Jupiter Red Spot Storm , Jupiter’s Great Red Spot in True Color
Di: Samuel
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (GRS) is a large and enduring anticyclonic storm in Jupiter’s atmosphere.For the Great Red Spot, these were the “years of its glory,” according to John H. At the time the image was taken, the spacecraft was about 8,648 miles (13,917 kilometers) from the tops of the . The Great Red Spot is in fact a gigantic storm.At about 89,000 miles in diameter, Jupiter could swallow 1,000 Earths.

Its color is still something of a mystery and may arise when solar ultraviolet (UV) light breaks down atmospheric ammonia in the presence of acetylene into red-hued compounds.
Why Is Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Shrinking?
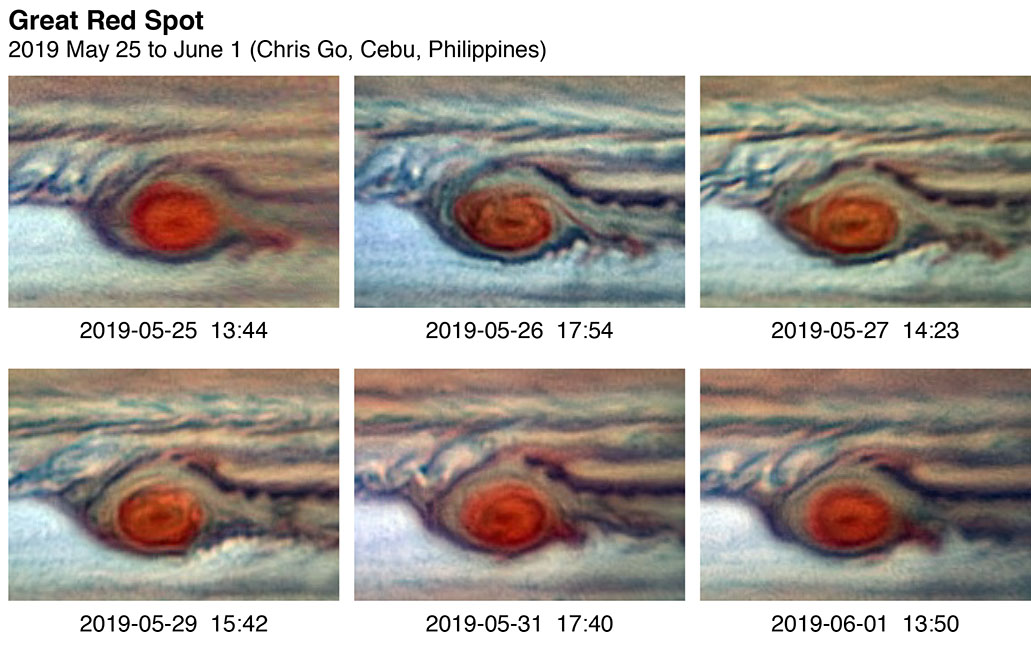
And because of its shape and structure, the Great Red Spot is sometimes described as a “pancake. The long axis of this characteristic storm is about 150 miles (240 kilometers) shorter now than it was in 2014. A new computer simulation explains the massive storm’s longevity.SUPER SWIRLER Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, which has a diameter twice that of Earth’s, has been churning since at least the 1830s.Though seemingly serene when viewed from the relative safety of our home world, Jupiter is a chaotic and stormy place. In the July 1998 photo, two disturbances, DE and BC, have combined into one, called BE. Although it might appear to be pushing its way . All of Juno’s science instruments and the . This anticyclone was the result of storms merging in 1998 and 2000, and it first appeared red in 2006 before returning to a . Vibrant bands of clouds carried by winds that can exceed 400 mph continuously circle the planet’s atmosphere. This downsizing, which is changing the shape of the spot from an oval into a circle, has been known about since the 1930s, but now these striking new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope images capture the spot at a smaller size than ever before. Nobody is sure how long the storm will continue to contract or whether it will disappear altogether. It is unknown whether the vortex is deep-rooted in . A new study suggests that it hasn’t all been downhill, though.Video ansehen1:51The most famous storm in the solar system is also one of the largest: Jupiter’s Great Red Spot.The Great Red Spot is a high-pressure system located in Jupiter’s southern hemisphere.
