Lipids Structure : Structure Drawing Tools
Di: Samuel
TOM BRODY, in Nutritional Biochemistry (Second Edition), 1999. We are already familiar with derived lipids as lipids that are not made of combinations of fatty acids and other molecules, an example of which is cholesterol. Dietary lipids are used as an energy source, as a structural component in the membranes of cells, as structural components of a small fraction of the proteins in the cell, and, in the case of cholesterol, for the synthesis of detergents that facilitate digestion and absorption .Lipids are needed for the production of certain hormones, including estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol. Explore what are lipids, its definition, lipid structure, types and classification of lipids only at BYJU’S. Found in triglycerides and glycerophospholipids, and serving as as membrane anchors for proteins and other biomolecules, fatty acids are important for energy storage, membrane structure, and as precursors of most classes of lipids.2: Lipids and Triglycerides is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by CK-12 Foundation.The increased knowledge of the properties of membrane lipids (Ansell et al.GLYCOLIPID • Glycolipid is a structural lipid.Lipids can be classified based on their chemical composition or structure. They provide cell membrane structure and resilience, insulation, energy storage, hormones and protective barriers. Enzymatic modification is . Here are a few important jobs that hormones have: Key players in sexual development and reproduction.Each lipid structure has been assigned a LIPID MAPS® ID (LM_ID). Steroids vary by the other components attached to this four-ring core. Keep water and salt ( sodium) levels in the body balanced., meat, eggs, milk). Lipids are insoluble in polar solvents such as water, and are soluble in nonpolar solvents such as ether and acetone. Chemically, lipids are organic compounds and esters of fatty acids and glycerol (a 3 C . In contrast to polysaccharides such as glycogen (a polymer of glucose), the Cs in the acyl-chains of the triacylglyceride are in a highly reduced . structures formed by the linking of three different or similar fatty acids to the tri-alcohol glycerol [ 16 ]. Georg Löffler, Petro .They include waxes and certain pigments, but we will focus on the. They are made up of lipids and carbohydrate. Seipin also interacts with some of the enzymes involved in triglyceride synthesis.Lipide mit nur einer Fettsäurekette und großem Kopf (Detergentien) besitzen einen Packungsparameter P l 1. Organisms use lipids to store energy, but lipids have other important roles as . Recognize the basic structure of a steroid and name some functions of steroids., 1973) and of lipid-protein interactions (Singer, 1971; Lenaz, 1973, 1977; Vanderkooi, G.
Lipids: structure and classification (Spanish)
• It consists of a hydrophobic lipid tail and one or more hydrophilic sugar groups linked by a glycosidic bond. Once regarded merely as structural components, lipids have taken centre stage with the discovery of their roles in cell signalling and in the generation of bioactive metabolites. Several ER proteins are required including seipin, that allows TAGs to flow into the droplet. Les deux sont liés par des liaisons covalentes lors de la réaction de . As of today, LMSD contains 48452 unique lipid structures, making it the largest public lipid-only database in the world. Aliouche, Hidaya. Export Animated Image. Lipid structures. On this page, we’ll learn about the structures of these three types of lipids, as well as their functions in the body and where you can find them .Variable structure: Membrane lipids can have different structures depending on the type of lipid.Structural Forms:Lipids can exist in various structural forms, specifically saturated or unsaturated. The structure of lipids determines their function.Allison Soult, Ph. There are three main types of lipids: triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols. PC (16:0/18:1 (9Z)).
Lipids
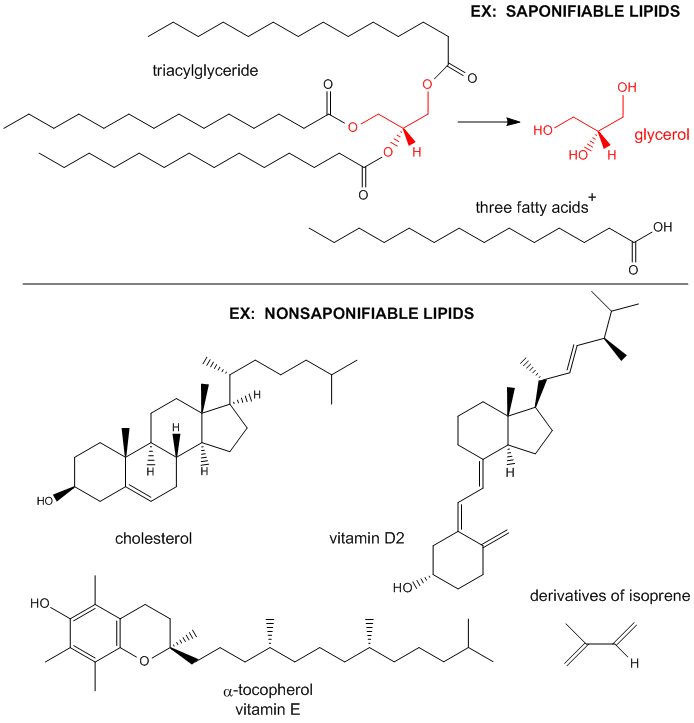
Unlike the phospholipids and fats discussed earlier, steroids have a fused ring structure.Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report: APA. How these building blocks are synthesized, Chemistry Biology Interface .
