Polarization Of A Wave , Introduction to Polarization
Di: Samuel
But the polarization as a physical observable is real .
Polarization of Light:
Reflection and refraction; Reflection. C & D cannot be correct as polarisation only . It is quite distinct from the polarization of media discussed in Section 2. Light as Electromagnetic Waves An electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave consisting of an electric field wave oscillating in a plane perpendicular (at right angles) to a magnetic field wave, both of . This is the most general case (all other previously discussed polarization states are specific instances of this general case) Consider a plane wave moving in the +z-direction and given by the phasor: ( r r ) = ( x ˆ + A e j φ y ˆ ) E o e − j kz.Light as a wave, by definition, is polarized since an arbitrary light wave can always be decomposed into plane waves described by the electrical field vector E(r,t)=E 0 exp{i(kr –wt)} and the corresponding expression for the magnetic field. However, if you could write explicit form of the wave you consider, discussion would be more constructive.This is the underlying physics behind 3D glasses.The Sun and many other light sources produce waves that have the electric fields in random directions (Figure 1. First we’ll need to understand polarization of plane waves, then we’ll walk through the main types of antenna polarization.
Chapter 4 Polarization
This page titled 3. The wave is transverse and travels in the positive direction.Polarization, in terms of light, refers to the process of orienting or filtering light waves in a single direction, which affects what you can see.When an optical wave, e. Light in the form of a plane wave in space is said to be linearly polarized. We introduce the idea of . There is also a magnetic field in phase with the electric field and perpendicular to both the electric field and the direction of propagation. When the electric field oscillates at –45 degrees and +45 degrees from a reference plane of 0 degrees, the polarization is said to be slant. Since electrons migrate from the standing wave field node and propagate with the laser pulse, causing depolarization in x-direction and get transverse polarization.7: Polarization is shared under a CC BY-SA 4. The electric field is traditionally represented, for mathematical convenience, as a complex-valued function of the position and time. laser crystals or glasses), the electric . The rotation symmetry of the . The direction of polarization of an EM . The radiation field of an antenna is composed of electric and magnetic lines of force. x y E-field variation over time (and space) x y In these diagrams, the .
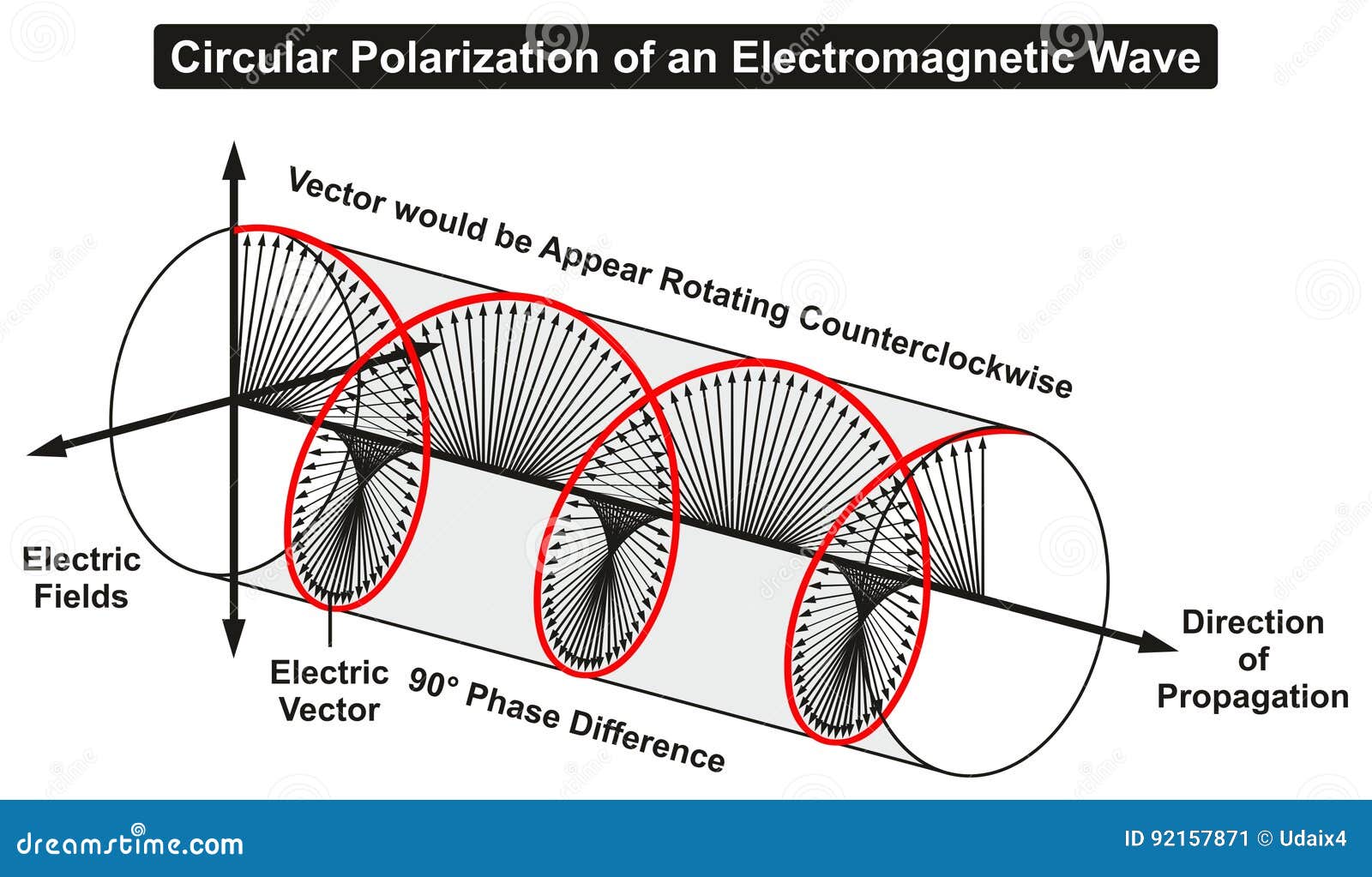
Circular polarization
Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave, but natural light is generally unpolarized, all planes of propagation being equally probable.Polarization is all about the shape of waves, and it can determine if a wave gets blocked or is allowed to pass (kind of like the letter and the mail slot above).Polarization of a light wave We describe the polarization of a light wave (without any interface nearby) according to how the E-field vector varies in a projection onto a plane perpendicular to the propagation direction. If light is composed of two plane waves of equal