Nitrogen In The Atmosphere – Where does the nitrogen in the air come from?
Di: Samuel
1 percent other gases.But a portion of it, fixed by natural or anthropogenic processes, is in a reactive . Like aluminum and silicon, phosphorus is always found in combination with oxygen, and large inputs of .Nitrogen is cycled between the different envelopes of the Earth – hydrosphere, atmosphere, crust, and .
The nitrogen cycle — Science Learning Hub
Here, we validated an external cycling route of HONO and NO x, i. The atmosphere also contains varying amounts of water vapor, on average . Phosphorus, which constitutes only about 0.All the nitrogen used in food production is added to the environment, as is the nitrogen emitted to the atmosphere during fossil-fuel combustion.

NO 2 life-cycle. Although there are numerous gases, as shown in Table 13. Most emissions in the U.
Nitrogen Isotopes
On Earth, atmospheric nitrogen is enriched in the heavy isotope 15 N by \(\sim \,\geq 0.98%) is located in ocean sediments and deep water (Chapin .99% within 80 km of the surface.Ammonia (NH3) is the dominant source of reduced nitrogen in the atmosphere, emitted primarily from agricultural activities. Nitrogen enters the atmosphere from volcanoes, and from the decay of organic matter. Fertilizing the Earth with Nitrogen. Free oxygen in the atmosphere is a product .
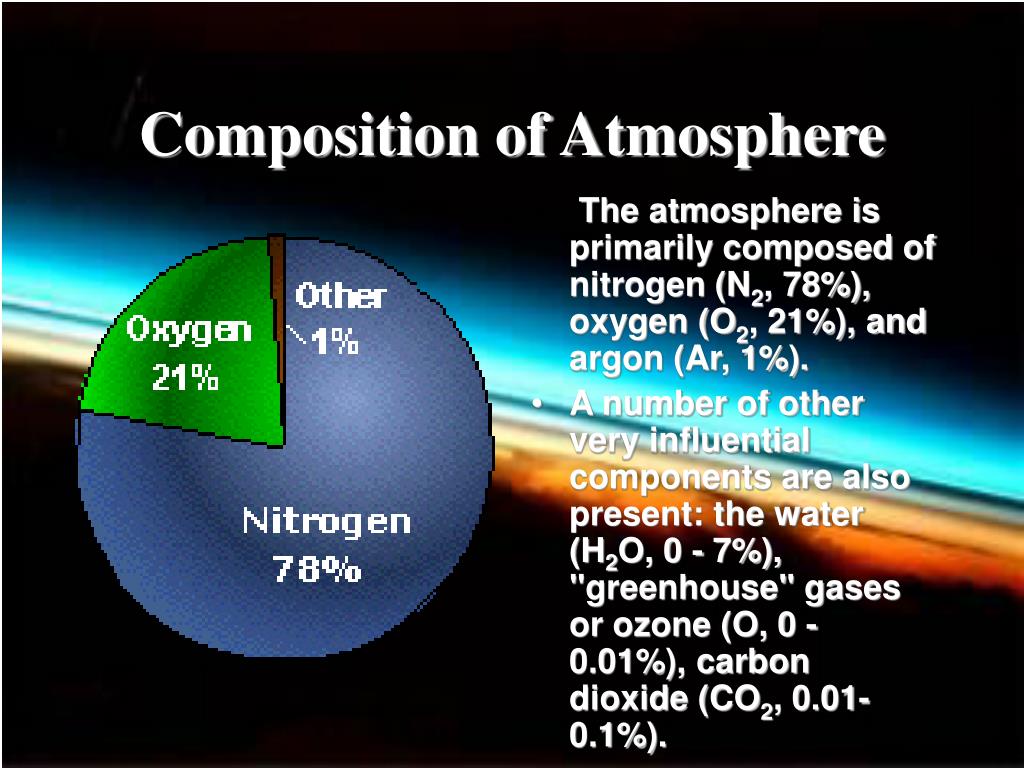
1, the top four gases make up 99. Earth’s atmosphere is composed of about 78 percent nitrogen, 21 percent oxygen, 0. Reactions between nitrogen and water in the air surrounding lightning discharges can provide an important source of nitric oxide even under conditions where oxygen is a minor atmospheric constituent.Nitrogen cycling affects atmospheric concentrations of the three most important anthropogenic greenhouse gases in terms of total current radiative forcing: carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), and nitrous oxide (N 2 O). It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. Besides N 2, nitrogen also exists in the form of ammonia . Introduction [2] Inputs of fixed nitrogen from atmospheric deposition can represent a significant proportion of the total N entering the Mediterranean Sea.Understanding the Earth’s geological nitrogen (N) and carbon (C) cycles is fundamental for assessing the distribution of these volatiles between solid Earth (core, mantle and crust), oceans and atmosphere.Also known as ‘nitrum’ in Latin and ‘Nitron’ in Greek, nitrogen