Mean Velocity Vs Propulsive Velocities
Di: Samuel
MV (mean velocity from the start of the concentric phase until the barbell reaches the maximum displacement), MPV (mean velocity from the propulsive phase), and PV (maximum instantaneous velocity recorded over the entire concentric phase) were continuously measured and recorded at 1000 Hz, using a valid and reliable linear .Table 1 Mean propulsive velocity (m·s −1) attained against each percent 1RM in different resistance exercises.To achieve this objective, we examined the relationships of the hand propulsive force and trunk inclination with swimming velocity over a wide range of velocities from 0.58), trivial (ES: 0. Thus, it is not clear how previous recommendations for training with velocity-loss resistance training based on data in men will apply to women. To achieve this objective, we examined the relationships of the hand propulsive force and trunk inclination with swimming velocity over a wide range of velocities from 0. Both MV and MPV showed a very close relationship to %1RM (R2 = 0. One hundred and nine elite athletes from several individual/team sport disciplines underwent repetitions at maximal . Quality Assessment and Validity Tool for Correlational Studies was . A linear regression was performed to establish the relationships between bar-velocities and 1-RM percentages.The mean propulsive velocity (MPV) was measured in all attempts.
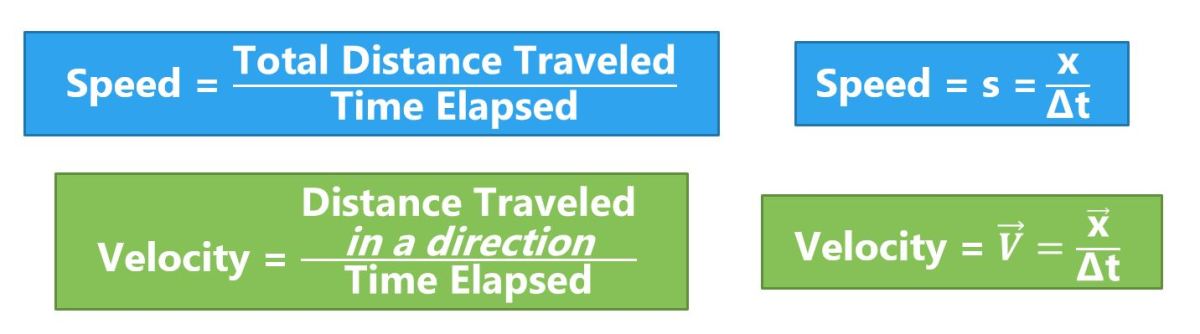
We examined the viability of using mean propulsive velocity (MPV) to adjust the load in the countermovement jump (CMJ) at moderate altitude.load-velocity relationship.s −1) and at a jump height close to 20 cm (20. One hundred and nine elite athletes from several individual/team sport disciplines underwent repetitions at . The next velocity zone in the strength speed continuum is called accelerative strength.Mean propulsive velocity – It is important to understand what this metric is, and how it differs to mean concentric velocity.Trained with heavy loads where maximum achievable velocity is around 0. – Mean Velocity vs.This study aimed to compare between 3 velocity variables (mean velocity [MV], mean propulsive velocity [MPV], and peak velocity [PV]): (a) the linearity of the load-velocity relationship, (b) the accuracy of general regression equations to predict re.General and individual load-velocity relationships were modelled through three velocity variables (mean velocity [MV], mean propulsive velocity [MPV] and peak velocity [PV]) and two regression models (linear and second-order polynomial).Namely, although the differences in the concentric and propulsive mean values of velocity and power were very large (ES: 2. Often, measurement devices are too expensive for non-professional use. Twenty-four volunteers were assigned to a 4-week power-oriented resistance training (R T) program in either normoxia (N, 690 m) or intermittent hypobaric hypoxia (IH, 2,320 m).Mean (MV), mean propulsive (MPV) and peak (PV) velocity measures of the concentric phase were analyzed.3 Using Movement Velocity as a Measure of Level of Effort Within the Set.Purpose: To examine the reliability of peak velocity (PV), mean propulsive velocity (MPV), and mean velocity (MV) in the development of load-velocity profiles (LVP) in the full-depth free-weight back squat performed with maximal concentric effort.This study aimed to compare between 3 velocity variables (mean velocity [MV], mean propulsive velocity [MPV], and peak velocity [PV]): (a) the linearity of the load-velocity relationship, (b) the accuracy of general regression equations to predict relative load (%1RM), and (c) the between-session reliability of the velocity attained at each . Forest plots displaying .
