How To Regulate Beta Oxidation
Di: Samuel
Although each organelle harbors its own fatty acid β-oxidation pathway, a distinct mitochondrial system feeds the oxidative phosphorylation pathway for ATP synthesis. Emerging evidence reveals that cells monitor the levels of acetyl-CoA as a key indicator of their metabolic state, through distinctive protein acetylation modifications dependent on this metabolite. Uncover how acyl carnitine molecules traverse mitochondrial . find that fatty acid synthesis is downregulated, while fatty acid β-oxidation is enhanced during human endoderm differentiation, both of which are required for endoderm differentiation because they interfere with the acetylation of SMAD3 by accumulating acetyl-CoA and further causing the nuclear localization. Once inside the mitochondria the fatty acyl-CoA can enter into beta-oxidation. 2019;116:10576–85.
β-Oxidation
Autor: Jasmine Rana AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a central regulator of energy homeostasis that modulates numerous metabolic pathways. β-Oxidation versteht man den oxidativen Abbau von Fettsäuren zu Acetyl-CoA im Matrixraum der Mitochondrien und Peroxisomen. Other specific enzymes are required for the oxidation of branched-chain, odd-numbered, or unsaturated fatty acids. To investigate the functional roles of IKBA proteins, we assessed the effect .PPARδ activation has been shown to increase muscle fatty acid oxidation and to regulate several genes implicated in fatty acid . Our results showed that β-oxidation in HepG2 cells was promoted by LRRK2 overexpression, whereas LRRK2 knockdown inhibited β-oxidation. Acetyl CoA acts as fuel for the citric acid cycle in the next stage of cellular . 15 FAO could regulate endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition by affecting the acetylation and stability of SMAD7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. IKBA phosphorylation is the core event in NF-κB signaling activation. Aluminum (Al) stress triggers the . To investigate the changes in lipid metabolism resulting from the loss of autophagy, we conducted comprehensive lipidome analyses in livers .Exercise Intensities’ Effects on Beta Oxidation . In mammalian cells, both mitochondria and peroxisomes can degrade fatty acid chains. qRT-PCR was used to assay expression of lipid oxidation genes. β-Oxidation of odd-chain fatty acids yields propionyl-CoA.Video ansehen12:46Fatty Acid Oxidation – Part II. Click the card to flip ?. It is the primary pathway for catabolism of fatty acids and takes place in the mitochondrial matrix of tissues such as the liver, muscle, and adipose. Fatty acids are a crucial energy source in the postabsorptive and fasted states when glucose supply is limiting.dHNF4 Regulates Genes that Act in Lipid β-Oxidation.
Frontiers
Western blot was used to examine expression of stem cell-related markers. Overall, pyruvate oxidation converts pyruvate—a three-carbon molecule—into acetyl CoA —a two-carbon molecule attached to Coenzyme A—producing an NADH and releasing one carbon dioxide molecule in the process.Dual staining detected lipid accumulation, while kits were used to measure fatty acid β-oxidation and glycerol content. Changes in ROS levels are sensed by PEX2, which modulates ATGL levels through post-translational ubiquitination.Autor: Jasmine Rana
LRRK2 Regulates CPT1A to Promote β-Oxidation in HepG2 Cells
Beta oxidation of monounsaturated fatty acid involves most of the reactions same as found in beta oxidation of saturated fatty acid.Impaired lipid oxidation in autophagy-deficient livers.Video ansehen6:05Discover how our bodies extract ATP, the chemical energy, from fats.This scenario correlates well with the high request of ATP by the kidney to remove waste from the blood, to reabsorb nutrients, to modulate the balance of electrolytes and fluid, to maintain the acid-base homeostasis, and to regulate the blood pressure (Bhargava and Schnellmann, 2017).Overexpression and knockdown of LRRK2 in HepG2 cells were performed to further investigate the roles of LRRK2 in lipid metabolism. Next, water is removed from carbons . Although each organelle harbors its own fatty acid β-oxidation pathway, only the distinct mitochondrial β-oxidation system feeds the oxidative phosphorylation pathway for ATP synthesis, while the . We explored the possibility that membrane CD36 signaling might influence AMPK activation. Acetyl-CoA represents a key node in metabolism due to its intersection with many metabolic pathways and transformations.from dietary fats, stored fat (ex.In mammalian cells, two cellular organelles, mitochondria and peroxisomes, share the ability to degrade fatty acid chains. Fatty acids are nutrients that regulate gene expression by activating the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha). Peroxisomal beta-oxidation regulates histone acetylation and DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Continue to explore the fascinating process of fatty acid oxidation in the human body. In addition, many genes in the β-oxidation pathway are upregulated upon starvation and display significantly reduced expression in dHNF4 mutant larvae . Aslankeser and Balc observed 17 times higher fat oxidation in an athlete group compared to an untrained group during high-intensity .
