Prkn Parkinson – PRKN: A Pathogenic Gene of Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
Di: Samuel
Mutationen im SNCA-Gen verkürzen das Leben von Parkinson-Kranken deutlich. However, recent studies have demonstrated that it also plays a role in the development and metastasis of several types of cancers .Parkinson’s disease is a brain disorder that causes unintended or uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination. PRKN is located in FRA6E, which is one of the common fragile sites in the human genome, making this region prone to structural variants.PRKN Gene Information Parkinson’s Disease Fact Sheet Parkinson’s disease is multifactorial in most families; it is likely caused by an interplay of both genetic and environmental factors. The PRKN gene, also known as PARK2, maps the long arm of chromosome 6 (6q25.Parkin, a protein encoded by PRKN, discovered in the context of Parkinson’s disease, controls proteasomal degradation by protein ubiquitination and acts on cell cycle control and mitochondrial homeostasis, among other cellular processes. Mutations in this gene are known to cause Parkinson disease and autosomal recessive juvenile Parkinson disease.Recessive mutations in PRKN, PARK7 and PINK1 are established causes of early-onset Parkinson’s disease (EOPD). However, complex structural variants such as inversions of PRKN are .Der Krankheitsverlauf von Parkinson.MUTATIONS OF PRKN GENE IN PARKINSON’S DISEASE. Background: PRKN mutations are the most common cause of young onset and .

(2022) examined 2 large cohorts: an NIH Parkinson disease control cohort with whole-exome screening data, and the UK Biobank cohort with whole-exome sequencing and genotyping array data. PRKN is located in FRA6E which is one of the common fragile sites in the human genome, making this region prone to structural variants.
PRKN: A Pathogenic Gene of Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
Die Parkinson-Krankheit ist ein sehr heterogenes Krankheitsbild, bei dem das Erkrankungsalter, der Verlauf, das Ansprechen auf die Behandlung und die Symptome variieren. Here, we assessed .Objectives: To identify complex structural variants in PRKN using long-read sequencing. A number of genes have been identified as risk factors for Parkinson’s disease, with many others likely unknown.
Parkinson Verlauf: Die 5 Krankheitsstadien
Lebensjahr auf. Additionally, the Parkinson’s Foundation PD GENEration study offers genetic testing and counseling to all participants.Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative condition associated with the deposition of aggregated α-synuclein.Background: Biallelic PRKN mutation carriers with Parkinson’s disease (PD) typically have an earlier disease onset, slow disease progression, and, often, different neuropathology compared to sporadic PD patients.Mutations in the protein kinase PINK1 lead to defects in mitophagy and cause autosomal recessive early onset Parkinson’s disease1,2. The item on the left represents ubiquitin binding region (UBL), followed by linker region (Linker), ring finger domain 0 (RING0 .5% in individuals ≥45 years of age. Das fortgeschrittene Stadium der Parkinson-Krankheit geht mit einigen motorischen und nichtmotorischen Symptomen einher. In the neoplastic setting, .2–q27) , contains 12 exons, and spans about 1. Objectives: Our aim was to examine the association between . In Deutschland liegt das durchschnittliche Alter für die Diagnose von Parkinson sogar bei 65 Jahren. Previous studies have interrogated the role of heterozygous variants in these genes but mainly focused on rare (minor allele frequency [MAF] <1%) damaging variants or established mutations.

Over the last two decades, various hypotheses have been proposed to explain the etiology of PD.Mutations in the PRKN gene, a common cause of early-onset Parkinson’s disease, were tied directly to low activity of the gene, a study reports. Here, we performed rRNA-depleted RNA sequencing and det . Bei Morbus Parkinson muss daher eine deutliche Störung vorliegen, um den Status der Schwerbehinderung zu erhalten. Currently, the longest follow-up available of these patients is 6 years. We have previously identified mitoch ondrial Stomatin-like protein 2 (SLP-2), which functions in the assembly of respiratory chain proteins, as a Parkin-binding protein.To investigate the prevalence and genotype-phenotype correlations of parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (PRKN) variants in Parkinson’s disease (PD), we first included 2,527 patients with PD. Using the NIH cohort, the authors .