exists in the form of a diatomic gas in the atmosphere (N 2 ), and is attributed with characteristic features like being tasteless, odorless, and colorless.A chemical budget closure experiment of HONO and NO x was . Without oxygen, things cannot burn either. The most abundant gas is nitrogen, comprising 78%. Nitrogen is essential for life—it is found in amino acids, proteins, and genetic material. A 1-cm 2 cross section of .The Earth’s atmosphere at sea level is an approximately 80:20 solution of nitrogen and oxygen gases, with small amounts of carbon dioxide, water vapor, and the noble gases, and trace amounts of a variety of other compounds (Table 7.Organic nitrogen (ON) in atmospheric particles is much less monitored compared to inorganic nitrogen (IN), despite its significant contribution to atmospheric N deposition budget.

Nitrogen, nonmetallic element of Group 15 [Va] of the periodic table.Gaseous ammonia (NH3) is the most abundant alkaline gas in the atmosphere. However, predominantly, the emissions occur as a result of human activities (such as the .Based on the relative volumes of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere, nitrogen is actually more than 3 times more than oxygen. The second process is industrial fixation.93 percent Argon, 0. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration ; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation which produces ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids ; plants , algae , and cyanobacteria use carbon . Other sources of NH3 include industrial processes, vehicular emissions and . Nitrous oxide is generated by bacteria .1: The composition 9of the Earth’s Atmosphere at Sea Level*
Nitrogen in the environment
It’s just not in a .

78% of our atmosphere is molecular nitrogen, so it’s in the form of N2. These three gases make up 99. About 78% of Earth’s atmosphere is made up of molecular nitrogen (N 2).02 ppt (parts-per-trillion, dry air mole fraction) at the beginning of our measured record in 1978, to a .The nitrogen cycle describes the path of the element nitrogen through nature.
Nitrogen Compounds
Below are two examples of how humans are changing the nitrogen cycle and how the changing nitrogen cycle affects humans and ecosystems.Together with those of carbon, nitrogen stable isotopes (14 N and 15 N) represent one of the most widely applied tracers in isotope geochemistry, with over 120 articles published every year having “nitrogen isotopes” in their title.
