Inflammation In Multiple Sclerosis
Di: Samuel
This disorder is a heterogeneous . However, the pathological mechanisms of meningeal inflammation-induced cortical pathology are still largely .Notably, the pro-inflammatory action of CNS-resident innate-like immune cells in progressive neurodegeneration may be intrinsically linked to multiple sclerosis chronicity.Inflammation in a myelinated portion of the nervous system is the mainstay of multiple sclerosis (MS). These changes are strictly associated with compartmentalized sustained inflammation within the brain parenchyma, the leptomeninges, and the cerebrospinal .
Meningeal inflammation as a driver of cortical grey matter
Despite intense research, the underlying pathomechanisms driving inflammatory demyelination in MS still remain incompletely understood.As a multifactorial disease, the etiology of MS is complex. Multiple sclerosis is a progressive inflammatory, demyelinating, and neurodegenerative autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS), with the formation of focal and diffuse lesions and leading to atrophy and chronic progressive and irreversible disability in the majority of patients [1]. Multiple sclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system which leads to the formation of focal confluent lesions of primary demyelination in the white and gray matter and to diffuse damage and neurodegeneration in the entire brain ().Meningeal inflammation strongly associates with demyelination and neuronal loss in the underlying cortex of progressive MS patients, thereby contributing significantly to clinical disability. These symptoms often lead to reduced physical activity, negatively impact .Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory immune-mediated disease of the central nervous system (CNS) with white matter demyelinating lesions and chronic diffuse neuronal degeneration, causing variable and unpredictable clinical manifestations and disease course.Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that is characterised pathologically by demyelination, gliosis, neuro-axonal damage and inflammation. We aimed to determine the dose-response relationship between tolebrutinib and the reduction in new active brain MRI . The molecular mechanisms underlying astrocyte activation remain incompletely understood.Demyelination and neurodegeneration in the MS brain is .
Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis
Due to the inflammatory nature of MS, targeting of the immune response is the most widely used therapeutic . Elevation of inflammatory markers such as procalcitonin, ESR and hs-CRP is suspected to occur in MS patients. The evidence leads to the conclusion that inflammation is tightly regulated, and .24% of the population in the United States and Canada, and approximately 0.
T Helper Cells: The Modulators of Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis
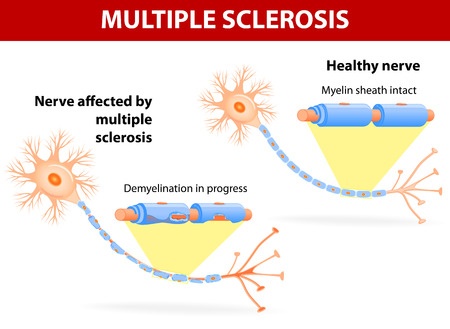
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a neurophysiological . The present study characterized demyelinated lesions in the cerebral cortex of MS patients.Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a long-lasting (chronic) disease of the central nervous system. In MS, neurological disability results from inflammation, demyelination, and ultimately, axonal .There are currently many treatment options to reduce .This review focuses on the role of MMPs in multiple sclerosis (MS) and bacterial meningitis (BM), two neuro-inflammatory diseases where current therapeutic approaches are insufficient to prevent severe disability in the majority of patients.Astrocyte activation is associated with progressive inflammatory demyelination in multiple sclerosis (MS).
