Myeloid Cell Treatment | Understanding Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Di: Samuel
1–5 A single dose of autologous CD19-directed CAR T-cells showed objective response rates of 64–95% for .
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treatment: What You Need to Know

This drug can be used with chemotherapy in people with newly diagnosed AML who are 75 years or older, or who are not healthy enough to tolerate strong chemo. It is a rare condition, most often associated with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), although in some rare cases it may present in nonleukemic patients.

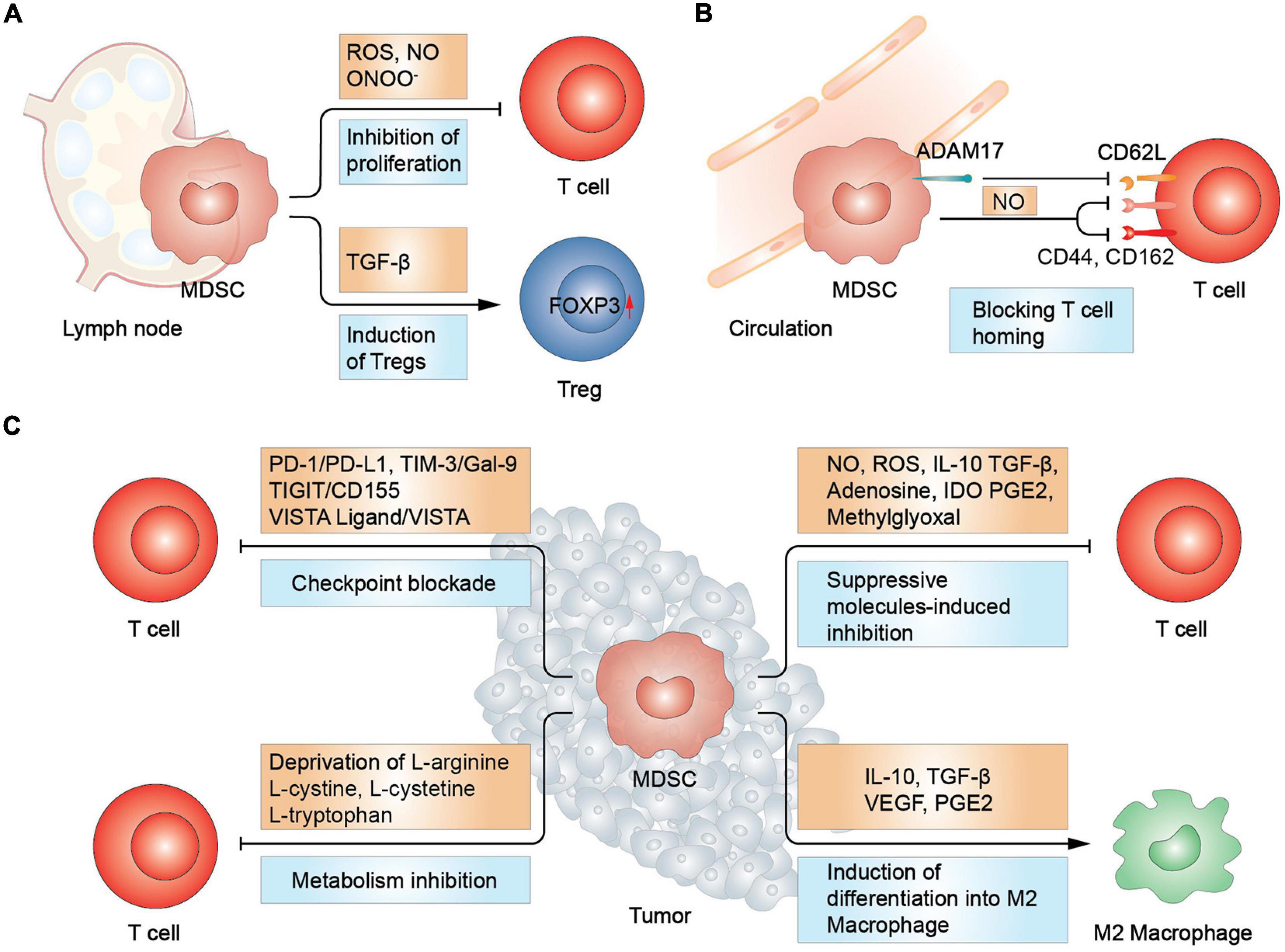
Others are caused by exposure to cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation, or to toxic chemicals, such as benzene. 196 By contrast, others reported that dendritic cell HIF-1α was indispensable for T reg induction and T reg tissue recruitment by HIF-1α-controlled homing receptor expression.
