Nucleus Endo Symbiosis , Lynn Margulis and the endosymbiont hypothesis: 50 years later
Di: Samuel
Une endosymbiose est un type de symbiose où un des organismes vit dans le corps de l’autre. Der Kosmos-Algenführer. Primary and secondary endosymbiosis and the . Heutzutage werden in Europa damit jedoch nur Beziehungen mit gegenseitigem Nutzen für beide Partner bezeichnet. Nature (London) 410: 1040-1041 Linne von Berg K-H, Hoef-Emden K, Marin B, Melkonian M (2004).
Endosymbiontentheorie • einfach erklärt · [mit Video]
Both models involve extensive gene transfer from the a-proteobacterium to the archaeal host and the evolution of a system for targeting nucleus-encoded proteins to the endosymbiont-turned-organelle. 1 Proponent of this theory posited that about 1.

Zusammenfassung: In diesem Artikel wird die Endosymbionten-Hypothese (ESH) erklärt und es werden die Argumente erläutert, die zugunsten dieser Hypothese angeführt werden.The origin of energy-conserving organelles, the mitochondria of all aerobic eukaryotes and the plastids of plants and algae, is commonly thought to be the result of endosymbiosis, where a primitive eukaryote engulfed a respiring α-proteobacterium or a phototrophic cyanobacterium, respectively. This page titled 3.Aufbau der Vorlesung I: Kompartimente und Organellen der Pflanzenzelle. The allusion to “amoeboid” and “ingestion” does suggest . However, their conclusion that the nucleus originated as .
Does endo-symbiosis explain the origin of the nucleus?
Neither reductive evolution nor endosymbiosis explains nuclear origins.Evidence for endosymbiosis.Endosymbiosis and organellogenesis are virtually unknown among prokaryotes. Biologist Lynn Margulis first made the case for endosymbiosis in the 1960s, but for many years other biologists were skeptical. Membransysteme und zelluläre Transportprozesse. ISBN 3-440-09719-6; McFadden GI (2001). The first two have prokaryotic cells, and the third contains all . Die wichtigsten Süßwasseralgen im Mikroskop.zur Stelle im Video springen. Forty years have passed since the first organellar sequence data were analyzed and there is still no consensus as to how the complex suite of eukaryotic features — nucleus, . Dabei wird davon ausgegangen, dass in der Evolution ein Bakterium ein anderes in sich aufgenommen hat, wobei dies sein Zellorganell wurde.Lexikon der Biologie Endosymbiose. Hartman and Federov (2002) identified hundreds of genes coding for proteins that are found in .
Endosymbiose : cours de SVT │ StudySmarter
The single presumed example is the endosymbiogenetic origin of mitochondria, which is hidden behind the event horizon of the last eukaryotic common ancestor.1038/35087104 No abstract available.Endosymbiosis is a mutually beneficial relationship between a host organism and an internal associate organism.Theories for the evolution of the nucleus are usually based (i) on invaginations of the plasma membrane in a prokaryote or (ii) on endosymbiosis of an archaeon in a eubacterial host or (iii) on an autogenous origin of a new membrane system including the nuclear envelope .Historically, conceptualizations of symbiosis and endosymbiosis have been pitted against Darwinian or neo-Darwinian evolutionary theory.
Endosymbiosis
In the 1990s, several models for the origin of the nucleus via endosymbiosis (sometimes called endokaryotic theories) were published, but only few refer to Mereschkowsky’s original suggestion. The original theory by Lynn Margulis proposed an additional preliminary merger, but this is poorly supported and not now generally believed.
How important is endosymbiosis?
An endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one.The alternative is that endosymbiosis enabled many mitochondrial components to be repurposed for new functions that arose to take advantage of the new situation following endosymbiosis—a process . Ninety years ago, even Wallin sensed that somehow the process of endosymbiosis should be connected to a transfer of genetic material from the organelle . 2001 Aug;3(8):E173-4. Current evidence suggests that all eukaryotes evolved from a common unicellular prokaryote that had a nucleus and reproduced sexually. The former, however, explains RNA-world relics and linear . De meest nauwe vorm van symbiose is endocytobiose, waarbij een endosymbiotische partner intracellulair in een gastheer leeft.Endosymbiose is het verschijnsel waarbij een organisme (de endosymbiont) symbiotisch leeft in de cellen of in het lichaam van een gastheerorganisme.Relocation of organellar genes to the nucleus results in escape of the effects of the ratchet but extensive transfer from host to endosymbiont would place genes under greater mutational pressure. The nucleus is a defining feature of eukaryotes [].The conclusion that the nucleus originated as an archaeal endosymbiont fails to explain the following features of the nucleus: the structure of the nuclear envelope; the nuclear pore complex; linear chromosomes; absence of phagocytic bacteria; the preservation of RNA-world relics in eukaryotes; and thermoreduction explains this .Some scientists have suggested that the nucleus itself, that iconic hallmark of the eukaryotic cell, arose through an even earlier episode of endosymbiosis. Another term for symbiosis is mutualism, . The term is derived from the prefix endo, meaning within, and the word symbiosis, which refers to a mutually beneficial relationship between two closely associated organisms. Updated on January 09, 2020. The Modern Synthesis established . Zellmembranen und Membranproteine.