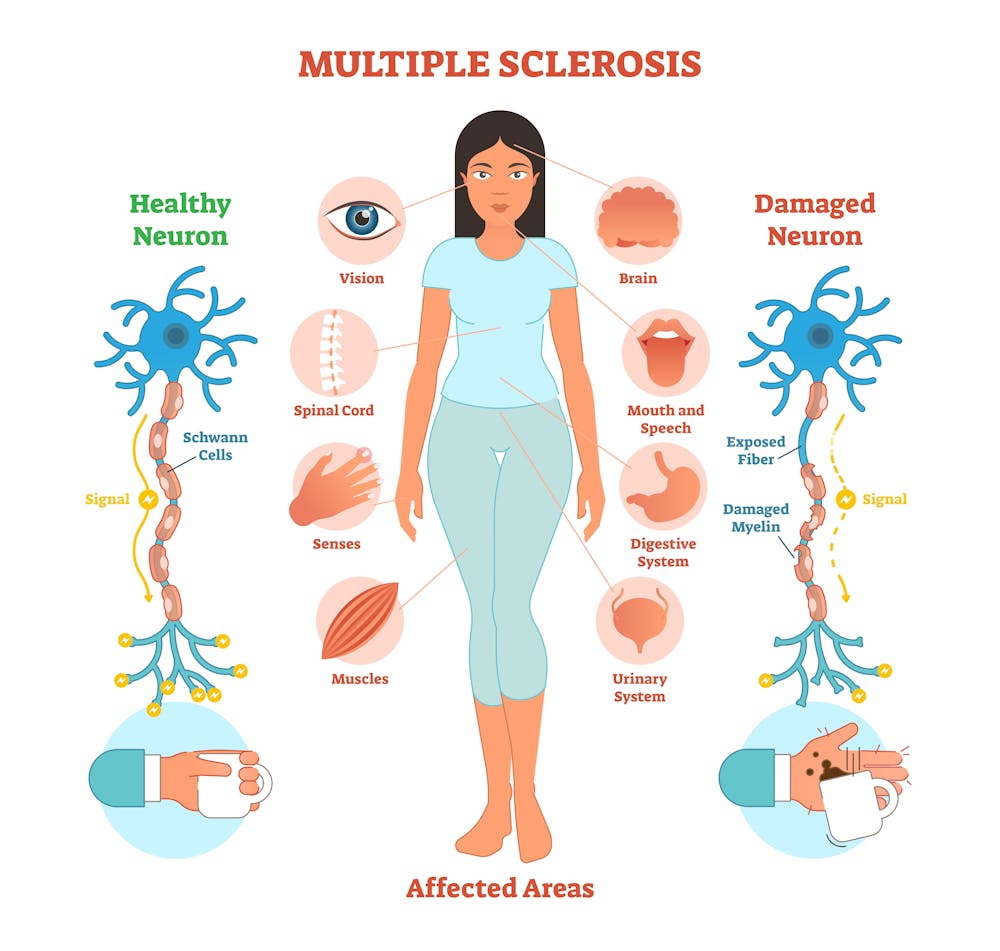
MS is characterized by its most common symptoms of spasticity, muscle spasms, neuropathic pain, tremors, bladder dysfunction, dysarthria, and some intellectual problems, including memory disturbances. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder of the central nervous system (CNS) affecting about 2–3 million people worldwide that is triggered by both environmental and genetic factors [1,2].Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that affects an estimated 2.19% in some European countries.
Chronic White Matter Inflammation and Serum Neurofilament
Inhibition of astrocytic . MS is an unpredictable disease that affects people differently.
Resolution of inflammation during multiple sclerosis
One hundred twelve cortical lesions were identified in 110 ti .To this end, 43 patients with multiple sclerosis (24 relapsing-remitting, 19 progressive), and 21 healthy control subjects were enrolled. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, immune-mediated inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that affects more than 2 million people around the world, with the highest prevalence among those between the ages of 20 and 40 years [1,2]. These are the protective covers (sheaths) that surround brain and spinal cord nerves.Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common chronic inflammatory, demyelinating and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system in young adults. Clinical features mainly include visual loss and sensorimotor symptoms as well as more atypical features such as fatigue and mental/cognitive impairment.Treatments for MS attacks. In addition, oxidative stress contributes to tissue injury and promotes existing inflammatory response. Depending on the location of the demyelinating lesions, MS patients can develop almost any neurological sign or symptom, including motor, sensory, .Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a frequent autoimmune demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS).Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS) characterized by loss of myelin and inflammation, leading to neurodegeneration. Clinical expressions of MS vary .Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) may drive inflammatory events in both the periphery and the central nervous system (CNS), leading to the development of the multiple sclerosis lesion in the CNS.Growing evidence indicates a central role for meningeal inflammation in driving multiple sclerosis (MS) pathology. The symptoms of MS are highly varied but frequently include pain, muscle spasticity, fatigue, inflammation, and depression. It is a leading cause of neurological disabilities in young adults and affects approximately 0. 1 In most of the patients the disease starts with a relapsing course (RRMS), which transforms at later stages into progressive . In recent years, several studies have examined the potential associations between mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
Current and Future Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis
A hallmark of the disease multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory autoimmune attack 1 on the proteins of the myelin sheath, a structure that wraps around the nerve fibres that project from neurons . White matter lesions were classified in T1-isointense, T1-hypointense and black holes.
Intrathecal Inflammation in Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
With MS, your immune system mistakenly attacks myelin cells.Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most frequent inflammatory demyelinating disease of the Central Nervous System (CNS) and a leading cause for permanent neurological disability in young adults. Moreover, CBD . Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the CNS (Charcot, 1880).In general the disease starts in patients in the third decade of life with a . In multiple sclerosis (MS), the inflammation and demyelination of the central nervous system (CNS) develop in distinct ways. Significant progress has been made during recent years in using systemic .