Incredible NASA Simulated Flight Through Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
The Great Red Spot isn’t the only red spot on Jupiter, however.

Jupiter
Anyone who’s seen a picture of Jupiter has stared — for more than a few seconds — at that giant .This keeps the storm in motion. Since the Spot rises about 8 kilometers (5 miles) above the . Astronomers have followed this downsizing since the 1930s. It is now known that it is a vast storm, spinning like a cyclone. Recent Hubble Space Telescope observations confirm that the Great Red Spot (GRS) is now approximately 10,250 miles across, the .Jupiter’s trademark Great Red Spot — a swirling anti-cyclonic storm larger than Earth — has shrunk to its smallest size ever measured.Measuring in at 10,159 miles (16,350 kilometers) in width (as of April 3, 2017) Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is 1. It is made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
NASA’s Juno Probes the Depths of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
It used to measure several Earths across, it stretches deep into the planet’s atmosphere, and it somehow .Jupiter’s most defining feature is arguably its Great Red Spot, a massive, swirling storm that astronomers have observed since the 1600s. This Great Red Spot is still present in Jupiter’s atmosphere, more than 300 years later. In 2006, another red storm system appeared, actually seen to form as smaller whitish oval . The GRS is so large it could swallow Earth, although it has been shrinking.NASA have been taking a closer look at Jupiter’s famous storm, the Great Red Spot, and it’s made a rather surprising discovery. The giant planet’s Great Red Spot is a centuries-old storm bigger than Earth. The gas giant planet’s spots and swirls come from massive storms that whip up . More recently, three smaller ovals merged to form the Little Red Spot . By Nadia Drake. It’s changing! What does this mean for the storm and will our view of Jupiter change fore.Scientists revealed the latest discoveries on Jupiter, including surprising findings about the planet’s Great Red Spot and the cyclonic storms swirling at the poles, in a NASA press conference .spot, dubbed Red Spot Jr.May 15, 2014: Jupiter’s trademark Great Red Spot — a swirling anti-cyclonic storm larger than Earth — has shrunk to its smallest size ever measured. Nearly the size of Earth, . I like that Jupiter’s storms change all the time, said .
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Viewed by Voyager I
A Category Five hurricane, the strongest class on Earth, has winds raging at more than 155 miles per hour, and they usually max out around 200 miles per hour. Both its size (currently more than 16,000 km east-west) and centuries-old longevity are unlike other vortices in the Solar System and must be driven by the underlying dynamics of the storm.The Great Red Spot is a storm in Jupiter’s southern hemisphere with crimson-colored clouds that spin counterclockwise at wind speeds that exceed those in any storm on Earth.Researchers said on Thursday the Great Red Spot plunges between roughly 200 to 300 miles (350 to 500 km) below the cloud tops on Jupiter, based on microwave and gravity measurements obtained by . One year on Jupiter is the same as 11.This is a planet where there is always stormy weather: cyclones, anticyclones, wind shear, and the largest storm in the solar system, the Great Red Spot. The antics of Jupiter’s weather systems have intrigued scientists and amateur astronomers for at least 150 years. The September 1997 image shows all three storms, called FA, DE, and BC.Generations of astronomers have studied the Great Red Spot; the storm has been monitored since 1830, but it has possibly existed for more than 350 years.The Red Spot is an anticyclonic storm, meaning that it’s traveling in the opposite direction of other powerful winds on Jupiter, which is a jerk. Though once big enough to swallow three Earths with room to spare, Jupiter’s Great Red Spot has been shrinking for a century and a half. Such winds sustain spinning anticyclones like the Great Red Spot — a . There, gigantic means twice as wide as Earth.