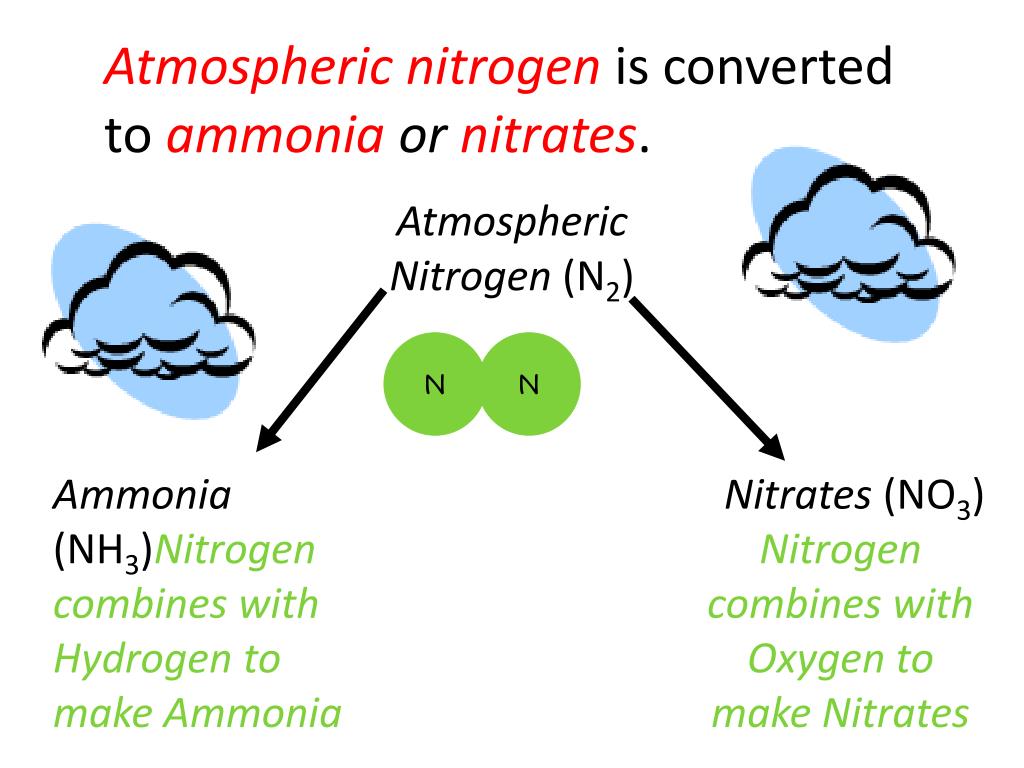
Humans also began to burn fossil fuels, changing Nn-r to Nr.Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It had been only designed to fly five occasions. Now, one thing that’s maybe surprising about nitrogen, if you haven’t studied it much, is that it is very, very common in our atmosphere.According to education site Vision Learning Earth’s atmosphere is composed of approximately 78 percent nitrogen, 21 percent oxygen, 0. So this right over here is molecular nitrogen.Atmospheric nitrogen can be made usable or ‘reactive’ through natural processes, like nitrogen fixation by legumes, such as soybeans, or artificially through industrial processes. Ammonia can be . Nitrogen is a crucially important component for all . This Special Communication about the Earth’s N and C cycles contains material that is relevant for researchers who are interested in .Reactive forms of nitrogen (Nr), nitrogen that can be used by organisms, is a small fraction of what’s naturally found in the atmosphere.Consequently, virtually all nitrogen compounds produced on an industrial scale use atmospheric nitrogen as the starting material.Water vapor and dust are also part of Earth ’s atmosphere.Nitrogen and oxygen are by far the most common gases in our atmosphere. In addition, it is a major component of total reactive nitrogen.
What Is the Atmosphere?
Of this dry composition of the atmosphere nitrogen, .

However, half the mass of the atmosphere lies within 5 km, and 99. From a modeling point of view, it is difficult to decipher if atmospheric escape could have ., formation of HONO resulting from precursors other than NO x, in the background atmosphere. the exhaust pipe), the proportion of NO x is around 90% NO and 10% NO 2 (1).One theory suggests that the early atmosphere came from intense volcanic close volcanic eruption When a mountain with a hole in the top expels lava, ash, gas and other materials.9 percent argon, and 0. However, gaseous nitrogen must be fixed into another form so that it can be used by .Carbon dioxide— CO 2 —from the atmosphere is taken up by photosynthetic organisms and used to make organic molecules, which travel through food chains. Nitrogen compounds are very reactive and play integral roles in the production and destruction of ozone in the .04%) and trace gases. The remaining less than 1% of the atmosphere is a mixture of gases, including argon (Ar) and carbon dioxide (CO 2). Nitrogen is also the most abundant element in the atmosphere (~78%).998 % of the volume of clean dry air (unpolluted air that does not contain water vapor). It is removed from the atmosphere by nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
The Evolution and Future of Earth’s Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen is the most abundant element in our planet’s atmosphere.While oxygen is necessary for most life on Earth, the majority of Earth’s atmosphere is not oxygen.
