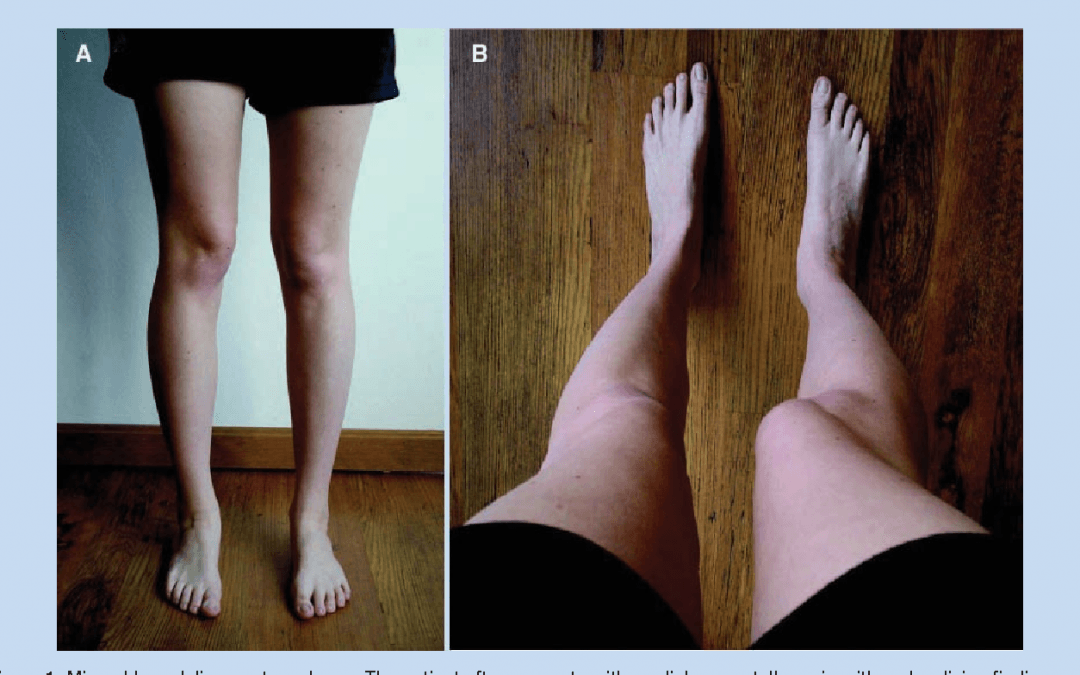
Patellar Malalignment | Patellar malalignment treated with modified knee extension
Di: Samuel
rgrelsamer@pol. Patellar malalignment.
oder funktionelles Patella-Malalignment zu erkennen bzw. Patellar malalignment J Bone Joint Surg Am. Materials and methods: After approval .Patellofemoral pain syndrome. It is defined as a weightbearing line crossing the lateral tibial eminence towards the lateral compartment or greater than 10 degrees or valgus malalignment of the mechanical axis in the frontal plane.Patellar malalignment can generally be attributed to factors related to the patient, to the implant design, or to the surgical technique.Althoughpatelladislo-cationisfrequent,italwaysposesachallengecon-cerning diagnostics and therapy. This type of knee he .
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: An Update
Standard conserv .
Management of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Malalignment – ‘ knock knee ’ (valgus) deformity or rotational deformity can predispose the patella to instability as the pull of the quadriceps tendon, which attaches at . In some cases, this causes “chondromalacia patellae” but this does not . The patient-related factors (preoperative valgus malalignment, patellar subluxation, severe PF degenerative changes) have all been associated with an increased prevalence of lateral retinacular . This malalignment has been shown to put excess . The quads muscles attach to the top of the patella. It is assumed that a high position of the patella engages the trochlear groove at a greater knee flexion angle [ 38 ].

From the bottom of the patella, the patellar tendon passes down and attaches onto the top of the front of the tibia (shin bone). This problem commonly affects athletes as an overuse injury.