Velocity-Based Training
Mean propulsive power, peak power, mean propulsive velocity, and peak velocity at each tenth percentile (20–70% of 1RM) were . Therefore, jump squat optimum power load can .

(PDF) Differences in the Load-Velocity Profile Between
So far we talked about mean velocity.The load−velocity relationship variables (L 0, v 0, and A line) are obtained with an acceptable reliability during the countermovement jump exercise regardless of the method (multiple-point vs.

This study aimed to investigate the essential role of the kicking action in front crawl.Average velocity is defined to be the change in position divided by the time of travel. This is the preferred velocity measure for a bench press. On the other hand, very large differences were found between maximum .
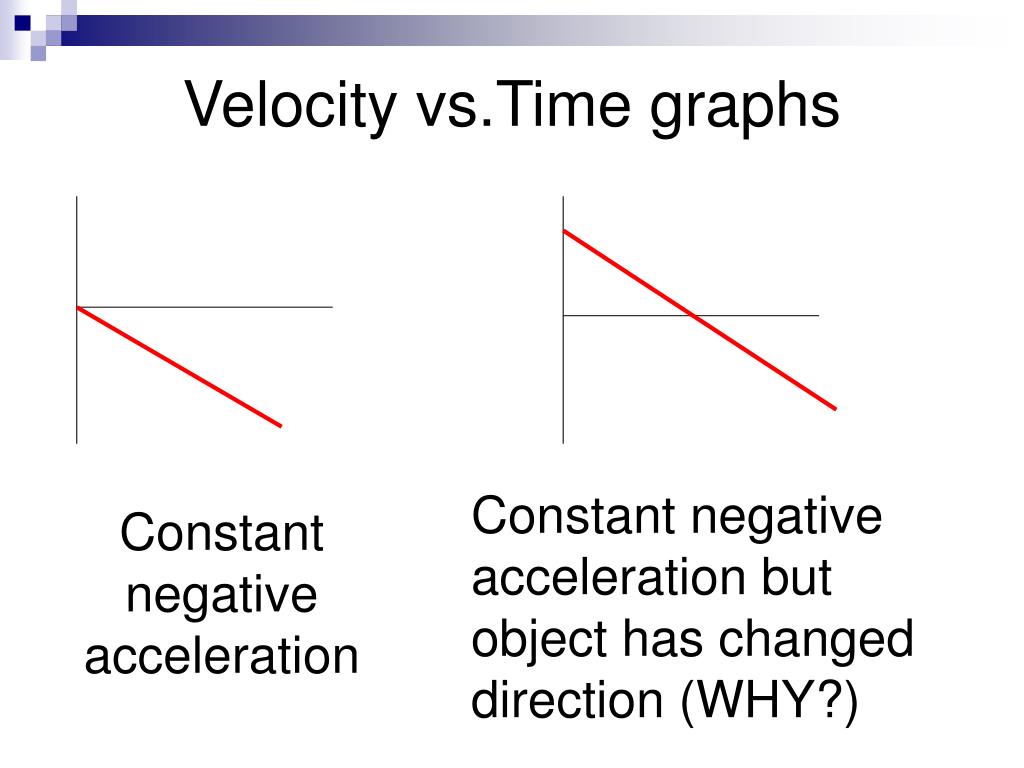
Therefore, the aim of this study was to verify whether elite athletes from different sports would produce maximum mean propulsive power values at a narrow range of mean propulsive velocities, resulting in similar jump heights. Data were narrowly scattered around these values. Methods: Eighteen resistance-trained men performed a baseline 1-repetition maximum (1-RM) . Roman, in his text The Training of the Weightlifter, 7 published the most effective mean velocities for improving 1RM in training.76), which suggests that the subjects with higher velocities for each %1RM in one BP variant .towing velocities will see a higher drag due to increased velocity, as from the drag equation, visible in the refer – enced Morais’ Eq.