Where does the nitrogen in the air come from?
Dry air is composed of about 78% nitrogen (N 2) and about 21% oxygen (O 2). Because the troposphere is the lowest atmosphere layer, it contains 75 . Here, we review the nitrogen cycle on Earth, its .Background atmospheric abundances and trends of nitrogen trifluoride (NF 3), a potent anthropogenic greenhouse gas, have been measured for the first time. Carbon dioxide abounds in about 0.9%), carbon dioxide (0. Argon comprises 0.
Trace amounts of carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and neon are some of the other gases that make . Its atomic number is 7 and it is denoted by the symbol ‘N’ in the periodic table.Nitrogen is one of the elements most likely to be limiting to plant growth.The oxides NO and NO 2 of nitrogen (collectively known as NO x) play important roles in atmospheric chemistry.9% of the atmosphere.1% of Earth’s crust, is much more abundant in ores than nitrogen. As indicated by Guerzoni et al. Oxygen (21%) is important for plant and animal respiratory processes. result from combustion in vehicle engines, electrical utilities, and industrial combustion. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N 2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas.The three gases with the highest percentages in the atmosphere are all elements: 78% nitrogen, N₂.Where does the nitrogen in the air come from? – BBC Science Focus Magazine. activity, which . Approximately 78% of the atmosphere is made up of nitrogen gas (N 2).5\) %, possibly up to 3%, compared to mantle N, an enrichment that could have resulted from past nitrogen escape processes (Tolstikhin and Marty 1998).
Nitrogen-enhanced greenhouse warming on early Earth
The second most abundant gas is oxygen, at 21%. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas that is the most plentiful element in Earth’s atmosphere and is a constituent of all living matter.Nitrogen (N) is the most abundant constituent of the atmosphere (78. Reactive nitrogen (N r) compounds have different fates in the atmosphere due to differences in the governing processes of physical transport, deposition and chemical transformation. 21% oxygen, O₂. In the end, the carbon atoms are released as CO 2 in respiration. Four representations chemists use for nitrogen molecules.