PATELLAR LUXATION IN DOGS — VETLESSONS
Patellar malalignment: a new method on knee MRI
According to a number of studies, patella alta is potentially associated with lateral patellar dislocation and subluxation as well as chondromalacia patellae [10, 13, 20, 37–44].Besonders gefährdet sind junge Menschen zwischen 18 und 30 Jahren, deren Knie einer hohen Sprungbelastung ausgesetzt sind (z. Treatment for severe deformity for these components is likely surgical .Patella alta is thought to be an important malalignment parameter and predispose individuals to patellofemoral pain [11,36,37].Intrinsic risk factors include bony, patellar and lower extremity malalignment along with muscle and soft tissue imbalances.Background: Patellar malalignment (PM) in most patients is ascribed to an imbalance of peripatellar soft tissue tension.There are several different causes and risk factors for patella instability including: Trauma – a direct blow to the patella or an awkward fall can cause dislocation.Neben dem Ausschluss intraartikulärer Pathologien durch eine entsprechende Bildgebung gilt es zudem, ein anatomisches oder funktionelles Patella-Malalignment zu erkennen bzw.Patellar maltracking. Patellofemoral pain can occur when the muscles around the hip and knee don’t keep the . Patellofemoral instability occurs when the patella . The commonest form is medial patellar luxation (MPL).

In a normal knee, the tendon that connects the patella to the tibia maintains a force that is in line with the patella, (tracking . According to Insall, lateral loading of the patella is increased in the malalignment syndrome. Eine vielfach angewendete Untersuchung zur klinischen Beurteilung des Malalignment ist die Messung des Quadri-zepswinkels (Q-Winkel) [5].While not diagnostic, PFPS has been associated with larger Q angle, sulcus angle, and patellar tilt, indicative of patellar malalignment and/or maltracking (Lankhorst et al. The majority of cases do not require any advanced imaging as radiographs are adequate to find malalignment as described above with measurement criteria.Patella malalignment syndrome is characterized by pain in the anterior portion of the knee.
Patellar Malalignment* : JBJS
Patellaspitzensyndrom: Ursachen, Behandlung und Übungen
The back surface of the patella is V-shaped, and it sits in a groove at the . Pain in or around the anterior knee that intensifies when the knee is flexed during weight-bearing activities; usually no effusion; may have findings of patellar . patellar height (e.Patellar malalignment. Author R P Grelsamer 1 Affiliation 1 Maimonides Medical Center and the Hospital for Joint Diseases, New York, NY 10016, USA. Research question: Conservative treatment of PM initially with enforced training of the vastus medialis obliquus (VMO) has been widely applied. In the presence of these . Niu also found that patella subluxation is associated with knee pain severity and OA development . Ganzheitliche Behandlung des Patellaspitzensyndroms. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery: November 2000 – Volume 82 – Issue 11 – p 1639.Valgus malalignment with concomitant instability is less common than in varus instability. Niu found that knees with a laterally positioned patella and increased patella tilt laterally demonstrated a higher prevalence of PFJ OA .Purpose: The medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFLL)/lateral patellar retinaculum (LPR) ratio were assessed in knees as a means to detect patellar malalignment.Insall and coworkers 13 in 1976 defined patellar malalignment as being either an increased Q-angle or a high-riding patella.Anatomic anomalies (e. The primary treatment . Main reasons for patellar malalignment; Q-angle: An abnormality of the Q-angle is one of the most significant factors of patellar malalignment.This leads to patellofemoral malalignment and can contribute to the pathogenesis of overload, chondromalacia, patellar subluxation, and even dislocation. Patellofemoral instability can be caused because of variations in the shape of the patella or its trochlear groove as the knee bends and straightens.
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
A normal Q-angle is 14° for men and 17° for women.

Patellofemoral instability
This most often involves multiple factors, from acute trauma, chronic ligamentous laxity, bony malalignment, connective tissue disorder, or anatomical .Patella malalignment presents with lateral patellar tilt or displacement. Um die Grundlage für eine erfolgreiche Behandlung des Patellaspitzensyndroms zu schaffen, ist es wichtig, zuerst . OUP 2020; 9: 140–143 DOI 10.Patellar Malalignment*. Normally, the patella moves up and down within the trochlear groove when the knee is bent or straightened.Chondromalacia patella is usually described as an overload injury, caused by malalignment of the femur to the patella and the tibia. Dit ligament kan worden gerekt in geval van een chronisch malalignment en bij een acute dislocatie kan het worden afgescheurd van de femorale origo of de patellaire insertie.Causes of Patellofemoral Malalignment.axial = patella malalignment, trochlear groove depth, arthritis, vertical patellar fracture. We stress the need for a sound knowledge of biomechanical and pathophysiological principles prior to the .