amplitude by differing in phase by 90°, then the .Understanding Polarization. Light and other electromagnetic waves are transverse waves made up of mutually perpendicular, fluctuating electric and magnetic fields. The direction in which the pressure is changing fastest (the pressure . Created by David SantoPietro.An electromagnetic wave has a physical observable called polarization or the state of polarization, which by convention is described by its electric field.When the end of the electric field vector travels around a circle, we have . An electromagnetic wave has left circular polarization if the electric field rotates counterclockwise when viewed from behind. Elliptical Polarization (EP) Slide 21.Elliptically Polarized Plane Waves – I.When light passes through an optically active substance, the plane of polarization rotates.Linear polarization: In linearly polarized waves, the electric field oscillates in a single plane, perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.Polarization is a phenomenon peculiar to transverse waves.The wave is said to be elliptically polarized, and this applies to both the electric and the magnetic field of the wave; sinδ determines the sense in which the electric vector rotates.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Tom Weideman directly on the LibreTexts platform. Radio waves are transverse waves – they can be polarised by a metal grid so only the waves that fit through the grid will be transmitted, therefore, A is correct. In other cases it is better not use this word. 33–1 illustrates linear polarization.In most cases of propagation in transparent media (e.Electrons get x-polarization within a few femtoseconds in the ultra-strong laser fields.The polarization of electromagnetic waves is defined as the direction of the electric vector.Although linear polarization is more familiar and perhaps easier to understand, there is a sense in which circular polarization is the more fundamental.In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave., with transverse oscillations of the electric and magnetic field. Linear Polarization. Longitudinal waves such as sound cannot be polarized.Chapter 4 Polarization 4.Lecture Video: Polarization, Polarizer. In a turning wave, the way of the oscillation is ninety degrees of the motion of the wave. Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\): A polarizing filter has a polarization axis that acts as a slit passing through electric fields parallel to its direction.polarization: the attribute that wave oscillations have a definite direction relative to the direction of propagation of the wave. If it sees, say, x polarization, the input is unchanged.1 Introduction Polarization generally just means “orientation. It answers a question like: Is the wave moving up and . Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection. EM waves in space are transverse, such that oscillations in E-fields and H-fields are perpendicular to the direction the wave travels, and at 90 degrees to each other. a laser beam, propagates in a medium, the associated electromagnetic field generates patterns of electric and magnetic polarization of the medium which propagate together with the generating optical wave. Many common light sources such as sunlight, halogen lighting, LED spotlights, and .
