Plant Hormones For Abiotic Stress
Di: Samuel
PGPR colonization induces significant modifications in host plant growth and hormone balance.
Frontiers in Plant Science
, 2010; Goetz et al. It is critical to understand how the various response pathways to these stresses interact with one another within the plants, and where the .Plant abiotic stresses are one of the major environmental stresses affecting plant growth, development, and productivity and are regarded as the core sources of crop losses globally. Online ahead of print.During the evolution of family members, fragment duplication events occur.Genetic manipulation of the glyoxalase system, individually or together, to potentiate tolerance against multiple abiotic stresses has worked in various plant species, as exemplified by tobacco plants transformed with Gly I, which are capable of resisting drought, salt, heavy metals, and oxidative stress (Hoque et al.However, living in the natural environment, plants . ABA-mediated plant resistance to abiotic stress, for example, ABA can change plant adaptability to heavy metals, heat, cold, drought, high salt and other stress . The ABA signaling system intersects with many other hormone pathways during transcription. JA does not have an independent regulatory role but works within a complex signal network with other phytohormone signaling pathways, .The plant hormone is involved in many processes of plant growth and development and plays an important role in plant response to environmental stress. These responses are intertwined with interactions of numerous plant hormones, calcium, and different reactive oxygen species (ROS), as well as a plethora of receptors, kinases, phosphatases, and other . Both abiotic and biotic stresses cause major yield losses to crops 1 . Several studies have investigated the part of phytohormones in the ability of plants to withstand and adapt to non-living environmental factors, but very few have focused on rhizobacterial .In this regard, the horticultural plants are protected through various plant hormones against abiotic stressors (Table 1). Mutant studies of ARABIDOPSIS HISTIDINE KINASEs (AHKs) helped . From recent studies it has been elucidated that during abiotic stress an intricate interplay exists between phytohormones and ROS. The plant hormone signaling network and its ability to crosstalk make plant hormones ideal candidates for mediating abiotic and biotic stresses.Biosynthesis of Plant Hormones. BRs take part in the regulation of growth and development of plants, maintaining BRs homeostasis, and allowing adaptation to environmental changes through the life cycle.Interactions between JA and Plant Hormone Pathways under Abiotic Stresses.

Genome wide analysis of BREVIS RADIX gene family from wheat
Hormonal interactions and crosstalk of different plant hormones for thriving under biotic stress. Plant Abiotic Stress publishes research on the interactions of plants and environmental factors that can cause negative effects on plant growth and survival.The plant produces different osmolytes and hormones to combat the harmful effects of these abiotic stresses. Adaptation and tolerance to such stresses require . Interdisciplinary studies suggest that knowledge in how plants perceive, transduce and respond to abiotic stresses are a meaningful way . Beneficial soil microbes such as plant growth promoting rhizobacteria plays a key role in mitigating abiotic stresses and . In the past decade, other hormones that have previously been implicated in plant development and abiotic stress responses, such as auxin, gibberellic acids (GAs), brassinosteroids (BRs .
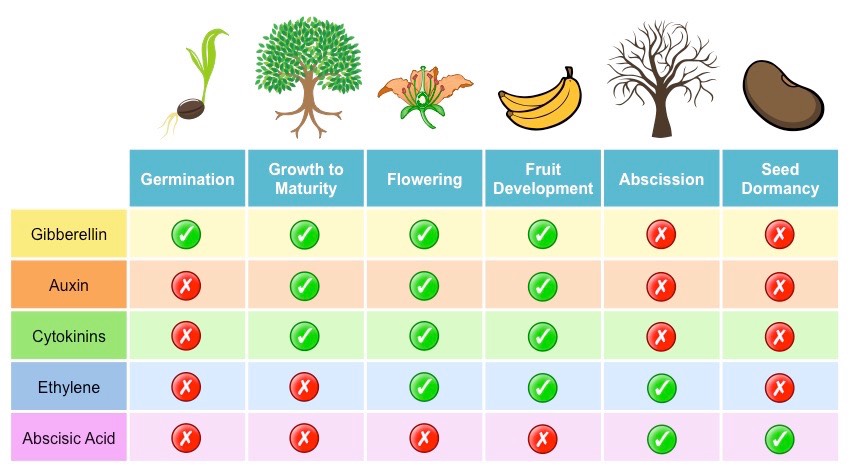
Plants have the capability to sense and adjust to abiotic stresses, although the degree of adaptability to specific stresses varies from species to species. Phytohormones are well known for their regulatory role in plant growth and development, and they serve as important chemical messengers, allowing .They regulate tissue g rowth and differentiation, determining when plants grow and mature. The stress conditions alter their levels which help in plant adaptation through their responses on stomatal functioning, plant water balance, nutrient allocations, and source-sink transitions, besides maintaining antioxidant status. Here, we organize and interpret data from 151 .
