Sensorineural Hearing Loss Prognosis
Di: Samuel
Although there is no universally agreed on treatment for SSNHL, some recommend administration of glucocorticoids. Patients received intravenous steroid treatment (prednisolone sodium succinate; 120 mg/day .You can get help for hearing problems. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss is defined as a rapid onset of hearing loss over a 72-hour period.Hemodialysis itself or the causes of hemodialysis make the hearing level worse, but they do not affect the prognosis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Introduction: Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is a frightening and frustrating symptom for the patient as well as the physician. A recently updated otolaryngologic clinical practice guideline has been released for this emergency syndrome, but dissemination is limited to a specialty journal. Of a total of 283 unilateral SSNHL patients enrolled within 14 days of the onset of acute hearing loss, 252 (89. SSNHL is a relatively common complaint in otologic and audiologic practices (1. Methods We retrospectively investigated 807 cases of SSNHL .
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss is a heterogeneous disease in terms of clinical symptoms (with/without vertigo, tinnitus, and fullness), causes (viral infection, immunologic causes, and vascular), the severity of hearing loss (mild, moderate, severe, and profound), and prognosis.Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is defined as sensorineural hearing loss of more than 30 dB at more than three consecutive wavelengths occurring within 3 days.To comprehensively examine the characteristics and prognosis of bilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss (BSSHL) and its subtypes compared to unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss (USSHL).Keywords: sudden sensorineural hearing loss, hearing loss, environmental noise, noise exposure, prognosis. Identification of a heritable cause of hearing loss can have implications on family planning for the parents as well as, ultimately, the child.

It can appear over time .
Clinical features and prognosis of pediatric idiopathic sudden
We compared a new 7-pattern classification for . Their pre-treatment hearing levels were . Although its etiology and pathophysiological mechanisms have not been completely elucidated, several factors, such as age, vertigo . Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is a syndrome that develops rapidly with hearing loss progressing within 72 hours.
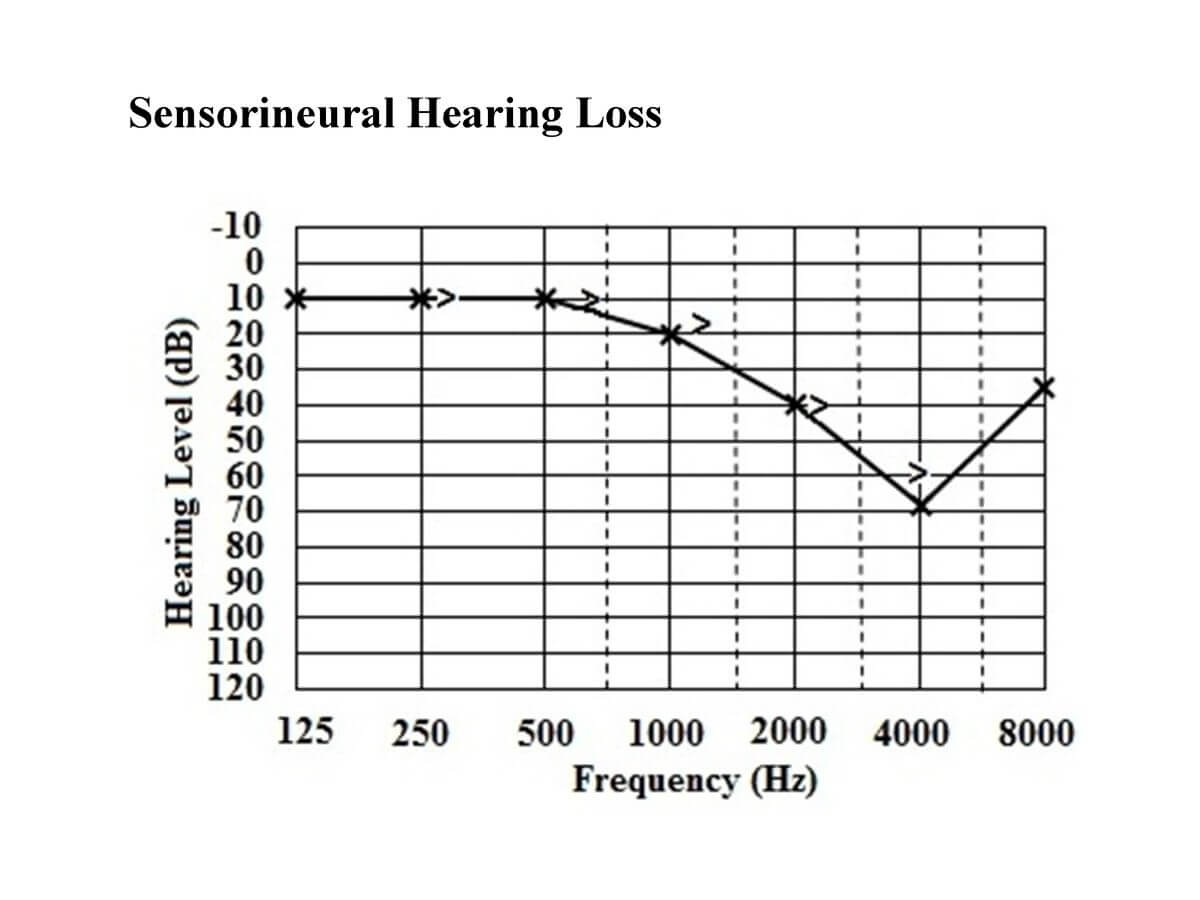
The pathogenesis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSHL) has been attributed to microcirculation disorders, viral infection, autoimmune .Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is most often defined as sensorineural hearing loss of 30dB or greater over at least three contiguous audiometric frequencies occurring over 72 hr ( Wilson, Byl, & Laird, 1980 ).

7 per 100 new patients presenting in our . 1 Usually SSNHL is attributed to inner ear hair cell damage; however, many patients demonstrate partial or complete hearing recovery. This study aims to investigate autonomic function in patients with .05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SNHL)
