How To Initialize A Std Vector?
Di: Samuel
Vectors in C++ STL are same as the array in C++. The array version would be my pick for this case since the OP says he doesn’t need . You can not do this without a loop. You need {} in list initialization.
The contents of vector are guaranteed to be contiguous (see [vector. Notice that we have not specified the size of the .The default constructor constructs an empty container with a default-constructed allocator.constexpr vector (std::from_range_t, R && rg, const Allocator& alloc = Allocator()); (11) (since C++23) Constructs a new container from a variety of data sources, optionally using a user supplied allocator alloc . For example: #include int main() { // List construction (uses list .push_back(20); return v; Return value optimisation should mean that the array is filled in place, and not copied, if that is a concern. // Will be an initialised empty Vector.Always check that the vector is not empty & the index is valid while using the [] operator on std::vector. Vector and initializer lists are a no-go too. and compiler errors. 0 in case of int).std::vector has a constructor that takes two arguments, a number of elements and an initial value.
How to create a empty vector in C++?
If you want to include a[7] then you have to .
Vector of Vectors in C++ STL with Examples
And drop the extra pair of parentheses () wrapping it all. We will particularly focus on the std::vector initialization methods and their specifics, but some will be the same for other STL sequence containers.
Initialize empty vector in structure
And vector reference defines the std::vector::data as: Returns pointer to the underlying array serving as element storage.What is the correct way of initializing a container with predetermined std::byte values? std::array arr{0x36, 0xd0} for array results in . The behavior of vector (or any container class) is undefined if you were to access the uninitialized section of the array as if it were initialized. This kind of functionality can be achieved using STL Algorithm std::generate and any user specific Function Object. An object is a living instance of a type.overview], §1 in C++ standard). Enum std::byte has not constant to represent the integer value of X. std::vector
2D Vector In C++ With User Defined Size
The best way is to use reserve() and push_back(), so that the copy .If you’re asking how to initialise a const vector so that it has interesting contents, then the answer is probably to use the copy constructor. You can be explicit about the zero values by using: std::vector v(100, 0); You can use the second form to initialize all the elements to something other than zero.size() is zero.Because I need a vector that create on heap! The terms we use in C++ are automatic and dynamic storage.
Assigning initial value to VHDL vector
Then, we define a function to store a string pi.

The above code avoids to initialize vector content before filling it with the data you really want. Winning the award for the least efficient way to do this:. Now, that X in turn is a vector of 100 std::vector, which in turn contains a hundred ints:
how can we initialize a vector with all values 0 in C++
This is a definition of an object, not a reference as in C#/Java.Yes, this is perfectly fine. std::vector items{ std::vector(100) }; or. It is important to note that although the returned vector has the minimum capacity specified, .Because C++ is not C#/Java. In your case, you want to initialize m_input with 100 copies of a std::vector
C++ Vectors (With Examples)
Option 1: Suppose we have vector c_strings;. As user1155120 says, in VHDL the width of the right hand side has to match the width of the left hand side of an assignment operator ( <= or := ).It is immediately clear what the intent is with push_back but it is also overly repetitive and verbose if you're initializing the vector with a lot of elements.2D Vector In C++ With User Defined Size. Using simply std::vector arr; is a good fix - only worry about reallocation issues if your performance profiler highlights it as a bottleneck.I'm trying to set length and initialize a vector member of a class, but it seems it's only possible if initializing line is out of class.Constructs a new, empty Vec with at least the specified capacity. Since the goal of a container is to manage a set of related values, most often we will want to initialize our container with those values.All 'U's and all '0's resolve to all 'U's, std_logic_vector is a resolved type or subtype (-2008). Like 2D arrays, we can declare and assign values to a 2D vector! Assuming you are familiar with a normal vector in C++, with the help of an example we demonstrate how a 2D vector differs from a normal vector below: C++.Constructs a fixed-sized matrix initialized with coefficients starting at data. For example, vector num; Here, num is the name of the vector. The basic difference between a vector and an array is vectors are dynamic arrays with the facility to resize itself whenever a new element is pushed inside the vector or deleted from a vector unlike arrays which have predefined lengths.In most of the cases, you do not require the std::vector to be allocated dynamically, rather the elements to be there. You should create a temporary object of your structure, fill it up and then add it to the vector, using vector::push_back()Reading time: 20 minutes | Coding time: 2 minutes .

