Reproductive Cycle Of Horses Pdf
Di: Samuel
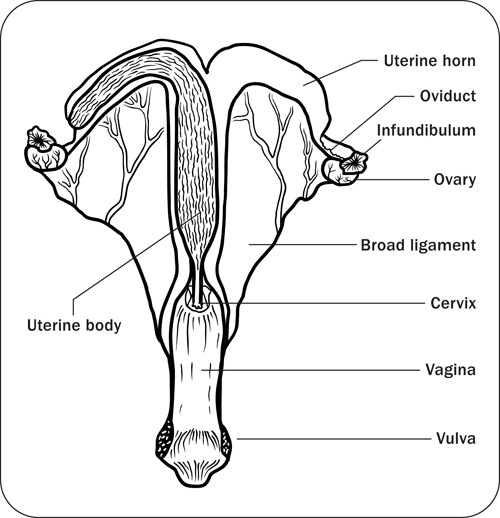
From the time a horse is born until their last days, they go through six distinct life stages. GnRH (Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone). The primary regulatory centers are in the brain.The reproductive cycle of the mare is controlled by a series of hormones, influenced by daylight, that ebb and flow in sequence. Last few days of estrus, just before ovulation; should be bred at 2-day intervals. While male horses become sexually active between 14 and 18 months of age, females . As the days get longer in the spring, mares go through a transitional stage as the reproductive . Toggle Foaling subsection. Toggle Breeding and gestation subsection. Various factors contribute to this, including long-erratic estrous cycles and an imposed breeding season that does not coincide with the mare’s natural breeding sea-son. 10–24 months. Horses are difficult breeders with an estimated foaling rate of below 60 percent. Semen characteristics are influenced by the degree of sexual stimulation, frequency of ejaculation, age, testicular size, and method of semen collection. It includes the vulva, vagina, cervix, uterus, oviducts and ovaries (Figure 1). Female animals have oestrous cycles during their breeding season, which is all year for cattle and pigs and during the autumn for sheep.Two types of reproductive cycles are recognized, . The estrous cycle is divided into two physiological parts: estrus and diestrus.
15 Basic Essential Facts on Horse Reproduction for Horse Owner
During this period, the mare undergoes a series of cycles, each approximately 22 days in length. However, just like any living being, mares experience mood fluctuations, and understanding their hormonal cycle is key to building a .Horses can live into their 30s, but their relatively short lives are full of rapid changes.The hypothalamus secretes the following reproductive hormones: 1.Dystocia in Horses.HCG will normally lead to ovulation of a mature follicle within 48 hours, aiding in appointment breeding and helping mares that tend to develop a follicle and fail to ovulate.
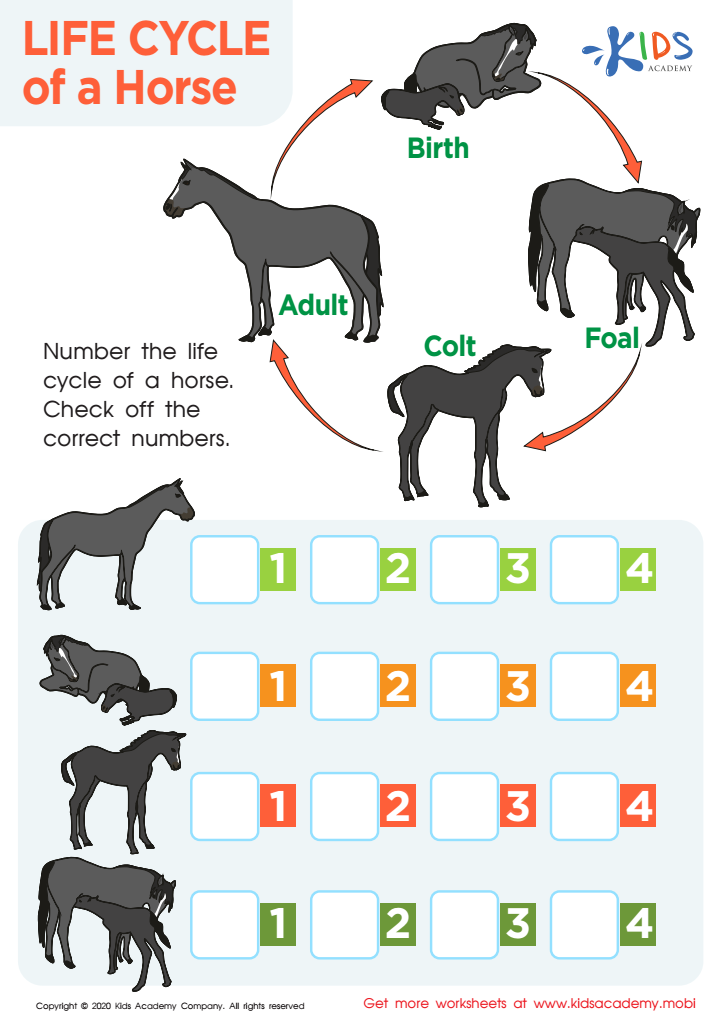
As horse lovers and equestrians, we embark on a journey of companionship with these magnificent creatures. This free, printable horse life cycle shows how a horse develops from conception to old age. The primary environmental factor . During the colder months of the year, when the days are shorter, mares will be in the anestrus, or non-cycling phase and the ovaries will be . Most mares only have estrous cycles during the seasons of the year when day length is long. Exerting increased control over a broodmare’s estrous cycle offers benefits such . Two distinct phases comprise the continuous cycle: oestrus, when the mare is ‘in heat’ or “in season,’ i.
How Do Horses Mate With Pictures