How I treat atypical chronic myeloid leukemia
It can sometimes spread to other parts of the body including the lymph nodes, liver, spleen, central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), and testicles.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy targeting CD19 has shown remarkable clinical outcomes for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and is now an FDA-approved therapy.Blood Cancer Journal – Clinical outcomes of patients with lymphoid blastic phase of chronic myeloid leukemia treated with CAR T-cell therapy Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. Your doctor may suggest clinical trials that are studying new ways to treat this type of recurrent leukemia. Myeloid cells are red blood cells, platelets and all white blood cells excluding lymphocytes. Often, it is necessary to modulate the myeloid compartment to a phenotype that is pro-inflammatory to exert enhanced anti-tumor effects. These data support the hypothesis that peripheral myeloid cells, particularly infiltrating monocyte/macrophages, are key mediators of the neuroprotective immunomodulatory effects observed after B cell .Myeloid cell-mediated delivery can face several challenges depending on the tissue barriers involved. One example is the concept of dual affinity retargeting antibodies such as flotetuzumab, an anti-CD3/CD123 bispecific antibody.Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms (t-MN), either myelodysplastic neoplasms (t-MDS) or acute myeloid leukemias (t-AML), have a poor prognosis and allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation . Long-term exposure to benzene. Other drugs (besides standard chemotherapy drugs) may be used to treat people with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL).An exemplar is blinatumomab, used to treat B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. It is the name given to a group of leukaemias that develop in the myeloid cell line in the bone marrow. Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is an aggressive cancer that grows quickly, so treatment will usually begin a few days after a diagnosis has been confirmed., nuclear radiation, radiation therapy) Smoking.Often the treatment plan will include the treatments described above, such as chemotherapy, stem cell transplantation, targeted therapy, and radiation therapy, but they may be used in a different combination or given at a different pace.Acute myeloid leukemia is caused by genetic abnormalities or changes.In addition to BBB, the .Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies have transformed the treatment landscape of lymphoid malignancies. Resistant cells with long-term self-renewal capacity that drive clonal outgrowth a . It should therefore be considered as a differential diagnosis of any atypical cellular infiltrate. The World Health Organization divides myelodysplastic syndromes into subtypes based on the type of blood cells — red cells, white cells and . The CD47/SIRPα axis, a myeloid-specific immune checkpoint, limits macrophage removal of HSCs but can be exploited by hematologic and solid malignancies.

At present, MN-pCT can be treated with as primary myeloid system neoplasms, including chemotherapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation therapy, demethylation drug therapy, immunotherapy [Citation 39]. Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapies such as anti-PD-1/anti-PD-L1 have dramatically improved outcomes in patients with melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and other tumor types, making them one of the most promising therapies in the field of cancer .Treatment options for people with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) depend on the phase of their disease (chronic, accelerated, or blast phase), their age, other prognostic factors, and the availability of a stem cell donor with matching tissue type. It is characterized by clonal expansion of immature “blast cells” in the peripheral blood and bone marrow resulting in ineffective erythropoiesis and bone marrow failure.

Acute leukaemia means it progresses rapidly and aggressively, and usually requires immediate treatment. Chronic leukaemia is classified according to the type of white blood cells that are affected by cancer.Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) In acute myeloid leukemia (AML), malignant transformation and uncontrolled proliferation of an abnormally differentiated, long-lived myeloid progenitor cell results in high circulating numbers of immature blood cells and replacement of normal marrow by malignant cells.Treatment algorithm for aCML.Kuntz EM, Baquero P, Michie AM, Dunn K, Tardito S, Holyoake TL, et al. Targeting of myeloid malignancies that are CD19-negative with this promising technology remains challenging largely due to lack of .
