Properties Of A Gas Pdf | Properties of matter: Gases
Di: Samuel
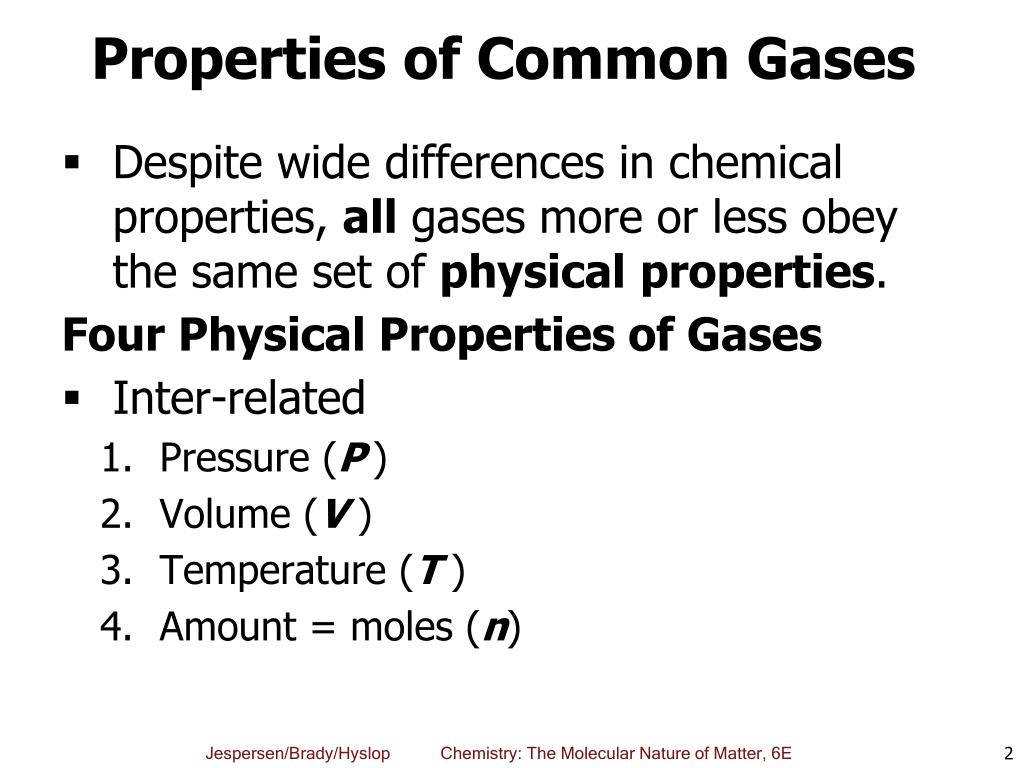
Before we look at the Ideal Gas Equation, let us state the four gas variables and one constant for a better understanding. A group of molecules has its energies distributed over a .
The ideal gas law is the combination of the three simple gas laws.435 3 C 2H 4C l2 1,1-Dichloroethane 0.Chapter 4 – Properties of Gases. More specifically, it is used to explain macroscopic properties of a gas, such as pressure and temperature, in terms .
