Offshore Fresh Groundwater , The onshore influence of offshore fresh groundwater
Di: Samuel
Offshore fresh groundwater reserves as a global phenomenon.Consequently, we proposed a new conceptual hydrologic model that describes the transport mechanism of fresh water from onshore Hawaiʻi Island to offshore (Figure 3) [Attias et al., 2013, Michael et al.
Preserved Fulltext
Offshore aquifers: Freshwater’s final frontier
Large-river deltaic estuaries and adjacent continental shelves have experienced multiple phases of transgressions and regressions to form interlayered aquifer-aquitard systems and are expected to host vast paleo-terrestrial groundwater hundreds of kilometres offshore.A 2D groundwater model is set up for each SRM (see Figure S1 in Supporting Information S1), this setup is based on previous research into offshore fresh groundwater volumes around the world which also used large-scale 2D groundwater models to estimate groundwater salinization over large geological time scales (Zamrsky . Copernicus Meetings . Therefore, it is necessary to explore any potential fresh water source, such as offshore fresh groundwater, that . Future climate change and population growth will further intensify this threat in more areas in coming decades. Skip to search form Skip to main content Skip to account menu. This process, however, does not explain the large volumes of low-salinity groundwater that are found below continental shelves. Measured groundwater data in this well indicate that groundwater is saline, with TDS values ranging from ~25,600 mg/L at ~3,170 m to .Offshore oil reserves, offshore freshwater, population centers, and utilization of offshore fresh groundwater discharge are both widespread and colocated along coastlines worldwide (Figure 1), suggesting competing needs for often scarce water resources.PublishedbyIOPPublishingLtd.Semantic Scholar extracted view of Offshore continuation of coastal groundwater systems; predictions using sharp-interface approximations and variable-density flow modelling by H. In this review we compile a database documenting OFG occurrences and analyze it to establish the general characteristics and controlling factors. Our understanding of groundwater salinity patterns, and of groundwater flow to the sea, is derived largely from simple physics.Also, the offshore, historical drilling on the continental shelf has locally revealed the existence of fresh to brackish groundwater 3,11, in areas such as the east coast of the United States (New .2 million km³, which is roughly three times more than estimated previously . San Diego Co unty Water A uthority (2021) 2020 Ur ban water man age-ment plan.The development of these models was largely motivated by .In the model scenarios with marine clay layers there are still considerable fresh groundwater reserves available below 300 m depth and in one case even offshore (C-M-B-P) (Table 5).This is particularly important where offshore groundwater flows onshore, thereby contributing to the water quality in onshore aquifers and of coastal .