Side effects may include insomnia, increased blood . Therefore, homeostatic processes that regulate inflammation may yield important insights into pathophysiology of MS. However, inflammation is a major driver of the pathology. Recent studies have suggested that classical neurotransmitter receptors are implicated in the modulation .Therefore, limiting CNS inflammation represents prospective therapeutic approach in diseases like Alzheimer’s, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s, ischemia, various psychiatric disorders and Multiple sclerosis (MS).

Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurodegenerative and demyelinating disease with a well-defined inflammatory component. In this Review, the authors summarize current knowledge regarding structural .What is multiple sclerosis? Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune condition that affects your brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
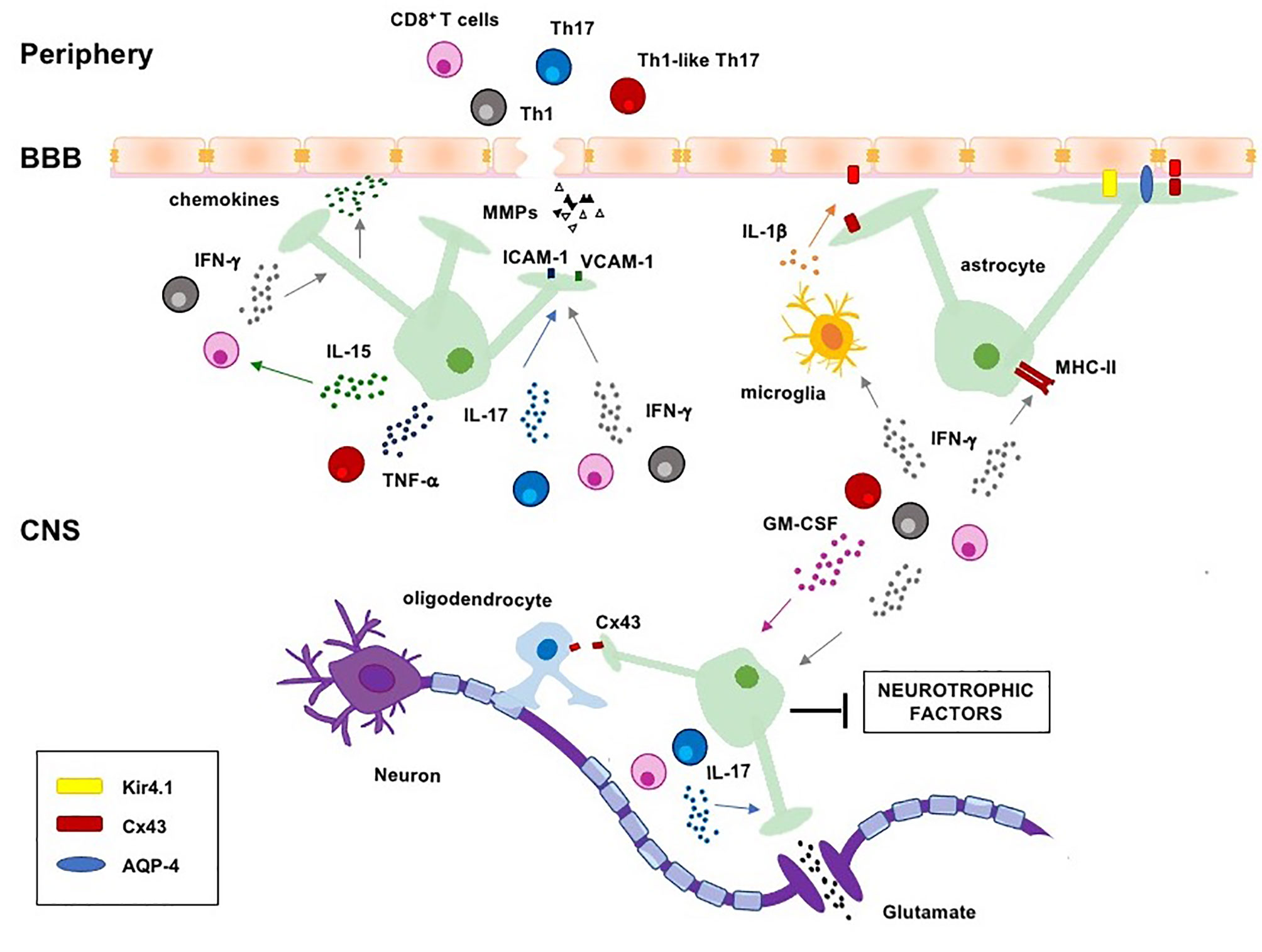
Research also suggests that ethnicity and geography play a role. In MS, the immune system cells that normally protect us from viruses, bacteria, and unhealthy cells mistakenly attack myelin in the central nervous system (brain, optic nerves, and spinal .

