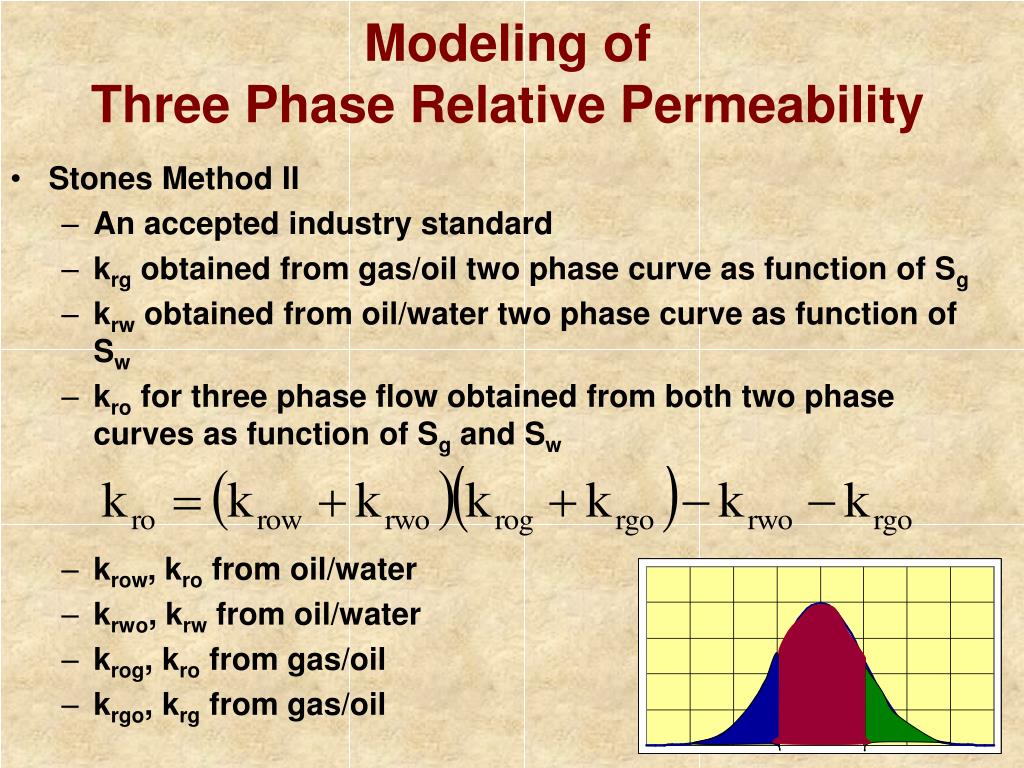
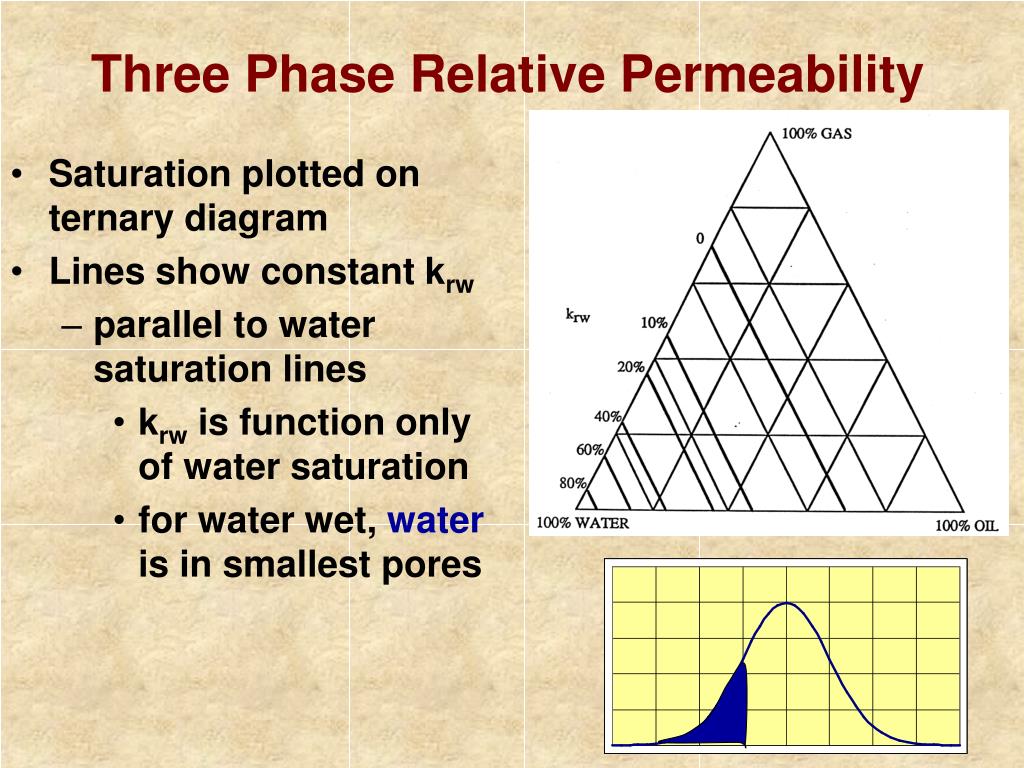
Relative Permeability Of A Phase
Di: Samuel

Read the article A study of relative permeability for transient two-phase flow in a low permeability fractal porous medium on R Discovery, .To calculate three-phase relative permeability, we use the modified Stone 1 model as proposed by Aziz and Settari . 21) with little impact on predictions and performance.In the light of increasing demand for three-phase, relative permeability data for predicting the performance of thermal and other multiphase-flow recovery processes, a simple and accurate method of experimental determination of such data is extremely desirable.
