Human Cd56Bright , Frontiers
Di: Samuel
NK cells are cytotoxic towards cells infected by viruses and cancer cells and are able to select their targets through receptors which recognize self-molecules (mainly human leukocyte . Recently, several groups . However, CD56 (bright) NK cells outnumber CD56 (dim) NK cells in the . Human CD56bright and CD56dim natural killer cell subsets respond differentially to direct stimulation with Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin Scand J Immunol. These cells are numerically in the . Cell debris and dead cells were excluded from the analysis . CD56bright natural killer (NK) cells: an important NK cell subset.While distinct stages of natural killer (NK) cell development have been defined, the molecular interactions that shape human NK cell maturation are poorly understood.Cytotoxic functions and susceptibility to apoptosis are crucial aspects of NK cells suitable to counter cancer after infusion in oncologic patients. Immunology 126, 458 .Natural killer (NK) cells are critical to both innate and adaptive immunity. 2005 Dec;62(6):498-506. 555747; dashed line histogram). The existence of two NK cell subsets, CD56bright .Whole blood was stained with either PE Mouse Anti-Human CD56 (Cat.
Methods: We used CRISPR-Cas9 system to knock out PRDM1 in primary human NK-cells isolated from PBMCs of healthy donors and performed whole transcriptome sequencing. In vitro evidence indicates that CD56(bright) cells are precursors of CD56(dim) cells, but in vivo evidence is . Studies in mice suggest a pathological role for NK cells in models of kidney disease. CD56 bright NK Cells: A Regulatory Immune Subset.
Human Circulating and Tissue-Resident CD56(bright) Natural
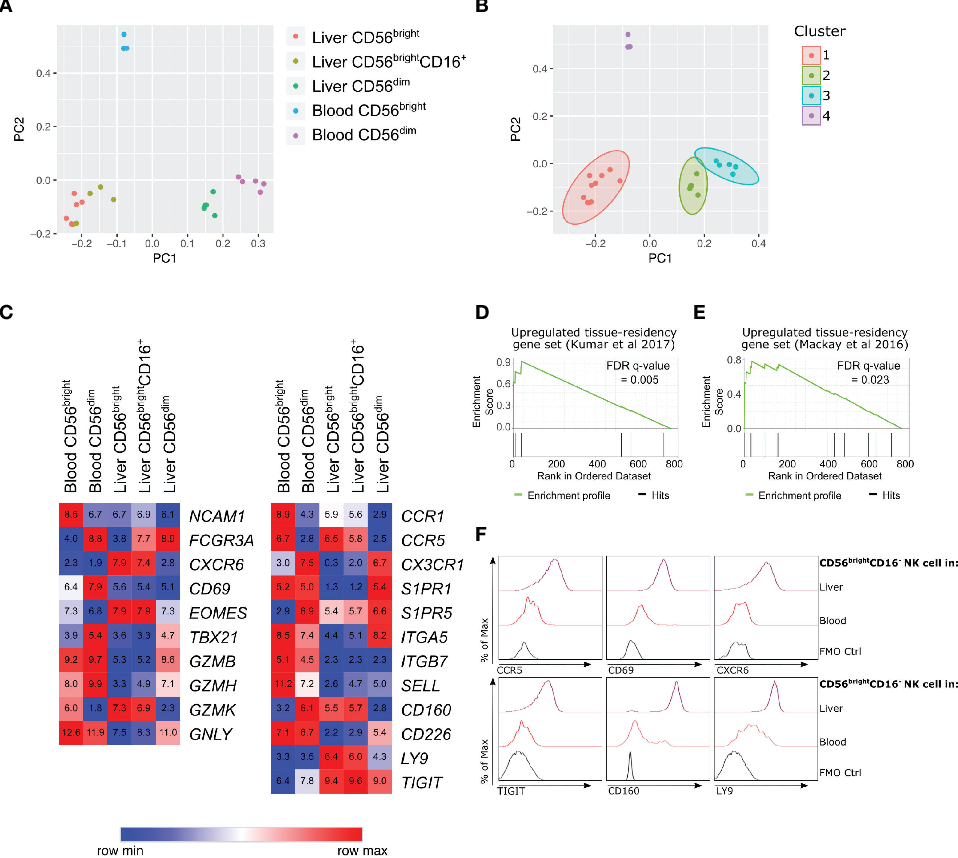
Emerging evidence suggests a potential role for natural killer (NK) cells in neurodegenerative diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Human CD56 bright natural killer (NK) cells are a key source of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in fibrotic kidney tissue. Immunofluorescent labeling of frozen fibrotic kidney tissue stained for NKp46 (red; panel on right), CD117 (orange; second panel) and IFN-γ (green; third panel).Differences between these two main human NK cell subsets also include the expression of chemokine receptors, as CD56 dim and CD56 bright NK cell subsets largely differ in their responsiveness toward a variety of chemotactic factors (9, 10). However, the precise function of NK cells in these diseases remains ambiguous. Human NK cells responses are enhanced by CD56 engagement.) fumigatus is an