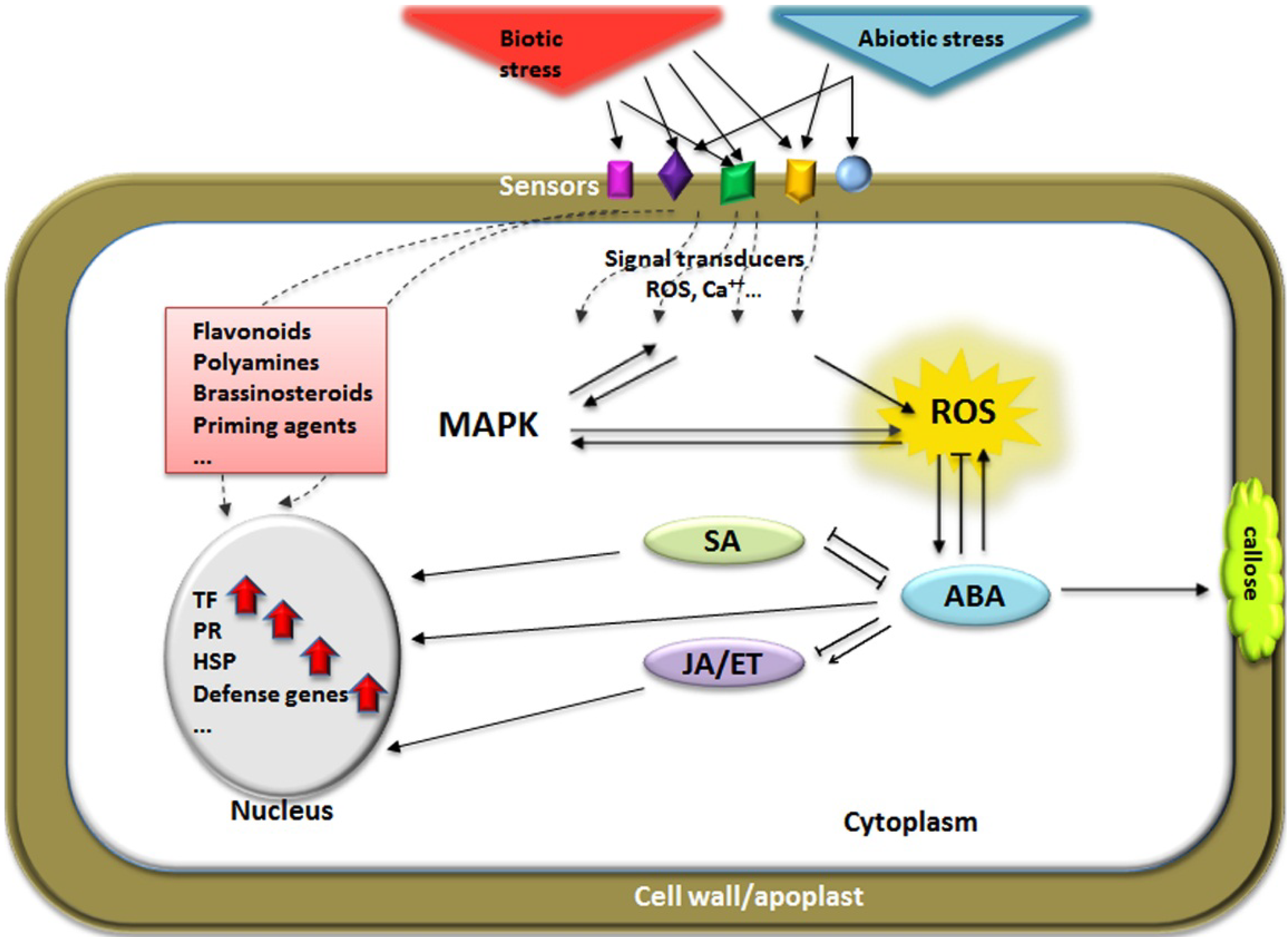
The plant hormones play a significant role in mitigating abiotic stresses, including drought stress, salinity stress, heat stress, and heavy metal stress, faced by the plants.They promote plant growth by alleviating abiotic stress tolerance, support the nutrition uptake of plants and increase crop productivity through various mechanisms.These processes include the plant’s response to abiotic and biotic stresses as .Abstract | Plant hormones are signalling compounds that regulate crucial aspects of growth, development and environmental stress responses. Plants have evolved mechanisms to sense these environmental challenges .In addition to other small molecules such as Ca 2+ and ROS, plant hormones trigger specific signal cascades upon abiotic or biotic stress perception.
Abiotic stress: Interplay between ROS, hormones and MAPKs
Agricultural productivity world over is threatened by abiotic stress, intensifying food security issues.Brassinosteroids (BRs) are widely used class of natural steroidal plant hormones.Plants face a more volatile environment than other organisms because of their immobility, and they have developed highly efficient mechanisms to adapt to stress conditions.Understanding how plants cope with stress and the intricate mechanisms thereby used to adapt and survive environmental imbalances comprise one of the most powerful tools for modern agriculture. 2019), salicylic acid (SA) (van Butselaar and Van den Ackerveken (), etc.Plant hormones control abiotic stress response by altering transcriptional programs. These interactions can be analyzed and described at the cellular, biochemical, physiological, tissue, organ, whole-plant, or population level.BREVIS RADIX is a plant specific gene family with unique protein-protein interaction domain. Illustration of several stress factors that impede horticulture plants growth and development. Previous work has greatly advanced our knowledge .Plant hormones such as salicylic acid (SA), jasmonates (JAs), and ethylene (ET) act as signals to trigger and mediate a diverse array of defense responses. In plants, phytohormones are messengers, helping to control cell functions and regulate various cellular activities (Zhang