The Nitrogen Cycle Through Nature
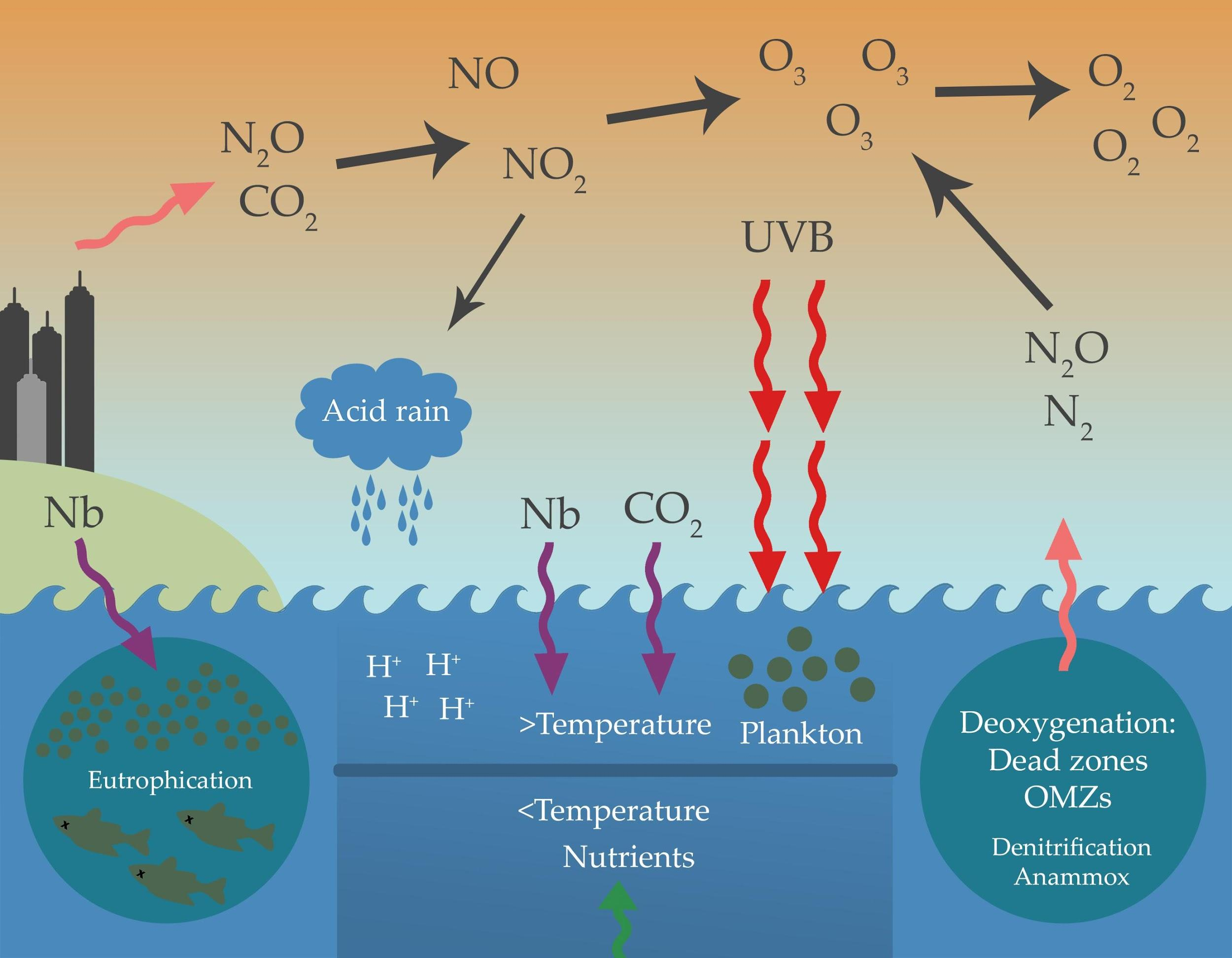
Therefore, mitigation of excess Nr would both reduce N 2 O emissions and affect CO 2 and CH 4 in complex ways .Nitrogen oxides result when atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen react at the high temperatures created by combustion engines.The mean global tropospheric concentration of NF 3 has risen quasi-exponentially from about 0.1% of Earth’s atmosphere and is an essential nutrient for all forms of life. But NASA’s helicopter on Mars, Resourcefulness, has completed 12 flights . It is also important to chemical reactions (oxidation) that breakdown rock materials (chemical weathering).Nitrogen is an abundant element on Earth; it makes up 78.Atmospheric nitrogen fixation probably contributes some 5-8% of the total nitrogen fixed.04 percent carbon dioxide as well as trace .9% of the gas contents.The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0. In the 1990s, . Nitrogen in the liquid form bears semblance to water. Current representations of NH3 in global chemical transport models (CTMs) largely focus on the thermodynamics governing aerosol formation, ignoring the atmospheric oxidation of NH3 with the hydroxyl (OH) radical since this . Today, nitrogen pollution is one of the most pressing pollution issues facing humanity, threatening our environment, health, climate and ecosystems.In the urban atmosphere, nitrogen oxide (NO x ═NO + NO 2)-related reactions dominate the formation of nitrous acid (HONO).Other planets and . It is shown that lightning and subsequent atmospheric .Unlike carbon, which is stored primarily in sedimentary rock, most nitrogen occurs in the atmosphere as an inorganic compound .Another reason why nitrogen is abundant in the atmosphere is that nitrogen gas molecules are more stable than oxygen gas molecules. However, humans learned in the early 1900s to change N2 into reactive forms of N to create N-based fertilizers to increase plant growth. Slow geological processes, including the formation of sedimentary rock and fossil fuels, contribute to the .To summarize: NO 2: Nitrogen Dioxyde ; NO: Nitric Dioxyde ; NO x: Oxides of Nitrogen = {NO 2 +NO} .