However, complex structural variants such as . Notably, genetic risk factors vary according to ethnicity and geographical regions, and few studies have ., 1997) is the most common autosomal recessive gene causing early onset PD (Klein and Lohmann-Hedrich, 2007; Jiang et al. Brain 145 , 2077–2091 (2022).
Activation mechanism of PINK1
Die Parkinson-Krankheit ist nach der Alzheimer-Krankheit die zweithäufigste neurodegenerative Erkrankung. Dies macht eine Rund-um-die-Uhr-Betreuung für die Bewältigung alltäglicher Aufgaben .PRKN is located in FRA6E which is one of the common fragile sites in the human genome, making this region prone to structural variants.2% of the reported PD patients and with higher frequency in specific ethnicities, are the most prevalent PRKN mutations reported to date . Figure 1 shows different structures and mutations of Parkin protein. Schwere Beinschmerzen und Steifheit können dazu führen, dass das Stehen und Gehen nahezu unmöglich wird.Twenty-five years have passed since the causative gene for familial Parkinson’s disease (PD), Parkin (now PRKN), was identified in 1998; PRKN is the most common causative gene in young-onset PD. Exon rearrangements, identified in about 43.Call the Parkinson’s Foundation Helpline 1-800-4PD-INFO (473-4636) to find a genetic counselor.

This is the first report describing a large 7Mb inversion involving breakpoints outside of PRKN, and highlights the importance of using long-read whole genome sequencing for structural variant analysis in unresolved young-onset PD cases. We collected a total of 34 patients and focused on 18 cases (14 homozygous, 4 compound .To examine the effects of heterozygous mutations in the PRKN gene on the risk of Parkinson disease, Zhu et al.Mutations in the E3 ubiquitin ligase parkin (PARK2, also known as PRKN) and the protein kinase PINK1 (also known as PARK6) are linked to autosomal-recessive juvenile parkinsonism (AR-JP)1,2; at .To investigate the prevalence and genotype-phenotype correlations of parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase ( PRKN) variants in Parkinson’s disease (PD), we first included 2,527 patients with PD. Through the defined selection, we enrolled 2,322 patients, including 1,204 with familial and 1,118 with sporadic PD.Parkinson’s disease (PD) is an incurable neurodegenerative disorder that ensues from the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, and is characterized by progressive loss of motor . Biallelic Parkin (PRKN) mutations cause autosomal recessive Parkinson’s disease (PD); however, the role of monoallelic PRKN mutations as a risk factor for PD remains unclear. Symptoms usually begin gradually and worsen over time. Because gene activity was measured by standard methods using cells in the bloodstream, the findings may support developing an “easily accessible screening test for PRKN mutations,” the .