Studies support the opinion that MS is caused when people with the right combination of genes are exposed to some trigger in the environment. Methods: In 118 patients with MS with no gadolinium-enhancing . The variability in disease course amongst cases is well known. Our objective was to evaluate the cellular substrates of the cortical damage to understand the role of .Progressive forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) are associated with chronic demyelination, axonal loss, neurodegeneration, cortical and deep gray matter damage, and atrophy. This makes diagnosing patients difficult, imperative to initiating early and proper treatment.Myelin sheath damage interrupts messages .Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory neurological disease characterized by demyelinating lesions of the central nervous system (CNS) and typically presenting with recurrent neurological .Inflammation-driven synaptic dysfunction is emerging as a prominent pathogenic mechanism in multiple sclerosis (MS). It is thought to be an autoimmune disorder, a condition in which the body attacks itself by mistake.
Multiple sclerosis
The aim of our study was to analyse the interdependence of inflammation, neurodegeneration and disease progression in various multiple sclerosis stages in relation to lesional activity and clinical course, with a .Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a multifactorial autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that is characterized by chronic inflammation, demyelination, and axon and neuronal loss. Others may lose their ability to see . Scientists believe that a combination of factors trigger the disease.Background: Tolebrutinib is an oral, CNS-penetrant, irreversible inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, an enzyme expressed in B lymphocytes and myeloid cells including microglia, which are major drivers of inflammation in multiple sclerosis.In the demyelinating disease multiple sclerosis (MS), chronic-active brain inflammation, remyelination failure and neurodegeneration remain major issues despite immunotherapy.Active demyelination and neurodegeneration in the multiple sclerosis brain and spinal cord are consistently associated with the presence of perivascular and parenchymal inflammatory infiltrates, composed of T and B .
(PDF) Inflammation in multiple sclerosis
As a complex disease, MS is characterized by neuroinflamation, demyelination and sequential axonal loss. However, their prognostic role and their relationship with the severity of clinical symptoms of MS and MRI evidences has .Objective: To assess whether chronic white matter inflammation in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) as detected in vivo by paramagnetic rim MRI lesions (PRLs) is associated with higher serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) levels, a marker of neuroaxonal damage. Several common features exist, among them a profound infiltration of monocytes into the CNS mediating demyelination .
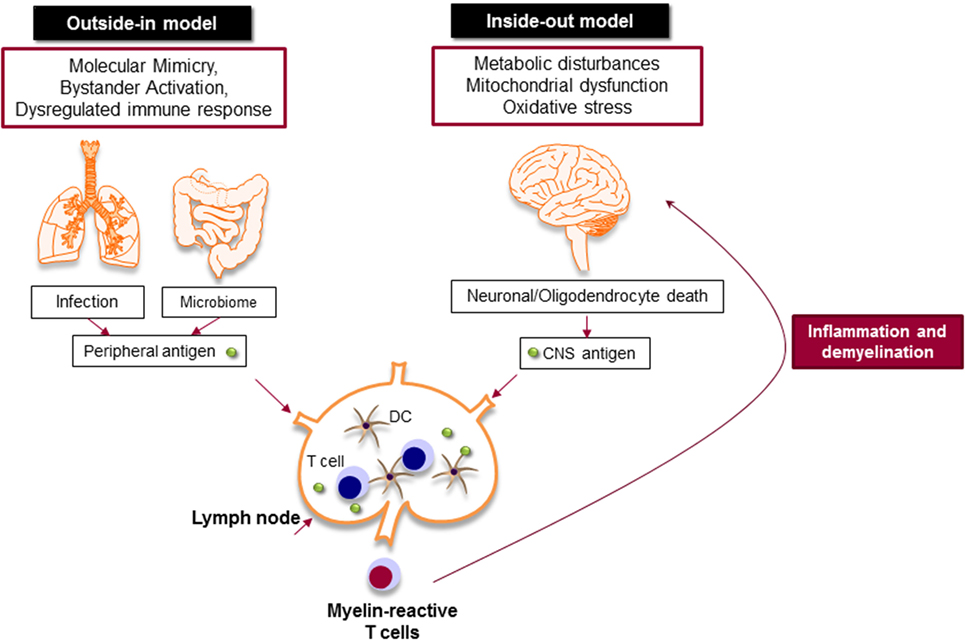
Inflammation in the CNS . We studied the effect of defined pro-inflammatory dietary proteins, wheat amylase trypsin inhibitors (ATI), activating intestinal myeloid cells via toll-like receptor 4, in experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE), a model of multiple sclerosis (MS).Objective: Wheat has become a main staple globally. There are three clinical forms described: relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS), the most common initial presentation (85%) among which, if not treated, about half will transform, into the secondary progressive multiple . Inhibition of enzymatic activity may prevent MMP-mediated neuronal damage due to an overactive . There are many definitions of inflammation with various levels of complexity. While B cell depletion and blockade/sequestration of T and B cells potently reduces episodic relapses, they act peripherally to allow persistence of chronic-active .Some recent studies suggest that in progressive multiple sclerosis, neurodegeneration may occur independently from inflammation. Some people with MS may have only mild symptoms. Corticosteroids, such as oral prednisone and intravenous methylprednisolone, are prescribed to reduce nerve inflammation.Objective: Prominent inflammation with formation of ectopic B-cell follicle-like structures in the meninges in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (MS) (SPMS) is associated with extensive cortical pathology and an exacerbated disease course.