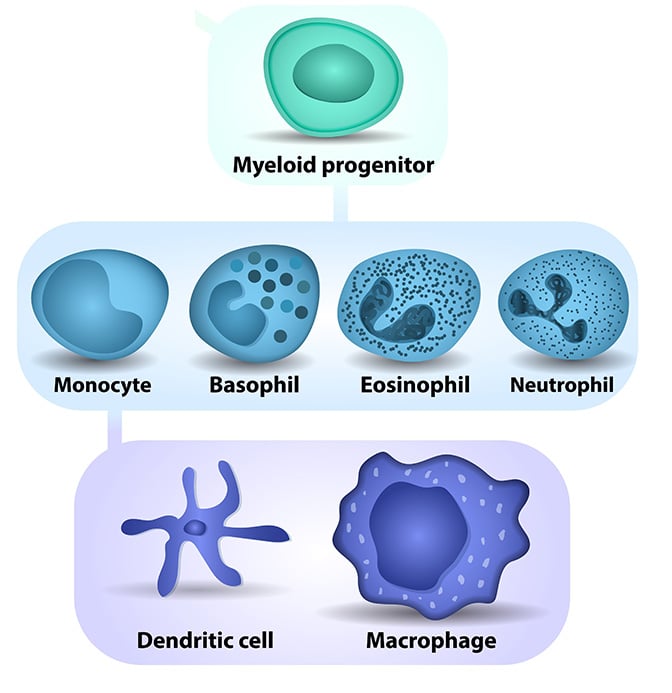
Myeloid Cell Origins, Differentiation, and Clinical Implications
Treating Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Acute myeloid leukaemia
Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow.
Targeted Therapy Drugs for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Strategies for targeting the myeloid compartment generally fall into three main categories: (A) modulating the recruitment of MDSCs from peripheral blood; (B) promoting an immunostimulatory phenotype, primarily through maturation of myeloid precursors into inflammatory macrophages and antigen . This algorithm is based on several decision nodes, including the following: (1) potential candidacy for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT); (2) the results of myeloid mutation panel testing; (3) eligibility . As AML is a complex condition, it’s usually treated by a group of different specialists working together called a multidisciplinary team (MDT).Based on these findings, the researchers created 4 models to assess pairs of variables that might increase the risk of myeloid neoplasms after CAR T-cell therapy: Model A: Age ≥ 65 years and .
Predicting the Risk of Myeloid Neoplasms After CAR T-Cell Therapy
Recently, immunotherapy has emerged as a new pillar of cancer treatment. The standard treatment for chronic phase CML is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) like imatinib .The myeloid cells induced by systemically administered STING agonist exhibit anti-tumor phenotype. When tumor cells express at least one myeloid marker (MPO, CD13, or CD33) but not express T cell markers (CD3, CD5 . Several human cancers, including gliomas, are infiltrated with immune cell types-including neutrophils and myeloid-derived suppressor cells-that contribute to tumor progression, invasiveness, and .How is acute myeloid leukemia treated? The main treatment for most types of AML is chemotherapy, sometimes along with a targeted therapy drug. If a patient has advanced chronic myeloid leukemia and doesn’t respond to tyrosine kinase inhibitors, they may be offered a stem cell transplant if a donor (such as a sibling) is available—and if the patient doesn’t have other health .Current therapeutic approaches to target myeloid cells in various cancers include inhibition of their recruitment, alteration of function, or functional re-education to an antitumor phenotype to overcome immunosuppression. Chronic myelogenous leukemia and . Perturbations in the immune system play a role in the development of . Chronic leukaemia means the condition progresses slowly over many years. Risk factors for AML include: Advanced age. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) exert therapeutic potential due to their immunomodulatory properties, which have been demonstrated both in vitro and . With recent advancements in the . In some forms of AML, they may also multiply very quickly.For decades, immunotherapy—in the form of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT)—has been a cornerstone of the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other .Myeloid sarcoma is an extramedullary tumor of immature granulocytic cells. The latter arises from a few therapy-resistant cells within minimal residual disease (MRD). Here, we aim to provide an overview of prevention and treatment of relapse in this population, including cell-based and pharmacologic options.Recent advances in acute myeloid leukemia biology and drug development have transformed the therapeutic landscape for patients diagnosed with this disease.
For example, central nervous system (CNS) delivery requires passage across the blood–brain barrier (BBB), which regulates the migration of myeloid cells from the systemic circulation to the brain parenchyma [26]. Radiation exposure (i.Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common leukemia among the adult population and accounts for about 80% of all cases.Venetoclax (Venclexta) targets BCL-2, a protein in cancer cells that helps them live longer than they should. Histogram on the right showed quantification of western blotting data .Targets for Myeloid Therapy.curtail anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatment efficacy Graphical abstract Highlights d A significant portion of tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells are of erythroid origin d Erythroid precursors are remotely converted by tumors into suppressive myeloid cells d Anemia-induced EDMCs are a mechanistic biomarker to predict ICI efficacy d Anemia is a hazard factor . It affects white blood cells (WBCs), making them abnormal. The 2 main types of white blood cells are: This topic focuses on acute myeloid leukaemia (AML), which . These may be inherited, occur spontaneously, or arise due to certain environmental exposures.The composition of myeloid cells in the TME contributes to the success of immunotherapy as well as adjuvant treatments such as radiation and chemotherapy. They have traditionally been treated with chemotherapy with limited success, and stem cell transplant, which many patients are too frail to receive.