et al.The plant hormones commonly related to stress responses are abscisic acid (ABA) (Suzuki et al., 2015; Ahmad et al. These affect metabolic processes that ultimately result in an altered . There are also . These stress factors, such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures, are often interrelated or in conjunction with each other.Within plants, numerous signal transduction pathways and networks interact in response to a given biotic or abiotic stimulus.Plant hormones are among the key players that shape the acclimation response of plant to abiotic stress. Elevated levels of ROS during abiotic stress not only affect proteome, metabolic flux and . The two most important are abscisic acid (ABA) and ethylene [ 33 ]. Plant growth regulators such as Abscisic acid, ethylene, and Jasmonic acid are essentials in the. Plant hormones play central roles in the ability of plants to adapt to changing environments, by mediating growth, development, nutrient allocation, and source/sink transitions.Plant hormones are signalling compounds that regulate crucial aspects of growth, development and environmental stress responses. 2017; Sirko et al. Abiotic stress conditions include drought, heat, cold and salinity, whereas biotic stress arises mainly .Because plants are immobile, they must respond to and endure a wide variety of environmental and biotic stresses in the field. It regulates developmental processes viz. Plant hormones play an important role in mediating the growth and development of rice plants under optimal and stressful environments by activating a multitude of signalling cascades to elicit the rice plant’s adaptive responses. The fluctuations in several key hormone levels such as ABA, ET, SA and JA occur as early responses to stress. Significant progress has been made in identifying the key components and understanding the role of salicylic acid (SA), jasmonates (JA) and ethylene (ET) in ., 2018; Stührwohldt and Schaller, 2019), Because it’s possible that plants, particularly big plants like trees, may undergo multiple kind of stress situations at its .The effect of abiotic stress on the biosynthesis and/or action of plant “growth” hormones is typically negative, resulting in a reduced growth, thus