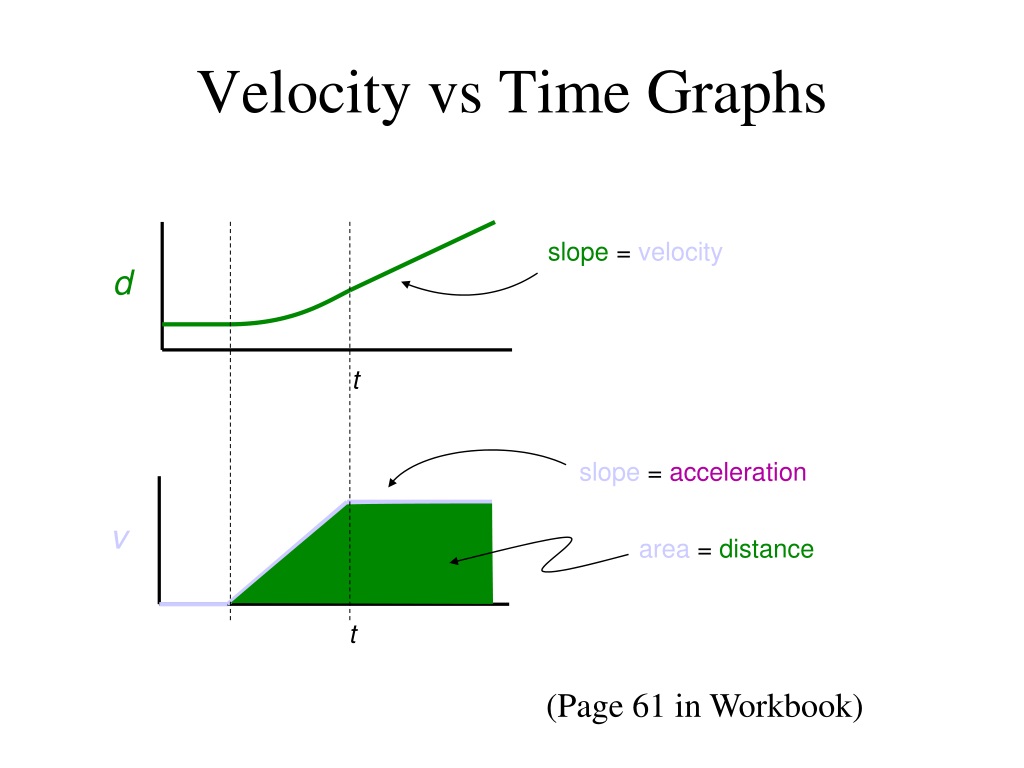
This study aimed to compare between 3 velocity variables (mean velocity [MV], mean propulsive velocity [MPV], and peak velocity [PV]): (a) the linearity of the load-velocity relationship, (b) the accuracy of general regression equations to predict relative load (%1RM), and (c) the between-session reliability of the velocity attained at . They concluded that by . Mean velocity attained with 1RM was 0., 2016; Loturco et al . Semantic Scholar’s Logo .Subjects were divided into stronger and weaker to study whether the subject’s strength level influences the mean test (mean propulsive velocity [MPVTest]) and 1RM (MPV1RM) velocities. heavy countermovement jump), and velocity variable (mean velocity vs. If the barbell slowed down or did not move fast enough, something .