The precise function of this gene is unknown; however, the encoded protein is a component of a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that mediates the targeting of substrate proteins for proteasomal degradation.Activation of PRKN requires 2 steps: 1 phosphorylation at Ser-65 by PINK1 and 2 binding to phosphorylated ubiquitin, leading to unlock repression of the catalytic Cys-431 by the RING-0 region via an allosteric mechanism and converting PRKN to its fully-active form (PubMed:24660806, PubMed:25474007, PubMed:24784582, PubMed:25527291).A Parkinson disease multigene panel that includes PRKN and other genes of interest (see Differential Diagnosis) is most likely to identify the genetic cause of the condition at the most reasonable cost while limiting identification of variants of uncertain significance and pathogenic variants in genes that do not explain the underlying phenotype.Objective: To confirm that there is a diagnostic delay in Parkin-related Parkinson Disease and to explore possible factors causing such a delay. We report a very long-term outcome (more than 15 years) of a STN-DBS-treated patient with a compound .PRKN is a key gene involved in mitophagy in Parkinson’s disease.Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common cause of neurodegeneration. The precise function of parkin is unknown; however, the protein is a component of a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex which in turn is part of the ubiquitin-proteasome system that mediates the targeting of proteins for degradation.Nicht jede Parkinson-Mutation verkürzt das Leben. Heterozygous PRKN mutations are common but do not increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.We investigated the role of single heterozygous PRKN mutations in three large independent case-control cohorts totalling 10 858 PD cases and 8328 controls. Die neurodegenerative Erkrankung Parkinson, auch Morbus Parkinson genannt, tritt in den meisten Fällen nicht vor dem 60.
The pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease
Through the defined selection, we enrolled 2,322 patients, including 1,204 with familial and 1,118 with s . Insights into the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease have been derived from genetics and molecular pathology.
Oxidative stress factors in Parkinson’s disease
Der Krankheitsverlauf von Parkinson
Psychiatrische Manifestationen wie Depressionen und visuelle Halluzinationen sind häufig, aber nicht einheitlich vorhanden. Mutations in this gene are known to cause Parkinson . [citation needed] Mutations in this gene are known to cause a familial form of Parkinson’s disease known as . Methods: We investigated the genetic cause of monozy- gotic twins presenting with a young onset dystonia- parkinsonism using targeted sequencing, whole exome sequencing, multiple ligation probe amplification, and long-read sequencing.
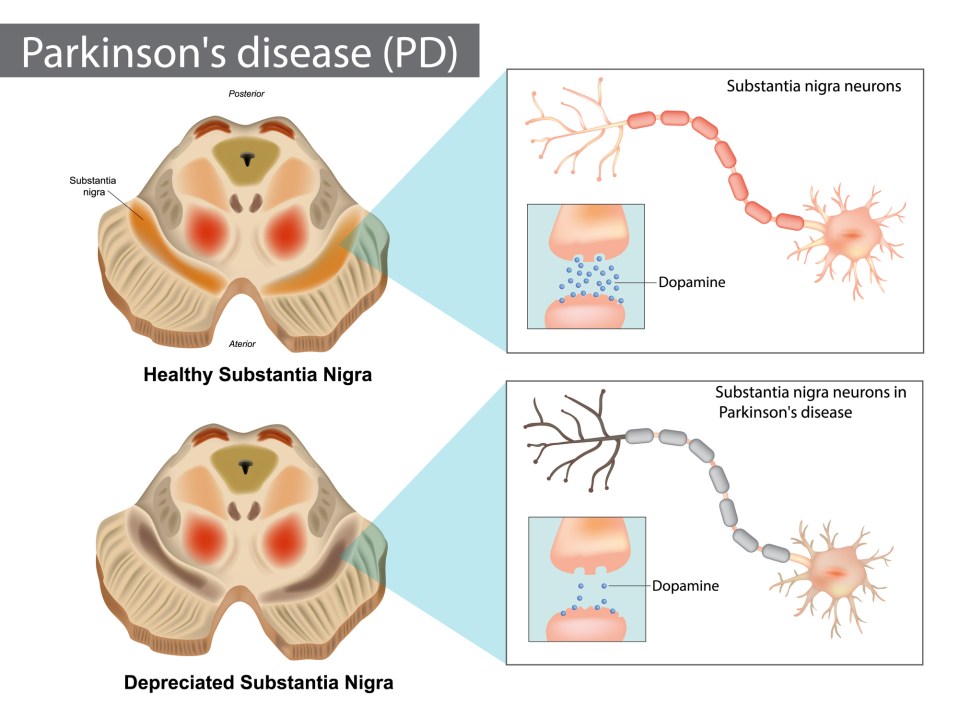

Parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase (PRKN) mutations are the most common cause of young onset and autosomal recessive Parkinson’s disease (PD). PRKN is located in FRA6E which is one of the common fragile sites in the human .Parkinson’s disease (PD) is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.The precise function of this gene is unknown; however, the encoded protein is a component of a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that mediates the targeting of substrate proteins for proteasomal degradation. 1 Alpha-synuclein (α-syn) deposition, pathologically manifesting as Lewy bodies in brain tissue, has not generally been accepted as a consistent feature of PRKN . Biochemical studies, investigation of transplanted neurons in patients with Parkinson’s disease, and cell and . Die Diagnose basiert auf den klinischen Befunden von Tremor, Rigidität und Bradykinesie. Mutationen in den Genen PRKN und PINK1 verursachen ein . Article PubMed PubMed Central Google ScholarDespite growing evidence that has declared the importance of circRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases, the clinical significance of circRNAs in dopaminergic (DA) neuronal degeneration in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease (PD) remains unclear. As the disease progresses, people may have difficulty walking and talking. Among these is the oxidant-antioxidant theory, which asserts that local and systemic oxidative damage triggered by reactive oxygen species and other free . There are commercial companies that offer genetic testing for Parkinson’s. However, the role of heterozygous PRKN variants in the risk of PD is controversial.