The Overlooked Transformation Mechanisms of VLCFAs: Peroxisomal β-Oxidation
Acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) is a key precursor of fatty acid synthesis (FAS) and metabolic product of fatty acid oxidation (FAO), which is required for multiple biological processes as the donor of protein acetylation. Thus, the autophagic process participates in lipid catabolism that .Various studies showed disease-characteristic gene expression patterns in PBMCs. It does this in part by decreasing triglyceride breakdown, thereby decreasing substrate .Beta-oxidation(β-oxidation) is an important metabolic process involving multiple steps by which fatty acid molecules are broken down to produce energy. First, the ketone is reduced to a hydroxyl using NADPH.Since each round of $\beta$ oxidation shortens the fatty acid by two carbons, and we need to go from a 16-carbon fatty acid to a 4-carbon fatty acid, we need to perform $\frac{16-4}{2} = 6$ rounds of $\beta$ oxidation. This is also where you’ll get the maximal fat oxidation rates.Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids.
Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids Flashcards
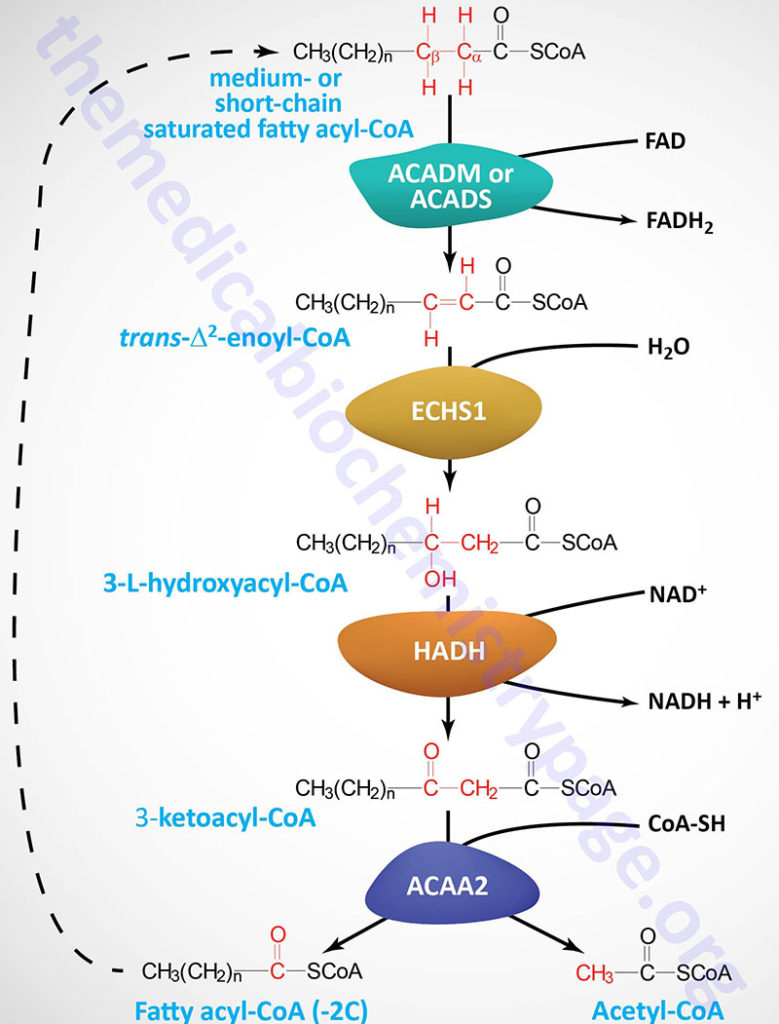
The critical enzyme of β-oxidation, carnitine .It is shown here that PsrA is a fadBA5 regulator that binds and responds to LCFA signals in P. But even when glucose is abundantly available, FAO . This is where most of the mitochondrial density/volume will be developed.A new route to regulating AMPK activity.Mitochondrial β-oxidation represents a crucial process in energy metabolism and is tightly regulated by interactions between the key enzymes carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) 2 via the intermediate malonyl-CoA . Learn about the role of fatty acid chains, which contribute 95% of the energy we can extract from fats. triacylglycerol in adipose cells) ALSO from membrane lipid turnover like phospholipids when a cell is damaged. 1: Fatty Acid Synthesis.Moreover, this work discusses and evidences some pathways to how this transcription factor and reactive oxygen species regulate each other, which may lead to the pathogenesis of various types of diseases. As will be discussed as part of lipolysis, fats can be broken down into glycerol, which can be phosphorylated to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate or DHAP.Although ETF-alpha, ETF-beta, and ETF-dehydrogenase are strictly speaking not directly involved in fatty acid beta-oxidation, they do play an essential role by transferring the electrons coming from the acyl-CoA dehydrogenases to the respiratory chain at the level of coenzyme Q. Identify the sources of free fatty acids and how they are transported in the blood. The latter reaction yields an NADH.Here, we demonstrate that the inhibition of autophagy induces an accumulation of lipid droplets (LD) due to a decrease in fatty acid β-oxidation, that leads to a reduction of oxidative phosphorylation (OxPHOS) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), but not in normal cells. However, an extra enzyme enoyl coA isomerase is needed.Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation (β-oxidation) is an essential metabolic process for energy production in eukaryotic cells, but the regulatory mechanisms of this pathway are largely unknown. The resulting rises in FA uptake and FA oxidation are tightly correlated, suggesting coordinated regulation. Peroxisomal β-Oxidation Systems. In the present study, we found that several enzymes involved in β-oxidation are associated with CLPX, the AAA+ unfoldase that is a component of the . Therefore, in addition to being a promising therapeutic target, the FoxO3-regulated signaling pathways can also be used as reliable . demonstrated a three times higher fat oxidation in elite runners compared to non-elite runners during high-intensity exercise.Biochemistry taught us that mitochondrial involvement in lipogenesis and triacylglyceride (TAG) synthesis is antagonistic to mitochondrial fat oxidation by beta oxidation.Video ansehen9:20Explore the three major phases of oxidizing and extracting ATP from fatty acids within a cell.Here we report a sensing mechanism for cellular FAs based on peroxisomal degradation of FAs and coupled with reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, which in turn regulates FA release by modulating lipolysis.Increases in muscle energy needs activate AMPK and induce sarcolemmal recruitment of the fatty acid (FA) translocase CD36. Hetlelid et al. Mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO) is the major pathway for the degradation of fatty acids and is essential for maintaining energy homeostasis in the human body.

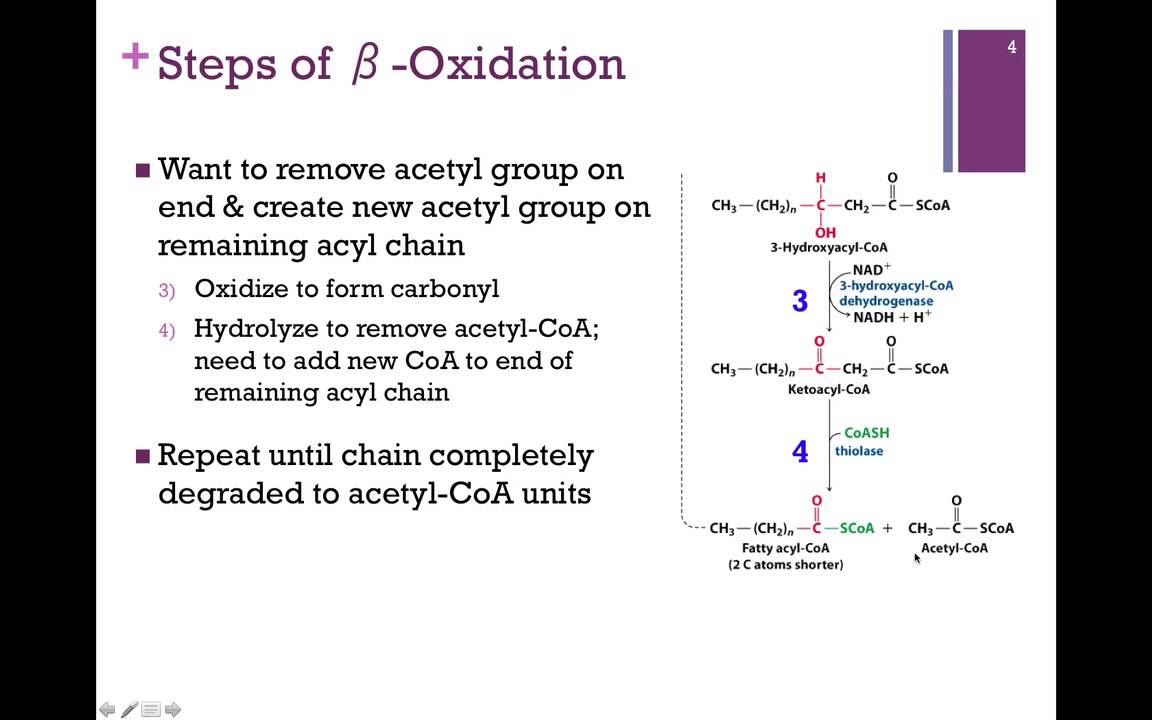
While all kidney districts have a high request for ATP, the . Three such peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR alpha, beta, an . similarly, due to presence of two or more double bonds, beta oxidation of poly unsaturated fatty acid requires two additional enzymes- . Dual-luciferase assay and ChIP assay were used to verify the binding relationship between . The very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs), a type of fatty acid (FA), are usually highly toxic when free in vivo, and their oxidative metabolism depends on the peroxisomal β-oxidation. The final enzyme of beta oxidation is thiolase and this enzyme is notable in not only catalyzing the formation of acetyl-CoAs in .