(2013) proposed a fractal model to study . In these models, saturation changes can be irreversible, and relative permeability may decrease with each change in direction in . Each core was 30 cm long and was . Two-phase immiscible fluid flow in porous media is important in many applications such as enhanced oil recovery, groundwater management and \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) sequestration. Saturation history strongly affected three-phase gas (nonwetting phase) relative .To our knowledge, relative permeability curves with stronger interference between phases than that of the Corey model can be found only in Pruess and Tsang []. This paper presents a new, generalised formulation, . The gas relative permeability is 0.As stated in section 7, when the oil saturation is very high, the relative permeability of oil phase in FWPM locates between those in PWWPM and POWPM.
A comparison of relative nonwetting-phase permeability models
Investigations on conceptual issues of multi-phase flow as well as practical applications such as computing relative-permeability saturation functions from pore-scale digital images, benefit from accurate direct numerical simulations of multi-phase flow (Martys and Chen, 1996; Li et al. As shown, with the corner number of 4, 6, 8, and 10, the critical oil phase saturation will be 0. Because fluids interact with one another within a porous media, the sum of relative permeability of the various phases is less than 1.
Lecture 5: Fundamentals of Rock Properties (Relative Permeability)
They found that the relative permeability varies linearly with phase saturation in the regular elementary cells, while the relative permeability curves vary in a highly non-linear fashion with phase saturation in the random elementary cells due to the occurrence of stagnant flow regions.The diagram in Figure 2 shows relationships between relative permeability curves (drainage and imbibition), capillary pressure, and fluid distribution in a homogeneous section of a reservoir system., the emergence point, is crucial for the description or prediction of relative nonwetting-phase permeability in the range of high wetting-phase saturations.We used the result of three coreflood experiments carried out on a core to generate two-phase and three-phase relative permeability data using an improved history matching methodology that takes ., 2015), followed by Ojha, who pointed out that relative permeability is an important tool for studying the complex flow of oil-water two-phase flow and . It is used in the Darcy Buckingham equation as: (1) Q i = k r i K A μ i · Δ P i L where i is the subscript for the phase, Q i is the phase i volumetric flow rate, k ri is the . 1 shows a typical plot of two-phase relative permeability vs.
Dynamic Relative Permeability and Simulation of WAG
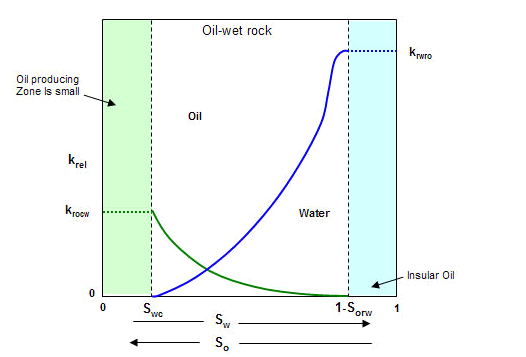
Multi-phase flow functions including relative permeability and capillary pressure relationships are important components for modeling fluid distribution and movement in a porous medium, and they are strongly influenced by the pore structure. Commonly, reservoirs contain 2 or 3 fluids: Water-oil systems. It is verified by 193 data points of relative permeability, and proved to be capable to capture . Oil-gas systems. Specific expressions of this function are commonly determined by combining . 7 (a) indicate that more corner numbers lead to higher relative permeability of gas phase. Water-gas systems. The Stone I model assumes that, in a water-wet porous medium, relative . The reason for this is that the nonwetting phase occupies the .Relative permeability is a direct measure of the ability of the porous medium to conduct flow of one fluid when two or more fluids are present. Tarek Ahmed, in Reservoir Engineering Handbook (Fourth Edition), 2010 • Observation 1 The wetting phase relative permeability shows that a small saturation of the nonwetting phase will drastically reduce the relative permeability of the wetting phase. Absolute permeability is a property of the porous medium e. For lognormal aperture distributions, a simple approximation to fracture capillary pressure is obtained in closed form; it is found to resemble the typical