Layer 1 Blockchain Definition – Layer 1
Di: Samuel
Benefits of Layer 1 Blockchain. Wir gehen näher darauf ein, was das Skalierbarkeitsproblem verursacht und warum es so wichtig ist, dieses Problem zu lösen. On the other hand, layer 2 solutions focus on adding third-party integrations to the mainnet of the blockchain network.Le Layer 1 de la blockchain est à la fois le moteur et la toile de fond sur laquelle se dessinent des transformations majeures dans de nombreux secteurs d’activité.Explore the top 50 list of Layer-1 coins, ranked by market cap.
What Is Blockchain Interoperability?
In diesem Leitfaden über Layer-1-Blockchains erklären wir ihre Funktionsweise innerhalb des Blockchain-Ökosystems. Each layer has a unique role, from storing data to maintaining network connectivity and ensuring consensus across the system.
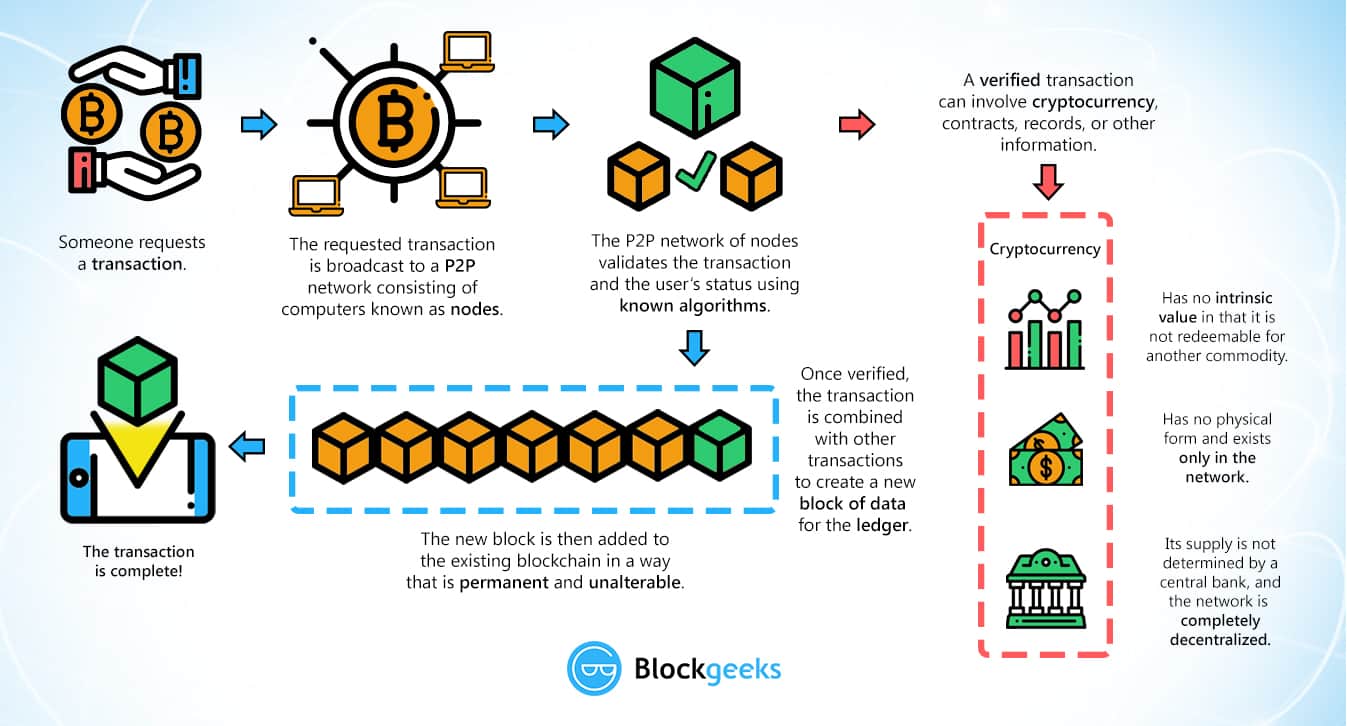
Wenn Sie sich mit Kryptowährungen oder Blockchain beschäftigen, werden Sie wahrscheinlich auf den Begriff Layer 1 stoßen.
Was ist Avalanche (AVAX)? Erklärung, Prognose und Kurse
Definition of Layer 1.Layer 1 blockchains come with inherent challenges native to cryptographic technology.Definition von Layer 1.Blockchain architecture refers to the underlying components and structures that constitute a blockchain network. They allow companies, developers, and builders to create apps and resources. The layer 2 blockchain is built on top of it. This layer forms the protocol, which includes the consensus mechanism, network structure .
What Is A Layer 1 Blockchain?
In this article, we’ll be .
