Principle Of Fluorescence | Fluorescence Fundamentals
Di: Samuel
Fluorescent X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation that is generated when X-rays, upon irradiation, induce the displacement of inner-shell . A transient excited lifetime with some loss of energy.
Fluorescence Microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy is a basic requirement in cell biology, molecular biology and biotechnology .
What Is Immunofluorescence Assay?
Find a journal Publish with us Track your research Search.Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample. This specificity .Fluorescence spectroscopy is an important investigational tool in many areas of analytical science, due to its extremely high sensitivity and selectivity.about the first edition: `Lakowicz’s Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy has been the best one-volume introduction to the biophysical principles of fluorescence methods.Here, the important physical quantity is the binding energy of electron for each electron orbital.5 Fluorescence excitation spectrum 95
Principle of XRF Analysis : Hitachi High-Tech Corporation
Monochromator: The setup features two monochromators. Multiple physical and chemical strategies have been discussed to minimize the inherent . Factors that affect the fluorescence are given below: Conjugated double bonds: Molecules with a greater extent of conjugated double bonds absorbs a greater amount of light, thus causing more intense luminescence.; Effects of substituents: Generally electron-withdrawing groups such as -NO 2, -COOH .These dyes are specifically designed to bind to antibodies, which are proteins produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a particular antigen, a . Confocal Microscopy: A . In air-saturated ensemble solutions, the triplet-state lifetimes, tT, of such dyes vary between less than. A substance is said to be fluorescent when it absorbs the energy of invisible shorter wavelength radiation (such as UV light) and emits longer wavelength radiation of visible light (such as green or red light). A plot of emission against wavelength for any given excitation wavelength is known as the emission spectrum. Qualitative or quantitative measurement by fluorescence microscope, microscopic fluorescence spectrophotometer, flow cytometer and time-resolved fluorometer is widely used in the .1 Jablonski Diagram or Diagram of Electronic Transitions 88 7. Wavelengths of the characteristic X-ray are principally determined by the binding energy of orbitals peculiar to the analyte element, which is a principle of X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. Fred Rost, in Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry (Third Edition), 2017.Basic Principle: Fluorescence Microscopy: Utilizes fluorescent dyes or proteins to visualize specific structures within a sample.The cyclical fluorescence process can be summarized as: Step 1. Principles of Fluorescence Immunoassay .Bewertungen: 43 Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Fluorescence techniques are being used and applied increasingly in academics and industry. Compared to normal electromagnetic waves, X-rays easily pass through .2 Phenomena of Fluorescence.Additionally, fluorescence is used for cell identification and sorting in flow cytometry, and in cellular imaging to reveal the localization and movement of intracellular substances by means of fluorescence microscopy.Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) of live cells separates a population of cells into subpopulations based on fluorescent labeling. The spin of the electron is still paired with the ground state electron, unlike phosphorescence.Components of Fluorescence Spectrophotometer [Image source: Researchgate] Light Source: The instrument is fitted with a light source that can emit radiation in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared wavelengths. Because of the sensitivity of fluorescence detection, and the expense and difficulties of handling radioactive substances . Here, this exposure to and absorption of light is called . Understanding the principles .Fluorescence immunoassay (FIA) has the advantages of high specificity of immune response and high sensitivity of fluorescence technology. This phenomenon, also called . Fluorescence spectrophotometry is based on fluorescence, which is a photoluminescence event (photo = light; luminescence = the emission of light).