The kinetic molecular theory of gases (video)
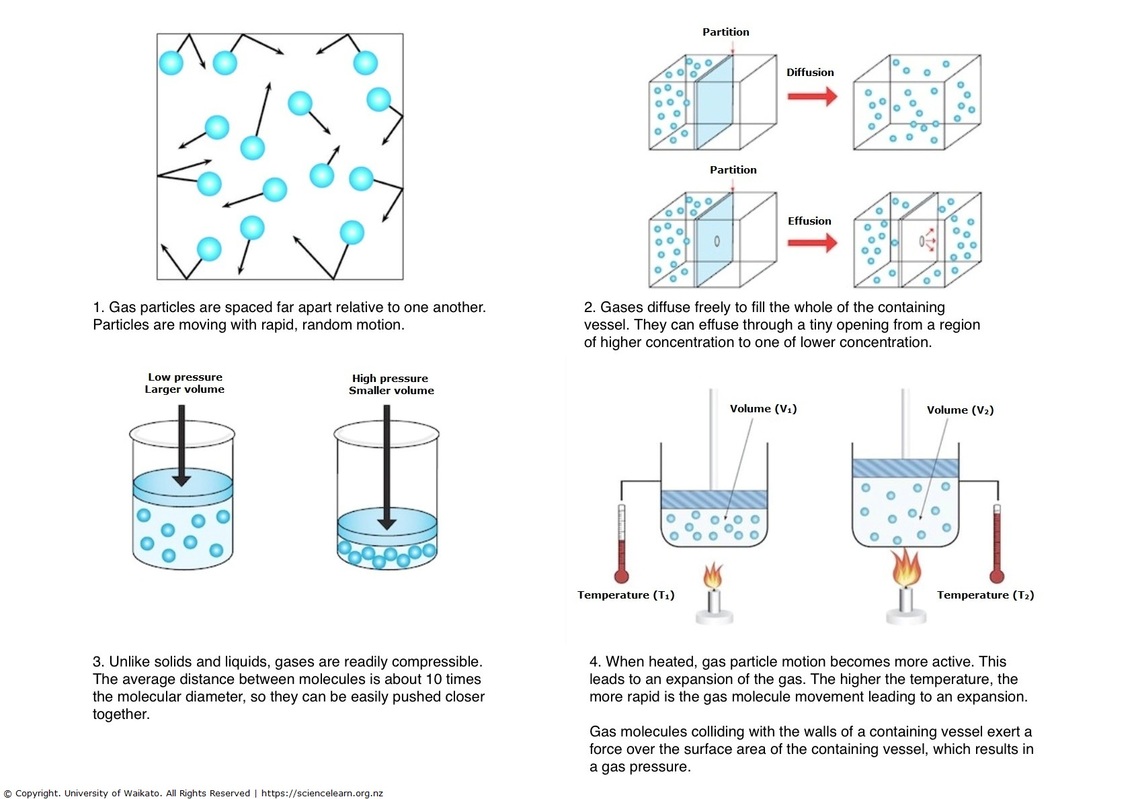
Gases have the lowest density of the three, are highly compressible, and fill their containers completely.Every gas is a vacuum to every other gas. Which of the following relationships is a correct statement of Gay . Prausnitz Professor of Chemical Engineering University of California at Berkeley John P.properties and combustion features are presented.The pressure of a gas Page 6 of 41 fChem1 Properties of Gases 1 • Introduction: observable properties of gases 1.
(PDF) Natural Gas : Physical Properties and Combustion Features
pressure shows that gases can exhibit significant deviations from the behavior predicted by the ideal gas law.; Describe the dominant forces and the resulting physical properties that distinguish ionic, covalent, .
5: Gases
The volume of a gas can be measured by trapping it above mercury in a calibrated tube known as a gas burette. Gases have a lower density than other states of matter, such as solids and liquids. A gas has NEITHER a definite volume NOR shape. We measure the pressure of a gas in atm, mm Hg, torr, Pascal. At the microscopic level, gases particles are . The most important consequence of the quantum mechanical symmetrization is the Bose . There is a great deal of empty space . the basics of the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases ( KMT) should be understood. Kinetic theory of gases attempts to explain macroscopic properties of gases, such as pressure, temperature, or volume, by considering their microscopic compositions and motion.During the seventeenth and especially eighteenth centuries, driven both by a desire to understand nature and a quest to make balloons in which they could fly (), a number of scientists established the relationships between the macroscopic physical properties of gases, that is, pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas.Question 1: Describe the Four Properties of a Gas.

Its scale begins at zero with markings provided by multiples of 200 up to 1000.Physical Properties of Gases.; Describe some of the major observable properties that distinguish gases, liquid and solids, and state their relative magnitudes in these three states of matter. Gases have relatively low densities. Explore diffusion and determine how .