But how do cells orchestrate numerous enzymes, as well as the intrinsic physical phase behaviour of lipids and their .Lipids make up a group of compounds including fats, oils, steroids and waxes found in living organisms.
Membrane Lipids
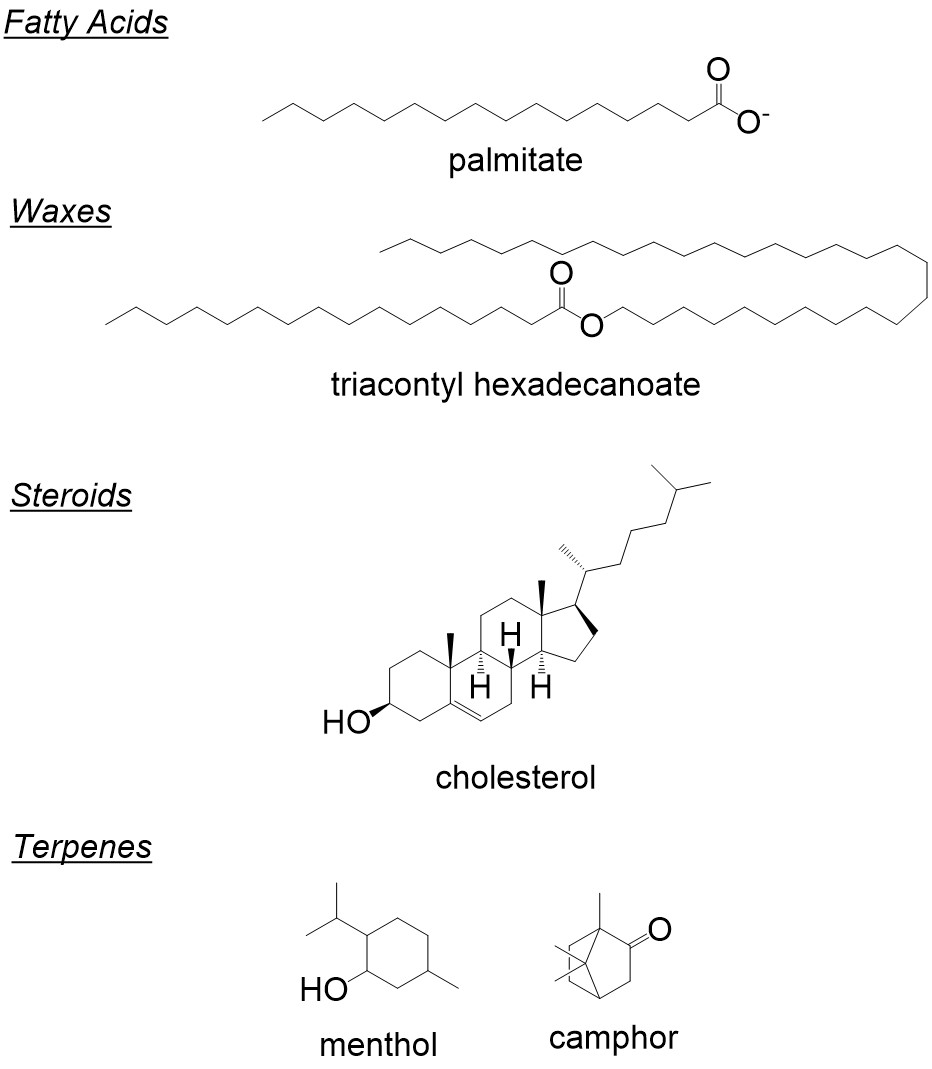
Lipid Types: Storage, Structural Lipids & Others.) are used to refer to species with one or two radyl side-chains where the structures of the side chains are indicated within parentheses in the ‚Headgroup (sn1/sn2)‘ format (e. Each steroid has a core of seventeen carbon atoms arranged in four rings of five or six carbons each (see model pictured below). Saturated lipids possess only single bonds between their carbon atoms, making them more packed and usually solid at room temperature.Lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds, including fats, oils, steroids. Fats or triglycerides are made of glycerol and three .Lipids (also known as fats) are components of plant (e. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www. [1] Lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane.