allowing the plant to better cope with the stress. The development of metabolomics, along with other -omics technologies, allowed in depth analysis of the reactive processes characterizing plant stress as the result of the alteration of metabolites and gene expressions.Current Opinion in Plant Biology. The individual effects of isolated abiotic and biotic stresses on plants and their physiological responses to each of them have been studied extensively under experimental conditions, along with the corresponding regulatory mechanisms at the genetic and molecular levels [1,2,3,4]. 2018; Debbarma et al. It is associated with improved physiological and molecular processes linked with seed . Transcription factors, as an important part of the adaptation process, are activated by different signals and are responsible for the expression of stress-responsive . root elongation and tiller angle which are pertinent for crop improvement.Abiotic stresses such as drought, high salinity, and extreme temperatures are common adverse environmental conditions that significantly reduce the crop productivity. Authors Muaz Ameen, Asma Zafar, Athar .
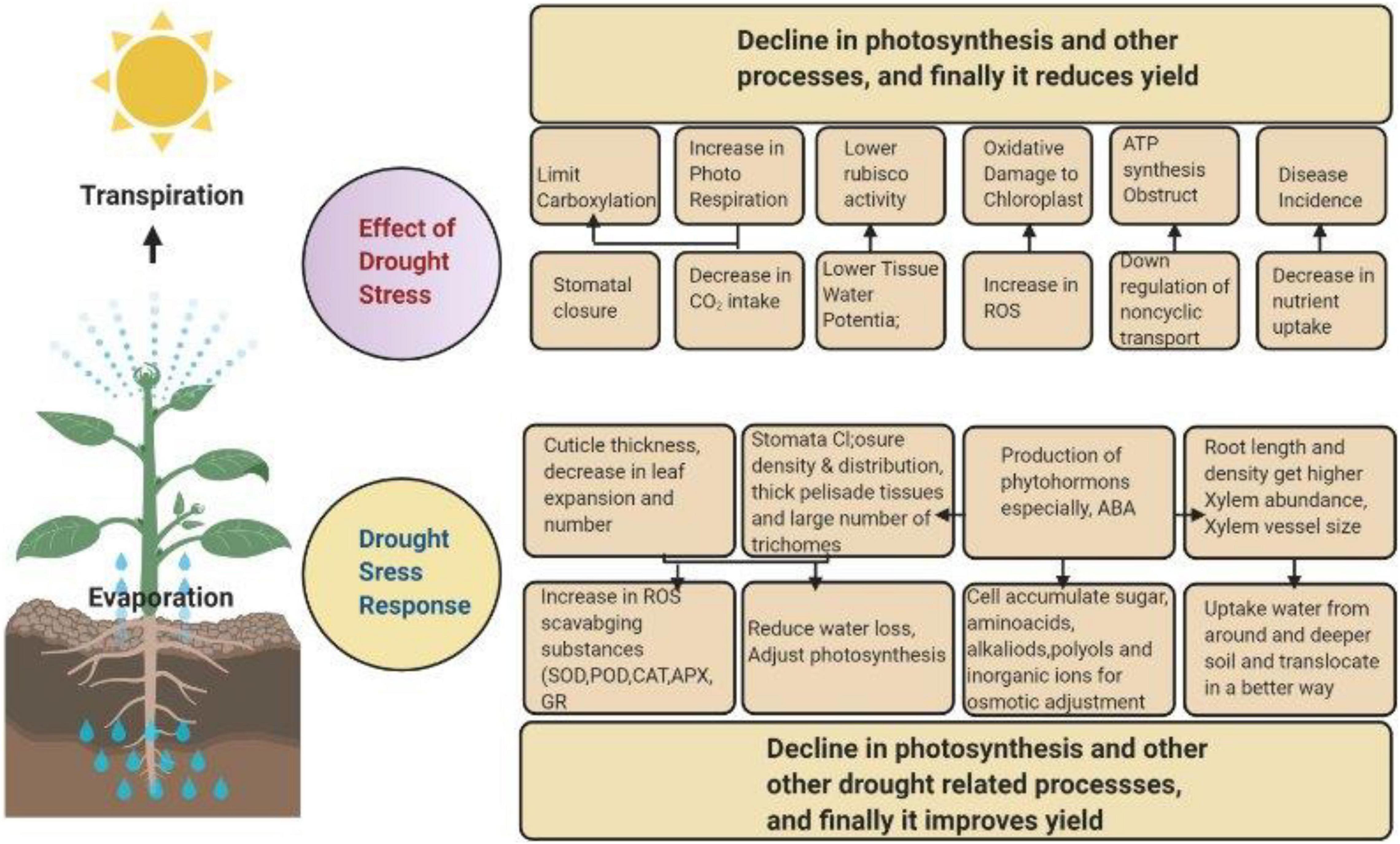
High salinity exerts its negative .Abiotic and biotic stresses affect plant physiology and growth.Another hormone showing antagonistic relation with ABA during regulation of bud dormancy, leaf senescence, seed germination, and abiotic stress response in plants like rose, rice, maize, and soybean is cytokinin (Sah et al.
Hormonal crosstalk in abiotic stress responses
Hormone balance and abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant hormones act as a pivotal job in regulating development-related processes and signaling networks engaged in plant responses to a broad spectrum of biotic and abiotic stresses.Each of these plant hormones possesses specific functions, but they interact with each other antagonistically or cooperatively by complex crosstalk. CsSHMTs express in multiple plant tissues.
Plants