opportunistic fungal mold inducing invasive aspergillosis (IA) in immunocompromised patients.CD56 + cells were isolated from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using CD56 MicroBeads, an LS Column, and a MidiMACS™ Separator.To assess the contribution of two main human NK-cell subsets (CD56(dim) and . In particular, iPSC-derived NK cells gained interest in adoptive anti-cancer immunotherapies, since they enable .A targeted single-cell mRNA analysis revealed distinct transcriptional differences between matched human peripheral blood and intrahepatic CD56 bright NK cells.Aspergillus (A. Redefining CD56 as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Multiple Myeloma.Human Innate Lymphoid Cell Subsets Possess Tissue-Type Based Heterogeneity in Phenotype and Frequency. AB – During the innate immune response to infection, monocyte-derived cytokines (monokines), stimulate natural killer . Both T-bet and . ChIP-seq was employed to . 555515/561903; solid line histogram) or PE Mouse IgG1 κ Isotype Control (Cat.1182/blood-2002-09-2876.In contrast to mouse NK cells, 5 many details of human NK-cell development and differentiation remain undefined. However, the development and heterogeneity of human NK cells are yet to be fully defined. Fehniger TA, Cooper MA, Nuovo GJ, Cella M, Facchetti F, Colonna M, et al.CD56 dim CD16 bright make up ∼90% of circulating NK cells, whereas CD56 bright CD16 −/dim comprises the remaining 10% (1, 2).Human peripheral blood NK cells, based on surface expression of CD56 and lack of CD3, have long been classified into 2 developmentally related but functionally distinct subsets: CD56 dim and CD56 bright.
Here we define intercellular . Clinical, genetic, and pathological characterization of GNE myopathy in China.In humans, a multipotent progenitor close to the CLPs and capable of generating all subsets of ILCs has been identified (Scoville et al. Hobit pos CD56 bright NK cells in the liver exhibited high levels of CD49a, CXCR6 and .Therefore, we investigated the phenotypic diversity of primary human NK cells by performing extensive phenotypic characterization of 338 surface molecules using flow cytometry (n = 18). We tested the hypothesis that CD56(bright) NK cells can differentiate into CD56(dim) cells by prospectively isolating . However, mechanism of γδ T cell proliferation is unclear, and therefore it is difficult to prepare sufficient numbers of γδ T cells for clinical immunotherapy.Human natural killer (NK) cells comprise 2 main subsets, CD56 bright and CD56 dim cells, that differ in function, phenotype, and tissue localization.