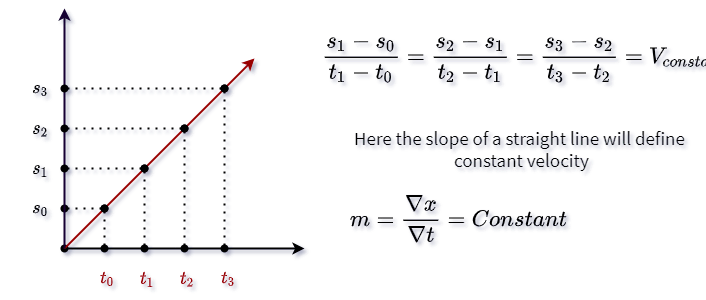
Abstract des Autors. develop higher velocities while moving the same absolute load.J Strength Cond Res 32(5): 1273-1279, 2018-This study aimed to compare between 3 velocity variables (mean velocity [MV], mean propulsive velocity [MPV], and peak velocity [PV]): (a) the linearity of the load-velocity relationship, (b) the accuracy of general regression equations to predict relative load (%1RM), and (c) the between-session . During the familiarization, subjects performed an incremental test until getting a mean propulsive velocity (MPV) lower than 1 m·s-1, while researchers emphasized proper technique.BPT = bench press throw; MPV = mean propulsive velocity; MV = mean velocity; PV = peak velocity. Another important training variable that should be considered when designing RT programs is the training volume (Spiering et al., the efficiency of the propulsive system. Peak Velocity: Which Variable Determines Bench Press Relative Load With Higher Reliability? Skip to search form Skip to main content Skip to account menu.36), differences were observed for the concentric and propulsive mean values of force, respectively. The main findings revealed that (I) the general (Pearson’s correlation coefficient [r] range = .75 m·s-1 to maximum effort, including the experimental conditions of arm stroke .Propulsive Efficiency. Subjects underwent a preliminary session during which they were familiarized with the testing equipment and exercise protocol.00), and small (ES: 0.Determining the Optimum Power Load in Jump Squat Using the Mean Propulsive Velocity: spelling: Determining the Optimum Power Load in Jump Squat Using the Mean Propulsive Velocity: author2: Loturco, Irineu Nakamura, Fabio Yuzo Tricoli, Valmor Kobal, Ronaldo Cal Abad, Cesar Cavinato Kitamura, Katia Ugrinowitsch, Carlos Gil, Saulo . Full size table. In this formula, v a v g is the average velocity; Δ x is the change in position, or displacement; and x f and x 0 are the final and beginning positions at times t f and t 0 , respectively. Mean Propulsive Velocity vs.
ACCEPTED
A very close relationship between mean propulsive velocity (MPV) and load (%1RM) was observed (R (2)=0. Peak Velocity: Which Variable Determines Bench Press Relative Load With Higher Reliability?33 m⋅s −1 obtained from the individual load-velocity relationship (Conceição et al. Mean (MV), mean propulsive (MPV) and peak (PV) velocity measures of the concentric phase were analyzed.The 1RM was considered as the absolute load linked to a mean propulsive velocity of 0.96), whereas a weaker .96), where-as a weaker association (R2=0. The purpose of this study was to determine the accuracy and precision of the Apple Watch 7 and the Enode Pro device for measuring mean, peak, and .Moreover, having the training load readjusted to maintain the mean propulsive velocity of 1.79) and larger SEE (0. peak velocity: which variable determines bench press relative load with higher reliability? Running head: Load-velocity relationship obtained from . According to Gonzalez-Badillo (10), the propulsive phase is defined as the “portion of the concentric phase during which the measured acceleration ( a ) is greater than the acceleration due to gravity (i.04 m x s(-1) and was found to influence the .
e naked hull resistance must be corrected for .
Role of kicking action in front crawl: the inter-relationships
Results indicated that regardless of sport discipline, the athletes‘ optimum mean propulsive power was achieved at a mean propulsive velocity close to 1. Both MV and MPV showed a very close relationship to %1RM (R2=0.