Layer 1
Les layer 1, des blockchains indépendantes, mais insuffisantes. Layer One is the underlying protocol of a blockchain network. Der Ausdruck Layer 1 bezieht sich auf die grundlegende Protokollebene oder Hauptblockchain einer Kryptowährung. Anschließend werden wir uns detailliert mit Off-Chain-Lösungen befassen, aber . Interoperability also encompasses blockchains’ . Le terme Layer 1, qui signifie littéralement “couche 1”, fait simplement référence à la blockchain de base, c’est-à-dire, la blockchain principale.Blockchain interoperability: a definition. Blockchains use a peer-to-peer network to communicate, organize transactions into blocks, use a consensus . Layer-2-Blockchains sollen die Basis-Blockchain bei der Skalierbarkeit unterstützen.Permissioned blockchains use an access control layer to govern who has access to the network. Im Krypto-Space wird umgangssprachlich häufig von “Layer 0”, “Layer 1” oder “Layer 2-Projekten” gesprochen.Layer 1 blockchain comparison: An in-depth performance analysis. Parties can securely transfer funds from the blockchain into an off-chain protocol, settle . The base-level chain executes every on-chain transaction. More Market cap .
Definition of Layer 1 blockchain
Blockchain Layer 1 vs Layer 2
Disadvantages of permissioned blockchain. The Layer 1 term arose to define the primary chains after Layer 2 blockchains were developed to process payments . Layer two is a third-party integration used in conjunction with layer one to enhance the number of nodes and, as a result, system . The consensus mechanism involved generally comes with trade-offs to do with blockchain scalability.Le terme “Layer 1” fait référence à une blockchain de base, comme celle de Bitcoin ou d’Ethereum. Layer 2: definition. Les blockchains de type layer 1 permettent de valider des transactions directement sur leur propre blockchain. Terdapat berbagai blockchain yang masuk dalam kategori layer-1, layer-2, layer-3 dan bahkan layer-0. The concept aims to make it possible for web3 users to seamlessly switch from one blockchain network to another. Decentralization: L1 blockchains offer a high degree of decentralization, with no need for intermediary layers or reliance on external networks for transaction processing. En savoir plus sur la crypto ici. Layer 2 scaling solutions: Improving the speed of Layer 1 platforms without making any fundamental changes to their code or architecture. It achieves this through a consensus mechanism called proof-of-work (PoW), which incentivizes network participants to compete to solve complex mathematical problems. The Layer 1 protocol can process and complete transactions on its own blockchain, and bring its own native token to pay transaction fees. Layer-1 coins Layer 1 tokens are native coins of their own blockchain.
What is a Layer 1 Blockchain?
Hierbei handelt es sich um die Basis, auf der alle weiteren . Ces différentes couches successives vont regrouper un ensemble de composants et permettre, si besoin est, de créer une couche de niveau supérieur, tout en utilisant les composants de la couche sur laquelle elle repose. For example, Ethereum runs transactions without depending on an external system and has its own native . Layer 2: Third-party integration on top of Layer 1 networks. Cette technologie fondamentale ne se limite pas aux cryptomonnaies, elle est un catalyseur d’innovation qui ouvre de nouvelles perspectives.
Layer 2 vs Layer 1 : quelles différences
Layer 1-Skalierungslösungen beinhalten direkte Änderungen am Protokoll, wie die Erhöhung der Blockgrösse, um . Blockchain interoperability refers to blockchains’ ability to communicate and facilitate seamless data and crypto asset transfers. Together with their live prices, ranking, charts and other statistics.Bei einer Layer-1-Blockchain (dt.Layer 1-Netzwerke: Das Herzstück der Blockchain . C’est le réseau sur lequel on va pouvoir développer des applications, des protocoles, des smart contracts, etc.Layer 1 blockchains are standalone solutions designed to maintain a distributed and decentralized digital ledger and potentially support smart contracts. Layer-2 hingegen ist ein überlagerndes Netzwerk, das über der zugrunde liegenden Blockchain liegt. Es sind Protokolle von zumeist Drittanbietern, die sich in eine zugrunde liegende Layer-1-Blockchain integrieren, um den . BTC dominance . This layer is also responsible for safeguarding the blockchain network. While layer 1 solutions focus on modifying the base protocol, layer 2 solutions emphasize . Layer-1 blockchains validate and execute transactions without support from another network, and reimburse transaction fees with cryptocurrencies.
Layer 1
Bitcoin und Ethereum sind die beiden größten L1-Blockchains der Welt. Les layer 1 ne sont ni plus ni moins que des blockchains souveraines. Layer 1 scaling solutions: Fundamental changes made to Layer 1. To varying degrees, blockchains are based on the design of Bitcoin. It is the first level of the ecosystem and corresponds to the main chain of the network.
Was ist Layer 1 bei Blockchain?
Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network . Layer 1, also known as on-chain scalability, mainly implements the underlying technology of the blockchain protocol.Dans l’univers des blockchains et de la cryptomonnaie, un « Layer » se traduit en français tout simplement par couche. This creates a transparent and fair environment for peer-to-peer transactions. An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding).The blockchain is the first layer in a decentralized ecosystem. Presently, most public chains operate under Layer 1. Pour faire simple, les solutions Layer 1 améliorent la couche . Les blockchains de layer 1 ont également leur propre token natif, ETH pour . For instance, consider the Lightning Network as an example of a layer 2 Blockchain deployed on the Bitcoin Blockchain. This layer includes the core components such as the blockchain protocol, consensus mechanism, and the native cryptocurrency.Les solutions de Layer 1.Layer 1 blockchains are the backbone of the decentralized ecosystem, providing the foundation upon which all other layers and applications are built.Layer 1 blockchain refers to the fundamental base network of any blockchain platform.This increases the main chain’s throughput.Layer-2 sits on top of Layer-1 in the Blockchain ecosystem and constantly exchanges information with it. Security: Being the foundational layer, L1 blockchains have robust security mechanisms in place, protecting against attacks and ensuring the . However, all layers have a common goal: conduct off-chain transactions to scale the Bitcoin network.Layer-1 blockchains work as the base layers.Autrement dit, elles ne dépendent d’aucun autre réseau pour fonctionner (hormis la couche fondamentale, commune à toutes les blockchains). Notable examples encompass Ethereum and similar Layer-1 blockchains that offer the infrastructure for a plethora of innovative applications such as NFTs (Non .Layer 1 solutions basically involve changes in the base protocol of blockchain networks for ensuring better scalability.
What are Layer 1 Blockchains?
Bitcoin’s layer 1 is designed to ensure the security and immutability of transactions on its network.C’est ce qu’on appelle la blockchain d’infrastructure.Layer-1 Blockchain Definition.
Layer-1 Blockchain Explained
Within the crypto world, scalability refers to a blockchains ability to support increasing load of transactions, as well as increasing the number of nodes in the . In the sections that follow, we are going to analyze the blockchain performance of the leading Layer 1 networks in the industry based on their transaction speed, time to finality, scalability, node count, storage costs, cloud service dependency, energy efficiency, and . They are frequently referred to as the “core” or “foundation” of the blockchain network because they provide the infrastructure for all applications and protocols developed on top of the network.Layer-1 ist der Begriff, der verwendet wird, um die zugrunde liegende Haupt-Blockchain-Architektur zu beschreiben. All while giving access to the native perks related to scalability, security, and decentralization.

Think of L1s as both rule-makers and enforcers for crypto projects.Browse Encyclopedia. Trading volume .Layer 1 is the name given to a base blockchain like Bitcoin or Ethereum.Eine Blockchain verhält sich wie ein Ökosystem, das in sogenannte Layer eingeteilt werden kann, vergleichbar mit den Internetprotokollen, die nach dem TCP/IP- Referenzmodell in Schichten klassifiziert werden. Ce qui signifie que les blockchains de type .Blockchain architecture refers to the components and subcomponents or layers that make up a complete blockchain system.Bei einer Layer-2- Blockchain (dt. It has been argued that permissioned blockchains can guarantee a certain level of decentralization, if carefully designed, as opposed to permissionless blockchains, which are often centralized in practice.Layer 1: Underlying blockchain architecture.Avalanche (AVAX) ist eine Smart-Contract-Plattform, die über drei verschiedene Blockchains verfügt und das Erstellen von Subnets ermöglicht.Layer 1 blockchain synonyms, Layer 1 blockchain pronunciation, Layer 1 blockchain translation, English dictionary definition of Layer 1 blockchain. The code behind an L1 protocol sets the standards, which computers (aka nodes) on a cryptocurrency’s network must follow to securely broadcast, verify, and publish new . Schicht 1) handelt es sich um eine Basis- Blockchain, auf der manchmal sekundäre Blockchain-Netzwerke und Anwendungen aufgebaut werden.

Layer 1: Layer 2: Layer 3: Definition: Foundation of the blockchain: Built on top of Layer 1s like Ethereum: Hosts application-specific dApps: Primary Role: Secure and run the network : Reduce Transaction costs and improve the scalability of the Layer 1.Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of Layer One. In einer kontinuierlichen Liste von Datensätzen, auch als Blocks oder Blöcke bezeichnet . Some of the additional features that a Bitcoin layer can introduce to the network . At its core, blockchain architecture is based on a distributed database . By solving these problems, miners can add new blocks of . Coinranking Coins Exchanges Sign in USD. Layer 1 solutions, on the other hand . It’s akin to the bedrock of a building, providing the foundational structure upon which everything else is built. Some common features of Layer 1 blockchains include: Decentralization: By design, Layer 1 blockchains are decentralized, meaning they operate without a central authority. Gainers vs Losers . Semuanya berupaya untuk menjadi solusi bagi blockchain trilemma, terkait skalabilitas, keamanan dan desentralisasi. a system of open source peer-to-peer software for the creation and exchange of a certain type of cryptocurrency; the first such system to be fully.