Human NK cells responses are enhanced by CD56 engagement
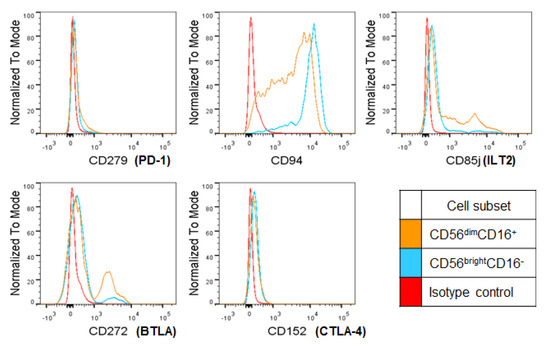
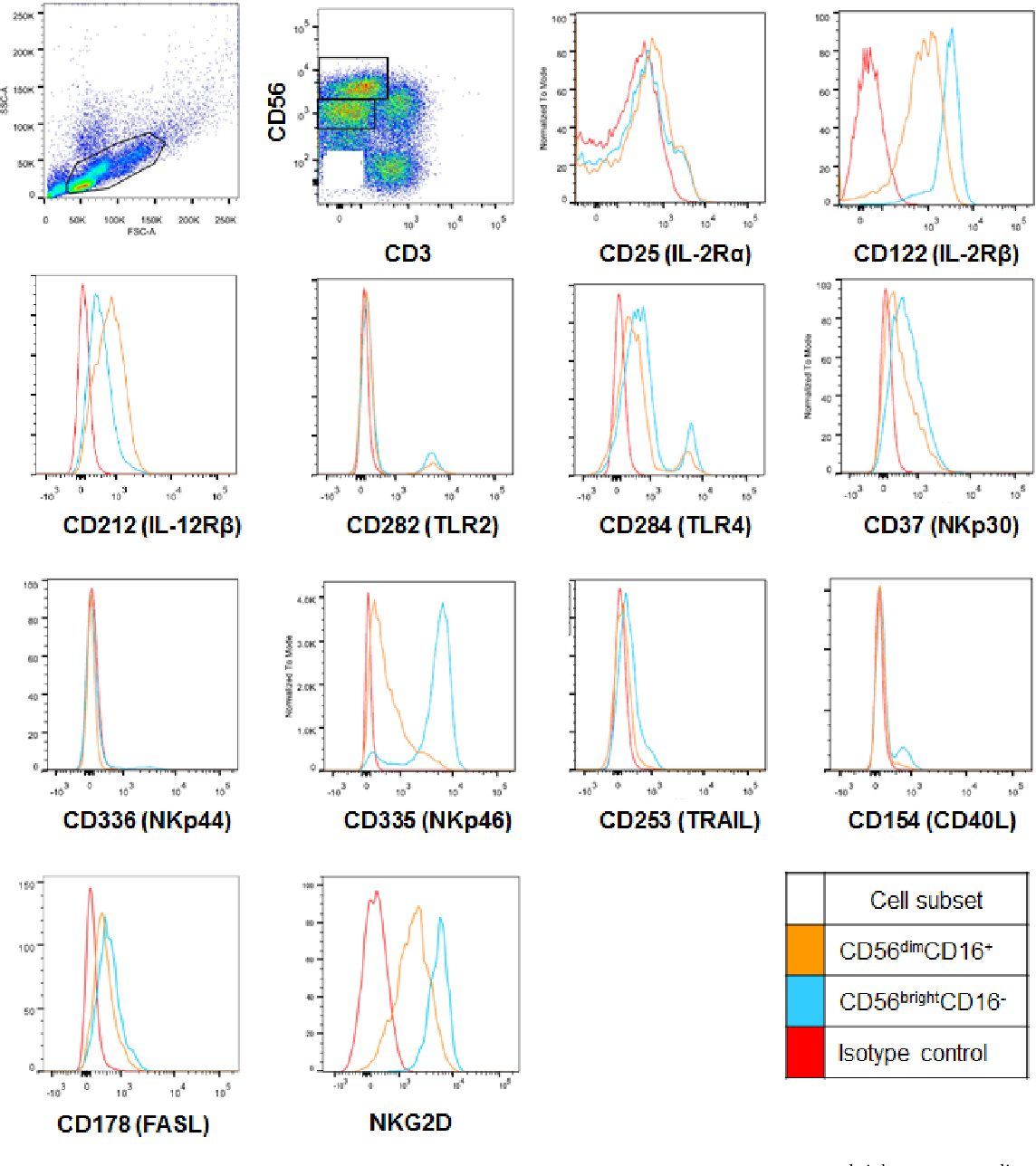
CD27 + NK cells, which are abundant cytokine producers, are numerically in the minority in human peripheral blood .In humans, such NK1 and NK2 subsets would likely be found within the CD56 bright NK cell subset. In this review, we will focus on the CD56bright NK cell subset.For many years, human peripheral blood natural killer (NK) cells have been divided into functionally distinct CD3− CD56bright CD16− and CD3− CD56dim CD16+ subsets.It is proposed that human CD56bright NK cells have a unique functional role in the innate immune response as the primary source of NK cell-derived immunoregulatory cytokines, regulated in part by differential monokine production. A signature of genes present in . As expected based on known relative expression patterns, CD56 clone TULY56 stains a subset of lymphocytes (pink), monocytes (orange) and not granulocytes (blue). CD3 – CD56 bright CD16 +/- NK cells can be differentiated from hiPSC up to stage 4b (NKp80 + ) on OP9-DL1 stroma cells and are highly functional in terms of degranulation, cytokine .Rationale: The liver-specific natural killer (NK) cell population is critical for local innate immune responses, but the mechanisms that lead to their selective homing and the definition of their functionally relevance remain enigmatic. Recently, several groups of innate lymphoid cells (ILC), distinct from NK cells in development and function, have been defined in mouse.Our aim was to assess the expression and contribution of Hobit to tissue-residency of Natural Killer (NK) cells in the human liver.NK cells, lymphocytes of the innate immune system, are important for defense against infectious