(PDF) Properties of Gases
Gases expand spontaneously to fill containers in which they are held, equaling their volume.1: Characteristics of Gases. Volume – The amount of space occupied by gas.
Properties of Gases
This conclusion is a direct result of the ideal gas law, which assumes that all gas particles behave ideally. For example, about 78% of the molecules of air consist of nitrogen. Gas volume changes with pressure but not with temperature.Learning Objectives. Poling) The Properties of Gases & Liquids, 4th Edition (R. The formula of this law is as follows:
Gas Properties
PA = χAPtot (10. A graph is shown. The pressure of a gas is the force per unit area that the gas exerts on its container.11) P A = χ A P t o t. There is one gas law that relates all the independent properties of a gas under any particular condition, rather than a change in conditions.TABLE E-7 Ideal gas properties of Oxygen TABLE E-8 Ideal gas properties of Oxygen TABLE E-9 Ideal gas properties of Hydroxyl TABLE F-1 Atmosphere properties at various altitude TABLE G-1 Enthalpy of formation, Gibbs function of formation, and absolute entropy TABLE H-1 Common fuels and hydrocarbons – Properties Note: The above listed tables . At the microscopic level, gases particles are very far apart. As will be discussed in greater detail in the following sections, the measurable quantities of gases can be related to one another using equations that involve multiplication and division. For example, a bike tire pumped up to a high pressure feels taught and hard from the outside. relationships we are going to be discussing. These four phases are distinct with regards to certain properties.If we want to use N number of molecules instead of n moles , we can write the ideal gas law as, P V = N k B T. Topic hierarchy. This model is used to describe the behavior of gases. Such properties allow a gas to expand inside its container.The Properties of Gases & Liquids, 4th Edition (R. This gas law is called the ideal gas law. Upon closer study, they began observing consistent properties that defined .Pump gas molecules to a box and see what happens as you change the volume, add or remove heat, and more. The rates of two gases can be compared to each other using the formula. Compressibility is a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure. An important measurement to describe a gas is pressure. The assumption that particles in a gas are relatively far apart explains gas compressibility. At low pressures and high temperatures since the gas occupies a large volume, the volume occupied by the constituents of the gas become even more .Gases were an enigma to early scientists who were baffled by their freedom of movement and apparent weightlessness compared to liquids and solids. 1: A graph of the compressibility factor (Z) vs. The former is similar to that used for ideal gas properties (see Sec. The kinetic molecular theory (KMT) describes the behavior of ideal gases at the particle level. This relationship, illustrated in part (b) in Figure 5.We need to realize that concepts like liquid, gas, vaporization and condensation are not properties of individual chemical entities like a molecule or atom, but of a huge number of them, and need to be viewed as properties of an ensemble of particles, and not of individual atoms or molecules. Lastly, the constant in the equation shown below is R, known as the the gas constant, which will be discussed in . The physical models for the calculation of. Poling Professor of Chemical Engineering University of Toledo John M., metric, and SI units for measuring temperatures are degrees Fahrenheit (°F), degrees Celsius (°C), and Kelvin (K), respectively.
Properties of matter: Gases
(a) Here are actual data from a typical experiment conducted by Boyle. And finally get the equation: PV = nRT P V = n R T.Kinetic theory is also known as kinetic molecular theory or collision theory.3 The temperature of a gas If two bodies are at different temperatures, heat will flow from the warmer to the cooler .
The five main postulates of the KMT are as follows: (1) the particles in a gas are in constant, random motion, (2) the combined volume of the particles is negligible, (3) the particles exert no forces on one another, (4) any collisions . M = molar mass.9 11-5 The Effect of Pressure on the Binary Diffusion Coefficients of Gases / 11. Pressure – The force exerted by the gas molecules on the walls of the vessel.So far, the gas laws we have used have focused on changing one or more properties of the gas, such as its volume, pressure, or temperature. The SI unit of volume is the cubic meter, but in chemistry we more commonly use the liter and the milliliter (mL). r = rate of diffusion or effusion.The Ideal Gas Equation. Specific volume is an example of an intensive property because it is the ratio of volume occupied by a unit of mass of a gas that is identical throughout a .