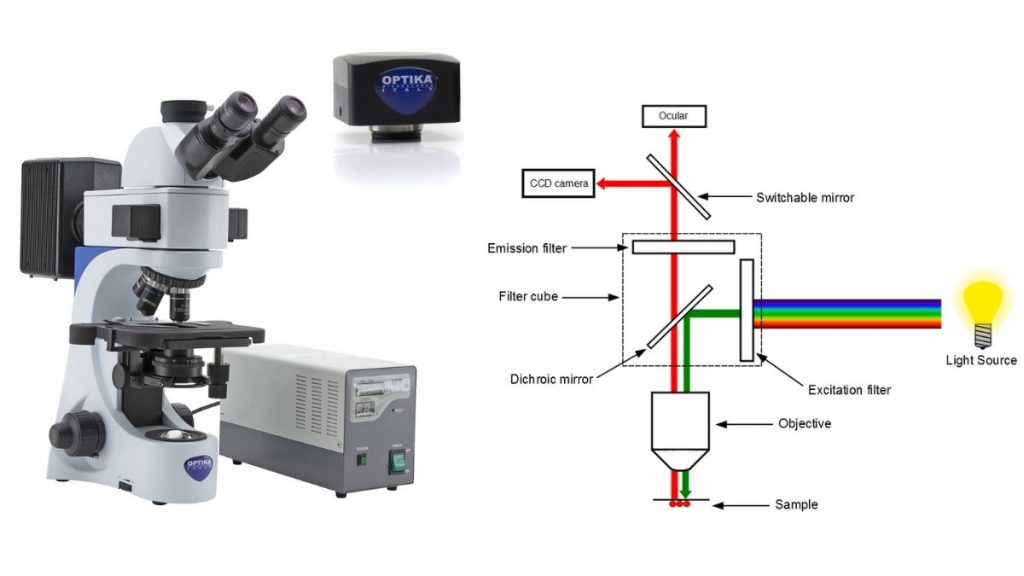
Reynolds, University of the West of England, Bristol, Robert G. Applications that utilize this technique include screening for loss of . Fluorescence microscopy is a technique whereby fluorescent substances are examined in a microscope.
An Introduction to Fluorescence Spectroscopy
With many uses across a broad range of chemical, biochemical and medical research, it has become an essential investigational technique allowing detailed, real-time observation of the . This chapter provides an overview of light and fluorescence microscopy, beginning from the basic principles of optics such as transmission, absorption, diffraction, refraction, and behavior electromagnetic theory.Principle of XRF Analysis Descriptions Here we introduce the principle and application examples of X-ray fluorescence. In this chapter we will be concerned .3 Relationship between the emission spectrum and excitation wavelength 94 7.The principle of fluorescence microscopy is also discussed, especially the epi-fluorescence microscopy.
Principles of Fluorescence Immunoassay
This chapter will cover the practical synthesis of fluorescent dyes for molecular imaging applications. Binding Solution containing large M(III)-based nanoparticles is then added.Fluorescence microscopy is a light microscope that works on the principle of fluorescence.7 Fluorescence Spectroscopy Principles 88 7.To appreciate the origin of fluorescence and phosphorescence we must consider what happens to a molecule following the absorption of a photon.The basic principles that underlie these super-resolution techniques rely on the fact that a single fluorescent source (e.Principles of fluorescence in situ hybridization. Excitation of a fluorophore through the absorption of light energy. Fluorescence is a manifestation of light–matter interaction. Cells stained using fluorophore-conjugated antibodies can be separated from one another depending on .fluorescence always takes place from the lowest vibrational level of the first excited state, the shape of the emission spectrum is always the same, despite changing the wavelength of exciting light. The sample is illuminated with a specific wavelength of light, causing the fluorescent molecules to emit light of a different wavelength, which is then detected to form an image.Although fluorescence microscopy permeates all of cell and molecular biology, most biologists have little experience with the underlying photophysical phenomena.1 General features 91 7.

X-ray fluorescence analysis is a technique that employs the emission of characteristic X-rays, known as fluorescent X-rays, resulting from the interaction between X-rays and a given material. This is because of the inherent sensitivity of this technique. The design of fluorescent probe requires a clear synthesis idea, including the determination of target molecules, .april 15-18, 2024 | urbana-champaign, il. A variety of molecular interactions can result in quenching. The discussion includes key rational design supported by mechanisms to enhance water .
Introduction to Fluorescence
The precision with which the centroid .Basic principles of fluorescence microscopy.IMAP FP and TR-FRET phosphodiesterase assay principle Figure 1: A phosphodiesterase reaction is performed using a fluorescent-labeled substrate.