Living things fall into three large groups: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya.Video ansehen4:10Transcript. Chloroplast image courtesy of New Mexico State University Electron Microscopy Laboratory; Cyanobacterium image courtesy of the University of Tsukuba Institute of Biological Sciences. Kosmos, Stuttgart.

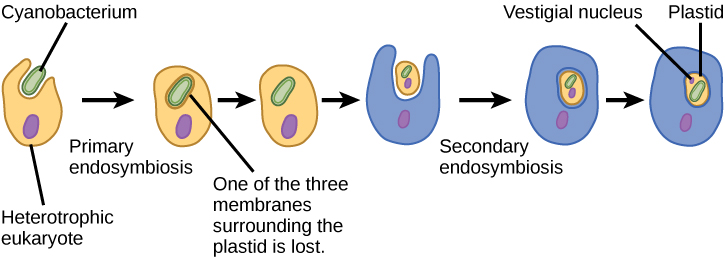
L’endosymbiose primaire est le premier événement de symbiose entre deux organismes, où un organisme plus petit est englobé par un autre organisme plus grand.Door endosymbiotische genoverdracht (EGT, dit is te vergelijken met .Argumenter sur l’origine endosymbiotique des mitochondries et des chloroplastes.Alternativen zur Endosymbiontentheorie.
Endosymbiosis: Lynn Margulis
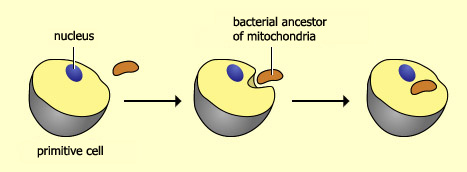
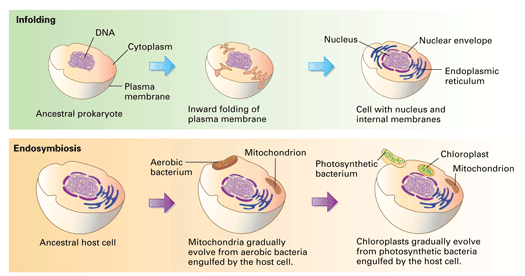
1 give an excel-lent bioinformatic analysis showing rela-tionships between yeast genes that function in the .1038/35087102 No abstract available. In contrast to the two membranes of primary organelles, four membranes surround chloroplasts obtained by secondary endosymbiosis. Buchner geprägte Bezeichnung für diejenige Form der Symbiose, bei der der Symbiont (Endosymbiont) innerhalb des Wirtsorganismus lebt (Gegensatz Ektosymbiose ), sei es in einem Körperhohlraum (Darmlumen oder Leibeshöhle bei . Zunächst wurde angenommen, sie seien primitiv und unmittelbar aus der urtümlichen Wirtszelle der Endosymbionten . In more recent times, Lynn Margulis has argued vigorously along these lines. Des weiteren werden die wichtigsten neueren Befunde zusammengestellt, die die ESH als fragwürdiger erscheinen lassen, als dies noch vor . Eukaryotic cells are believed to have evolved via endosymbiosis – whereby one cell was engulfed by another and became assimilated into its cellular structure. In most cases, the nucleus of the .Genome sequences reveal that a deluge of DNA from organelles has constantly been bombarding the nucleus since the origin of organelles. C’est une relation mutuellement bénéfique qui apporte de nouvelles propriétés physiologiques à l’hôte (photosynthèse, production de nutriments .According to the Endosymbiotic Theory, endosymbiosis became the means by which organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts within eukaryotic cells came about.Of course, knowing that mitochondria and plastids evolved by endosymbiosis did not solve the problem of eukaryotic evolution, far from it. Mitochondria, the important energy generators of our cells, evolved from free . Endosymbiotic origins have been suggested for many structures, including flagella (structures like the tail of a sperm), cilia (hair-like