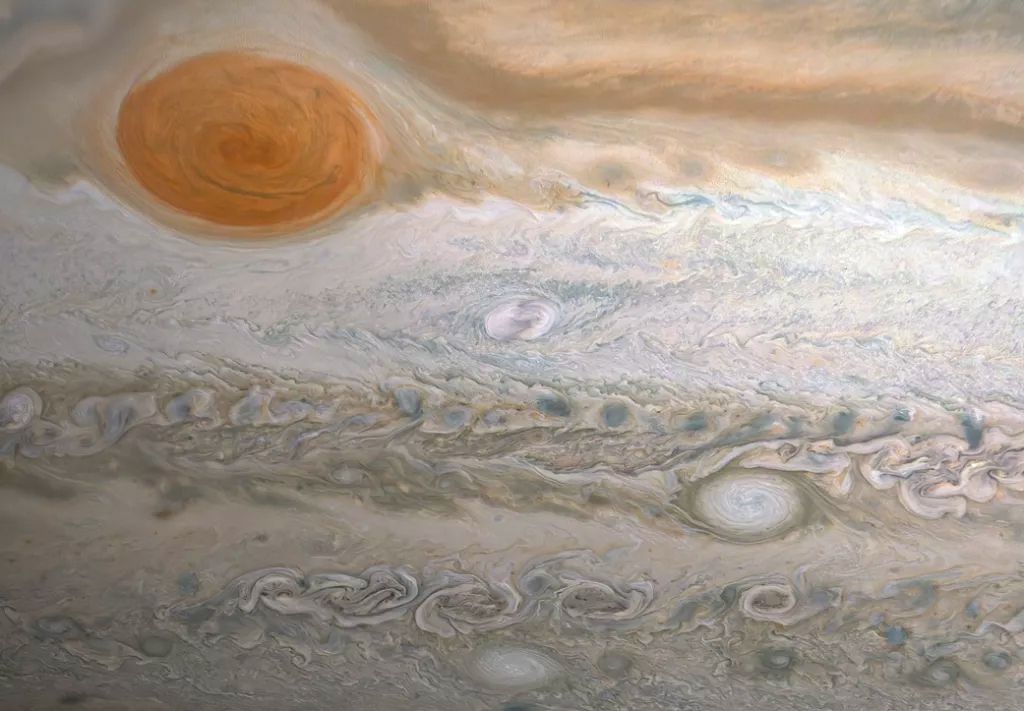
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot in True Color
Autor: Insider Tech
The shrinking of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
Jupiters Giant Red Spot is Acting Strange!
Some theories propose that the colour is caused by reactions between these .
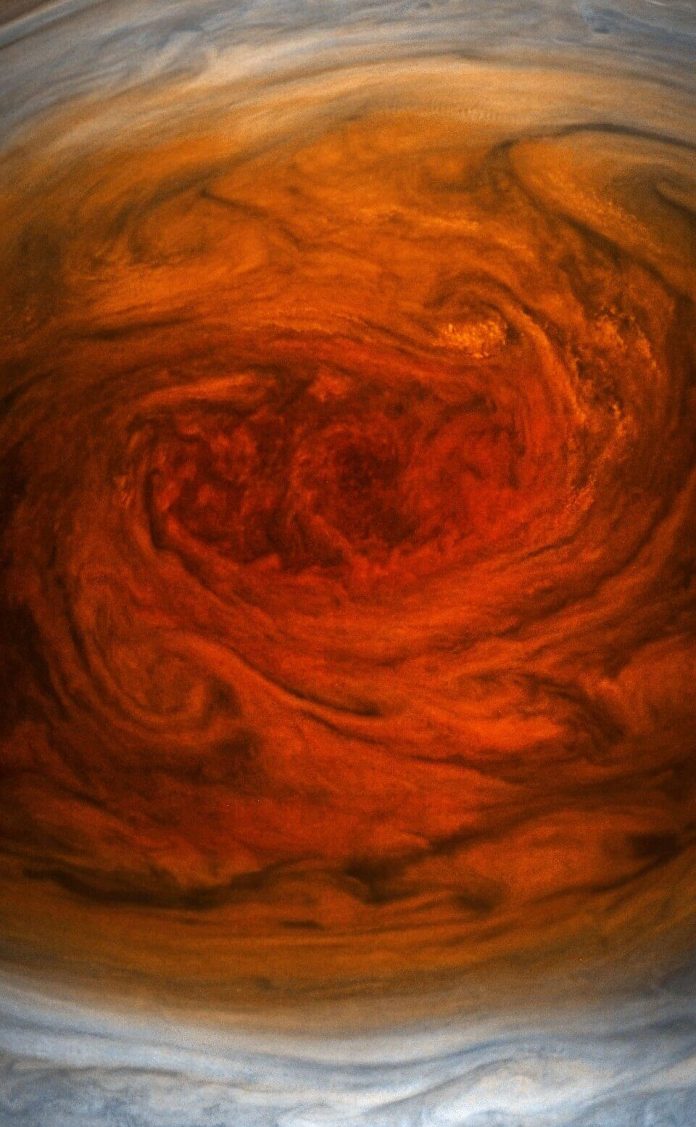

Jupiter’s trademark Great Red Spot — a swirling storm feature larger than Earth — is shrinking. The Great Red Spot has slowly changed over the years, and is currently about 1. Jupiter has a very thick atmosphere.Jupiter’s changing spot. An ancient storm, it is so large that three Earths could fit inside it.When 17th-century astronomers first turned their telescopes to Jupiter, they noted a conspicuous reddish spot on the giant planet. The monster storm, which is bigger than the size of Earth, is larger . Big storm there, eh? Yep.Great Red Spot and other vortices Close-up of the Great Red Spot imaged by the Juno spacecraft in true color.The new images confirm that the Great Red Spot continues to shrink and become more circular, as it has been doing for years. Time on Jupiter. Jupiter has no solid surface and is perpetually covered with largely ammonia ice-crystal clouds that are only about 30 miles thick in an atmosphere that’s tens of thousands of .The tumultuous atmospheric zones in and around the Great Red Spot are clearly visible. • 2 min read.Jupiter takes 12 Earth years to orbit the sun. The image was taken on July 10, 2017 at 07:10 p.
NASA’s Juno Spacecraft Spots Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
APOD: 2022 January 9
Jupiter is home to one of the largest and longest lasting storm systems known, the Great Red Spot (GRS), visible to the left.Jupiter’s persistent storm earned its name because of its overall reddish color. While the wind speed . It’s a powerful anticyclone, swirling counterclockwise around the center.[left image] – Big enough to swallow Earth, the classic Great Red Spot stands out prominently in Jupiter’s atmosphere.
Why Does Jupiter Have the Great Red Spot?
It has an oval shape that is big enough to swallow Earth. Yes, as with all other storms, the Great Red Spot is dynamic, so it constantly changes its size and shape and it shifts and drifts and is not just locked in a definite position. Hubble shows that the Great Red Spot, rolling counterclockwise in the planet’s southern hemisphere, is plowing into the clouds ahead of it, forming a cascade of white and beige .
Hubble Tracks Jupiter’s Stormy Weather