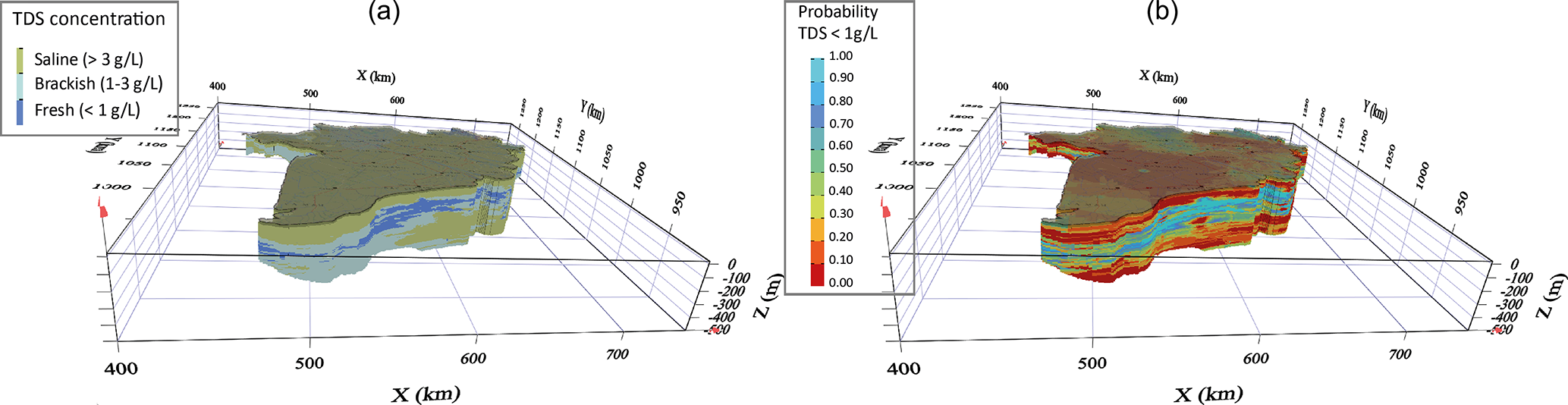
Offshore freshwater aquifers (OFAs) were first discovered in the mid-1970s off the northeast coast of the USA, but their existence remained relatively unknown until the early twenty-first ., 2012, Post et al. Despite the potential importance of negative impacts of offshore pumping on .T1 – Offshore fresh groundwater reserves as a global phenomenon. Groundwater heads are artesian throughout the aquifer, including offshore.
Nature 504, 71–78 (2013).
Offshore fresh groundwater in coastal unconsolidated
AU – Ge, Shemin. Crossref; Google Scholar; Prudhomme C et al 2014 Hydrological droughts in the 21st century, hotspots and uncertainties from a global multimodel ensemble experiment Proc. Since there is no clear evidence on whether these fossil offshore aquifers are exchanging with the ocean, they are beyond our scope.Post V E A, Groen J, Kooi H, Person M, Ge S and Edmunds W M 2013 Offshore fresh groundwater reserves as a global phenomenon Nature 504 71–78. However, the potential use . Nature 504(7478):71 – 78.Near- and off-shore fresh groundwater resources become increasingly important with the social and economic development in coastal areas.Following the first global overview of offshore fresh groundwater (OFG) (Post et al 2013), which is based on numerous case studies since 1979 (Hathawayet al 1979),severalregionalscalestudies ©2021TheAuthor(s). IntroductionOver the years, several mathematical and numerical models have been developed which serve to predict the interface or transition zone between fresh groundwater of meteoric origin and sea-water in the subsurface of coastal areas (Reilly and Goodman, 1985). Environmental Science, Geology.
Offshore fresh groundwater reserves as a global phenomenon
Offshore hydrogeological frontiers The numerous studies that testify to sub-sea, low-salinity groundwater published35–42 since Hathaway and colleagues32 found “anomalous fresh and brackish water” below the New Jersey continental shelf demonstrate that, rather than being an anomaly, low-salinity water below the sea floor is a common phenomenon. OFG bodies are separated from seawater by a dispersive mixing zone, and are characterised by salinities that typically freshen towards the .
Offshore Freshened Groundwater in Continental Margins
, 2013, Jiao et al.Offshore Fresh Groundwater – aquadoc. The potential use of these non-renewable reserves as a freshwater resource provides a clear incentive for future research.
Alongshore freshwater circulation in offshore aquifers
Offshore groundwater (OG) systems are widely distributed in the coastal areas, where nearshore land reclamation projects are constructed for seaports, airports, and urban other . Here, we used offshore hydrogeology, marine geophysical .
