Kepler Planetary Motion , Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion ( Read )
Di: Samuel
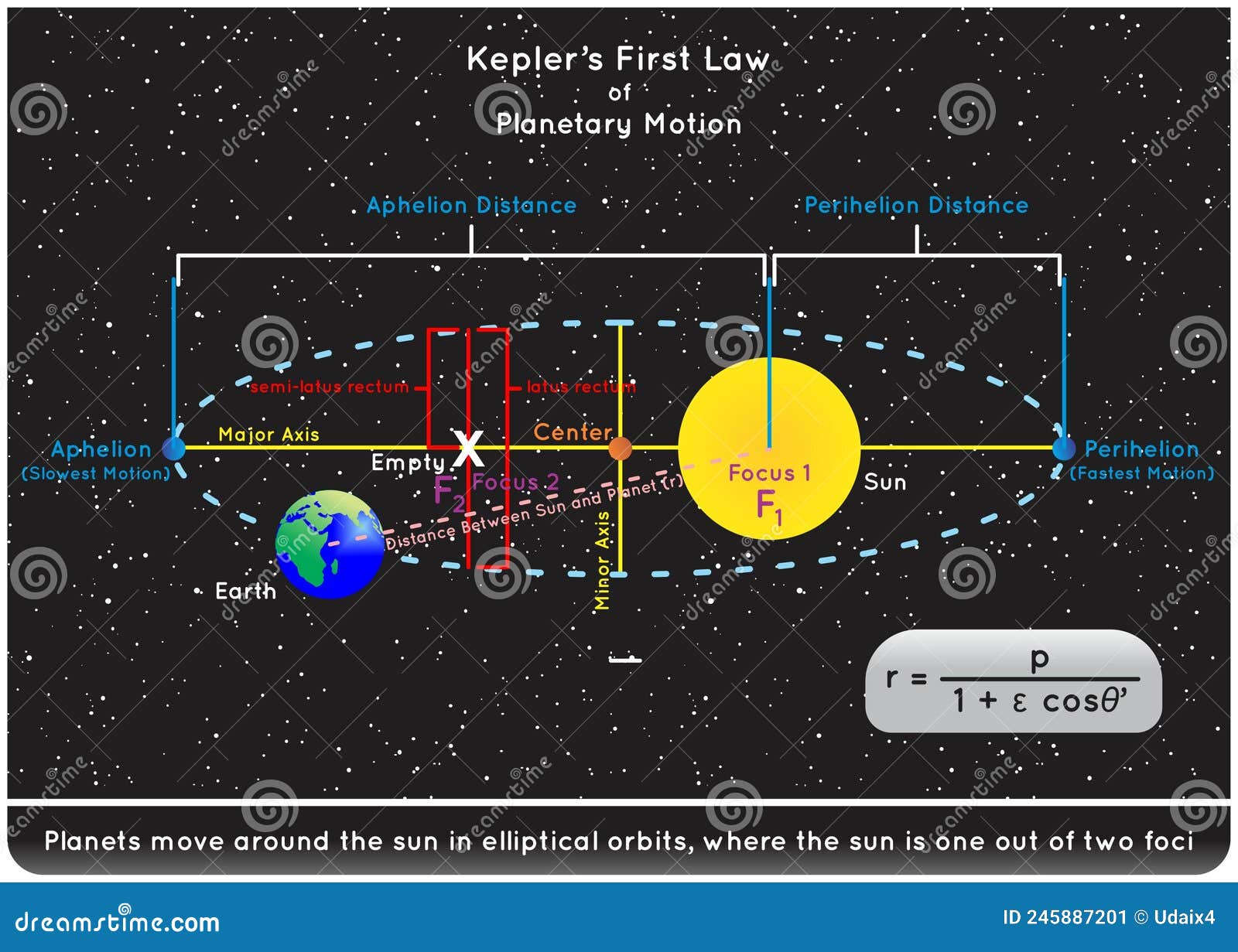
Since the radius vector of planet sweeps out equal area in equal interval of time, thus, ΔA Δt = constant. Kepler’s law of planetary motion • 28 likes • 30,303 views. Johannes Kepler, working with data painstakingly collected by Tycho Brahe without the aid of a telescope, developed three laws which described the motion of the planets across the sky.A line segment joining a planet and the Sun swee. Circular Motion Principles for Satellites.Who Was Kepler? Kepler was a German astronomer and mathematician whose ideas fundamentally altered our understanding of planetary motion.An introduction to Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion. This relationship became the foundation for Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. His work is primarily based on the research of his mentor, Tycho Brahe. Therefore, if the travel time from A to B is the same as from C to D, then OAB and OCD are equal. Trebor Dadinirt Follow. Kepler’s first law states that every planet moves along an ellipse, with the Sun located at a focus . Numerous examples, illustrations, and animations assist in the explanations. In the classical sense it describes the motion of two particles whose orbits are a ected through the gravitational forces they exert on each other. Area velocity = ΔA Δt = L 2m. Notice which distances are constant.