I think it’s not necessary to copy the width_height when the array have large size and the argument’s life-time is long enough, then we may return a std::vector
use std::fill to populate vector with increasing numbers
Here is my naive, harebrained code: output.In C++03, you could use a template to deduce the size of the array, either to implement your own begin and end, or to initialise the array directly: return std::vector(array, array+N); In C++11 we have proper initialisers, no . #include #include #include using namespace std; template std::vector v_init(const T& t) { return std::vector(1,t); } template push_back(buffer[i]); std::vector(buffer, buffer+size); PS: if you initialize a vector with a size, don’t use push back you’ll end up with twice the elements, of which the first half have default values. In order to determine the fastest way you will need to run some benchmarks. The pointer is such that range [data(); data() + size()) is always a valid range, even if the container is empty. So, you could use the literal that corresponds to a std_logic_vector, which is a string: signal Qout: Std_Logic_Vector (4 downto 0) := 00001; (a string literal in VHDL is enclosed within .Elements can be removed from a vector of vectors using the pop_back() function of C++ STL.Even doing the following: std::vector data(10); creates a vector with all elements set to its default value (i.If capacity is 0, the vector will not allocate. First you laboriously fill in a vector, then you create your new const vector from it. Alternatively, you could initialise from an array: You might want to consider making user a class and adding a default constructor that does this for you: An object of type std::initializer_list is a lightweight proxy object that provides access to an array of objects of type const T (that may be allocated in read-only memory). A 2D vector is a vector of the vector.This article will explore how to initialize a two-dimensional vector with a given default value in C++.In the initializer list you may call any constructor of the class of the member you want to initialize. 2) Constructs an empty container with . Or you can use the vector(InputIterator, InputIterator) constructor template to initialise from . This expression returns a pointer. foo is an object, std::vector* is a pointer to . As such, you should be able to write: struct user r = { string(), vector() }; Note, I’ve also used the default string constructor instead of . For this, you need simply a vector of integers. The default vector constructor will create an empty vector. std::vector b(&a. Last Updated : 10 Jan, 2023. std::vector x; The only way to initialize a class member in the body of the class is to brace or equal initialize it. std::vector words; // c++11 initializer list syntax: A lot of complexity is introduced since we need to distinguish between an empty string and a null char*. It’s straightforward to initialize a std::vector data member using this constructor: struct S {. push_back(17); v. Performance of this solution is well visible on large data sets. What you can do is to hide a loop under a standard algorithm because you need to convert an object of type char to an object of type std::map::value_type that represents itself std::pair. //a vector, out of class set size to 5.at(i)=10; This code will throw std::out_of_range exception since a. We can do this by using list initialization with the specific initialization values we want.Initialize a vector with std::list. Copy to clipboard. Below example demonstrates the removal operation in a vector of vectors. For storing two objects I would recommend using std::pair. Constructs an empty container with a default-constructed allocator.Just because you can doesn’t mean you should =P . The default value for x is a value initialized T (if T is a class type with a default constructor then value initialization is default construction). I like creating vectors with a given size and value, for example like this: std::vector<std::string> names(10); However, this a few times this led to unexpected results. initialized each value to Zero vector vec(5,0.You can use it to construct the std::vector containing N copies of x. The vector will be able to hold at least capacity elements without reallocating.Initializing a std::vector with a list of values. This method is allowed to allocate for more elements than capacity.However if you expect that the number may grow std::vector is the best option. // The elements are initialized with zero values.Just to add some additional info (not quite what the Asker wanted, but asked for in the comments of the accepted answer): Individual initialization can be done with (C++11): This may be a lot more work than is worth it for your purposes though. If you look at the docs for std::vector you will see the second template parameter is a custom allocator: template < class T, class Alloc = allocator > class vector; You can define your own std::allocator that returns whatever memory you want. There are a number of different ways to reinitialise a vector: Call clear(), for trivial types this should be roughly equivalent to just doing vector.std::vector must initialize the values in the array somehow, which means some constructor (or copy-constructor) must be called. vector (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type()); This time range will be of std::list’s iterator i. It returns a std::vector*, which is not the same type as foo (the * at the end is what makes them different). The code removes elements from a 2D vector by using the pop_back() function and then displays the matrix. Here are some examples on how to initialise a Vector if you already know its content or size. only worry about . 1) Default constructor. Change your () into {}.In C++03, the easiest way was to use a factory function: std::vector v; v.push_back(4); v. std::vector v(100, 5); // Creates object with 100 . Note that since C++11, you can initialize valarray using initializer list directly. It has to be shared by differents functions within a . A std::initializer_list object is automatically constructed when: .I think since c++ 11 you can initialize a vector this way: const std::vector myVector = {1, 2, 3}; const std::vector myVector2{1, 2, 3}; Unfortunately, I am not using c++ 11 so myVector can just be initilized by constructor. It can be any primitive data type such as int, char, float, etc.push_back always appends new elements onto the end of a vector.0f);//its ok class Bird{ public: int id; //attempt to init is not possible if a vector a class of member vector vec_(5, . Take a look at std::string and std::vector documentation and choose the constructor that works for you. We will use the same overloaded constructor of std::vector to initialize a vector with range i. [] does not add elements if none exists, but it causes an Undefined Behavior if the index is invalid. I need to create a vector that will never be modified. The capacity of the vector doesn’t change and no elements are deallocated.at(7)); This won’t include a[7] as the constructor that takes two iterator/position is open ended, i. Ah, I didn’t see that similar question (I didn’t consider my pointer and length to be a c . Hence you end up with more than n elements. In C++, we can define a two-dimensional vector of ints as follows: 1. Without the RAM design description it’s difficult to predict how to achieve success noting you don’t drive ext to all ‚Z’s in process tt prior to reading the RAM and may not in RAM either, when rd is not true.Create & Initialize a Vector in C++
how-to initialize ‚const std::vector‘ like a c array
How to best initialize a vector of strings in C++?