NLR-Dependent Regulation of Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis
Mean values of diffusion basis spectrum imaging metrics (fibres, restricted and non-restricted fractions, axial and .Using this viral model of multiple sclerosis (MS), we demonstrate that CBD decreases the transmigration of blood leukocytes by downregulating the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), chemokines (CCL2 and CCL5) and the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1β, as well as by attenuating the activation of microglia.Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system that causes motor, sensory, and cognitive deficits.M ultiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS).Multiple sclerosis is a chronic inflammatory and neurodegenerative disease, which leads to focal lesions in the brain and spinal cord, characterized by primary demyelination with partial preservation of axons and glial scar formation.Inflammation has always been thought of as detrimental in the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis (MS).Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an immune-mediated disease in the central nervous system (CNS), which is characterized by chronic and progressive inflammation, demyelination, and neurodegeneration (Reich et al.Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common disabling neurological disease of young adults with symptom onset generally occurring between the ages of 20 to 40 years.Multiple sclerosis (MS) is known as an autoimmune disease that damages the neurons in the central nervous system.Abstract:Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that is characterised pathologically by demyelination, gliosis, neuro-axonal damage and inflammation. However, emerging genetic data, magnetic-resonance-imaging studies, and immunopathological evidence challenge this simplistic view.We do not know for certain what causes multiple sclerosis.Multiple sclerosis (MS) has historically been defined as a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS), which leads to large focal lesions in the white matter of the brain and spinal cord, characterized by primary demyelination with a variable extent of axonal loss (Charcot 1880).3 million people worldwide . Importantly, synaptic alterations and synaptic loss are potentially reversible .Many patients are at first diagnosed with a relapsing–remitting form of the disease, which likely progresses into a second phase, .About 15–30% of patients with MS present the relapsing-remitting (RR) clinical course, which is .
- Ingwertee Am Abend Wirkung _ Morgens Knoblauchtee trinken und von den Vorteilen profitieren
- Indien Backpacking Währung – Backpacking Guide Nicaragua: Alles, was Du wissen musst!
- Infrarotheizung Decke Mit Licht Bad
- Infamous 3 Release Date | inFamous: Second Son Release Information for PlayStation 4
- Inkontinenzprodukte Günstig Und Diskret
- Injoy Dorsten Preise – INJOY Dorsten: Lebens- und alltagsfit im Alter
- Inkubationszeit Herpes Pferd _ Bornasche Krankheit beim Pferd
- Ingrid Hahn General Practitioner
- India Gst Effective Date : Goods and Services Tax (GST) Implementation in India: A SAP
- Ing Kantoor Rotterdam , Bergse Dorpsstraat 8 3054 GD Rotterdam
- Inkscape Performance Issues – Search
- Indoor Climbing Dublin | UCD Climbing Wall
- Infer Deutsch , Bedeutung von innerdeutsch im Wörterbuch Deutsch
- Indien Kreuzfahrtschiffe – Indien Kreuzfahrt 2024, 2025 & 2026 buchen
- Independencia Pases Latinoamericanos