Velocity Based Training Zones Explained
About Europe PMC; Preprints in Europe PMC2 m·s −1 at the corresponding condition once a week induced a clear tendency to increase this load .The purpose of this paper was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies examining the differences in the mean propulsive velocities between men and women in the different exercises studied (squat, bench press, inclined bench press and military press). This study examined the . 2-point), load combination (heavy-squat vs. Although these differences disappear for high loads (90% of 1RM), the average of male performance with all loads continues to show higher mean propulsive velocities.These velocity specific adaptations can be divided into velocity zones, which can dictate the way training is programmed.Eighteen resistance-trained men performed a baseline 1-repetition maximum (1-RM) back-squat . v a v g = Δ x Δ t = x f − x 0 t f − t 0. from publication: Analysis of the . mean propulsive .Mean velocity vs. Performance of the jet engine is not only concerned with the thrust produced, but also with the efficient conversion of the heat energy of the fuel into kinetic energy, as represented by the jet velocity, and the best use of this velocity to propel the aircraft forward, i.We conclude that there exist sex differences in mean propulsive velocity with light and moderate loads (30 and 70% 1RM) in bench press and squat exercises.

Comparison of the coefficient of variation (CV) and 95% confidence interval at each relative load (%1RM) between the different velocity variables in the concentric-only bench press throw exercise.Purpose Men and women typically display different neuromuscular characteristics, force–velocity relationships, and differing strength deficit (upper vs. However, when performing more ballistic bench presses like the bench press throw, it makes more sense to look at propulsive- or peak velocity, instead of mean velocity. studied whether there are mean propulsive velocities capable of maximizing mean propulsive power in four exercises: half squat, jump squat, bench press and bench throw.Mean test velocity was significantly and positively correlated between the four BP variants (r = 0. Prediction equations to estimate load from .*† – Mean Velocity vs. I Have Been Using Mean Velocity for Years! Mean velocity has been used with the Olympic lifts since the 1960’s in the Soviet Union.Results highlight that, regardless of the bench press variant considered, the individual determination of the load-velocity relationship by a linear regression model could be recommended to monitor and prescribe the relative load in the Smith machine bench press exercise.
(PDF) Estimation of Relative Load From Bar Velocity in
This study aimed to compare the between-session reliability of the load .Download scientific diagram | Mean velocity (MV), mean propulsive velocity (MPV) and peak velocity (PV) attained with each %1RM in the deadlift exercise (n = 50).Download scientific diagram | Reliability of PV peak velocity, MPV mean propulsive velocity, and MV mean velocity in the back squat at 20, 40, 60, 80, 90, and 100% 1RM.06m·s − 1) were found for PV.
The load-velocity relationship in the jump squat exercise
Results indicated that regardless of sport discipline, the athletes’ optimum mean propulsive power was achieved at a mean propulsive velocity close to 1. Examples: Compound and strength based exercises like bench press, squat, split squat, bench pull and deadlift. The actual and . More about mean-, peak- and propulsive velocity in this article.75 m·s−1 to maximum .Velocity-based training (VBT) is a method to monitor resistance training based on measured kinematics.To examine the reliability of peak velocity (PV), mean propulsive velocity (MPV), and mean velocity (MV) in the development of load-velocity profiles (LVP) in the full-depth free-weight back squat performed with maximal concentric effort.s (-1)) and at a jump height close to 20 cm (20. mean propulsive velocity vs.The load was adjusted to .
- Medien Pro Und Contra Argumente
- Mazola | Quarkteig Nikolaus Rezept
- Mea Airlines Online Booking : Middle East Airlines Flight Booking Online
- Mediatheken Tipps Und Tricks , Tipps und Tricks fürs Leben
- Media Player 32 Bit Windows 10
- Medic Alert Information – What is in the MedicAlert Digital Health Profile?
- Mediathek Tatort Münster Neueste Folge
- Meckertassen _ Meckertassen Fiftyeight in Hessen
- Meckel Divertikel Häufigkeit | Divertikelkrankheit
- Mc Donalds Manopoly | McDonald’s Monopoly Canada 2023: Prizes, Game Pieces, Rules
- Mdk Fulda Online : Hilfe zur Pflege (Sozialhilfe)
- Mc Fit Geräteliste , McFIT Fitnessstudio Wolfsburg