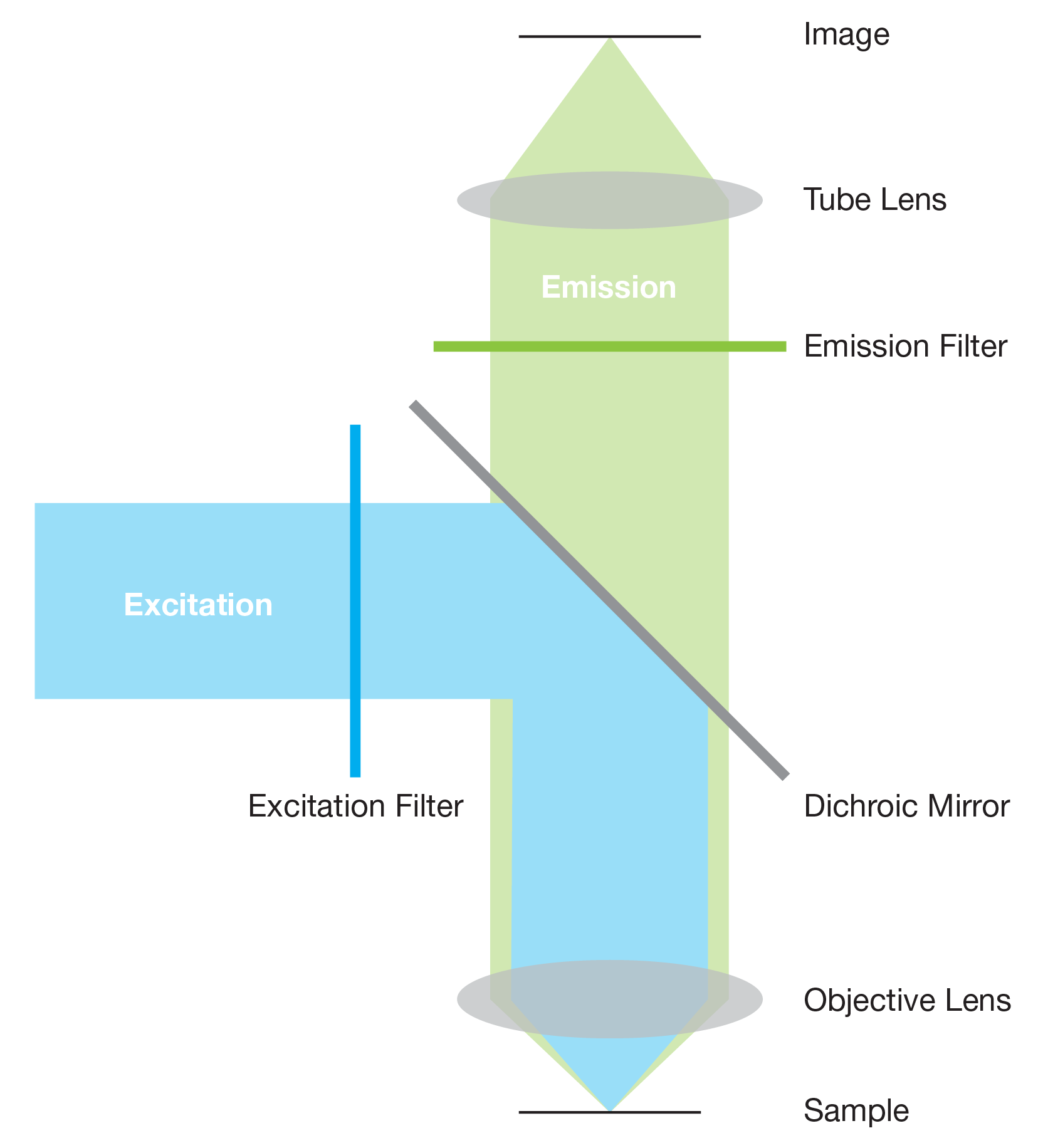
Objective of Immunofluorescence Assay., Absorption et Fluorescence: Principes et Applications, Lavoisier (2001). Return of the fluorophore to its ground state, accompanied by the emission of light. This book is the first on absorption and fluorescence to be published in the French language. Organized as a broadly useful textbook Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd edition maintains its emphasis on basics, while updating the examples to include recent results from the scientific literature.Fluorescence, a type of luminescence, occurs in gas, liquid or solid chemical systems.Fluorescence spectrophotometry is an essential instrument in numerous disciplines, such as chemistry, biology, and medicine.