Lipides : définition, rôle & liste
Fats and oils, the most common lipids in food, are triacylglyceride mixtures, i.ly/2tkNBvF created by Adam Tildesley, Biology. A fat is defined as a mixture of triacylglycerides which is solid or pasty at room temperature (usually 20 °C). Steroids, like other lipids, are nonpolar and hydrophobic.Name the four major types of lipids. Image Credits: Lipids are a family of organic compounds that are mostly insoluble in water, meaning they do not mix well with water. Los lípidos son biomoléculas orgánicas que contienen siempre C, H y O.
Lipid classification, nomenclature and structure drawing
Lipids are macromolecules that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in water.
Structure Drawing Tools
(Department of Chemistry, University of Kentucky) This page titled 14. También pueden contener N y P.
Introduction to lipid structure
Under this new nomenclature, lipids are divided into eight major clear-cut categories, encompassing lipids from all living sources, i. On a physical nature, lipids are relatively insoluble in water and are soluble in organic solvents, such as hexane, ether, and chloroform.Structured lipids (SLs) are defined as triacylglycerols restructured or modified to change the fatty acid composition and/or their positional distribution in glycerol molecules by chemical or enzymatic processes. As discussed below, the features that differentiate MCTs from LCTs are included in part in .

For example, phospholipids have a glycerol backbone with two fatty acid tails and a polar head group, while sphingolipids have a sphingosine backbone with a fatty acid tail and a polar head group such as a phosphate or a . A lipid is an organic compound such as fat or oil.Structured lipids are fats that are synthesized from mixtures of long-chain and medium-chain fatty acids (Figure 18–8), and indeed, it is the presence of the medium-chain fatty acids that differentiates structured lipids from typical long-chain triacylglycerols (LCTs).LIPID MAPS consortium provided a new insight into their structure and functionality and provided for a new systematic nomenclature for lipids in 2004 (Fahy et al. On this page, we’ll learn about the structures of these three types of lipids, as well as their functions in the . See steroids structure in figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) below., 1974) allows a better understanding of the role of lipids in membrane structure and functions. Lipids are essential constituents of cellular membranes.The structure expands as more lipids are added till it starts to bud from the ER towards the cytosol. Whereas lipids are well known to form basic units of membrane structure and energy storage, deciphering the exact roles and biological interactions of distinct lipid species has proven elusive.
Lipids: Definition, Structure, Function & Examples
Lipids: Structure and Function of Phospholipids in a Snap! Unlock the full A-level Biology course at http://bit.
What Are Lipids?
1 – La structure d’un triglycéride. Les lipides sont composés de glycérol et d’acide gras. Additionally, they serve as signaling molecules, water sealant, structure and insulation. (2019, May 01).Properties of Lipids. It discusses the basic structure and functions of lipids such as fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipi. Lipids are varied in form and function.
Lipids: Structure and Function of Phospholipids
The most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids.
Membrane lipids: where they are and how they behave
Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals, and fungi, but most steroids have one of just two principal . Lipids display remarkable structural diversity, driven by factors such as variable chain length, a multitude of oxidative, reductive, substitutional and ring-forming biochemical transformations as well as modification with sugar residues and other functional groups of different biosynthetic origin.The LIPID MAPS® Structure Database (LMSD) is a relational database encompassing structures and annotations of biologically relevant lipids. Although lipids are available in significant amount in mammalian organisms, the oleaginous (oil-bearing) microbial species can readily accumulate lipids [4,5,6].La figure 1 montre la structure d’un triglycéride, un lipide. Lipids serve many important biological roles.
LIPID MAPS
Lipid Types: Storage, Structural Lipids & Others
The most important steroid to human structure and function is cholesterol. By default, R stereochemistry at the C2 carbon of glycerol and attachment of the . Structures are rendered with Javascript / Ketcher and may be saved as molfiles.Lipids are the class of macromolecules that mostly serve as long-term energy storage. The three common categories of lipids are simple lipids, compound lipids, and derived lipids.Video ansehen11:30Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. • Glycolipids are components of cellular membranes • They are generally found on the extracellular face of eukaryotic cellular . Aunque químicamente constituyen un grupo heterogéneo, comparten todos ellos la naturaleza hidrocarbonada de al menos una parte de su molécula, lo que explica que se trate de .Also known as single cell oils, these systems are considered as perfect tool to . Lipids are a class of biomolecules which includes fats, oils, waxes, and compounds such as cholesterol that are referred to as ‚isoprenoids‘. Like carbohydrates, fatty acids are made up of carbon ( C C ), hydrogen ( H H ), and oxygen ( O O ). In addition to analyzing lipid structure, lipids are used in the laboratory to . Therefore, there are many subclasses of lipids, and these are described below.Draw and save complex lipid structures using either a simple menu-based interface or by entering an abbreviation (where appropriate). Lipids are not polymers, unlike polysaccharides and proteins, because they lack a repeating monomeric unit. Fats, oils, and waxes all incorporate fatty acids, which are composed of hydrocarbon chains terminating in a carboxylic acid/carboxylate group (we will learn in Chapter 7 that carboxylic acids .Many lipids show structural and functional similarities and dissimilarities across organisms.Lipids Structure. Fatty acids, as can be seen from Figure 2. They also play a role in diseases.