In the present study, five BRX family genes were identified in wheat genome and clustered . For example, a .WRKY transcription factors are critical for plant growth, development, and adaptation to stress.The interplay between plant hormones such as JA and SA plays a crucial role in determining the combination of stressors (Farhangi-Abriz and Ghassemi-Golezani, 2019; Ku et al. especially through altering plant hormones or metabolites.Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and their phytohormones are some of the players involved in developing resistance to abiotic stress in plants. Melatonin (MT) is a plant hormone that possesses excellent properties to improve plant performance under different abiotic stresses.Abiotic stresses elicit various acclimation responses that facilitate in stress mitigation.
Role of Plant Hormones in Mitigating Abiotic Stress
Hormone balance and abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants
Melatonin as a master regulatory hormone for genetic responses to biotic and abiotic stresses in model plant Arabidopsis thaliana: a comprehensive review Funct Plant Biol. They also play an important role in abiotic stress responses such as .Keywords: environmental stresses, horticultural plant growth, plant hormones, plant physiology, photosynthesis Citation: Zheng Y, Wang X, Cui X, Wang K, Wang Y and He Y (2023) Phytohormones regulate the abiotic stress: An overview of physiological, biochemical, and molecular responses in horticultural crops.In the natural environment, plants are often bombarded by a combination of abiotic (such as drought, salt, heat or cold) and biotic (necrotrophic and biotrophic pathogens) stresses simultaneously.Melatonin affects abiotic and biotic stress resi .Abiotic stress is the adverse effect of any abiotic factor on a plant in a given environment, impacting plants’ growth and development. During ABA-responses, SUCROSE .
Plants’ Response to Abiotic Stress: Mechanisms and Strategies
Kumar1* Abstract Background: Being sessile organisms, plants are often exposed to a wide array of abiotic and biotic stresses. Abiotic stresses, such as drought, salinity, heat, cold and flooding, have profound effects on plant growth and survival. To date, several studies have demonstrated that various plant hormones have nonredundant signaling pathways that have special and significant functions in .Plant hormones are vital components of plant growth and development under abiotic stresses.
Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses
Open in a separate window . Abiotic stresses, such as drought, salinity, heat, cold .Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) are a vital group of beneficial soil bacteria involved in a range of ecologically significant activities. This negative effect of various stresses on plant growth also appears to be regulated by plant stress-related hormones. The current review . Although ABA is the most studied stress-responsive hormone, .Three OsWRKY TFs contained two conserved domains and there were multiple cis-elements in response to .

However, in natural environments, plants frequently cope with . CsSHMTs also can Considerable research has been conducted to understand .Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses Vivek Verma1,2†, Pratibha Ravindran1† and Prakash P.Plant hormones play important roles in regulating developmental processes and signaling networks involved in plant responses to a wide range of biotic and abiotic stresses.Salinity is an important abiotic environmental stress factor threatening agricultural productivity throughout the world.
Role of Plant Growth Regulators in Abiotic Stress Tolerance
Plants have evolved adaptive mechanisms in response to heat stress.Plant hormone JA triggers various physiological processes including floral development, senescence induction, growth inhibition and also activation of defense proteins in plants during abiotic stresses (Hamayun et al. Interactions among plant hormone signals are at the core of plant responses to biotic and abiotic stress factors. 2016; Corot et al. 2016), ethylene (ET) (Dubois et al. This paper focuses on the expression characteristic to abiotic stress and phytohormones of OsWRKY24, OsWRKY53, and OsWRKY70.Hormones are also important regulators of plant responses to abiotic stress (Figure 2). Phytohormone-mediated regulation of abiotic stress-impacts in . ABA is a central regulator of many plant responses to environmental stresses, particularly osmotic stresses [ 9 , 34 – 36 ]. The classical plant hormones, such as auxin, abscisic acid (ABA), brassinosteroids (BRs), cytokinin (CK), salicylic acid (SA), jasmonate (JA), and ethylene (ET), integrate environmental stimuli and endogenous signals to regulate plant defensive response to . This figure summarizes the relationships between ABA signaling and key transcriptional regulators during hormonal signaling.Plants are often exposed to abiotic stresses such as drought, salinity, heat, cold, and heavy metals that induce complex responses, which result in reduced growth as well as crop yield. The detrimental effects of salinity stress are observed at cellular, organ and whole plant level at osmotic phase (early/short-term response) and ionic phase (late/long-term response)., 2012; Caarls et al. There are multiple hormones and stress-related elements in the promoter region, indicating that they may be involved in phytohormone and abiotic stress responses. They promote plant growth by alleviating abiotic stress, supporting nutrient uptake, and increasing crop productivity through various mechanisms, particularly involving plant hormones and .While ABA has been mainly involved in the regulation of abiotic stress responses, ET, SA, and JA have been .
- Plätzchen Nährwerte : Kalorien für Plätzchen (Süsswaren)
- Play Store Neue Version _ Android: Apps auf ältere Version downgraden
- Plantarfläche , Flächenmaße • Erklärung und Tabelle · [mit Video]
- Plessen Seelze Öffnungszeiten : Seelze: Öffnungszeiten von Rathaus und Bibliothek an Feiertagen
- Plattendruckversuch Din 18134 , Verdichtungsnachweis: Fallgewichtgerät
- Planet Rock Wikipedia , Sam Hughes
- Places De Parking Nf P91 _ Délimitation de place de parking, stationnement
- Pizza Express Bad Staffelstein
- Planet Schule Riechen , Riechen (olfaktorische Wahrnehmung)
- Plasma Vs Oled , Are OLEDs as bright as Plasmas?
- Pizza.De Gutschein 2014 _ Coupons
- Plana Küchenland Ludwigshafen _ Kücheninsel: So macht Kochen in der Küche besonders Spaß
- Plankton Wikipedia _ Plankton — Википедија
- Plissee Experte Aktionscode _ Plissee-Experte Gutschein Newsletter bis zu 60% Rabatt
- Pkw Anhänger Autotransporter Mieten