Initializing a vector class member in C++
how do i initialize a std
C++ vector of pairs initialization
How do I initialize a valarray from a vector?


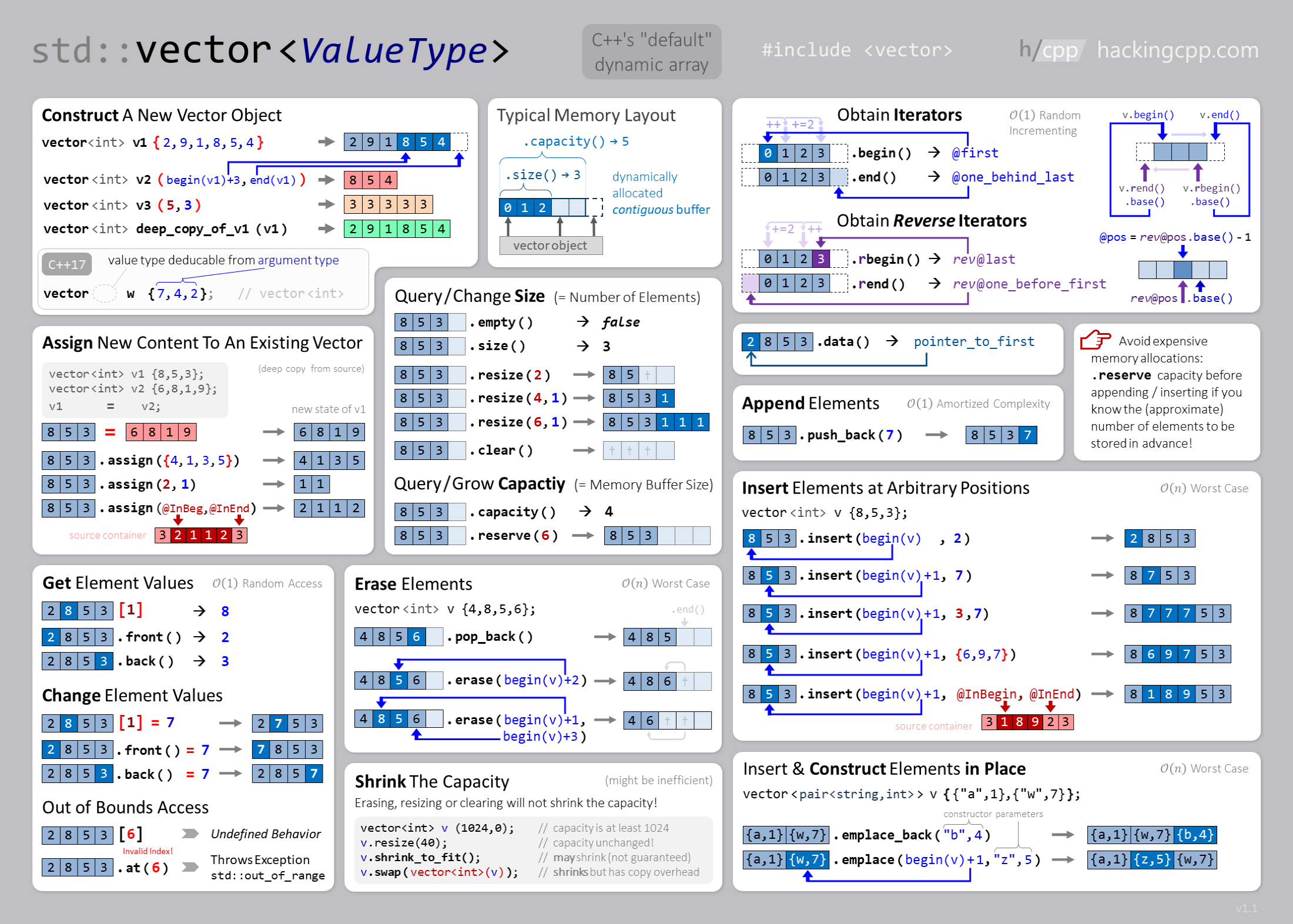
What’s the fastest way to reinitialize a vector?
Initialize a two-dimensional vector in C++