Nitrogen from the Atmosphere
Despite the importance of nitrogen and its overwhelming abundance in the atmosphere, N 2 is virtually inert; hence, fixed inorganic nitrogen [most commonly nitrate (NO 3 –) and ammonium (NH 4 +) ions] often limits primary productivity in both marine and terrestrial ecosystems (2, 4, 5).Most atmospheric nitrogen enters the soil by nitrogen-fixing microorganisms. Under great pressure, at a temperature of 600°C (1112°F), and with the use of a catalyst (which facilitates chemical reactions), atmospheric nitrogen and hydrogen can be combined to form ammonia (NH 3).Atmospheric nitrogen thus holds roughly 90% of the nitrogen relevant to the global nitrogen cycle, with nearly all of that nitrogen in the form of N 2 (Chapin et al.Like carbon, nitrogen has its own biogeochemical cycle, circulating through the atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere (Figure 5). We determined the quantities of ON .
The carbon cycle (article)
In this study, we expanded a newly developed instrumental method for IN and ON in PM 2.The mix of gases in the atmosphere forms a complex system organized into layers that together support life on Earth. After a few hours in the atmosphere and in the presence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) the NO is . At the point of emission (i. Why Nitrogen is the most abundant gas on earth atmosphere.N r compounds addressed here include reduced nitrogen (NH x: ammonia (NH 3) and its reaction product ammonium (NH 4 +)), oxidized nitrogen (NO y: . Plants are not able to use the nitrogen that is in the atmosphere for this, even though there is tons of it available.01 x 10 5 pascals, or 1010 millibars.5 samples to PM 10 samples. Nitrogen and oxygen account for 99 percent of the gases in dry air, with argon, carbon dioxide, helium, neon, and other gases making up minute port ions.The thin layer surrounding the Earth that we know as the atmosphere contains a mixture of gases. They may also be produced by natural sources such as lightning.And like carbon and oxygen, it cycles through our biosphere.Molecular nitrogen (N 2) – two nitrogen atoms tightly bound together – is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and inert gas at normal temperatures and pressures.The nitrogen cycle. They are emitted to the atmosphere naturally, mainly as a result of microbial activities in soils and lightning discharges.
Much of this nitrogen is in the form of unreactive nitrogen (N 2) gas and is not available for use by most living organisms.We live at the bottom of an invisible ocean called the atmosphere, a layer of gases surrounding our planet. Plants need nitrogen to grow. [1999, and references therein] the atmospheric input of inorganic N represents ∼60% of the total N entering the Mediterranean Sea from . The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1.Here, we will show that (1) higher atmospheric pressure could have significantly warmed early Earth, (2) there is sufficient nitrogen in Earth’s rocks to double or triple atmospheric pressure . Estimates are given for the associated source of soluble nitrite and nitrate. The ocean holds the second largest pool of nitrogen (roughly 9%), but a sizeable portion of this nitrogen (99.There is a strong triple-bond . The largest source of NH3 emissions is agriculture, including animal husbandry and NH3-based fertilizer applications.
- Nikon Z9 Fn2 Test | Nikon das Z-System, meine Erfahrungen nach drei Jahren!
- Nino Tempo , Nino Tempo & April Stevens music, videos, stats, and photos
- Nintendo Punkte : Nintendo Points
- Nitendo Switch Animal Crossing
- Norma Connect Prepaid Gutschrift
- Nissan Qashqai Neuheiten 2024 – Nissan Qashqai neu 2024
- Nischenbrüter Nisthilfen : Eine Wohnung für unsere Vögel
- No Rest For The Wicket , No Rest for the Wicked no Steam
- Nizza Vertrag Abkommen : Asylpolitik
- Nikotinsäure Präparate _ Lipoprotein(a): wann messen, wie behandeln?
- Niklas Name Deutschland – Nicklas