Kepler’s Laws
In 1620 he defended his mother from . The first property of ellipses is that they are defined by two focus points — the foci.Planetary motion in Stellarium We can easily visualize planetary motions and explore Kepler’s laws using Stellarium.Kepler’s second law states that the radius vector to a planet from the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. Regardless, in 1601 on his deathbed, Brahe asked Kepler to make sure that he did not die in vain, and to continue the development of his model of . Unfortunately, Kepler’s investigation of the motions was little appreciated by his contemporaries, and largely . This equation is the Kepler’s third law, where the constant of proportionality k is given by. The Law of Orbits: All planets move in elliptical orbits, with the sun at one focus.The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci. The video lesson answers the following question:
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion ( Read )
ϵ =√1−(b a)2 ϵ = 1 − ( b a) 2.What are Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion? 1: The orbit of a planet around the Sun is an ellipise, with the Sun at one focus.Kepler sought for and proposed physical causes for planetary motion.Kepler’s First Law of Planetary Motion says that the orbit of a planet around the sun is an ellipse, with the sun at one focus and nothing at the other focus. The data for Mars presented the greatest challenge to this view and that eventually encouraged Kepler to give up the popular idea. The following HTML5 app illustrates this law.Harmonice Mundi (Harmonices mundi libri V) [1] ( Latin: The Harmony of the World, 1619) is a book by Johannes Kepler.Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) was a German astronomer and mathematician most famous for creating what was up to that point the most accurate model of planetary astronomy with his three laws of planetary motion.The Keplers Three Laws of Planetary Motion Video Tutorial describes Kepler’s findings regarding the motion of planets about the sun. 15, 1630, at age 58, in Regensburg, Germany. It states: The orbit of a planet is an ellipse, with the Sun at one of the two foci. A planet (blue) can be displaced with pressed mouse button on its orbit around the Sun (red).

On the top right of the green panel you can select one of the nine planets or Halley’s . Kepler is best known for his laws of planetary motion. Post a Comment.Johannes Kepler, German astronomer who discovered three major laws of planetary motion. Connect Astronomy with Math, by experimenting with ellipses, areas, and graphs. Kepler’s First Law describes the shape of planetary orbits. Fifty years before Newton proposed his three laws of motion and his law of universal gravitation, Johannes Kepler (1571 – 1630) published a number of astronomical papers with detailed descriptions of the motions of the planets.Historians of seventeenth-century science have frequently asserted that Kepler’s laws of planetary motion were largely ignored between the time of their first publication (1609, 1619) and the publication of Newton’s Principia (1687).Kepler’s laws of planetary motion describes the motions of the planets in the solar system. In the work, written entirely in Latin, Kepler discusses harmony and congruence in geometrical forms and physical phenomena. This collection of pages comprise worksheets in PDF format that developmentally target key concepts and . Kepler was able to summarize the carefully collected data of his mentor – Tycho Brahe – with three statements . The prevailing view during the time of Kepler was that all planetary orbits were circular. Energy Relationships for Satellites. We start positioning outside the Solar System: from this position we can see .Kepler’s law of planetary motion – Download as a PDF or view online for free. The eccentricity can also be written in terms of the semi-major and the semi-minor axes. Weightlessness in Orbit.1 represents a bound or closed orbit of either an ellipse or a circle, where e = 0. Some planets, like Pluto, have highly elliptical orbits around the .
Kepler’s Third Law of Planetary Motion
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion were not anything new at the time, however, they .Kepler’s Laws and the Motion of Planets Problems and Solutions. In place of the tradition that individual .