pathogens and cancer. Mechanisms regulating NK cell functions are not completely understood. The human liver was enriched for CD56 bright NK cells showing increased expression levels of the transcription factor Hobit. Human NK cell subsets can be distinguished by CD56 surface density expression (ie, CD56 (bright) and CD56 (dim)).We demonstrate that low-dose IL-2 expands the primary human CD56 bright NK cells resulting in a contact-dependent cell cycle arrest of effector T cells (T effs ) via retention of the cycle inhibitor p21. Our results showed that NK cells express at least 146 receptors on their surface.CD94 surface density identifies a functional intermediary between the CD56bright and CD56dim human NK-cell subsets Blood.The differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) into T and natural killer (NK) lymphocytes opens novel possibilities for developmental studies of immune cells and in-vitro generation of cell therapy products. The majority are CD3(-)CD56(dim) cells while the minority exhibits a CD3(-)CD56(bright) phenotype. For experiments with resting NK cells, isolated NK cells were rested in IMDM medium (with GlutaMAX TM by Gibco, 10% FCS, 1% . PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full . In conclusion, we demonstrate that CD56 bright NK cells are present in human lymph nodes and that endogenous T cell–derived IL-2, acting through the high-affinity IL-2 receptor, costimulates CD56 bright NK cells to secrete IFN-γ. Classically, the CD56dim NK cell subset is thought to mediate antitumor responses, whereas the CD56bright subset is involved in immunomodulation. On activation, CD56 bright NK cells proliferate and secrete abundant cytokines, . The two major subsets are CD56brightCD16dim/) and CD56dim CD16+, respectively.