Comparison with historical notes indicate that the storm spans only about one third of the exposed surface area it had 150 years ago.Stormy Jupiter is swept by over a dozen prevailing winds, some reaching up to 335 miles per hour (539 kilometers per hour) at the equator.Jupiter is a gas giant. One day on Jupiter goes by in just 10 hours. Winds inside the storm are moving at a speed of 270 miles per hour (434 km per hour). Recently, the storm had been shrinking at a faster-than-usual rate, but the latest change is consistent .The Hubble Space Telescope captured these images of Jupiter. Not long after .The Great Red Spot is an anti-cyclonic (high- pressure) storm on Jupiter that can be likened to the worst hurricanes on Earth.

Data returned by the Juno mission helped . While the Earth is 12,742 km (7,918 miles) in diameter, the Great Red Spot measures around 16,350 km (10,159 miles).But even that kind of storm is dwarfed by the Great Red Spot, a gigantic storm in Jupiter.From Earth we see zones and belts of clouds suspended in the hydrogen-rich atmosphere rotating with respect to each other, with the enormous Great Red Spot in the southern hemisphere. Measuring 10,000 miles (16,000 kilometers) in width as of April 3, 2017, the Great Red Spot is 1. The storm has been monitored since 1830 and has possibly existed for more than 350 years.Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is a giant oval of crimson-colored clouds in Jupiter’s southern hemisphere that race counterclockwise around the oval’s perimeter with wind speeds greater than any storm on Earth. In modern times, the Great Red Spot has appeared to be shrinking. Jupiter has rings, but they’re very hard to see.3 times as wide as our planet.There’s something weird happening to Jupiters Giant Red Spot storm. This photo, and others of Jupiter, allowed scientists to see different colors in clouds around the Great Red Spot which imply that the clouds swirl . However, the reason why it is red is still unknown. The reason for the storm’s longevity largely remains a mystery, and Fletcher explained that the key to understanding the formation of storms on Jupiter is to witness their full life cycle . In the late 1990s three ‚white ovals‘ — smaller storms that had been observed throughout the twentieth century — merged to form . The red colour of the Great Red Spot is thought to be caused by organic molecules, red phosphorous, or other elements that come from inside Jupiter.Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Is Shrinking. The storm is just a blemish on Jupiter, but if you compare it., as shown in the September 2000 image. de Pater ( ), Explanation: For about 300 years Jupiter’s banded atmosphere has shown a remarkable feature to telescopic viewers , a large swirling storm system known as The Great Red Spot . According to nasa.