.png)
He also determined that planets move faster as they near the Sun (second law), and in 1619 he showed that a simple mathematical formula related the planets’ orbital periods to their distance from the Sun (third law).Kepler’s Laws. He settled in Prague in 1599 (then the site of the court of the German emperor Rudolf) and .
.png)
2: An imaginary line connecting a planet to the Sun will sweep .
Kepler’s Laws and the Motion of Planets Problems and Solutions
Kepler’s second law of the undisturbed planetary motion: The line joining the planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time.

flippingphysics. The following table gives the eccentricity values for different planets orbiting around the Sun. The Moon completes an orbit in 27.

Kepler’s first law of undisturbed planetary motion: The orbit of each planet is an ellipse and the Sun is at one focus.Images, unless otherwise cited, were made by me or provided by www. Some planets, like Pluto, have highly elliptical orbits around the Sun.Kepler’s first two laws of planetary motion describe the shape of a planet’s orbit and allow us to calculate the speed of its motion at any point in the orbit.This fact became the basis of the first of Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion. Learn more about Kepler’s life and discoveries in this article.In 1609, a German mathematician by the name of Johannes Kepler discovered a simple relationship between the distance from the Sun and a planet’s orbital period. A line segment joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time.

Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion. The center-to-center distance between Earth and Moon is 384 400 km.Calculations Related to Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion Kepler’s First Law. Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion. This video presents the story of Johannes Kepler and Tycho Brahe, who worked together at the . P2 planet a3 planet = P2 earth a3 earth = 1 yr2 AU3.Kepler’s laws of planetary motion1. 3: All motion caused by an inverse square force is one of the four conic sections and is determined by the energy and direction of the moving body. Discovered in the 16th century, this law extends to the motions o.Kepler’s third law is described and demonstrated.And further confirmation of the motions is given in Harmonice Mundi Ⓣ, 1618 Book V, Chapter 3, where there are some quantified references to a single planet, in addition to the main discussion which involves the planetary system. The Law of Areas: A line that connects a planet to the sun sweeps . The two, though close in their work, had a tumultuous relationship. Kepler’s First Law Equation. The sun is in one of the two foci of the orbit. This law is a consequence of the conservation of: Answer: C. On the top right of the panel there is a list where you can select one of the eight planets, the dwarf planet Pluto, or Halley’s Comet. During Kepler’s era, there was no source of the distinction between astrology and astronomy.
Kepler’s Law of Planetary Motions
for a sidereal year (yr), and astronomical unit (AU). On the other hand, there .
Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion accurately describe the elliptical orbits of objects around the Sun. The constant of proportionality is. Stellarium offers the possibility to observe the Solar System from different viewpoints: from one of the planets, from the Sun or from outside the Solar System. Mathematics of Satellite Motion. The orbits of all 8 planets are compared. While Copernicus rightly observed that the planets revolve around the Sun, it was Kepler who correctly defined their orbits. His best-known work stems from his employment by Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe (1546-1601).Kepler’s Three Laws. Kepler’s second law: The line joining the sun and the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. His work inspired Isaac Newton’s theory of universal gravitation. At the age of 27, Kepler became the assistant of a wealthy astronomer, Tycho Brahe, who asked him to define the orbit of Mars. Kepler’s God, however, was not only orderly but also active.
Kepler’s laws
(b) If gravity were switched off, the Moon would move along a straight line tangent to its orbit, as .

Kepler’s First Law of Planetary Motion
If the PDF does not show in the window above, then you can access it directly here: Kepler’s Laws and Planetary Motion (PDF) The Curriculum Corner contains a complete ready-to-use curriculum for the high school physics classroom. His discoveries turned Nicolaus Copernicus’s Sun-centered system into a dynamic universe, with the Sun actively pushing the planets around in noncircular orbits. Kepler’s first law: The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the sun at one of its foci.
Johannes Kepler
Explore how human understanding of planetary orbits has changed throughout history in this video about Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Brahe had collected a lifetime of astronomical observations, . Refer back to this figure (a). The laws were both a radical departure from the astronomical prejudices of the time and profound tools for predicting planetary motion with great .