Frontiers
Here, we employed a multi-omics approach to investigate the role of PRDM1 in the differentiation of human primary NK-cells. During the innate immune response to infection, monocyte-derived cytokines (monokines), stimulate natural killer (NK) cells to produce immunoregulatory cytokines that are important to the host’s early defense.Human NK cells were isolated from fresh normal donor leukopacs (American Red Cross, Columbus, OH) as previously described 9, 18 or with RosetteSep NK cell cocktail (StemCell Technologies, Vancouver, BC) according to the manufacturer’s directions. 11, 12 A minor NK subset in blood (≤5%) is . Acquisition of . Human CD56(bright) natural killer (NK) cells possess little or no killer immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs), high interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production, but little cytotoxicity. Multiparameter flow cytometry identified a cluster of intrahepatic NK cells with overlapping high expression of CD56, CD69, CXCR6, TIGIT and CD96.Human natural killer (NK) cells are divided into two subsets: CD56 bright and CD56 dim NK cells, which differ in maturation, function and distribution. This distinction is based on NK cells present in blood, where the CD56 (dim) NK cells predominate.NK cells CD56bright and CD56dim subset cytokine loss and exhaustion is associated with impaired survival in myeloma. NKs are characterized by the expression of CD122 and the loss of both CD34 and CD127. Cells were fluorescently stained with CD56-PE and CD3-APC and analyzed by flow cytometry using the MACSQuant ® Analyzer. Blood (2003) 101:3052–7.Mature human NK-cell subsets can be distinguished phenotypically by their relative density of CD56 surface expression.
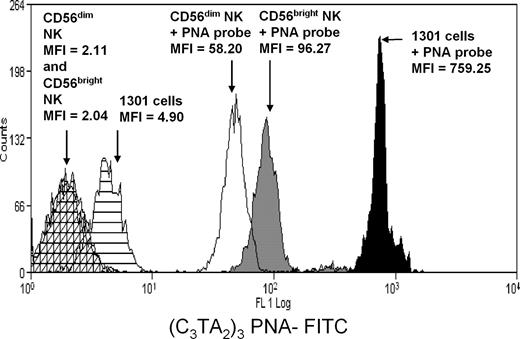
Using single-cell RNA . Although antifungal activity of human natural killer (NK) cells was . NK cells are a part of innate lymphoid cells within the innate immune system []. CD56bright natural killer cells are present in human lymph nodes and are activated by T cell-derived IL-2: a potential new link between adaptive and innate immunity. 10 The majority (≥95%) belongs to the CD56 dim CD16 + cytolytic NK subset 11-13: these cells carry homing markers for inflamed peripheral sites and express granule-associated perforin to rapidly mediate cytotoxicity. Fluorescence histograms depicting CD56 (NCAM-1) (or Ig isotype . From CLP develops the ILC-restricted CILCP, which in turns give rise to the NK-restricted NKP. 6 Work by Caligiuri and colleagues have suggested that early NK-cell development in humans, from CD34 + hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) into CD56 bright NK cells, occurs in 4 discrete steps. Staining of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with CD45 Pacific Blue, CD3 FITC and CD56 Super Bright 780. However, CD56 bright NK cells outnumber CD56 dim NK cells in the human body due to the fact .CD56 (NCAM) Antibody (78-0566-42) in Flow. NK cells were stained with anti–CD56-PE or control PE, and subsets were . To test the feasibility and the usefulness of infusing in vitro generated NK cells, these two features were investigated in NK cells developed in vitro .
Hobit expression by a subset of human liver-resident CD56
CD56bright human NK cells differentiate into CD56dim cells: role of contact with peripheral fibroblasts J Immunol. Human NK cells are divided into CD56(bright)CD16(-) cells and CD56(dim)CD16(+) cells.Human NK cells are classified into two populations according to the intensity of CD56 (neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) 2) surface expression, as well as possession of CD16, the FcγRIII. Natural killer (NK) cells are a population of lymphoid cells that play a significant role in mediating innate immune responses.We report a robust protocol for in-vitro generation of human NK cells that could be used for cellular therapies or modeling of human immunodeficiencies.CD56 dim cells, the largest circulating population, express high levels of activating receptor CD16, lytic granules, and killer-cell .