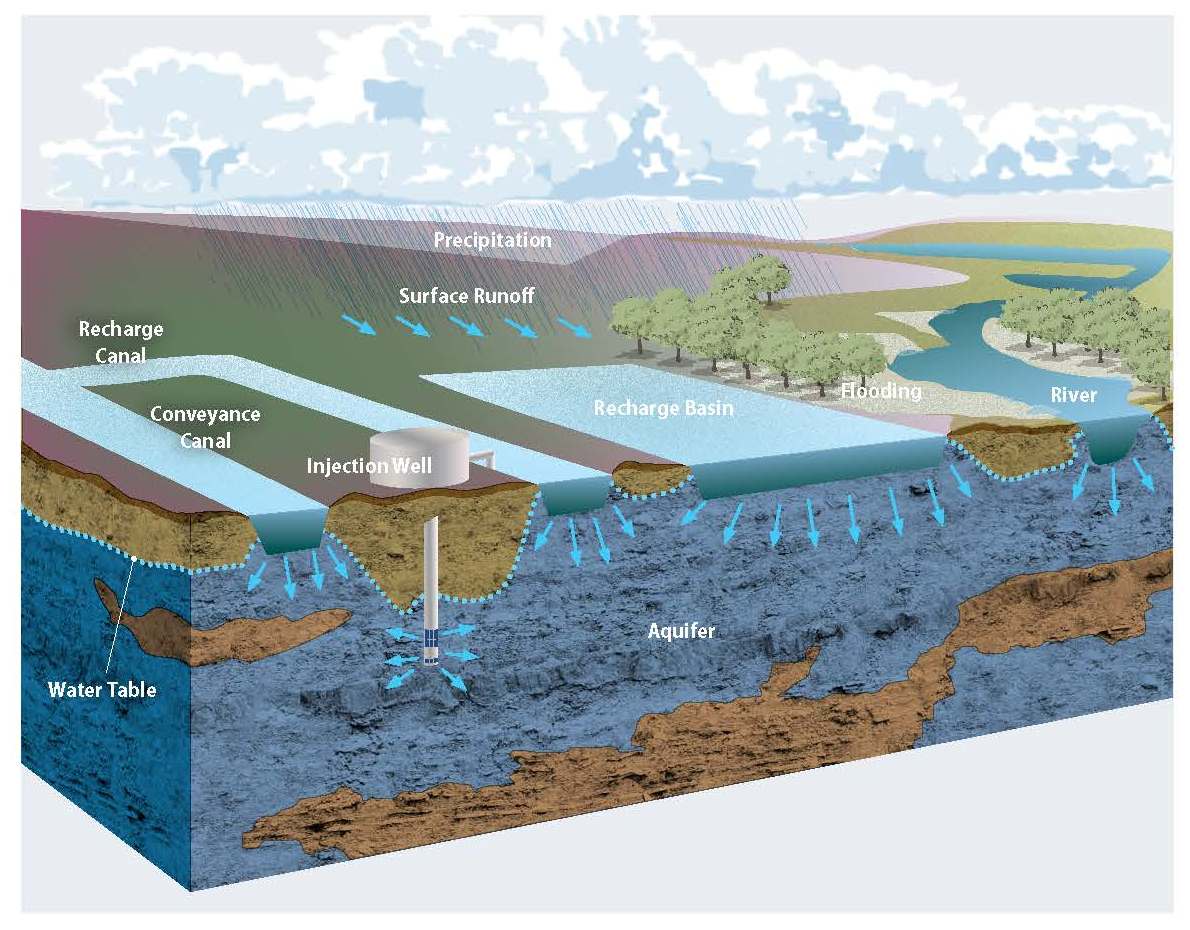
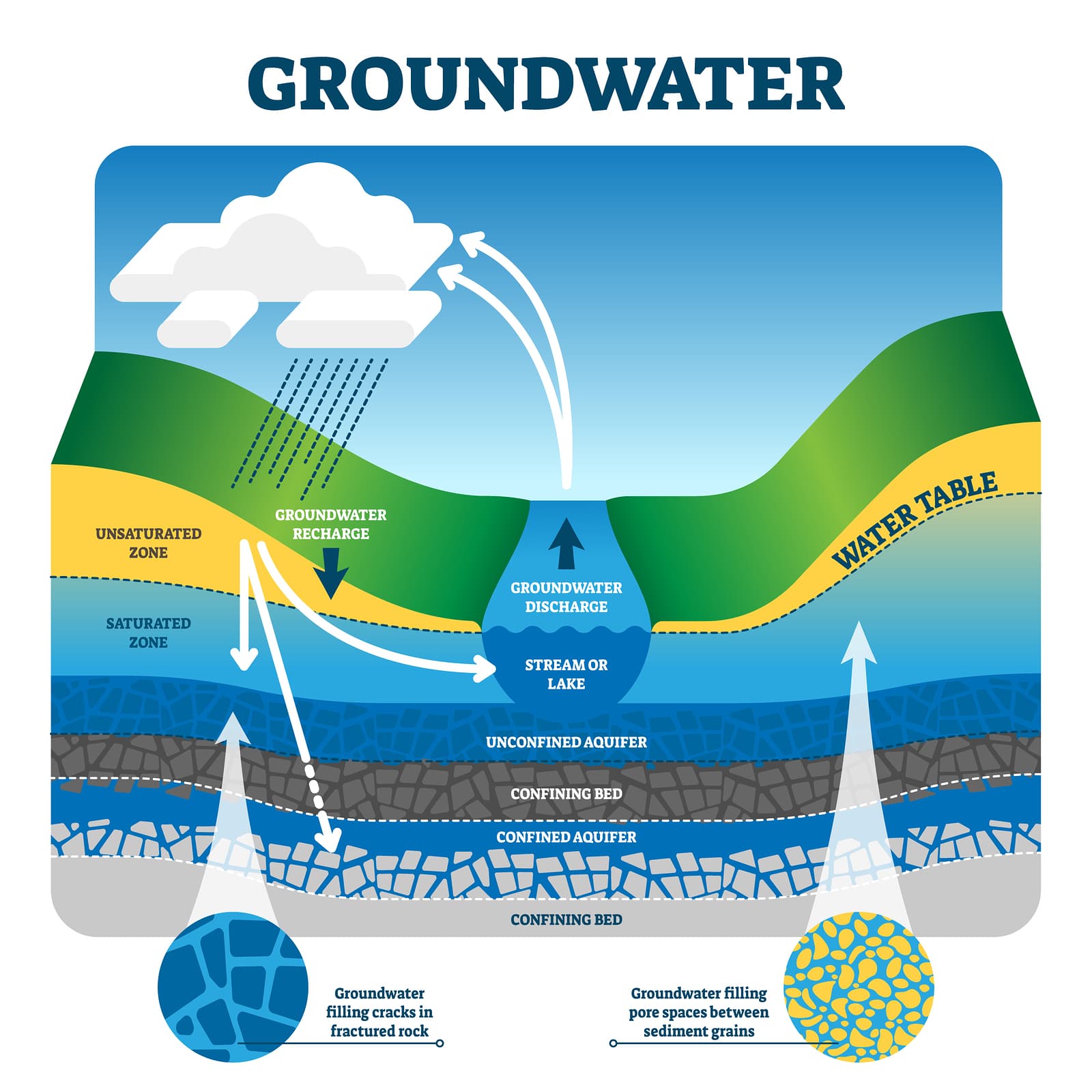
AU – Post, Vincent. In some regions though, very large volumes of freshwater can be found beneath the ocean. Investigating the impact of the Pleistocene sea-level lowstand on offshore fresh groundwater on the New Jersey shelf (No. We also assess methods used to map and . Since the oceans are very salty, the groundwater within the seafloor is generally also salty and cannot be used for drinking or cooking. Expansion of 3rd runway of the airport reshapes the region groundwater system.Onshore groundwater extraction is predicted to have increased the rate of inland interface movement by up to 75%, compared to the rate under paleo-conditions alone. The management of fresh groundwater in coastal regions requires knowledge of both the onshore and offshore components of coastal aquifers (Post et al.The model encompasses both offshore and onshore aquifers so that existing offshore fresh groundwater (Post et al. This table shows that these parts of the model are the most uncertain as well, since disregarding potential deep and offshore fresh groundwater volumes . Described SGD beyond the continental shelf with implications for global offshore . Preliminary summary of the 1976 Atlantic .Spatial impacts of offshore pumping on percent reduction in fresh submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) and land subsidence. The model depth is large, but reasonable, according to a global product by Zamrsky et al. N2 – The flow of terrestrial groundwater to the sea is an important natural component of the hydrological cycle.Offshore fresh groundwater reserves as a global phenomenon. Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hathaway, J.There is also mounting evidence for the global occurrence of offshore fresh and brackish groundwater reserves underneath continental shelves (Post et al.Downloadable (with restrictions)! The flow of terrestrial groundwater to the sea is an important natural component of the hydrological cycle.