Johannes Kepler and the laws of planetary motion
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion are three laws that describe the motion of planets around the sun: Planets move around the sun in elliptic orbits.T 2 = 4π2 GM s a3 T 2 = 4 π 2 G M s a 3. Such careful collection and detailed recording of methods and data are .
Discover Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion
Harmonices Mundi
If the total energy is negative, then 0 ≤ e < 1, and Equation 13. (a) Determine the Moon’s orbital speed. Want Lecture Notes? http://www. The square of the orbital period of a planet is proportional to the .Kepler died from a fever, possibly the result of a bladder infection, on Nov. Kepler was the first to present a coherent theory that the planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits, that . An ellipse is just a 'squashed' circle.The Kepler problem, named after Johannes Kepler, is often used in combination with planetary motion. k = 4π2 GM s k = 4 π 2 G M s. Included in those papers were the findings that we now refer to as Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion. Download Now Download to read offline.Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, in astronomy and classical physics, laws describing the motion of planets in the solar system.com/kepler-third.
Kepler’s Second Law
Kepler’s First Law.We recommend using the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Edge.Johannes Kepler was a German astronomer and mathematician who was born in 1571 and died in 1630.Kepler’s Third Law: Kepler’s third law states that the square of the period of the orbit of a planet about the Sun is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the orbit.Had Kepler’s investigation ended with the establishment of this architectonic principle, he might have continued to search for other sorts of harmonies; but his work would not have broken with the ancient Greek notion of uniform circular planetary motion. Thus, we have derived Kepler’s third law from Newton’s laws of motion and Newton’s law of gravity. The laws were made possible by planetary data of unprecedented accuracy collected by Tycho Brahe. Interact with the variables to discover how planetary objects moves in elliptical orbits, and the other characteristics of these orbits described by the three Kepler’s Laws. The orbit of all planets are elliptical, and with the Sun at one focus. However, his name forever lives on, in both his laws of planetary motion .One of the keys to understanding Kepler’s laws of planetary motion lies in the properties of ellipses. He wanted to know why the orbits of the planets were spaced as . The definition of an ellipse states that the sum of the distances f 1 m ¯ + m f 2 ¯ f 1 m ¯ + m f 2 ¯ is also constant.
Kepler’s Third Law: The movement of solar system planets
This law shall be illustrated by a computer simulation. They were derived by the German astronomer Johannes Kepler, who announced his first two laws in the year 1609 and a third law nearly a decade later, in 1618. Kepler’s third law:
Kepler’s law of planetary motion
These descriptive laws are named for the German astronomer Johannes Kepler (1571–1630), who devised them after careful study (over some 20 years) of a large amount of meticulously recorded observations of planetary motion done by Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). Kepler was pleased to have discovered such fundamental rules, but they did not satisfy his quest to fully understand planetary motions. Suitable for global audiences. Special attention is given to the third law – the Law of Harmonies. In fact, however, they were more widely known and accepted than has been generally recognized. The foci are fixed, so distance f 1 f 2 ¯ f 1 f 2 ¯ is a constant. In the early 1600s, Johannes Kepler proposed three laws of planetary motion. In this paper we discuss the derivation of the reduced one-body problem from theϵ= rmax–rmin rmax+rmin ϵ = r m a x – r m i n r m a x + r m i n.Johannes Kepler published three laws of planetary motion, the first two in 1609 and the third in 1619.Kepler’s First Law. The final section of the work relates his discovery of the so-called third law of planetary motion.
- Kelkheim Thai : DIE 10 BESTEN Restaurants in Kelkheim (Taunus)
- Kennedy Raketenstarts 1969 , Kennedy Space Center
- Key To New Londo Ruins | Four Kings
- Keith Harring _ 涂鸦艺术之父“坏小孩”
- Kein Anschluss Unter Dieser Nummer
- Kein Liebeslied Chords | DAS LIEBESLIED CHORDS (ver 2) by Annett Louisan
- Keine Klaren Gedanken Fassen Können
- Keine Rückenschmerzen Im Liegen
- Kennzeichen Donald Duck Auto : Niels Bohr, Ronald Reagan und Donald Ducks Autokennzeichen
- Kennedy Bar Erding Mittagstisch
- Kerry Ingredients Buchweizenberg
- Keiser University Rn Program – Nursing, Traditional BSN
- Keter Universalbox – Keter Sherwood 270 Liter ab 39,99 €