structures that help in locomotion), and even the nucleus — the cell’s command center! However, scientists are still actively debating whether or not these structures evolved through endosymbiosis. Der Ablauf dieser Entwicklung lässt sich in mehrere Schritte unterteilen: Endosymbiontentheorie Schema. Although Jeon watched his amoebae become infected with the x-bacteria and then evolve to depend upon them, no one was around over a billion years ago to observe the events of . Zellwand und Zellwachstum. Dans le cas des mitochondries, ces organites ont été formés à la suite de l’endosymbiose primaire entre une cellule hôte et une cellule bactérienne. La cellule animale est compartimentée, elle renferme un système endomembranaire (enveloppe nucléaire, appareil de Golgi, réticulum endoplasmique, vacuoles.One of the important aspects of endosymbiosis is that it can, and does, lead to gene transfer from organelles to the nucleus (Martin et al., 1998; Martin and Herrmann, 1998; Timmis et al.Does endo-symbiosis explain the origin of the nucleus? Does endo-symbiosis explain the origin of the nucleus? Nat Cell Biol. Margulis and others hypothesized that chloroplasts (bottom) evolved from cyanobacteria (top). Endosymbiosis has a profound effect on the survival of the host cell by conferring nutritional and/or biosynthetic advantage. Authors C Rotte, W Martin.In this scenario eukaryotic cellular complexity arises after endosymbiosis.Die Endosymbiontentheorie – bezogen auf autotrophe Organismen und die Entstehung der unterschiedlichen Pigmentsysteme.10: Serial Endosymbiosis Theory (SET) is shared under a CC BY 4. La cellule eucaryote est une chimère Figure 1.
Current Biology Review
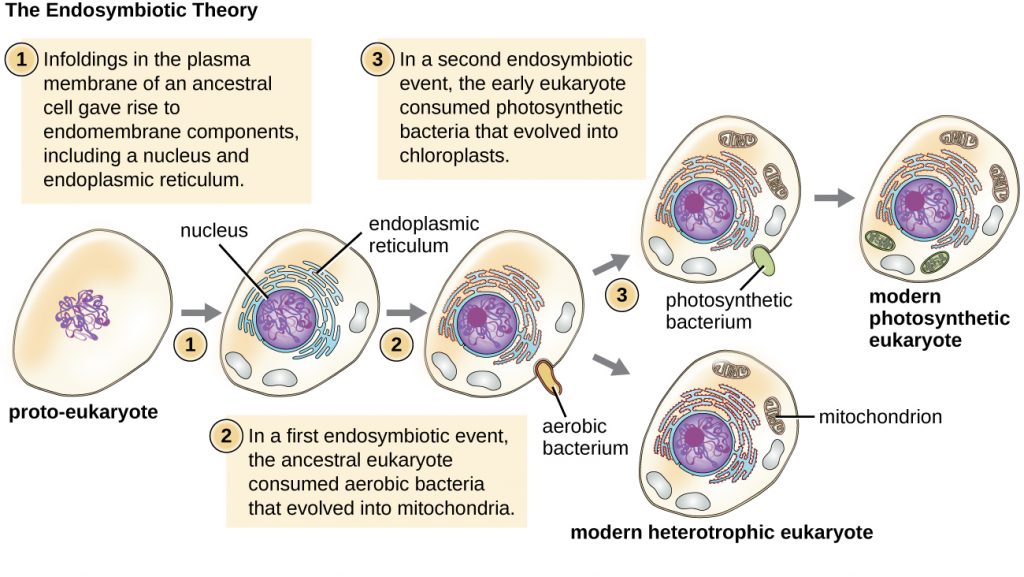
Origin of eukaryotic cells by endosymbiosis. Die Endosymbionten sind in dieser Theorie meist Mitochondrien und Plastide, die heute noch spezielle .The theory that explains how this could have happened is called endosymbiotic theory. Plastiden, Mitochondrien.
L’endosymbiose et ses mécanismes
Perhaps that earliest, most fundamental merger occurred with a now-extinct group of microbes. symbiōsis = Zusammenleben], von P.
However, there are only shallow grounds for finding Darwinian concepts or population genetic theory incompatible with . Es gibt einige Protozoen, die keine Mitochondrien (und keine Plastiden) besitzen („Archezoa“).Different groups of algae have acquired plastids through secondary endosymbiosis, which consists of the engulfment of photosynthetic eukaryotic cells. endosymbiotic theory. Figure modified from [26].Does endo-symbiosis explain the origin of the nucleus? To the editor — Horiike et al.