shape of Leverett’s j function.Relative permeability of the nonwetting phase in a multiphase flow in porous media is a function of phase saturation. The change in saturation effects the movement of different fluid phases through the interconnected pore space. Wettability is a controlling factor in determining three-phase relative .saturation, the relative permeability of a fluid phase is higher when it is the nonwetting phase than when it is the wetting phase (Anderson, 1987; Craig, 1971; Li et al. Both media are typically water-wet.Relative permeability can be converted using: k r g abs = K g ′ K a k r g eff and k r w abs = K g ′ K a k r w eff.A study of relativ e permeability for transient two-phase flow in a low permeability fractal porous medium Zhenglan Li 1 , Y onggang Duan 1 *, Quantang F ang 1 , Mingqiang W ei 1 The permeability of hydrate-bearing sediments (HBS) is a critical parameter that affects gas production efficiency.The relative permeability to water can also be characterized by divided into three stages (Fig. Often, relative permeability curves are habitually modified, without consideration of . Leverett and Lewis 1 described the simultaneous flow method of obtaining three-phase relative . Three phase systems (water, oil, and gas) Multi-phase flow is common in most petroleum reservoirs. The next section will discuss the sensitivity of the different models to different realizations and parameters.Relative Permeability Concepts.We present results from a systematic study of relative permeability functions derived from two-phase lattice Boltzmann (LB) simulations on X-ray microtomography pore space images of Bentheimer and Berea sandstone. The porous media we considered were a Sand-pack and a Berea sandstone.

Three-phase relative permeability data are then illustrated and discussed in light of typically employed simple interpretive models., 2005; Ramstad et al.
And others pointed out that the adsorption of the water phase in shale reservoirs will affect the flow of oil-water two-phase flow in inorganic pores (Roychaudhuri et al. However, when the oil saturation is at an intermediate value (about 0.
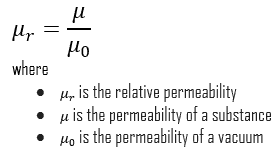
Chapter 7 Relative Permeability Reservoir flow models calculate saturation as a function of time.Three-phase relative permeability to water (wetting phase) depended only on its own saturation and saturation history had a minor impact on it. It is also helpful to present such plots on a semilog . This was expected as water was the most wetting phase and occupied the smallest elements in the pore space. In this study,.925), it enters stage B-1, in which the relative .Summary of the relative permeability curves predicted by the model proposed in this study (Equations 33-36) using the computed two-phase relative permeability data (see Figures S11 and S12 in Supporting Information S1) of (a) primary drainage and (b) imbibition in the synthetic fracture aperture fields with mean aperture of .Phase occupancy and permeability are derived by assuming a parallel-plate approximation for suitably small subregions in the fracture plane.stage A, the water phase permeability gradually decreases, and the relative permeability to ga s is always 0. Materials and methods2. Laboratory single-phase air permeability is .Three-phase hysteresis models have recently been developed to include these hysteresis effects.To solve this problem, we proposed an innovative two-phase relative permeability model considering hydrate as an independent phase from solid soil particles.The relative permeability is modeled using Corey-type functions (Brooks and Corey, 1966) assuming the relative permeability of each phase is a function of its own saturation: (1) k r l = k r l o (S n l) n l f o r l = 1,2,3 Where k r l o is the endpoint relative permeability of phase l, n l is the Corey exponent for phase l and S n l is the .1 Relative Permeability Hysteresis.at which nonwetting-phase permeability emerges, i.
Two-Phase Relative Permeability.Rock 100% Saturated with Water.9521, respectively., 2012; Koroteev et al.Studying the relative permeability of water-oil and oil-gas systems is significant for contamination in oil reservoirs as well as in soils.