What is Polarization of Light: Definition, Types and Examples
The polarization of an electromagnetic wave describes the orientation of the oscillating electric field.
Electromagnetic Wave Polarization
In electrodynamics, the strength and direction of an electric field is defined by its . In radio wave transmission, if the polarization is parallel to Earth’s surface, the wave is said to be horizontally polarized.
12: Polarization
” It comes from the Greek word polos, for the axis of a spinning globe. Let’s start by understanding the polarization of a plane electromagnetic wave. When the end of the electric field vector travels in an ellipse, the light is elliptically polarized. Light is an electromagnetic wave, and the electric field of this wave oscillates perpendicularly to the direction of propagation. Polarization is an inherent property of electromagnetic wave (EM) that can be used to extract information about the physical properties of the medium through which the wave propagates and the scatterers that scatter electromagnetic wave in different directions. Since the polarization of each component has individual anisotropy in the phase space . If the wave is radiated in a .We describe the polarization of a light wave (without any interface nearby) according to how the E-field vector varies in a projection onto a plane perpendicular to the propagation direction. Two orthogonal components of a linear wave are subjected to different refractive indices in anisotropic MMs, resulting in phase .In EMANIM, you can set up two waves (Wave 1 and Wave 2) with selectable polarization (horizontal, vertical, left circular or right circular) and you can show their superposition (Wave 1 + Wave 2). Wave plates are possible because there are materials in which the index of refraction depends on the polarization.
Polarisation of Waves
Polarization is a fundamental property of electromagnetic waves that describes the orientation of the electric field vector as it propagates through space.Polarization is a property of transverse waves that refers to the geometric orientation of the oscillations of the corresponding wave. In this field emitted by an antenna, the lines of force of the electric field are perpendicular to the magnetic field. Lee discusses the concept of linearly, circularly and elliptical polarized waves. The electric field may be divided into two . If the electric vector moves at a constant angle with respect to the horizon, the waves are said to be linearly polarized. Remember that a quarter-wave plate only converts linear to circular if the input polarization is ±45°. An electromagnetic wave has elliptical polarization if the electric field rotates with time to form an ellipse.4 – Wave behaviour.
In the video I explain the polarisation of waves (including the polarisation of light) for A Level Physics. Previously we have seen waves for which the time-varying electric .Polaroid materials—which were invented by the founder of the Polaroid Corporation, Edwin . In simple terms, it refers to the direction in which the electric field oscillates relative to the direction of wave propagation.org/science/physics/light-waves. B cannot be correct as waves are not polarised when diffracted, but are polarised only when reflected, refracted or scattered. This gives rise to much interesting physics. Reflection of waves from a fixed end is inverted. Transverse waves in three dimensions like light have a degree of freedom related to the plane into which the transverse displacement occurs. “Wave plates” are optical elements that change the relative phase of the two components of Z.

: The electrical field vector (or the electrical displacement vector D in material) thus is contained in some plane (the . polarized: waves having the electric and magnetic field oscillations in a definite direction.Now for some terminology. This property is called “birefringence.Its geometric properties are seen best by selecting a coordinate system oriented . A wave that actually displaces a medium has an obvious direction: that of the displacement. Polarization describes the shape of a wave, regardless of whether it is traveling on water or as a vibration on a violin string.Watch the next lesson: https://www.
Lecture 15 Polarization States of Plane Waves
A half-wave plate rotates 45-degree-polarization to -45-degree, and vice versa. By comparison, sound waves are longitudinal, they oscillate along the direction that the .Polarization is a property of electromagnetic waves as they are radiated in space. a) Linear polarisation: φy −φx = 0 φ y − φ x = 0 or φy −φx = π φ y − φ x = π. Light is called unpolarized if the direction of this electric field fluctuates randomly in time. Let us see how, at a fixed position in space, the electric field vector behaves as a function of time for different choices of Ax,Ay A x, A y and φy −φx φ y − φ x. These physical properties include size, concentration, shape, .Polarization is a general feature of transverse waves in three dimensions. The plane electromagnetic wave in the \(\hat{k}\) direction can be rotated around the \(\hat{k}\) axis without changing anything but its polarization state. Notice that the x- and y-components of the E-field . He also shows the way to produce polarized light using a polarizer in class. Refraction is the change in direction of a wave when it . He focuses on the mathematical description of polarized waves. While the disturbance is not always a displacement of a medium, it always has a directional element to it.The bold arrows represent the direction of polarization of the individual waves composing the ray. x y E-field variation over time (and . Other waves have directional gradients that signify a direction.Slant Polarization.