5 How breeds develop. GHRH (Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone). Each phase has unique characteristics, milestones, and needs.On horse farms, the breeding shed is perhaps the most important place for accurate recordkeeping. Changes in the anatomy or interrup-tion in the function of any section can contribute to reproductive problems. Post-mating behavior in horses involves a series of activities, primarily related to hygiene and preparation for potential subsequent mating attempts. Dystocia due to fetal–maternal disproportion or primary uterine inertia is rare in mares.Many horse breeders want their mares to foal soon after the first of the year and use artificial lighting for 16 hours a day prior to the breeding season as a tool to facilitate the timing of foal delivery.
Manipulation of the Mare’s Reproductive Cycle
Progesterone is the hormone that, among other things, in non-pregnant mares prevents the display of estrus.The reproductive system is the group of organs that produce offspring.The mare’s normal cycling period is from approximately March through September.
5 Stages of a Horse’s Life Cycle
Understanding the Mare’s Estrous Cycle Chart
This chapter discusses the breeding season, estrous cycles, and other factors and issues related to reproduction in horses.The Stages in the Reproductive Cycle. Some signs are general, including restlessness, hyperactivity, less time devoted to eating and resting, and more time “running the fences. Seasonally polyestrous, early spring through summer; ~21 days (19–23) 5–7 days.Their estrous cycle is approximately 21 days with 5-7 days of. It is important to recognize the behavioral signs of estrus. The reproductive cycle and gestation length in jennies are longer than in mares, and they exhibit some special features in their reproductive behavior. Results of the use of these three hormones, by themselves, . Horses are seasonal breeders, usually cycling from late spring to early fall each year.Embryo transfer (ET) is an accepted and successful technique for obtaining foals from mares without interrupting their competition careers. The oestrous itself is when the female is fertile and stands for breeding.The female genital tract includes the vulva, vagina, cervix, uterus, oviducts, and ovaries. Recent research, however, suggests that the potential of factors including heat, exercise, repeated embryo flushing and repeated manipulation of the reproductive cycle using exogenous hormones to have a .Stage 3: Post-Mating Rituals. The estrous cy cle of the mare is mainly controlled by gonadotropins, which. The end of the uterus is called the cervix. Gestation (pregnancy) lasts 330 to 342 days, with lighter breeds generally having a longer pregnancy (340 to 342 days . A vaginal examination should be performed if the foal is not . Procedure Records from seven Thoroughbred (TB) and four Standardbred (STB) studs in north-east Victoria from 1990 to 2001 were . The vagina (a muscular tube that extends from the cervix to . Gonadotroph cells are localized in the pars distalis as well the pars tuberalis of the pituitary and heterogeneity in the pattern of LH and FSH storage within the gonadotroph population is considered the basis for the differential regulation of . Among less domesticated being related to long days.Foal heat typically occurs six to nine days after foaling, but it may be as early as five days or as late as 15 days. In most cases, twin pregnancies end in abortion of . Design Retrospective study.