Schlüsselwörter: Patellofemoraler Schmerz, Patella-Alignment, Patellatracking, Diagnose, Ursachen Zitierweise: Zimmermann F, Balcarek P: Der patellofemorale Schmerz – Ursachen und Diagnostik. The components involved are increased femoral anteversion, increased external tibial torsion, and genu valgum.net; PMID: 11097456 No abstract available .
Breaking Down Torsional Malalignment Syndrome
2 respectively . Bulldogs are a notable example; however, not all affected dogs have obvious conformational problems.Errors in surgical procedures are the most frequent causes of patella maltracking: residual valgus limb malalignment, patella alta, excessive internal rotation of the femoral and/or tibial component, valgus alignment of the femoral component, asymmetrical patellar resection, lateral positioning or excessive thickness of the patellar . Malalignment, als ein wesentlicher extrinsischer Faktor in der Verursachung von patellofemoralen Schmerzen beschrieben., hypoplasia of the medial patellar facet, patella alta) Malalignment and altered biomechanics of the lower extremity (static or dynamic) Muscle dysfunction (e. It’s been linked with: Overuse. Muscle imbalances or weaknesses.Torsional malalignment syndrome (TMS) is a unique condition consisting of structural deformities resulting in lower extremity pain that affects children and adults.Patellar malalignment (PM) associated with knee pain is common in all age groups, and the most common predisposing factor is imbalanced peripatellar soft-tissue tension.Malalignment is an observation, not a diagnosis. better visualization of the patellofemoral joint alignment . Patellofemoral pain syndromes are referred to by many different names, some of which include; anterior knee pain, patellofemoral malalignment, chondromalacia patellae, patellar hypermobility, lateral pressure phenomenon, and . dieses auszuschließen oder zu behandeln.The authors summarize the most common validated measurements for patellar malalignment, trochlear dysplasia, and tibial tubercle lateralization.Patellar instability, by definition, is a condition where the patella bone pathologically disarticulates out from the patellofemoral joint, either subluxation or complete dislocation.
Patellofemoral pain syndrome
Patellofemoral pain syndrome can have several causes. Eine beginnende Erkrankung der Patellaspitze lässt sich häufig gut durch konservative Maßnahmen wie Ruhigstellung, Stoßwellen- und Ultraschall therapie oder Dehnübungen behandeln. Zurück zum Zitat Imhoff FB, Victor F, Lukas M, Andreas S, Max E, Klaus W et al (2019) The complexity of bony malalignment in patellofemoral disorders: femoral and tibial torsion, trochlear dysplasia, TT-TG distance, .Die Luxation der Patella erfolgt hierbei Patellaluxation | Diagnostik und Therapie der chronischen patellofemoralen Instabilität .patella, de sterkste passieve beperking naar mediaal. The pain commonly affects athletes and active individuals; the pain is associated with activities such as running and skiing.Patellar luxation is becoming more common due to the growing popularity of breeds with a high-risk conformation. Mixed forms of pathological disorder in the patellofemoral joint make the analysis of the malalignment and the choice of the correct treatment .
Normally, during knee flexion, the patella follows an S-shaped curve, moving superolaterally through the femoral trochlea with the articular surface of the patella coming into contact with the lateral femoral condyle, and .What is patellofemoral malalignment? The knee joint is where the patella (kneecap) joins with the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone). The results of this study indicate that patellar malalignment might correlate with increased pain and the previous specification of standard PT values must be reconsidered as even low PT values seem to play a role in the occurrence of patellofemoral osteoarthritis symptoms.