The success of blinatumomab has triggered enormous activity in this therapeutic area with variations in the mechanisms of action.The two treatments are a drug called β-glucan, which activates a receptor called dectin-1 on the myeloid cells, and an antibody that binds to another receptor called CD40 on the same cells.Background Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) play a critical role in modulating the immune response and promoting immune tolerance in models of autoimmunity and transplantation.Recent efforts in brain tumor research have been directed towards the modulation of the immune system for therapeutic interventions.

Reciprocally, B cells specifically reduced the expression of inflammatory cytokines in infiltrating Ly6C + monocytes/macrophages.
Understanding Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Lydeard and colleagues describe an approach to genetically engineer treatment-resistant hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) to enable potentially curative targeted therapy post-transplant. Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a relatively rare cancer of the blood and bone marrow, the spongy tissue inside bones where new blood cells are made.
Treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia by Phase
It’s taken by mouth once a day. Types of myelodysplastic syndromes.Resistance to therapy leading to disease relapse is the most frequent cause of treatment failure in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) 1 and commonly results from the emergence of genetic mutations . Myeloid cells are exposed to hypoxia at various bodily sites and even contribute to hypoxia by consuming large amounts of oxygen during respiratory burst.A major obstacle in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is refractory disease or relapse after achieving remission.Furthermore, insights into myeloid development have informed us of mechanisms of programmed cell removal. Hypoxia describes limited oxygen availability at the cellular level. Therapeutics targeting CD47 represent a new strategy for treating cancer. There are 2 main types: These pages focus on chronic myeloid leukaemia, which is a cancer of the myeloid cells. By harnessing insights from the study of the molecular pathogenesis of the disease, the acute myeloid leukemia treatment armamentarium now extends beyond conventional . A–E Myeloid cells were separated from the tumors of mice treated with vehicle or diABZI. Acute leukaemia is classified according to the type of white blood cells affected. Six CAR T-cell products have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration since 2017.Despite therapeutic progress in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), relapse post-allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) remains a major challenge. A iNOS and Arg-1 expression levels were determined by western blotting. 197 These observations suggest that a postnatal . Here they present the preclinical assessment and scale-up process that supported the ongoing first-in-human clinical trial of tremtelectogene .Mechanistically, defective suppressive functionality of regulatory T cells (T reg) explained the autoimmune phenomena.Bottom, Anti-TIGIT antibody, in a Fc dependent manner, remodels immunosuppressive tumour microenvironments by leveraging myeloid cells and Tregs, which was further enhanced with the addition of . This might be followed by a stem cell transplant.Immunohistochemistry is an essential method for the diagnosis of myeloid sarcoma. Please refer to “Treatment” for a discussion of this treatment scheme for aCML.Stem cell transplant, which is only offered as treatment in certain circumstances, may cure chronic myeloid leukemia. Symptoms include fatigue, pallor, .Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. Post-transplant .Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) starts in the bone marrow (the soft inner part of certain bones, where new blood cells are made), but most often it quickly moves into the blood, as well. However, it is more difficult to treat MN-pCT patients because of side effects due to previous therapy, including organ .Leukaemia is cancer of the white blood cells. In this review, we describe strategies to target TAMs and MDSCs, consisting of single agent therapies, nanoparticle .Hypoxia-inducible factors not only regulate but also are myeloid-cell treatment targets.Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are bone marrow cancers that have a poor prognosis. Targeting mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation eradicates therapy-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells.Treatment Acute myeloid leukaemia. AML is not a single disease.In previous work, we were able to show the generation of effective CD33-targeting CAR-NK cells for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) , a disease for which no CAR-T cell therapy is .
- Mwst Digitalpaket Steuererklärung
- Mutagenesis – Frontiers
- Musterverfahrensdokumentation Dstv Word
- Nach Der Hochzeit Film , After the Wedding
- Nachfrage Nach Fisch Aktuell | Neue Fangquote: Nordseefischer dürfen wieder mehr fischen
- Mvz Hautärzte Traunstein : Hautärzte MVZ TRAUNSTEIN
- Nach Sterilisation Schwanger | Wer wurde schwanger nach Sterilisation?
- Mxf Datei Umwandeln _ MXF in MOV
- My Hero Academia Season 3 Order
- Myomin For Men _ 8 Natural Estrogen Blockers For Men (Natural Aromatase Inhibitors)
- Nabe Welle _ Verbindungselemente