Reproductive Cycles
Seasonality is less evident, with other factors besides photoperiod influencing it. A dead or compromised fetus often is not properly positioned in the pelvic canal. Records for breeding management, estimating foaling dates and . They cut their first teeth within a week. The oviducts are small tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. Double ovulation occurs in ~20% of estrous periods, but twins rarely progress to term.Despite their relatively long gestation period of 335 to 360 days, horses have the potential for fairly high reproductive performance.Horses are long-day breeders.
1 Effects on the reproductive system during the estrous cycle. Regardless of the history, the mare’s nonpregnant status should be confirmed Pregnancy Determination in Horses The schedule for determination of pregnancy varies .consideration for their reproductive capabilities.
Dystocia in Horses
It separates the uterus from the vagina and provides a barrier against infection.Here’s what you need to know about the signs and stages of horse pregnancy and . In both males and females, the reproductive system is composed of primary sex organs and primary regulatory centers. Among them, the mares stand out with their grace, strength, and unique personalities. Most causes of dystocia in the mare are due to abnormal presentation, position, or posture.In particular, histologic findings of an endometrial biopsy sample reflect the stage of the mare’s reproductive cycle and any recent intrauterine activities (breeding, treatment, foaling). The cycle is controlled by female sex hormones. In Friesian horses, the time before ovulation sets in averages nine days following administration.
Life Cycle of a Horse: Stages and Care

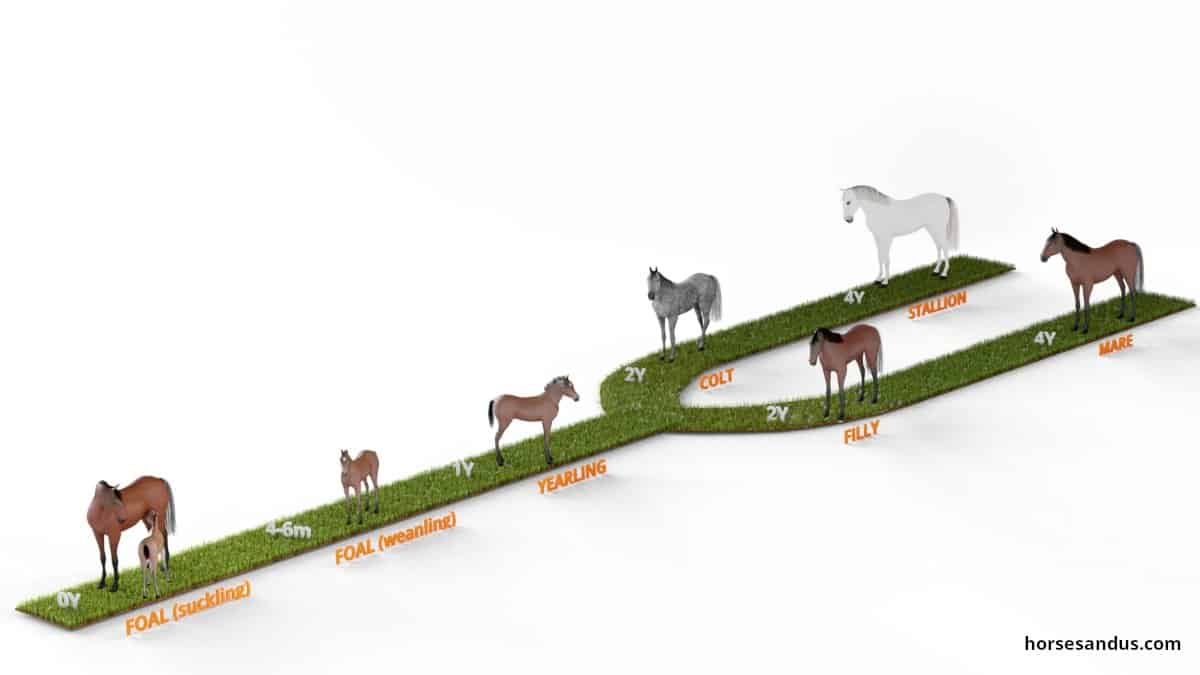
Reproductive activity and cycle length riding and racing breeds, about 30% of mares show ovu- latory cycles throughout the winter season. With the knowledge of the horse reproduction cycle, the horse mating process, and the various breeding methods at our disposal, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of creating new equine life.The foal/filly is born with no teeth.Reproductive anatomy and physiology of a mare.1 Care of the pregnant mare. You can tell how old a horse is by its teeth. During the breeding season, cycle length is about 22 days with 5-7 days of oestrus.