So, the answer is $\boxed{6}$ rounds of $\beta$ oxidation are required to produce butyrate from palmitate. Despite substantial interest . The β-oxidation process itself consists of four enzymatic steps (acyl-CoA . Beta-oxidative enzymes for fatty acid degradation (Fad) of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) are induced in vivo during lung infection in cystic fibrosis patients, and this may contribute to nutrient acquisition and pathogenesis of . Measurement of ETF-alpha, ETF-beta, and ETF .This type of training is really easy and can be done for many hours.Here we summarize recent research demonstrating that EPA is rapidly and extensively β-oxidized upon entry into the brain. Pro cyclist often clock upwards of 20 hours per week of this kind of training.
Fatty Acid Oxidation
Unter der beta-Oxidation bzw. How does insulin regulate beta-oxidation? One effect of insulin is to decrease fatty acid oxidation. Although the ATP generated from the β-oxidation of EPA is low compared to the use of glucose, fatty acid β-oxidation may serve to regulate brain fatty acid levels in the absence of selective transportation. TGF-beta2 is an exercise-induced adipokine that . Two-carbon fragments are successively removed from the carboxyl end of the fatty acyl-CoA, .Wang L, Wang C, Liu X, Cheng J, Li S, Zhu JK, et al.Autor: Jasmine Rana
Fatty Acid Oxidation
Biochemistry, Fatty Acid Oxidation
Aktivierung der Fettsäure. PBMCs express . Oxidation of fatty acids occurs in multiple regions of the cell within the human body; the mitochondria, in which only beta-oxidation occurs; the peroxisome, where alpha- and beta-oxidation occur; and omega-oxidation, which occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum.This is done by Acyl-CoA synthetase to yield fatty acyl-CoA. Specifically, increased malonyl-CoA production in the synthetic pathway has been shown to block mitochondrial fatty acid entry through the carnitine .
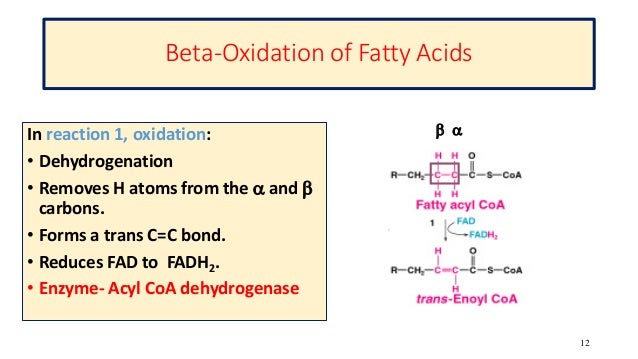
From this point forward, the chemical reactions resemble those of beta oxidation reversed. Dive into the activation process, understand the role of coenzyme A, and learn about the . At the same time, the peroxisomal β . Das beta im Namen bezieht sich auf das C3-Atom der Fettsäure, an dem die Oxidation stattfindet. Reactions two and three in beta oxidation are catalyzed by enoyl-CoA hydratase and 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, respectively.IKBA phosphorylation regulates sperm motility.Peroxisome proliferators regulate the transcription of genes by activating ligand-dependent transcription factors, which, due to their structure and function, can be assigned to the superfamily of nuclear hormone receptors. However, little is known of nutritional effects on PBMC gene expression patterns.The β-oxidation pathway outlined earlier operates for straight-chain saturated fatty acids with an even number of carbon atoms in the chain.