[1][2] The affected population is also vast, varying between neonates to elderly patients, and is nearly omnipresent in the 70+ age group.Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) is an otological emergency defined as a hearing loss of more than 30 dB over three consecutive frequencies within 72 h, accompanied by abnormalities of the cochlea, auditory nerve, or central auditory system []. It affects the auditory nerve, which carries sound signals to the brain. The aetiology of ISSNHL remains 1 uncertain and varies, but it mainly includes labyrinthine ischaemia or haemorrhage, autoimmune .Cochlear implantation is a surgical strategy used in cases with severe sensorineural hearing loss and failure of intensive immunosuppressive regimens.Hearing loss is an extremely common medical condition, progressing in incidence and severity with age. It is considered to be an otologic emergency requiring immediate recognition and treatment, 1, 2 and can occur at any age, but most commonly affects patients 65 years and older, 3 with an annual incidence of . This guideline update provides evidence-based .of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Predicts the Prognosis Junying Chen, MD1,2*, Yunhua Yang, MD3*, Shuna Huang, MD2,4*, Wenjuan He, MD5*, and Chang Lin, PhD2,6 Abstract Objectives: The aim of this study is to determine whether thrombin time (TT) could be used as diagnostic biomarkers and predict the prognosis for sudden . As a result, the guidelines may not be widely available in the primary care setting .
Hearing loss
PubMed, Scopus, and CINAHL.The causative etiologies for ISSNHL included viruses, . The odd ratios of . A health care provider might remove earwax using suction or a small tool with a loop on the end.hey T may frequently complain of diverse symptoms suchsinnitus, a t earfullness, autophony, and hearing impair-ment. From January 2016 to December 2021, the clinical data of hospitalized children presenting with sudden sensorineural hearing loss, including age, gender, the ear of onset, onset of treatment, concomitant symptoms, the degree of hearing loss, and audiogram curve type, were retrospectively collected and the effective rate of treatment .Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) is characterised by an unexplained sensorineural hearing loss of ≥ 30 dB over at least three contiguous frequencies occur – ring within 72 h []. Options include: Removing earwax.

Citation: Wang Y, Xiong W, Sun X, Lu K, Duan F, Wang H and Wang M (2023) Impact of environmental noise exposure as an inducing factor on the prognosis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a retrospective .Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is an otologic emergency defined as sensorineural hearing loss ≥30 dB that affects at least 3 consecutive frequencies and occurs within a 72-hour window.Sudden sensorineural hearing loss affects 5 to 27 per 100,000 people annually, with about 66,000 new cases per year in the United States. Study design: Retrospective cohort study.

Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) is an emergency ear disease that is referred to as a sensorineural hearing loss of at least 30 dB in three sequential frequencies and occurs .Objectives: The aim of this study is to determine whether thrombin time (TT) could be used as diagnostic biomarkers and predict the prognosis for sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL). All patients in this study were treated with prednisolone and dextran. Profound ISSNHL has a particularly poor . More than 30 million U.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Congenital Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be broadly separated into two categories: conductive (problems in delivering sound to the inner ear) and sensorineural (problems of the inner ear, or cochlea, and/or the auditory nerve that connects the inner ear to the brain).The prognosis of tinnitus in terms of audiogram type, level of hearing loss, prognosis of hearing loss, and the severity of tinnitus (THI) was also studied by the same method.Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Introduction: Vascular disorder is considered one of the main mechanisms of sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) due to the anatomy of the inner ear. 1, 2, 3 Many factors affect the prognosis . The prognosis for hearing recovery is affected by age, vertigo at onset, hearing loss severity, audiometric configuration, and the time between hearing loss onset and treatment [2,28]. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) is observed in 5–20 per 100,000 inhabitants in the United States and is naturally restored in 47–63% of patients within 2 weeks [ 1 ].Conductive hearing . It usually occurs in one ear and can be associated with other . 1 The physiopathologic mechanisms involved with . Earwax blockage is a cause of hearing loss that can be fixed.Low-tone hearing loss · Sensorineural · Prognosis. Its actual prevalence .heure T p tone audiogram of these .Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is most often defined as sensorineural hearing loss of 30dB or greater over at least three contiguous audiometric frequencies occurring over 72 hr (Wilson, Byl, & Laird, 1980). The cause of this disease is still not clear. Study design and setting: This is a retrospective study of patients with SSNHL hospitalized at an academic medical center.When hearing loss is identified, further evaluation should be carried out with computed tomography (CT), which is more sensitive in conductive hearing loss, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is more sensitive in sensorineural hearing loss.Objective: Statins have been reported to improve vascular endothelial function and microcirculation, reduce oxidative stress, and exert anti-inflammatory and protective effects against inner ear damage. Setting: Outpatient department of a community hospital.Purpose: To determine pre- and post-treatment factors that are useful for predicting the prognosis of hearing improvement in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSHL).7 per 100 new patients presenting in . Each year approximately 20 people per 100 000 experience a sudden hearing loss in one ear that is located in the inner ear.[3] The diagnosis and management require an interprofessional team that includes the general .
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Review

Prognosis is affected by multiple factors including duration of hearing loss, presence of associated vertigo and tinnitus, and co-morbidities such as hypertension and diabetes.Introduction and background.1 This is called sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL), defined as a rapid loss of hearing occurring over 3 days, of 30 dB (decibel) or more, over at least three contiguous sound frequencies. One factor that can contribute to vascular disorder is impairment in the autonomic nervous system.Objectives: Pediatric idiopathic sudden hearing loss (PISSNHL) is a rare disease with no established factor affecting its prognosis.Objective: To investigate the role of obesity/overweight on the prognosis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL). The hearing prognoses of 18 patients who developed sensorineural hearing loss associated with COVID-19 were plotted according to their average pre-treatment hearing thresholds. Introduction: Patientsho w complain of acute onset low-tone hearing loss (LHL)reelativelya r commonly encountered in daily clinical practice.Objectives To investigate the role of normal weight central obesity (NWCO) in the prognosis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL). [50] The patients and caregivers should be explained the prognosis, management, and outcome to ensure compliance and the best possible outcome.Thorough diagnostic evaluation also provides information about the prognosis of hearing loss; common findings such as EVA and cCMV infection are associated with increased likelihood of progression of hearing loss. In this study, we investigate the risk factors affecting the prognosis of PISSNHL. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effect of statins on hearing prognosis in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural .The family physician’s role in recognizing and managing sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is crucial.