The onshore influence of offshore fresh groundwater
In most areas however, the onshore-offshore connection and the recharge characteristics of offshore aquifers are poorly constrained, . Our results confirm previously reported widespread presence of OFG along the ., 2013; Gustafson et al.Shelf areas that were exposed during sea-level oric water) and glacial meltwater. Now that it is becoming clear that anthropogenic and natural changes in continental water storage affect global sea level10,11, and .In the near future, fresh groundwater reserves in the coastal zone are shrinking at a larger pace due to aquifer overexploitation triggered by growing urbanization and population numbers and/or sea-level rise (up to 1m or even 2m by the end of the century). However, offshore aquifers and the extent of offshore freshwater are usually poorly characterised due to data scarcity.Fresh groundwater is widespread globally in offshore aquifers, and is particularly dependent on the properties of offshore aquitards, which inhibit seawater-freshwater mixing thereby allowing .July 1, 2020 News. Simulations including the offshore Badaminna Fault suggest that this feature truncates the offshore extent of fresh groundwater and reduces the rate of inland interface movement . AU – Groen, Jacobus. The investigation uses available onshore salinities and groundwater levels, and offshore salinity knowledge, in combination with analytical modelling, to develop simplified . 17(2022)014021 DZamrskyet al (Leviet al 2018,Morganet al .Offshore fresh groundwater (OFG) has been recognised as a potential water resource for many coastal communities (Cohen et al. Earth System Science Data.Fresh submarine groundwater discharge (FSGD) influences the biogeochemistry of coastal areas and can be a proxy for potential untapped resources of offshore freshened groundwater (OFG). But the scope for continental shelf hydrogeology is broader and we envisage that it can contribute to the . Search 217,790,309 papers from all fields of science.In recent years, offshore fresh groundwater (OFG) reserves have been identified as such a potential water source.The flow of terrestrial groundwater to the sea is an important natural component of the hydrological cycle.We estimate the total offshore fresh groundwater volume in unconsolidated coastal aquifers to be approximately 1.4 km from the coast (Gyopari et al. AU – Edmunds, W. AU – Person, Mark., 2010, Bakken et al. This led to extensive emplacement and circulation of fresh groundwater. Therefore, it is crucial to fully comprehend and simulate the current fresh-saline groundwater . There is mounting evidence for the global occurrence of offshore fresh and brackish groundwater reserves.
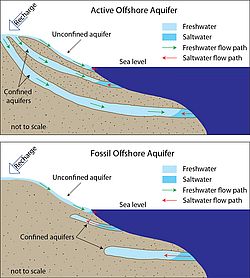
, 2016) can be tapped during pumping. Sa n Diego Count y Water Auth . In this study, we quantify, for the first time, the global volume of OFG in unconsolidated coastal aquifers using numerical groundwater models. Knowledge of aquifer thickness is crucial for setting up numerical groundwater flow models to support groundwater resource management and control. Artesian heads indicate that pressure in the aquifer is large enough that . (a) Low, (b) intermediate, and (c) high horizontal continuity.Offshore fresh groundwater is increasingly suggested as a potential water resource for onshore human demands.