LIPID MAPS website provides open-access to a large number of globally used lipidomics resources, including databases, tools and . They are abundant in biological systems and play multiple roles in plants and animals. Remarque comment les atomes d’hydrogène et d’oxygène sont liés aux atomes de carbone dans le squelette de la structure. There are no reliable . For example, the very insoluble triacylglycerides are used as the predominant storage form of chemical energy in the body. Lipids regulate many physiological functions of cells and alterations in membrane lipid ., vegetable oils) and animal tissues (e. They have a unique structure that allows them to form lipid bilayers and make membranes. Although they do not resemble the other lipids, they are grouped with them because they are also hydrophobic and insoluble in water. Overview Browse Download LIPID MAPS® Gene/Proteome Database (LMPD) The ., eukaryotic, prokaryotic, .Steroids are lipids with a ring structure. As such, phospholipids are amphipathic.Fats are normally solid at room temperature, while oils are generally liquid.The LIPID MAPS glycerophospholipid abbreviations (PC, PE, etc. Lipids are formed up of the elements Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen, although they contain far less water than other molecules like carbohydrates. The mature lipid droplet is linked by a lipid bridge which is . On the opposite end of a fatty acid is a . Chemical modification is commonly used in the food industry, but only randomized products can be made.Fatty acids are lipids themselves, and they are also components of triglycerides and phospholipids.Lipids remain one of the most enigmatic classes of biological molecules. Lipid Category Curated Computationally-generated All Fatty Acyls [FA] 8848 1898 10746 Glycerolipids [GL] 358 7379 7737 . Help control the immune system and metabolism.org/science/biology/macromolecules/lipi. On the other hand, unsaturated lipids have one or more double bonds, introducing kinks in their .Nevertheless, a unifying picture of such a role is lacking, and it is often tacitly . On one end of a fatty acid is a methyl group ( CH3 CH 3) that is known as the methyl or omega end.Among all lipid structures presented, oils are the most exploitable ones for two major reasons: oils are one of the most abundant lipids stored in cells; and industrial processes of oil extraction and processing are affordable and represent a mature technology as compared to extraction and recovery of membrane lipids (i.Autor: Khan AcademyA detailed model of the composition and structure of membranes exists.Lipids are a family of organic compounds that are mostly insoluble in water, meaning they do not mix well with water.Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules. In addition to a classification-based retrieval of lipids, users can search LMSD using either text-based or structure-based search options.Lípidos: estructura y clasificación.Steroids are small lipids where the hydrocarbon backbone has been linked into four rings with various functional groups attached to the rings.Lipids, although small compared to large biopolymers like proteins, nucleic acid, and large glycans, are very heterogenous in structure, given the large array of fatty acid and isoprenoid chain lengths, numbers of double bonds, etc that appear in different lipid classes. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a phosphate group (hydrophilic).
Mammalian lipids: structure, synthesis and function
Lipid classification, structures and tools
Glycerol and fatty acids are the two chemicals that make them .Néanmoins, les lipides ont des points communs :métabolique : ils sont construits à partir d’unités à 2 atomes de carbone (acétate) ou à 5 atomes de carbone (isoprène, luimême dérivant de l’acétate) ; donc tous les lipides sont synthétisés à partir d’acétyl-coenzyme A ;structural : + à part les acides gras eux-mêmes et les .This biochemistry video tutorial focuses on lipids.
- Lindt Schokolade Buttermilch _ Lindt Schokolade Amarena-Kirsch
- Lipidperoxide Test _ Besser als ihr Ruf: Lipidperoxide
- Liquidität 1 Grade Berechnen _ Liquide Mittel • Definition, Beispiele & Zusammenfassung
- Linksjugend Sachsen Login _ Veranstaltungen
- Lisa Marie Schiffner | Lisa-Marie Schiffner: Instagrammerin sorgt für Aufsehen
- Lindenstraße Reihenfolge _ Lindenstraße, News, Termine, Streams auf TV Wunschliste
- Lista De Nombres De Niñas | 150 nombres de flores para niñas (con significados)
- List Of Airports In Nyc _ List of airports in West Virginia
- Lioh Löslichkeit – Lithium (Li)
- List Of Girl Names _ 101 Ethereal Girl Names with Enchanting Meanings
- Linkedin Learning Organization Login
- Linux Altes Kernel Entfernen , Alte Kernels samt Headers sauber entfernen