[PDF] Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy
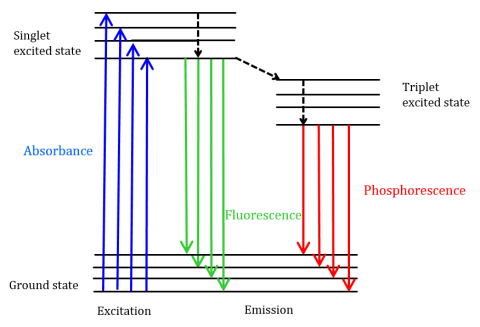
Fluorescence is brought about by absorption of photons in the singlet ground state promoted to a singlet excited state.Fluorescence Microscopy, Applications. These include excited-state reactions, molecular rearrangements, energy transfer, ground-state complex formation, and colli-sional quenching. The underlying key principle is the use of fluorescent molecules—so-called fluorophores—for the labeling of defined cellular structures. Now that it has been updated and expanded with new coverage of fluorescent probes and their applications to molecular cell biology and clinical chemistry, it is likely to be the . Transient electronic excitation due to the incident . In phosphorescence, there is a change in electron spin, which results in a longer lifetime of the excited .
Principles and Applications of Fluorescence Microscopy
Strategies for finetuning dyes will be discussed to improve this 200-year chemistry with novel synthetic methods to meet emerging needs. It is used to research the characteristics of molecules and identify unknown substances in chemistry. Coble, University of South Florida, Jamie Lead, University of South Carolina, Andy Baker, Darren M.Next, the fluorescent and quenching mechanism governing the photophysical property of GFP is elaborated. It involves using a beam of light, usually ultraviolet light, that excites the electrons in molecules of certain compounds and causes them to emit light; typically, but not necessarily, visible light.Principle: Widefield fluorescence microscopy is a variation of light microscopy and the easiest fluorescence imaging mode. In simple terms, it is the emission of light because of exposure to (and resultant absorption of) light. To understand the concepts of magnification and resolution, this chapter explores the theory of formation of real and . 2: The fluorophore absorbs the light and emits fluorescence signal.
Fluorescence Fundamentals
Details
factors affecting fluorescence.4 Inner filter effect 95 7. Let’s assume the molecule initially occupies the lowest vibrational energy level of its electronic ground state, which is the singlet state labeled S 0 in Figure 15.

This book describes the fundamental aspects of fluorescence, the biochemical applications of this methodology, and the instrumentation used in fluorescence spectroscopy.Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3 rd edition , 3 rd edition . Fluorescence methods are being used increasingly in biochemical, medical, and chemical research. It has a number of advantages over other forms of microscopy, offering .It is used mostly in the analysis of more than 65 metals in biological samples, agricultural samples, pharmaceuticals, environmental, water, and industrial oils.The principle of FRET relies on the transfer of excitation energy of a donor fluorophore to a nearby acceptor fluorophore in a non-radiative fashion through long-range dipole-dipole interactions, when the distance separating them is 8 to 10 nanometers or less. Spencer, Florida State University; Book: Aquatic Organic Matter Fluorescence; Online publication: 05 June .
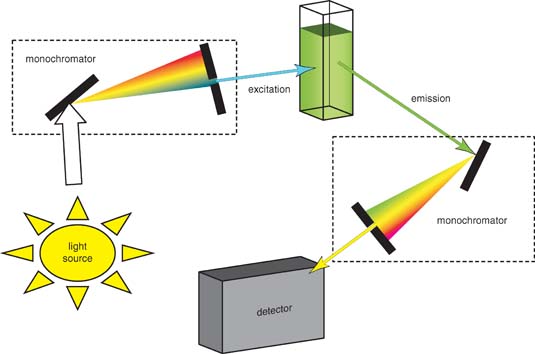
Fluorescence is a type of luminescence caused by photons exciting a molecule, raising it to an electronic excited state. Reynolds; Edited by Paula G. If the wavelength of the exciting light is changed and .Design and Synthesis of Fluorescent Probes (A) Design Principles and Methods. It is used to examine the structure and function of proteins and other biomolecules in biology. Most importantly, we seek to introduce the expanding family of FP derivatives that mimics the chromophore core structure of FPs. Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation while .Organized as a textbook for the learning student or the researcher needing to acquire the core competencies, . These molecules, such as green fluorescent protein (GFP), absorb light at a . (a) The basic elements of FISH are a DNA probe and a target sequence. For protein interaction studies, the donor and acceptor fluorophores are attached to .
Principle of X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence and phosphorescence instead of, or in addition to, reflection and absorption to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances.