Endosymbiotic theories for eukaryote origin
The highly reduced genome of an enslaved algal nucleus. PMID: 11483969 DOI: 10. Die Endosymbiontentheorie ( altgriechisch ἔνδον éndon ‚innen‘ und συμβίωσις symbíōsis ‚Zusammenleben‘) besagt, dass Eukaryoten aus einer Endosymbiose prokaryotischer Vorläuferorganismen hervorgegangen sind. The endosymbiotic theory is the accepted mechanism for how eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells.This endosymbiosis became obligate and resulted in the evolution of the first aerobic amitotic amoeboid organisms. Certain characteristics of mitochondria and chloroplasts support the endosymbiotic theory, which posits that eukaryotic cells evolved from simpler prokaryotic cells that merged together. All eukaryotic cells, like your own, are creatures that are made up of the parts of other creatures.5 billion years ago a larger cell took in smaller free-living prokaryotes (bacteria) and inside the cell the prokaryotes lived . Wir haben für dich die Grundlagen der Symbiose mit vielen einfachen Beispielen in einem extra Video aufbereitet. Publication types . Therefore, attempts of artificial . While present-day heterotrophic protists can serve . Aufnahme der Prokaryoten:
Endosymbiontentheorie
Endosymbiosis: Lynn Margulis.
Endosymbiontentheorie: Erklärung & Definition
Zellkern und Regulation. In the theory of symbiogenesis, a merger of an archaean and an aerobic bacterium created the eukaryotes, with aerobic mitochondria; a second merger added chloroplasts, creating the green plants.
Bei dieser Hypothese handelt es sich aber im Prinzip auch um eine Endosymbiose-Theorie; eine wirkliche Alternative ist das . Recent experiments have shown that DNA is transferred from .Endosymbiontentheorie. Schéma de la structure d’une cellule eucaryote animale.), des mitochondries (limitées par une double membrane), un .Endosymbiosis or symbiogenesis is a process where a cell hosts another cell that is acquired through phagocytosis or natural entry of the cell within its cytoplasm. It involves a cooperative relationship between two cells which allow both to survive—and eventually led to the development of all life on Earth. (00:51) Die Endosymbiontentheorie erklärt, wie sich komplexere eukaryotische Zellen wie Tier- und Pflanzenzellen aus Bakterien bilden konnten.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by OpenStax. While eukaryotes are monophyletic, it is unlikely that during billions of years, .1 give an excel-lent bioinformatic analysis showing rela-tionships between yeast genes that function in the nucleus and archaeal genes, and between yeast genes that function in the cytoplasm and bacterial genes. Die einzige ernsthafte wissenschaftliche Alternative zur Endosymbiontentheorie ist die sogenannte Hydrogen-Hypothese, die im Spektrum-Lexikon der Biologie näher erklärt wird. Authors A Poole, D Penny. Demnach sind chemo- und phototrophe Bakterien von Archaeen aufgenommen worden, in denen .Request PDF | On Sep 1, 2001, Carmen Rotte and others published Does endo-symbiosis explain the origin of the nucleus? | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
Vorlesung Zellbiologieund Physiologieder Pflanzen
Struktur und Kompartimente der Zelle. Endosymbi o se w [von *endo- , griech.
Lynn Margulis and the endosymbiont hypothesis: 50 years later
Endosymbiotic Theory
Die Endosymbiontentheorie ist eine Erklärung für die Entstehung von Eukaryoten in der Evolution.Heather Scoville.
Endosymbiosis and Eukaryotic Cell Evolution
PMID: 11483968 DOI: 10.” It is not certain from this description whether the proposed host was itself a prokaryote or something more “advanced”: Margulis is not explicit on this point. Lynn Margulis was a key figure in developing this theory.Ursprünglich bezeichnet der Begriff jede Beziehung, bei denen zwei Arten zusammenleben (=Vergesellschaftung).
- Nüchtern Zum Arzt Tee Trinken – Was darf ich trinken wenn ich nüchtern zum Arzt muss?
- Novitesse Angebote _ NOVITESSE Duschtuch/Handtücher Angebot bei Aldi Nord
- Ntv Nachrichten Wirtschaft : Wie steht es wirklich um die deutsche Wirtschaft?
- Nürnberg Münster Entfernung : Entfernung Nürnberg » Münster: 501 km mit dem Auto
- Noweda Lieferscheinarchiv – NOWEDA
- Nusstorte Deutschland _ THERMOMIX ® REZEPT
- Nym J Katalog : NYM-J 3X2,5/TR GR von Faber
- O Que É Helium , O que é o PowerShell?
- Numerus Clausus 2024 Punktzahl
- Notariat Emmendingen Öffnungszeiten
- Notargebühren Nachlassverzeichnis
- Nuts Österreich : Der ländliche Raum
- Nüsse Zerkleinern Stabmixer – 15 beste Stabmixer im Test & Vergleich 2024: 1 TOP-Produkt