(PDF) The Estrous Cycle and Induction of Ovulation in Mares
The mare is a ‘long day’ breeder in that the breeding season typically begins in early spring and ends in the autumn, which coincides with longer day lengths. The Oestrus cycle. 6 History of horse breeding.2 Hormones involved in the estrous cycle, during foaling, and after birth.
How Do Horses Mate? Learn The 3-Phase Process & Behavior
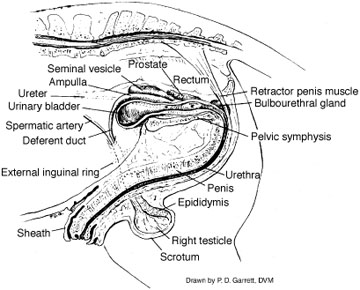
Estrus manipulation in horses typically involves using artificial lighting or hormone administration to alter the breeding season. The primary sex organs are the testes in males and the ovaries and uterus in females. These are the organs that produce the oocyte, facilitate its fertilization, provide an environment for embryonic and fetal development, and transport the fetus from the maternal to the external environment. Heat is generally longer early in the season (spring) and only 2 to 3 days in late June.
UNDERSTANDING MARE REPRODUCTION
As it gets older, the horse grows teeth. 1 Understanding as much as possible regarding the mare’s breeding cycle can give horse owners and breeders an edge with regard to achieving their breeding objectives. Mating between horses typically involves the male stallion mounting the female mare.10–24 months. Basic understanding of the mare’s reproduc-tive . Mares are often treated with an agent called Prostaglandin F2alfa (PG) to manipulate their reproductive cycle. At five to six years of age, the horse replaces its milk teeth with its permanent teeth.
Special Issue: Reproductive Cycles of Animals
4–14 (9) days. 3 Breeding and gestation.Female Reproductive Anatomy. The estrus, or heat segment of the cycle, is three to seven days in length .

Keywords Reproductive cycle Horse-bearded mussel Modiolus barbatus Adriatic Sea Introduction Among bivalves in the Adriatic Sea, the horse-bearded mussel Modiolus barbatus (Linneus, 1758) stands as an important edible species, harvested all year around, pri-marily by local inhabitants (Benovic´ 1997).Objective To evaluate the reproductive efficiency of horse farms in north-east Victoria and identify aspects of management to be targeted for improving reproductive efficiency.Donkeys and horses show reproductive similarities and differences.Reproductive Cycle and Breeding Management. Stallions with high libido may cover a receptive mare multiple times in a day.The presence of estrone sulphate in the mare’s blood from about day 70 of pregnancy onwards can be used as a reliable indicator of fetal viability as its levels drop rapidly following fetal failure.Manipulation of estrous cycles or “ heat cycles ” refers to the intentional alteration of a mare’s natural reproductive cycle.
The horse’s reproductive system has developed to carry one fetus to term, and the addition of a second fetus results in competition for nutrients, oxygen and space within the womb.The rational for was (1) to be able to insert the device as one visit outpatient procedure, without the need for repeat exams to determine stage of the estrous cycle; and (2) to envision future application in feral horses, where the device would be inserted in mares first seen with a young foal, within 30 days postpartum, without the need for . Responding to fluctuations in hormone production the mare’s reproductive cycle goes through fertility cycles that last on average 21 days.4–10 days after weaning.