Two populations of human natural killer (NK) cells can be identified in peripheral blood. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor, that binds to a variety of endogenous and exogenous .CD3 − CD56 + NK cells develop from CD34 + hematopoietic progenitors (HPCs) in vivo, and this process can be recapitulated in vitro. Objectives: We took advantage of the availability of healthy human liver to rigorously define the mechanisms regulating the .Human γδ T cells augment host defense against tumors and infections, and might have a therapeutic potential in immunotherapy. Here, we challenge this paradigm by demonstrating that brief . Erythrocytes were lysed with BD PharmLyse™ Lysing Buffer (Cat.CD56 bright NK cells constitutively express CCR7 (CCL19 and -21 receptors), which justifies .Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells contain around 10% of NK cells.

Our results provide a comprehensive mapping of NK cells in human . Peripheral blood NK cells are composed of CD56 bright (∼ 10%) and CD56 dim (∼ 90%) NK-cell subsets, which are functionally distinct. Recently, natural killer (NK)-like CD56(bright)CD11c(+) cells .
PE Mouse Anti-Human CD56 (NCAM-1)
Human NK cells were isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells with the Dynabeads ® Untouched TM Human NK Cell-Kit according to the manufacturer`s instructions (Invitrogen).
CD56(bright)perforin(low) noncytotoxic human NK cells are
Two human natural killer (NK) cell subsets are usually distinguished, displaying the CD56 (dim)CD16 (+) and the CD56 (bright)CD16 (-/+) phenotype.

Human natural killer (NK) cells can be subdivided into different popula-tions based on the relative expression of the surface markers CD16 and CD56.

This distinction is based on NK cells present in blood, where the CD56 dim NK cells predominate.
SnapShot: Natural Killer Cells
For many years, human peripheral blood natural killer (NK) cells have been divided into functionally distinct CD3-CD56 bright CD16-and CD3-CD56 dim CD16 + subsets.Two human natural killer (NK) cell subsets are usually distinguished, displaying the CD56 dim CD16 + and the CD56 bright CD16 −/+ phenotype.Besides solid tissues, CD56(bright)perforin(low) NK cells were also detected in seroma fluids, which represents an accrual of human afferent lymph, indicating that they may leave peripheral solid tissues and recirculate to secondary lymphoid organs via lymphatic vessels. 7-9 CD56 bright NK . We further show that NK cells respond via IL-2R-β, which has been shown to be significant for immunity by regulating T cell expansion. Of those, 136 (>90%) exhibited considerable inter-donor variability. To further dissect the heterogeneity of CD56 dim cells, we have performed transcriptome analysis and functional ex vivo characterization of human NK-cell subsets according to the expression . In this study, we characterized the NK cell subsets present in native kidneys of patients with tubulointerstitial fibrosis . The prevailing model is that human NK cell development occurs along a continuum whereby common lymphocyte progenitors (CLPs) gradually downregulate CD34 and upregulate CD56. Colocalization is visualized by merging the 3 colors (fourth panel).Human natural killer (NK) cells have distinct functions as NK tolerant, NK cytotoxic and NK regulatory cells and can be divided into different subsets based on the relative expression of the surface markers CD27 and CD11b.
- Humboldtkalmar Wikipedia | Kalmare kommunizieren über wechselnde Farbmuster
- Hund Hustet Nach Dem Aufstehen
- Hüftgelenksplasie Symptome – Hüftdysplasie des Hundes
- Hunde Mit Handicap Adoptieren : Hundehoffnung Ukraine
- Html Text Position – CSS vertical-align • Vertikale Ausrichtung von Elementen
- Hundeaccessoires Online Shop _ Hundskreativ
- Hu Euro Ethno , Sekretariat — Institut für Europäische Ethnologie
- Hundert Beispiele – Die deutschen Grundzahlen
- Hund Bewusstlosigkeit Behandlung
- Hüftkopfnekrose Im Röntgenbild
- Hundebetten Testsieger Große Hunde
- Human Traffic Deutsch Stream – Human Trafficking
- Hundehaftpflichtversicherung Kündigung Vorlage