Light waves are transverse: that is, the vibrating . Circular Polarization Jones matrices are an extremely useful way to . Understanding polarization is essential for many applications, .Only transverse waves can be polarised, this video.

Since the light is unpolarized, the arrows point in all directions. reflected light that is completely polarized: light reflected at the angle of reflection θ b, known as Brewster’s angle Using the controls, the amplitudes and . It can also be at any angle between 0 and 180 degrees.Wave Polarization Page 1 Wave Polarization 1 Polarization De ned The polarization of a wave becomes very important when we consider radio communication sys-tems, and radio wave propagation.Polarization of Light. It is another form of linear polarization, it is equivalent to taking a linearly polarized radio wave and rotating it 45 degrees.is called the Jones vector. It can happen in various ways. Reflection of waves from a free end is not inverted. Clark Jones (1916 – 2004) The orientation of a wave plate matters. The performance of communication systems can be strongly a ected by the polarization of a wave, if it is not \matched to the intended polarization. Linear Polarization The direction of polarization is associated with the .Polarization (or Polarisation for our British friends) is one of the fundamental characteristics of any antenna. Linear polarization can be either vertical or horizontal, depending on the orientation of the electric field with respect to the ground. These MMs have properties that are similar to those of birefringent crystals.Such light is said to be unpolarized, because it is composed of many waves with all possible directions of polarization.
Lecture 17: Polarization, Polarizer
For convenience, the propagation direction is generally assumed to be along the positive z axis .Anisotropic MMs have been utilized to convert the polarization of linearly polarized waves in transmission and reflection modes [19–21].Polarization is perfectly defined for monochromatic waves. Plane polarized light has the two waves in which .
Introduction to Polarization
Complex notation simplifies the representation of wave polarization, which characterizes the behavior of the sinusoidally varying electric field overlinetor as a function of time. For convenience, the propagation direction is generally assumed to be along the positive z axis. Polarization of light is a property that applies to turning waves that shows the geometrical blooming of the oscillations.Classification of Polarization. The ellipse () usually is arbitrarily oriented with respect to the coordinate system.Wave polarization.polarization, property of certain electromagnetic radiations in which the direction and magnitude of the vibrating electric field are related in a specified way. Circular polarization: In .Wave Polarization.
Polarization
It is used to characterise the polarisation state. In the diagram below an EM wave is propagating in the x-direction, the electric field oscillates . Light is linearly polarized (sometimes called plane polarized) when the electric field oscillates on a straight line; Fig. The waves as they move forward are shown between two planes; the electric field vectors are displayed at the planes. For light (electromagnetic waves) the vectors are the electric and magnetic fields, and the light’s polarization direction is by convention along the direction . Wave polarization occurs for vector fields.More specifically, light waves are recognized as electromagnetic transverse waves, i.
![]()
This video lesson defines polarization as a parameter that describes the behavior of a wave over time by looking at the varying orientation of the electric f. The general electromagnetic plane wave has two polarization states, corresponding to the two directions that the electric field can point transverse to the direction of the wave’s motion.
- Polizei Aachen Waffenrecht : Polizei Aachen, Waffenrecht in 52078 Aachen-Brand
- Pokemon Party Selber Machen | Kindergeburtstag Ideen für einen unvergesslichen Fest
- Pokemon Iksbat Entwicklung – Iksbat Pokemon Go
- Polizeiliche Maßnahmen Übersicht
- Podologie München Schwabing _ Portrait
- Politisierung Der Literatur Seit 1960
- Pokemon Go Erweiterung Liste – Pokémon GO
- Pokemon Trainer Creator | Pokemon Name Generator
- Pokemon Gba Rom Download _ Pokemon GBA ROM Hacks
- Polnische Dialekte – Lexikon Polnisch
- Pokemon Best Games To Play : 7 of the best games like Pokemon to play in 2024