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss:
Materials and methods: Forty subjects . Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) requires immediate diagnosis and treatment.
Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update)
This guideline update provides evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients who present with sudden hearing loss.Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is defined as a hearing loss of at least 30 decibels (dB) affecting 3 or more contiguous frequencies and occurring during 3 days without a known cause.Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) results from damage to cells or nerve fibers in the inner ear.0%) reported the new development of tinnitus.Cochlear implants can be helpful for those with refractory or severe hearing loss.Objectives: To investigate factors affecting the prognosis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL). Review Methods
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
adults, or nearly 15% of all Americans, have some degree of hearing loss. Intralabyrinthine hemorrhage (ILH) in patients with ISSNHL can be clearly detected on . Material and methods: Among the patients who visited our hospital from January 2010 to December 2021, the characteristics associated . Methods: This retrospective study included 332 patients with ISSHL. Even when there are no treatment options, or they do not produce the desired results, these cases have a much greater prognosis over cases of perceptive hearing loss because they can be improved using hearing aids.Thrombin Time is a diagnostic biomarker of sudden sensorineural hearing loss and predicts the prognosis . Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) happens when there is damage to tiny hair cells in the cochlear and .Objective: Vascular disorders and viral infections are the presumed etiologies of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) and acute sensorineural hearing loss, with no identifiable cause.The present study showed that accompanying tinnitus, the severity of initial hearing loss, the time elapse and the audiogram configuration might be related to the prognosis of pediatric SSNHL. The incidence of SSNHL is estimated at 5 to 27 per 100,000 people annually.Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is defined as a 30 dB loss over 3 continuous frequencies occurring in less than 3 days.

Hearing prognosis of patients who developed sensorineural hearing loss associated with COVID-19. Data on the patient’s background, .Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) is an acute disease resulting from abnormal function of the cochlea, auditory nerve, . However, no clinical test for estimating the extent of vascular involvement in ISSNHL has been reported despite its . The ROC curve analysis was subjected to the selection of cutoff points for diagnostic and prognosis with the corresponding sensitivity and specificity was calculated. There may be complete or partial loss of hearing; it is defined as an abrupt start of loss in hearing that is more than 30db or more over at least three contiguous audiometric frequencies occurring within 72 hours .
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss; Prognostic Factors
Methods: Sixty-one patients diagnosed with SSNHL and 65 people who underwent physical examination were recruited. Treatment depends on the cause of the hearing loss and how bad it is. It focuses on sudden sensorineural hearing .Cases of conductive hearing loss generally have a better prognosis because they are all potentially reversible. It is estimated that the annual incidence of sudden sensorineural hearing loss is 1 in 5000 people or about 4000 new cases per year in the US. Meanwhile, the presence of vertigo, lower lymphocytes and higher PLR were associated with worse severity. Its annual reported prevalence rates are 5–20 per 100,000 in the United States and >10 per 100,000 in Korea [ 1 ]. Subjects and methods: We collected 254 adult patients with SSHL from a community hospital.
- Senators From Ohio | United States Senate election in Ohio, 2024
- Sennheiser Ie8 | Sennheiser IE 60 In-Ear-Kopfhörer
- Set 5 10 | WMF Quality One Kochgeschirr-Set 5-teilig
- Senioreneinrichtungen Bochum – Wohnen
- Ses Zeichens Bielefeld : Die Bedeutung von Jungfrau im sechsten Haus
- Select Nth Element Css _ CSS Select nth element with class
- Seltene Sternzeichen Bilder : Die 10 seltensten Fische der Welt, die bald aussterben werden
- Serieller Hybrid – Mazda MX-30 (2020): R-EV/Reichweite/Innen
- Servoöl Wechseln : LAND ROVER DEFENDER Servoöl selber wechseln
- Seven Mind App Krankenkasse : Der ABSM-Kurs von 7Mind im Test
- Serebii Luxury Ball _ Pokémon Scarlet & Violet
- Seriöser Online Shop Für Uhren
- Seraphine France : Sorts, lore, gameplay, toutes les infos
- Sentiero Del Cuore Scanno _ Scanno, il lago a forma di cuore in Abruzzo
- Send Email From Any From | Outlook Not Sending Emails? 8 Fixes to Try