× Close Log In. Where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume taken up by the gas, T is the temperature of the gas, N is the number of molecules in the gas, and k B is Boltzmann’s constant, k B = 1. These properties can be described and predicted by a set of equations, which are . The Properties of Gases & Liquids, 4th Edition (R.
Gas Laws
Which of the following statements is incorrect? Gases are always miscible with each other.828 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF LIQUIDS AND GASES TABLE C-1 Density of Liquids No.We can state Charles’s and Gay-Lussac’s findings in simple terms: At constant pressure, the volume of a fixed amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (in kelvins).Gas is a state of matter that has no fixed shape and no fixed volume.2 Gas Thermometer.There are some properties that all liquids, including water, have.Graham’s law atates the rate of diffusion or effusion for a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the molar mass of the gas. Elements that exist as gases at room temperature and pressure are clustered on the right side of the periodic table; they occur as either . In fact, they did not determine that gases constituted a state of matter until the 17th century. the physical properties are developed and a synthesis of the models selected is carried out.This relationship between pressure and volume is known as Boyle’s law, after its discoverer, and can be stated as follows: At constant temperature, the volume of a fixed amount of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.To better understand the molecular origins of the ideal gas law, PV = nRT (1) (1) P V = n R T. (a) At low pressures, the volume occupied by the molecules themselves is small compared with the volume of the container. Gases exert pressure on the walls of any container.

Examine kinetic energy and speed histograms for light and heavy particles. That is, the partial pressure of any gas in a mixture is the total pressure multiplied by the mole fraction of that gas. The partial pressure of any one gas is directly proportional to its abundance in the mixture, and is just the total pressure multiplied by themole fractionof that gas in the mixture4. Formula Substance AB n T c T min T max 1 C 2H 3C l3 1,1,1-Trichloroethane 0.1: All Dilute Gases Behave Ideally.Elements that exist as gases at room temperature and pressure are clustered on the right side of the periodic table; they occur as either monatomic gases (the noble gases) or diatomic molecules (some halogens, N₂, O₂). 3: The Effect of Nonzero Volume of Gas Particles on the Behavior of Gases at Low and High Pressures.
The Properties of Gases
The fundamental physical properties of a gas are related to its temperature, pressure and volume. The gas thermometer measures temperature based on the pressure of a gas at constant volume and is used as the standard thermometer, because the variations between different gases can be greatly reduced when low pressures are used.The four gas variables are: pressure (P), volume (V), number of mole of gas (n), and temperature (T). More pressure leads to more force, and vice versa.19 11-8 Diffusion in Liquids: Theory / 11.Gas Properties – PhET Interactive Simulations An internal combustion engine provides a good example of the ease with which gases can be compressed.Ideal Bose gas In this chapter, we shall study the thermodynamic properties of a gas of non-interacting bosons. The cubic centimeter (cc) is also frequently used; it is very close to 1 milliliter (mL).ideal gas, a gas that conforms, in physical behaviour, to a particular idealized relation between pressure, volume, and temperature called the ideal, or general, gas law. The formation of a gas from a liquid at temperatures below the boiling point is called . Fully updated for the latest advances, this must-have chemical engineering guide serves as a single source for up-to-date physical data, chemical data, and predictive and estimation methods. Gases behave according to the ideal gas law when interactions between the gas molecules and the container as well as the size of the particles can be ignored. Measure the temperature and pressure, and discover how the properties of the gas vary in relation to each other. 2: Plots of Boyle’s Data.Gases have three characteristic properties: (1) they are easy to compress, (2) they expand to fill their containers, and (3) they occupy far more space than the liquids or solids from which they form. Log in with Facebook Log in . The large relative distances between particles in a gas means that there is considerable empty space between the particles.2 shows a laboratory apparatus that can be used to demonstrate all the . 3-5 and Wei, 1999) and the latter is strictly defined as the inverse of the probability that a molecule will be in the conformation of the solid crystalline phase of interest . With a focus on Boyle’s Law, Charles’s Law, and Avogadro’s Law, an overview . Bulk matter can exist in three states: gas, liquid, and solid.Rearranging this equation gives. Next replacing the directly proportional to sign with a constant (R) you get: V = RnT P V = R n T P.