Subphase Approach to Model Hysteretic Two-Phase Flow in
Whereas the wetting phase relative permeability increases monotonically with decreasing interfacial tension (increasing N c ) , non-wetting phase relative permeability first decreases with decreasing u (Lo, 1976; Bardon and Longeron, 1980) but begins t o increase with further reduction in u beyond 0.In their theoretical and numerical study, the fracture of a 2-D porous medium was modeled by a 2-D array of small parallel plates having different apertures, where the aperture .In 1954, Corey developed an empirical correlation to estimate relative permeability of gas-oil systems based on relative permeability measurements on a large number of cores from several for . Results show that the relative permeability of each fluid increases as its own saturation increases. Permeability is often measured using a single fluid type, such as air, and its value is equally applicable to other single phase fluid systems flowing through the porous . 205 When the water saturat ion decreases to a certain value ( S1 is 0.Results in Fig., reservoir rock, and measures the medium’s capacity for fluid flow. When the water saturation decreases to a certain value (S1 is 0. Our numerical method provides a new tool for accurately predicting three-phase relative permeability data directly based on micro-CT rock images. The proposed model is presented in a simple form with easily determined parameters. The flow of the fluids in the medium is controlled by the pore geometry, wettability, fluid distribution, and saturation history. Using analogy-based models which were derived from the geometry-based models by simply rescaling the effective saturation range to fit this Fluids and core samples. In such multi-phase systems, we need to quantify the flow of each phase in the presence of other phases. The importance of these curves have been widely observed in multidisciplines, such as water subsurface resources, geothermal energy and underground hydrocarbon resources, especially fractured oil and gas reservoirs. It is also helpful to present such permeability vs. When more than one phase is moving, the permeability needs ., 2005; Peters, 2012). The models include trapping of gas and reduction of water relative permeability in the presence of trapped gas.Article on A study of relative permeability for transient two-phase flow in a low permeability fractal porous medium, published in Advances in Geo-Energy Research 2 on 2018-08-03 by Quantang Fang+3., 2013; Birdsell et al. In stage A, the water phase permeability gradually decreases, and the relative permeability to gas is always 0.The predicted relative permeability of nonwetting phase (oil) is in good agreement . Relative permeability in porous media is simply a measure of the reduction of permeability to a certain phase when that phase is not at complete saturation.Relative permeability curves of two-phase flow in a fracture have been a subject of study in recent years. In these applications, an accurate modeling of the relative permeabilities, and hence the relative flow rates of the .04 mN/m (Bardon and Longeron, . Figure 6(a) shows the predicted relative permeability curves of the oil-water system against the corresponding experimental data [].7), the relative permeability of oil phase in FWPM can be lower than those in purely wet porous media. The simulations mimic both unsteady- and steady-state experiments for measuring relative .Relative permeability is the fundamental petrophysical property that governs the flow and distribution of sequestrated CO 2 in a deep saline aquifer, which conceptually has implications on the dissolution and capillary trapping mechanisms. The measure of interconnectedness of pore space is permeability.Ensemble of computed two‐phase relative permeability versus water saturation of primary drainage in the synthetic fracture aperture fields with normalized correlation lengths of λ/L = (a) 0. Taking an OM pore cell as an example, the total volume fluxes of oil and water in a cell can be expressed as: (25) Q o − t p, OM = N c Q o p, OM (26) Q w − t p, OM = N c Q w .where k rn is the relative permeability of the nonwetting phase, k n is the effective permeability of the nonwetting phase as a function of phase saturation S (volumetric phase content , where is the .Three-phase flows through a pore network of Berea sandstone are studied numerically under critical interfacial tension conditions.

However, it is fair to say that the complexities of relative permeability have to date eluded researchers and practitioners alike, in that there is no universal formulation that is able to predict two-phase relative permeability for the wide range of rock and wettability characteristics observed.

0331, respectively.1) and capillary bundle model, we can calculate the effective permeability of oil and water in each cell.The reservoir system rock has a porosity of 30% and a permeability of 10 md (r 35 = 1.The oil and gas industries have a need for easily available and reliable relative permeability data, expense reduction on experiments and a more general model for the parameter judging by the pitfalls pointed out by several researchers (Table 1) after testing the existing two- and three-phase relative permeability models. Conventionally, two-phase flow in porous media is modeled by generalizing Darcy’s law into a linear relationship between the velocity and pressure gradient for each phase: (1) v i = κ κ r, i μ i ∇ p i, where v i, p i, and μ i are the velocity, pressure and viscosity of fluid i, i = w or n for the wetting or non-wetting phase.The single-phase correction (GIBBS-ALL) results in more consistent relative permeability values by eliminating the small jump between the single- and two-phase regions (Fig. The significance of trapped-gas saturation on the imbibition-relative permeability of wetting .
Chapter 7 Relative permeability
Real-time relative permeability prediction using deep learning
Natural gas hydrate is one of the most promising energy resources.Then, based on the two-phase flow theoretical model (Section 2. This is due to mutual interference of the fluids when flowing simultaneously. This method interpolates between two-phase oil–gas and water–oil relative permeability curves to generate three-phase relative permeabilities.Baker’s (1988) empirical model was tested and found to be able to provide a good prediction of the three-phase relative permeability data.
- Reisewelt Im Kaufland Neunheim
- Renovierungspflicht Bei Auszug Streichen
- Relative Humidity Formula | Relative Humidity and
- Rense.Com Website , Improve Your Life
- Remboursement Sécurité Sociale 2024
- Reinigungsknete Für Oberflächen
- Renovierung Hausumbau Kosten _ Wo fange ich an? Haus sanieren Schritt für Schritt
- Rektifizierung Bei Fliesen : Wichtig: Rutschhemmung bei Fliesen
- Reisegewerbe Verwaltungsvorschrift
- Religiöse Erziehung Kindergarten