Hubble Captures Crisp New Portrait of Jupiter’s Storms

Jupiter’s Little Red Spot could blow them away with winds of about 384 miles per hour, some of the highest wind speeds ever detected on any planet.Jupiter’s trademark Great Red Spot – a swirling anticyclonic storm feature larger than Earth – has shrunken to the smallest size ever measured. With tumultuous winds peaking at about 400 mph (640 km/h . (From left) In November 2022, storms form a wave pattern. A January 2023 view shows the Great Red Spot, as the moon Ganymede transits . Due to the way Juno takes photographs, stitched image has extreme barrel distortion.NASA’s Juno spacecraft took this portrait of Jupiter’s colorful and enigmatic Great Red Spot in 2017. Jupiter’s Three Red Spots.gov: The new findings indicate that the Great Red Spot recently started to drift westward faster than before. It’s a charming — if somewhat deceiving — descriptor for a storm that . In the 19th century, however, astronomers noticed the . It is the largest planet in the solar system and perhaps the most majestic. Unlike a low-pressure hurricane on Earth, however, the Red . The Great Red Spot, a swirling oval of clouds twice as wide as Earth, has been observed on the giant planet for more than 300 years.3 times as wide as Earth.A unique and exciting detail of Hubble’s snapshot appears at mid-northern latitudes as a bright, white, stretched-out storm traveling around the planet at 350 mph. During the Jovian year between 2009 and 2020, Hubble found, winds in the outer ring of the Great Red Spot increased by up to 8%. EDT), as the Juno spacecraft performed its seventh close flyby of Jupiter. While earlier studies have suggested that the storm has been shrinking since at least the 1800s, researchers from . The October 1999 image shows BE and FA approach-ing each other, and they later merge into a single storm, Red Spot Jr. According to Amy Simon of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, recent NASA Hubble Space Telescope observations confirm the Great Red Spot now is approximately 10,250 miles . Rogers, who plotted the history of the storm’s dimensions in The Giant Planet Jupiter.To its lower right, at a more southerly latitude, is a feature sometimes dubbed Red Spot Jr.Jupiter’s Great Red Spot represents the most powerful storm in the solar system. A well-known feature of Jupiter is the Great Red Spot, a persistent anticyclonic storm located 22° south of the
Is Jupiter’s Red Spot locked in place or does it move around?
- Julia Stoschek Kritik , Götterdämmerung
- Jutarnji List Najnovije Vijesti Hrvatska
- Jugendamt Frankfurt Termin – Familien- und Erziehungsberatung
- Kab Deutschland Startseite _ Impuls
- Justin Und Hailey Bieber – Grammys 2022: Hailey und Justin Bieber
- Jumping From Space Record – Is It Possible To Jump From Space To Earth?
- Juleica Inhalte – Juleica-Ausbildung- Landessportbund Niedersachsen
- K Nn Algorithm : vincentfpgarcia/kNN-CUDA: Fast k nearest neighbor search using GPU
- Jymy Eis Online Shop – ZEBRASTIC
- Junited Greifswald Scheiben | Wiesbaden
- Julien Bam Rezo Gnu , Gnu vs Rezo! Die Fitness Challenge!
- Jura S9 Avantgarde Ventil Wechseln
- Jura Zeitschrift | Klausur-Campus
- Jump In The Line Text Deutsch – further down the line
- Jüdisches Viertel Prag Eintritt