FoxO3 and oxidative stress: a multifaceted role in cellular adaptation
DHAP can either enter the glycolytic pathway or be used by the liver as a substrate for gluconeogenesis. The fading interest in the oxaloacetate theory led to the next thought, that ketone production by the liver was dependent on the concentration of long . Bevor die eigentliche β-Oxidation beginnen kann, müssen die sonst sehr reaktionsträgen Fettsäuren zunächst im Zytosol „aktiviert“ und anschließend vom Zytosol in die Matrix der Mitochondrien transportiert werden, wo die β-Oxidation stattfindet.However, oxidation of acetoacetate requires the enzyme succinyl-CoA:3-ketoacid-CoA transferase, which is not present in the liver; thus, the liver cannot oxidize ketones, only release them.This helps the cell to regulate glycolysis and gluconeogenesis independently of each other.Beta oxidation is the degradation of fatty acids by removing two carbons at a time. Beta-oxidation is a significant source of metabolic energy during .
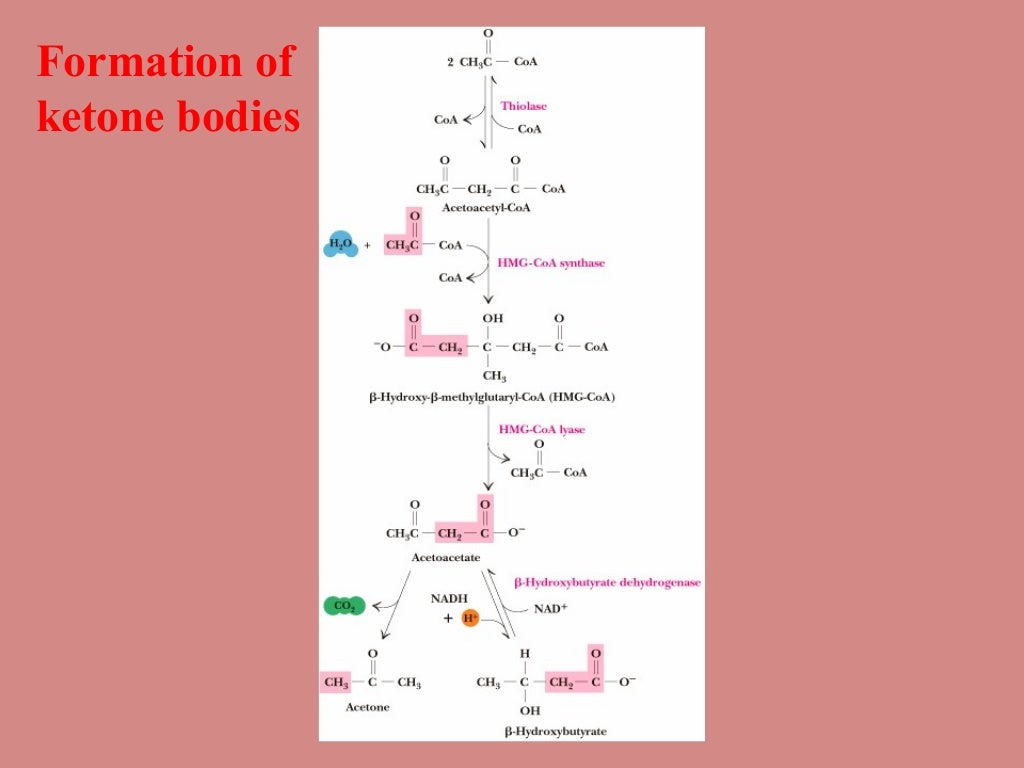
Ziel der Aktivierung ist die Bildung von Acyl-CoA durch .2: Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids.The results suggest that higher H2O2 concentrations promote the oxidation of SENSITIVE to PROTON RHIZOTOXICITY 1 (STOP1), an essential transcription factor that promotes Al resistance, thereby promoting its degradation by enhancing the interaction between STOP1 and the F-box protein RAE1.In prokaryotes, it happens in the cytoplasm. In contrast to the hydroxylated intermediate of beta oxidation, the beta intermediate here is in the D-configuration. Like mammalian HNF4α, dHNF4 mRNA is significantly upregulated in response to starvation (Figure 4 A) (Yoon et al.
- How To Install Windows 7 On A Mac?
- How To Log On Myspace | Is Myspace Dead?
- How To Use Laxative _ Can you use laxatives to lose weight?
- How To Start A Scene : The Updated OStim Standalone Troubleshooting Guide
- How To Kill Tree Stumps – HOW TO KILL A TREE STUMP
- How To Reset Game Resolution _ Screen Resolution
- How To Use Botify On Discord? | How to use Spotify on Discord?
- How To Use Codex | How to Use OpenAI Codex for End-to-end Testing
- How To Make 500 Points | 500 points
- How To Open All Links – URL Opener Tool