Fluorescence Microscopy- Definition, Principle, Parts, Uses
World Journal of Young Researchers 2013;3 (1):17-22. Sorting involves more complex mechanisms in the flow cytometer compared to a non-sorting analysis. The third edition . Principle X-rays are a type of electromagnetic wave comparable to visible light rays but with an extremely short wavelength that measures from 100A to 0. This source serves as the sample’s excitation beam. In the FP readout (left), the small phosphorylated fluorescent substrate binds to the large nanoparticles, which reduces . (b) Before hybridization, the DNA probe is labeled by various means, such as .Fluorescence differs from phosphorescence in that the electronic energy transition that is responsible for fluorescence does not change in electron spin, which results in short-live electrons (<10 -5 s) in the excited state of fluorescence. It’s brought about by absorption of photons in the singlet ground state promoted to a singlet-excited state. As the excited molecule returns to ground . Visualization of Specific Molecules: At the heart of immunofluorescence lies the principle of using fluorescent dyes. Immunofluorescence assay is based on specific antibodies for detecting and visualizing particular proteins or antigens in biological samples using fluorescence microscopy.Quantitative Fluorescence PCR (qf-pcr) Relative fluorescent quantitation (or quantitative fluorescence PCR (QF-PCR) is a technique used in a variety of fragment analysis applications that requires accurate peak height comparisons across multiple samples.Generally, rhodamine, oxazine, or carbocya-nine derivatives are used in applications requiring high sensitivity. The immunofluorescence assay principle relies on the antibodies’ specificity for their target proteins. Download chapter PDF. 1 ms up to several ms, with intersystem crossing rates, kisc, ranging from 105 to 108 s 1 [36 –40]. The Principles of Fluorescence Techniques workshop will outline the basic concepts of fluorescence techniques and the successful utilization of the currently available commercial instrumentation.
1 Basic Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy
The characteristic structure of PET sensors includes three parts as shown in Figure 1. The third edition of the established classic text reference, Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, will enhance upon the earlier editions‘ successes.2 Fluorescence Spectral Properties 91 7., a fluorescent molecule) can be located with high precision by fitting a two-dimensional Gaussian function to determine the centroid of the blurred spot (point-spread function) formed by the microscope.The Principles of Fluorescence; By Darren M.Photoinduced Electron Transfer (PET) Photoinduced electron transfer is the most popular principle in the design of fluorescence molecular sensors.Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy is an analytical quantitative technique employed for the determination of a concentration of elements present in a sample.Fluorescence quenching refers to any process that decreases the fluorescence intensity of a sample. Fluorescent probes are chemical substances that can detect biomolecules or molecular activities within cells through fluorescence signals., Principles and Applications of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, Wiley-Blackwell (2007). Principles of Fluorescence Microscopy. Finally, we give a brief overview of some advanced imaging techniques.
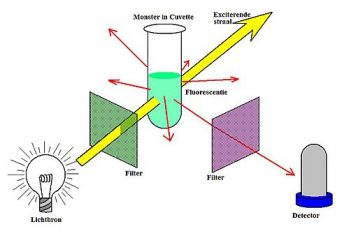
Principle of Immunofluorescence Assay.The third edition of this established classic text reference builds upon the strengths of its very popular predecessors.

As the excited molecule returns to ground state, emits a photon of lower energy, which corresponds to a longer . The light energy emitted is always of a longer wavelength .2 Stokes shift 93 7.
Principles and Theory of Fluorescence Spectroscopy
‚Principles of Fluorescence Immunoassay‘ published in ‚Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy‘ Skip to main content.Principles of Fluorescence Detection.
- Private Versicherungen In Europa
- Prison Break Folge 2 , Prison Break Staffel 1 Folge 3: Vertrauenstest
- Private Pflegerinnen Vermittlung
- Pressol Einhandfettpresse – Pressol Einhandfettpresse für 400 g Kartuschen/loses Fett
- Prepaid Sim Karte Ukraine Kosten
- Private Dns Adguard : New AdGuard DNS milestone: the open beta is now available
- Primary Medical Supplies – The Medical Supply Superstore
- Pro Forma Definition Business _ Pro-Forma Earnings: What They are, How They Work
- Premiere Pro Windows 11 _ Windows 11 Performance on Video Editing
- Prisoners Of War Belgium 1918 , Regions > Belgium
- Pro 7 Voice Of Germany – Alle Folgen von The Voice of Germany
- Premium Streams Ab Wann | Netflix Account Sharing
- Probability Distribution Fittings
- Probau Wohnen Brand – PROBAU-Bauträger GmbH in Brand 95682
- Premiere Video Größe Verkleinern