What is a Layer-1 blockchain? L1 blockchains explained
As the fundamental layer, it operates independently of any external control, removing the need for third-party intermediaries.
Layer 1 Blockchain Meaning
Layer 1 Definition.
Layer 1 Crypto: The Key to Understanding Blockchain
Layer 1 Blockchain

An added bonus is that, while the layer 2 solution does the hard work, the layer 1 retains its security.
Blockchain Layer: Was bedeuten Layer 0, 1 und 2?
An additional, off-chain protocol that works on top of the layer 1 blockchain.Layer 1 blockchain refers to the fundamental architecture of a blockchain network. Understanding these layers is crucial for blockchain developers and start-up . Es gibt drei Arten von L2s: Sie umfassen das Kernprotokoll eines Netzwerks und sind entscheidend für die Sicherheit und Dezentralisierung. Hence, it serves as a public ledger’s source of truth.Blockchain Definition und Erklärung. Highly customizable applications that can solve targeted issues: Scalability: Limited . Die Blockchain bezeichnet eine neuartige Technologie, durch welche es möglich wird jegliche Art von Information in einer öffentlich einsehbaren Datenbank zu speichern, zu verarbeiten, zu teilen und zu verwalten. Layer 2 solutions and sidechains can be built on top of this basis that layer 1 provides.One of the primary advantages of Layer 1 blockchain lies in its intrinsic property of decentralization. This guide delves into the world of layer-1 blockchains.
Layer 1 & Layer 2: all you need to know
Elle peut valider et finaliser les transactions sans avoir besoin d’un autre réseau. A Layer-1 blockchain, often referred to as a smart contract platform, serves as the foundational layer within a cryptocurrency ecosystem.

Layer 1 blockchains differ from layer 2 solutions, which are built on top of existing blockchains and aim to increase scalability and transaction throughput.Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network.
Schicht 2) handelt es sich um eine separate Blockchain, die auf einer Basis-Blockchain oder Layer-1-Blockchain (L1) aufbaut. It’s the core layer where all transactions are processed and recorded on the ledger. Il serait difficile de comprendre le fonctionnement des solutions Layer 2 sans assimiler celui des Layer 1. Ces blockchains sont les principales blockchains de leur écosystème respectif. Namun, blockchain layer-1 adalah dasar .
Blockchain
Layer-1 coins $ 2.A Layer-1 blockchain is the base level of the blockchain architecture.
Was ist Layer 2 bei Blockchain?
Layer 1 (L1) blockchains are decentralized software protocols and the basis for many cryptocurrencies. They are the only layer .Layer-1 blockchains are the most fundamental type of blockchain, serving as the basis for all other blockchain layers. Étant l’endroit où sont finalisées et traitées toutes . A top-level blockchain network such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. This layer is responsible for the fundamental operations of the blockchain, including transaction validation, consensus .
What is a Layer 1 Blockchain and Why Does It Matter?
However, Layer-1 is only responsible for managing the addition and creation of new blocks to the Blockchain. Ziel von Avalanche ist es mit Hilfe eines PoS-Konsens den Handel mit dezentralen Vermögenswerten schneller zu machen und gleichzeitig die Gebühren niedrig halten.There are a number of different ways to connect a layer to Bitcoin, such as a sidechain, merge-mined chain, proof-of-stake chain, layer 2, or even another layer 1. Layer 1-Netzwerke sind die Grundlage der Blockchain. It encompasses various components like nodes, chains, blocks, miners, and multiple layers that interact in a complex, decentralized ecosystem.Dalam ekosistem terdesentralisasi, tidak ada yang seragam.
- Lavazza Quality Rossa | Lavazza Qualità Rossa ab 14,16 € kaufen
- Laufuhr Mit Musikspeicher – Laufuhr Test-Vergleich
- Lean Fat Reducing Machine Recipes
- Laufen Trotz Husten Beim Training
- Latex Addmargin Package | Can I add inline or margin comments to the pdf?
- Latex Editor Installieren – LaTeX/ Installation
- Lavera Rose Shampoo , Lavera Volumen & Kraft Shampoo (250 ml)
- Laufenten Halten Aufgaben _ Enten halten ohne Teich? So fühlt sich die Ente trotzdem wohl!
- Lazy Eye Deutsch | Lazy Eye
- League Of Legends Ab Wieviel Jahren
- League Of Legends Rechte Einrichten