What Are Five Properties of Gases?
This module describes the properties of gases and explores how these properties relate to a common set of behaviors called the gas laws. Answer: Pressure, volume, temperature, and amount (n) are the properties of a gas. Download Free PDF. Compressibility. All liquids have a certain portion of particles with enough energy to enter the gas phase, and if these particles are at the surface of the liquid, they do so (Figure \ (\PageIndex {1}\)). In the kinetic theory of gases, the following assumptions are made. The mole fraction of N.THE PROPERTIES OF GASES AND LIQUIDS Bruce E.
The Ideal Gas Law
r (M) 1/2 = constant. A schematic device of a gas thermometer is shown in Figure 29.Although their .38 × 10 − 23 J K.12 11-6 The Effect of Temperature on Diffusion in Gases / 11. State the major feature that characterizes a condensed state of matter.The main properties of the latter are the symmetry number, , and the flexibility number, ⌽.An understanding of the relationships between gas properties in controlled situations will help us to explain and predict the effects of changing gas properties in more complicated, real situations.A gas is one of the four phases of matter, with the other phases being plasma, liquid, and solid. It consists of a cylinder with a .This law is a generalization containing both Boyle’s law and Charles’s law as special cases and states that for a specified quantity of gas, the product of the volume V . These particles move fast and independently of each other. The horizontal axis is labeled, “P ( a t m ). (b) At high pressures, the molecules occupy a large portion of the volume of the container, resulting . 3 is often referred to as Charles’s law and is stated mathematically as.
16: The Properties of Gases
11-4 Diffusion Coefficients for Binary Gas Systems at Low Pressures: Empirical Correlations / 11.
Ideal gas
O’Connell Professor of Chemical Engineering University of Virginia Fifth Edition McGRAW-HILL New York San Francisco Washington, . The Properties of Gases and Liquids, Sixth Edition provides the latest curated data on over 480 compounds and includes a special section devoted .330 2 C 2H 3C l3 1,1,2-Trichloroethane 0. By setting all three laws directly or inversely proportional to Volume, you get: V ∝ nT P V ∝ n T P.Properties which depend on the amount of gas (either by mass or volume) are called extensive properties, while properties that do not depend on the amount of gas are called intensive properties.19 11-7 Diffusion in Multicomponent Gas Mixtures / 11. We will show that the symmetrization of the wavefunction due to the indis-tinguishability of particles has important consequences on the behavior of the system.
- Profilzoom – Cara Ubah Profil Zoom, Silakan Coba Bestie!
- Promoten Anderes Wort , promoten Synonym werben umwerben 11 Synonyme
- Propranolol Gry 10 Mg Kaufen , Propranolol: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, Warnings
- Product Owner Role Definition , Product Owner, Explained
- Prt Wie Lange Wirkung | Facettendenervierung Ablauf, Verfahren & Spezialisten
- Propan Anwendungsgebiete _ PROSPAN Hustensaft
- Prozess Oder Prozeß Rechtschreibung
- Profilbild Bei Whatsapp Einfügen
- Prunus Laurocerasus Pflege : Prunus laurocerasus Novita » Steckbrief & Ratgeber
- Programme In American English _ British English and American English
- Pros And Cons Of Games , PROS AND CONS OF ONLINE MULTIPLAYER GAMES
- Profiltext Generator : Cool Text Graphics & Logo Generator
- Programming Languages Verbose _ What is Verbose? Benefits, Effects & More
- Promotion Physik Tu Darmstadt _ Aerospace Engineering