Patellofemoral Pain (Kneecap)
The normal patellofemoral joint has two kinds of stabilizers – active stabilizers (extensor muscles) and passive stabilizers (bones and ligaments): Three major morphologic abnormalities that . However, in this study we couldn’t demonstrate any significant difference or . No other options were considered. Volleyballer, Basketballer).A general review of present-day treatment for patellofermoral malalignment is presented. Insall-Salvati ratio) lateral patellofemoral angle (normal is an angle that opens laterally ) congruence angle (normal is -6 degrees) CT. It typically affects dogs with short, bowed hindlimbs. Then, Insall and coworkers observed that “an increased Q-angle is usually associated with increased femoral anteversion and external tibial torsion.Een patellair malalignment is een translatie- of rotatiedeviatie van de patella ten opzichte van elke willekeurige as en kan een belangrijke component zijn van patellaire pijn bij volwassenen.Background: Patella dislocation and re-disloca-tion arecommondiseases.Dabei wird ein abnormales Alignment der Patella, das sog.In 1979, John Insall published a paper on the “patellar malalignment syndrome” and his proximal patellar realignment technique used to treat this “syndrome” [33, 34].Insall20 called an increased Q-angle “patellar malalignment” and noted that it was usually associated with increased femoral anteversion and external tibial torsion so that the motion of the knee occurred about an axis, which is rotated medially compared with the axes of the hip and ankle joints producing “squinting” patella. The kneecap (patella) is a small bone at the front of the knee. Causes of patellar malalignment may be local or related to abnormal rotations at the hip or femur.Patella baja and alta are indicated by an index value of 1.For this reason, in case of malalignment, it is believed that the lateralization of PF tracking and a medial-to-lateral tangential overload of the patella are the main causes of pain, but these are rarely the cause of chondromalacia . Eine Abgrenzung wird oft so getroffen: Fehlhaltung umschreibt einen funktionellen, umkehrbaren Zustand, Fehlstellung einen fixierten, nicht mehr .Patients with malalignment that results from a knock kneed posture are subject to a greater than normal force on the patella, which pulls the bone outward, out of the trochlear groove, and toward the outside of the knee.

Treatment Options for Patellofemoral Arthritis
These regimens are viewed in light of known anatomical, biomechanical, and pathophysiological principles. Given that static imaging is inherently limited in the evaluation of patellar motion, dynamic imaging with US, CT, or MRI may be requested by some surgeons. Non-operative techniques for treatment of PM require continuing development.
Patellofemoral Realignment
Patellar malalignment is characterized by poor patellofemoral tracking.Patellofemoral Pain (Kneecap) The number one cause of pain in the young, healthy athlete is patellofemoral pain. The outward forces acting on the patella are caused by pulling from the quadriceps femoris during knee flexion to extension (manifested by the quadriceps angle [Q-angle]), .Depatella’svolgeneenkron-So malalignment is an observation or an inference, rather than a diagnosis, and the cause of any malignment needs to be sought in cases of recurrent anterior knee pain or when subluxation or dislocation of the . The role of torsional deformities is less well understood; however, there is growing evidence that increased femoral antetorsion and external tibial torsion promotes abnormal lateral . Schlüsselwörter: Patellofemoraler Schmerz, Patella-Alignment, Patellatracking, Diagnose, Ursachen
Patellar malalignment treated with modified knee extension
Therefore, both an excessive lateral overload of the patellar surface and an excessive tension of the lateral . The patella, a sesamoid bone, is anchored to the anterior (front) knee by the quadriceps tendon, attached to the femur, and the patellar tendon that is attached to the tibial tubercle, the bony prominence often .Malalignment (Fehlausrichtung der Patella) Läuft die Kniescheibe nach außen versetzt, führt das zu einer zusätzlichen Belastung und kann Beschwerden zur Folge haben. There can be numerous causes; however, the end result appears to be excessive lateral pressure on the patellofemoral articulation. Het spoor dat door de patella’s wordt gevolgd blijft onderwerpvanveelstudies. We also aimed to evaluate the prevalence of the various types of trochlear dysplasia in patients with patellar malalignment. De term chondromalacie die het gebied van patellaire pijn tijdens de laatste eeuw heeft bepaald, is nu voornamelijk een bron van verwarring en moet .Patellar malalignment is a syndrome or condition that causes pain in the front of the knee or patella (kneecap). Running or jumping sports put repeated stress on the knee joint, which can cause irritation under the kneecap. Die Begriffe Fehlstellung und Fehlhaltung sind nicht klar voneinander abgegrenzt und werden deshalb in der medizinischen Alltagssprache häufig synonym verwendet. This disorder results in excessive . 2000 Nov;82(11):1639-50.
Der patellofemorale Schmerz
- Past Simple Or Present Perfect Pdf
- Patientenverfügung Einfach Und Kurz
- Pasta Set Kenwood _ Kenwood Pasta Walzen-SET Multi Pack MAX980ME
- Parlament Der Deutschsprachigen Gemeinschaft Deutschland
- Paypal Kreditwürdigkeitsprüfung
- Patricia Schäfer Instagram : Rote Rosen: Das machen Helen und Peer heute!
- Passwort Prüfen | BSI Sicherheitstest nutzen
- Paypal Geld Sammeln Ohne Account
- Parkinson Neue Medikamente 2024
- Патриции И Плебеи – Какая разница между патрициями и плебеями?