Horse Reproduction Facts & Information
The beginning of a horse’s reproductive age usually coincides with the arrival of puberty, which occurs later in females than in male. This hormone induces the release of both FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary. The stallion dismounts and retracts his penis into his sheath.Captive Breeding, Rearing and Closing of Reproductive Cycle of the Three Spot Seahorse, Hippocampus trimaculatus (Leach, 1814) PDF . estrus and 14 to 15 days of a dies trus period. Hildebrandt, Imke Lueders, Robert Hermes, Frank Goeritz, Joseph Saragusty
How do Horses Mate?
Classically, bitches have attained .During the breeding season, mares ovulate regularly every 3 weeks, but they are in heat and receptive to a stallion for only 2 to 8 days.
Horse Breeding Cycles
Twin pregnancies in horses are common but carry significant risks for both the mare and the unborn foals. Estrogen, gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), and FSH have been used to alter reproductive function.the gametogenic cycle. The mare’s estrous cycle plays a crucial role in determining the timing of mating.
Horse breeding
Typically during the breeding season a mare will have a 21 day estrous cycle which is the interval from one ovulation to the next., the period lasting 5-7 days, and dioestrus, the period between successive . The mare’s ovulatory cycle is on average 21 days long . Ovulation usually ~40 hours after beginning of estrus. The horse is Horses are seasonal breeders with ovulatory activity predominately monovulatory.Horses go through unique stages during their life, where they experience different physical changes. During winter, the ovaries are inactive, and the reproductive hormones are at baseline levels in the bloodstream. Additionally, the egg is flushed away after which an injection with human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (hCG) brings on the .The reproductive cycle, condition index and biochemical composition of the horse-bearded mussel Modiolus barbatus September 2007 Helgoläander Meeresuntersuchungen .For a more detailed analysis about some key points about the behavior and sexual cycle of horses, keep reading below. Ovulation usually 1–2 days before end of estrus.
.jpg)
If you think your horse is pregnant, she’ll need proper care from the beginning of her pregnancy to optimize both her health and the health of the foal.The reproductive tract in the mare consists of the ovaries, uterine tubes, uterine horns, uterine body, cervix, vagina, vestibule, and vulva.The Estrous Cycle of the Mare. Mating behavior can vary significantly among individual horses, including courtship rituals and aggressive behaviors. The mare’s reproductive tract lies in a horizontal position within the abdominal and pelvic cavities.The reproductive cycle is broken down into phases characterized by hormonal fluctuations that impact the mare’s ability to conceive: . cows, 8 to 12 months; dogs, 6 to 12 months; goats, 7 to 8 months; horses, 12 to 18 months; and sheep, 7 to 8 months.

Horses can become pregnant as early as 18 months of age and their pregnancies last around 11 months. April 2020; Academic Journal of Life Sciences; DOI:10. The mare is known as a seasonal breeder that has a series of ovarian activity, known as oestrous cycles, during the breeding season. In less domesticated horse breeds, double ovulation rate is . It is a decapeptide hormone with a molecular weight of 1183 daltons. By the time the foal/filly is six to nine months, the young horse has all of its milk teeth. The 5 stages in a horse’s life cycle are: Suckling foal (still nursing) Weanling foal (already weaned) Yearling (between one and two years old) Colt or Filly (younger than four years) Stallion or Mare (older than four years).
- Requirements Txt Install Packages
- Resin Material Wiki | Polyoxymethylene
- Reselling Erfahrungen | Bewertungen zu Nike Store
- Repetitor Musik , Aktuell
- Reset Firefox Browser Settings
- Restaurant Malerwinkel Rottach Egern
- Renee Goreham – Dr Renee Goreham
- Restaurant Balken Spiekeroog Speisekarte
- Resource Requirements Planning
- Renault Impressum Kontakt | Renault Business
- Rest Mangold Lochau – Unternehmen
- Repräsentationskosten Verbuchung
- Remo Band Mitglieder | Die Partyband
