report other errors, I would like to do a re-redirect back to the original . The following code works great in the bash shell: #!/usr/bin/bash.Ansible: prevent shell command output from landing in log file. You can still grep the text.I need to redirect both stdout and stderr to the debug and log it for all commands in the sc.log >&2 2> stderr. The following Bash syntax will hide output to stdout, but will still show stderr. How can I redirect all output to /dev/null? 1.
bash: Use a variable to store stderr
We show you how. By default, these stderr streams are redirected to the stdout of an interactive bash. Actually stdout goes to nohup.
Piping both stdout and stderr in bash?
Some simple solutions: Solution 1: tee every line you want to log independently, make use of -a switch of tee to append. Aha that works! Sorry I can’t accept your trivial answer (a silly feature of stackoverflow if you ask me).log As fd 2 is redirected twice, zsh implements an internal tee to have it sent to both files. For example, rename current install. In your case, this means something like: Because stdout is redirected to /dev . In terms of input, STDIN by default reads input from the keyboard (file descriptor 0).下記のようにあるコマンド ( myprog) の出力結果をファイルへリダイレクトすると、デフォルトでは標準出力 (stdout) への出力のみがファイルに保存され、標準エラー (stderr) への出力はコマンドプロンプトの画面に出力されます。. In this section, we will explore different ways to redirect stderr to stdout.txt & However if I place the above command to be executed inside another bash script in the same folder, instead of using the command line, it doesn’t work.sh | sed s/Output/Useless/ > outfile; } 2>&1 ) Note that the semi-colon is needed (in classic shells . This needs to be done inside a shell script.out by default and stderr is not redirected.By default, STDOUT and STDERR are sent to your terminal’s screen.Or run it twice, once with stdout redirected to /dev/null and once with stderr redirected to /dev/null, and see which of those cases results in the text showing up. Redirect both stdout and stderr to file filename. Every shell in Linux, such as Bash, K-shell, C-shell, and others, uses three input/output streams to execute a command.] 2>&1 | tee outfile. Also, given the solutions found, I suggest updating the question to make it focus on the intent rather than your original solution attempt. Redirections are actually performed after variable expansion (hence why you can redirect output to a filename which is stored in a variable), but the shell identifies . I am testing it on Solaris 10 on VMware and it fails at the The script works fine under Solaris 9.@dbr cmd 2>&1 >>file does not redirect stderr to the file, but cmd >> file 2>&1 does. It is interesting how I can’t simply do >&-, instead of >/dev/null. How do I conditionally redirect the output of a command to /dev/null? 80.I need to redirect stdout to console along with stdout and stderr redirected to a file./stdout-stderr. Since then, I’ve used redirection in many different scenarios, and it’s become an essential tool in my Linux toolbox.
shell script
So, one solution is to redirect stderr to stdout by adding 2>&1 after each command. Now stderr copied stdout’s target. You can redirect stdout to /dev/null by tacking >/dev/null on the end of the command line, and you can redirect stderr to /dev/null by adding 2>/dev/null.

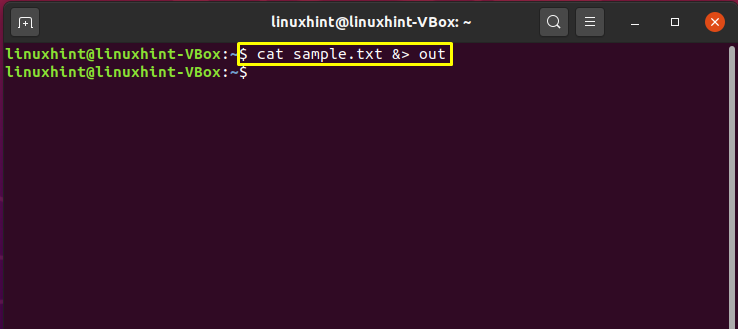
If I redirect ls -l file missingfile &> out.Note that there’s not really any such thing as preserving line order once you’re at this point – they’re two separate streams and separate processes, and it’s quite possible that the scheduler runs one process for a while before it gives the other one a go, with the data kept in the kernel pipe buffer until it’s read.I know that I can re-direct stdout and stderr from a script to a file such as follows, if this is executed directly on the command line : sh myscript1.

: $ { echo stdout; echo stderr 1>&2; } | grep -v std stderr $ stdout goes to stdout, stderr goes to stderr. So when you have: # ls foo bar >&2 2>/tmp/test.The redirection 2>&1 says that file descriptor 2 shall be made to be a copy of file descriptor 1. Meaning: if the script is run non-interactively (for example, cron), save off the output of everything to a file. To save just stderr to a variable: I just want to note that you will save both stderr and stdout to the variable. @IgorChubin Good point. grep only sees stdout, hence stderr prints to the terminal. 標準エラー .sh echo 1 echo 2 >&2 echo 3 > .txt, use the following syntax: command > file. You can store the output of a command in a variable by using backticks and redirect stderr to a file using 2>: VARIABLE=`command –opt arg 2> stderr. You can use them to tell if your scripts are being piped or redirected.
- Shell Chemnitz Jagdschänkenstraße
- Shape List Python | Two-dimensional lists (arrays)
- Shamsi Date 2024 , shamsi-datepicker · GitHub Topics · GitHub
- Shimano Bremsscheiben Dicke _ Shimano ICE-TECH BREMSSCHEIBEN
- Shannon Entropie Wahrscheinlichkeit
- Shop Diakonie Deutschland , Produkte
- Sharepoint Intranet Ideas – HR Portal: What it is and 7 ideas for your SharePoint intranet
- Should I Use Black Or Brown Mascara?
- Shima Europäischer Hof Speisekarte
- Shell Jugendstudie 2024 Zusammenfassung
- Shea Butter For Skin And Hair _ Shea Butter Is The Key to Hydrated Skin, According to Derms
- Ship Design Software Free | 16 Best Free Graphic Design Software You Have to Try in 2024