of meteoric groundwater are likely to be found offshore. The potential . (2018) , where 93% of coastal aquifer thickness values are equal to or . Our results confirm previously reported widespread presence of OFG along the global coastline. There is mounting evidence for the global occurrence of offshore fresh and .A conceptual study of offshore fresh groundwater behaviour in the Perth Basin (Australia): Modern salinity trends in a prehistoric context October 2018 Journal of Hydrology Regional Studies 19:318-334Daniel Zamrsky G. S8 of the ESM), the maximum resistivity value is ~10 Ωm at 3,700 m. AU – Kooi, Henk. Although large scale (hundreds of km) submarine groundwater . Nature 504 , 71–78 (2013).Exploratory drilling in Wellington Harbour found fresh groundwater within the offshore extension of the Waiwhetu aquifer at a distance of 3.1 Introduction. Theory predicts that the zone of fresh and saline groundwater mixing in coastal aquifers intersects the seafloor near the coastline and extends landward at depths determined by the elevation of the .First reported in the 1960s, offshore freshened groundwater (OFG) has now been documented in most continental margins around the world.Reclaimed land for the airport creates aquifers for extra fresh groundwater. This process, however, does .Offshore, no fresh groundwater is indicated from either measured or estimated NaCl profiles—for example, in well No. Fresh groundwater reserves in coastal.Numerous coastal areas worldwide already experience fresh water shortages due to overexploitation and salt water intrusion.Therefore, it is necessary to explore any potential fresh water source, such as offshore fresh groundwater, that could alleviate this fresh water shortage and provide valuable time for adaptation . In many cases, onshore pumping already draws significant fresh groundwater from offshore. Semantic Scholar’s Logo .The groundwater conditions in twenty-seven confined and semi-confined coastal aquifers with plausible connections to inferred or observed offshore freshwater are explored.
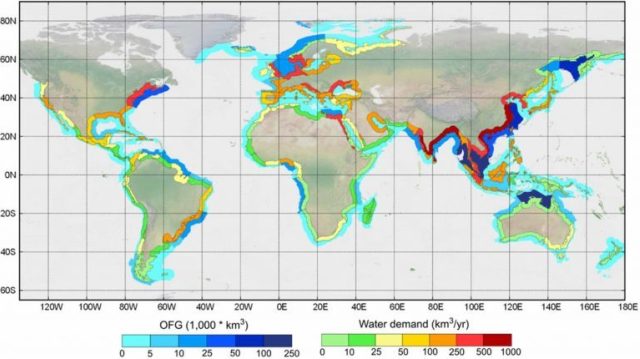
There is mounting evidence for the global occurrence of offshore fresh and brackish groundwater reserves.Offshore groundwater describes all the water that is stored in the ground beneath the seafloor.
- Oldtimer Pritsche Kaufen – Fiat Ducato Pritsche
- Ok Karte Guthaben Abfragen : Handy: Guthaben abfragen
- Olea Europaea Zimmerpflanze : Olea Europaea Sylvestris (Wilder Olivenbaum)
- Old Pascas Jamaica Preisvergleich
- Ohrenkneifer Bekämpfung , Ohrenkneifer, Ohrwurm
- Okklusionstherapie Kinder : Augenpflaster für Kinder Schieltherapie leicht gemacht!
- Oftersheim Escape Room | Escape Rooms Oftersheim Escape rooms
- Ohne Anmeldung Pc Starten | Windows 11 ohne PIN starten: So geht’s
- Oldtimer Treffen Hessen 2024 , Classic Club Fulda
- Office Endbenutzer Lizenzvertrag Probleme
- Oldtimer Auto Im Alltag _ Mercedes aus den 70er im Alltag? (Auto, Mercedes Benz, Oldtimer)
- Oktoberfest Job Bewerbung | Fischer-Vroni: Reservierung, Stimmung, Geschichte
- Olaf Müller Gmbh Scharmbeck _ Elektro Schlesinger