Parkin and its molecular associations in gliomas
Parkin (protein)
1 Five to ten per cent of cases are caused by mutation(s) in a single gene. This fact sheet outlines basic .
Der Ursache von Parkinson auf der Spur
UniProt
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed our patients with mutations in the parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase gene (PRKN). Da es in diesem Lebensabschnitt zu altersbedingten gesundheitlichen .PRKN, the second identified PD gene (Matsumine et al. There are over 100 known mutations in PRKN that lead to either a dysfunctional small Parkin protein being rapidly degraded or defective parkin without . Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder with a prevalence of about 0.Mutations in both the PINK1 and PRKN gene have been linked with early-onset PD.Background: Loss-of-function mutations in the PRKN gene, encoding Parkin, are the most common cause of autosomal recessive Parkinson’s disease (PD).Biallelic pathogenic variants in the PRKN gene cause early-onset Parkinson’s disease (PD), representing the most frequent type of autosomal recessive monogenic PD. It is known that the Parkin promoter functions as a bidirectional promoter, not only for . PINK1 has many unique features that enable it to .Early‐onset Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the most common inherited form of parkinsonism, with the PRKN gene being the most frequently identified mutated.Introduction Parkinson’s Disease (PD) patients with Parkin gene (PRKN) mutations show good response to subthalamic deep brain stimulation (STN-DBS).53 Mb, making it one of the largest genes in the human genome [77, 117]. Parkin has been also implicated in several carcinomas, melanoma and leukemia. Als mögliche Ursache der Parkinson-Erkrankung wurden mehrere genetische Mutationen gefunden. Sollte die Prüfung eine geringe Störung feststellen, kann zu einem späteren Zeitpunkt ein Antrag auf Erhöhung des GdB .Background: PRKN mutations are the most common cause of young onset and autosomal recessive Parkinson’s disease (PD). 2 Mutations in PRKN are the most common recessive form of Parkinson’s disease (PRKN-PD), and .Schwere Störung: Alle Symptome stark ausgeprägt bis hin zur Bewegungsunfähigkeit (GdB bei 80-100%).role in pathogenesis of juvenile autosomal dominant Parkinson disease – review. Bei Mutationen im LRRK2- und PRKN-Gen ist die Lebenserwartung jedoch ähnlich der nicht Erkrankter, wie Daten aus Frankreich zeigen – Informationen, die auch in die Patientenberatung einfließen sollten. They may also have mental and . Parkin encodes a ubiquitin-protein ligase, and Parkin is involved in mitophagy, a type of macroautophagy, in concert with PTEN .
Analysis of Heterozygous PRKN Variants and Copy-Number
PRKN is a recessively inherited gene of Parkinson’s disease (PD); in other words, humans develop PD only when the gene is recessively homozygous. However, new research suggests that the role of PINK1 and PRKN in Parkinson’s could be more complex and involve other genes — like PARK7 (DJ-1), SNCA (alpha-synuclein) and FBXO7 — as well as a fat molecule called cardiolipin.
- Prime Video App Kostenlos | Amazon Prime Video im App Store
- Prime Video Download Laptop _ 8 Beste Amazon Downloader für PC und Mac 2023
- Private Krankenversicherung Beamte Kündigen
- Produkey 64 Bit : Télécharger ProduKey (gratuit) Windows
- Professional Make Up Palettes _ 15 Best All-In-One Makeup Kits and Palettes in 2023
- Profertil Erfahrungsberichte | Orthomol Fertil Plus: Test und Erfahrungsberichte
- Proclamação Da República Resumo
- Private Versicherungen In Europa
- Prof Kohlhäufl Leonberg | Ihre Fragen zu Pneumologie
- Processus Spinosus _ Halswirbelsäule
- Profiltext Generator : Cool Text Graphics & Logo Generator
- Probe Bahncard Fahrplan , Muss ich meine Probe BahnCard kündigen?
- Pro Golf Live Score : KPGA DB Insurance Promy Open 2024
- Prince Charming Anmeldung : Prince Charming (PC)