How Is R-Squared Calculated In Multiple Regression?
Di: Samuel
In this example, the multiple R is 0. The F-stat and R2 adj R a .Ordinary least squares regression of Okun’s law. Let ri = Corr(y,xi) r i = C o r r ( y, x i) and ri,j = Corr(xi,xj) r i, j = C o r r ( x i . Default function anova in R provides sequential sum of squares (type I) sum of square.Video ansehen9:45So if you want the amount that is explained by the variance in x, you just subtract that from 1. You are a social researcher interested in the relationship between income and happiness. To learn more about the R-squared statistic, read the chapter on Linear Regression in the excellent textbook, An Introduction to Statistical Learning, available online for free. 1 indicates that the response . the multiple R be thought of as the absolute value of the correlation coefficient (or the correlation coefficient without the negative sign)! The R-squared is simply the square of the multiple R. Your independent variable (income) and dependent variable (happiness) are both quantitative, . Now, R-squared calculates the amount of variance of the target variable explained by the model, i. So, we’ll skip it and go to the two R-squared values.Definition The adjusted R squared of the linear regression, denoted by , is where is the adjusted sample variance of the residuals and is the adjusted sample variance of the outputs. R-Squared: This is the proportion of the variance in the response variable that can be explained by the predictor variables. The R-squared value of ~0.

Excessive multicollinearity can cause problems for regression models. So we have our r squared, which is the percent of the total .
calculating regression sum of square in R
The residual mean squares is calculated by residual SS / residual df. The variable we want to predict is called the dependent variable (or sometimes, the outcome, target or criterion variable).Explain why the sum of squares explained in a multiple regression model is usually less than the sum of the sums of squares in simple regression; Define \(R^2\) in terms of proportion explained; Test \(R^2\) for significance ; Test the difference between a complete and reduced model for significance; State the assumptions of multiple regression and . It is calculated as: Adjusted R2 = 1 – [ (1-R2)* (n-1)/ (n-k-1)] where: Because R2 always increases as you add more predictors to a model, adjusted R2 can serve as a metric that tells you how useful a model is, adjusted . We’ll use the marketing data set, introduced in the Chapter @ref(regression-analysis), for predicting sales units on the basis of the amount of money spent in the three advertising medias (youtube, facebook and newspaper).How to Assess the Fit of a Multiple Linear Regression Model.One of the most used and therefore misused measures in Regression Analysis is R² (pronounced R-squared). It’s sometimes called by its long name: coefficient of determination and it’s frequently confused with the coefficient of correlation r² . There are two numbers that are commonly used to assess how well a multiple linear regression model “fits” a dataset: 1.9016794217687075 R 2 = 0.The coefficient of determination, or r-squared, in multiple regression is computed in the same way as it is in simple linear regression.
Measuring Explanatory Power with the R-squared
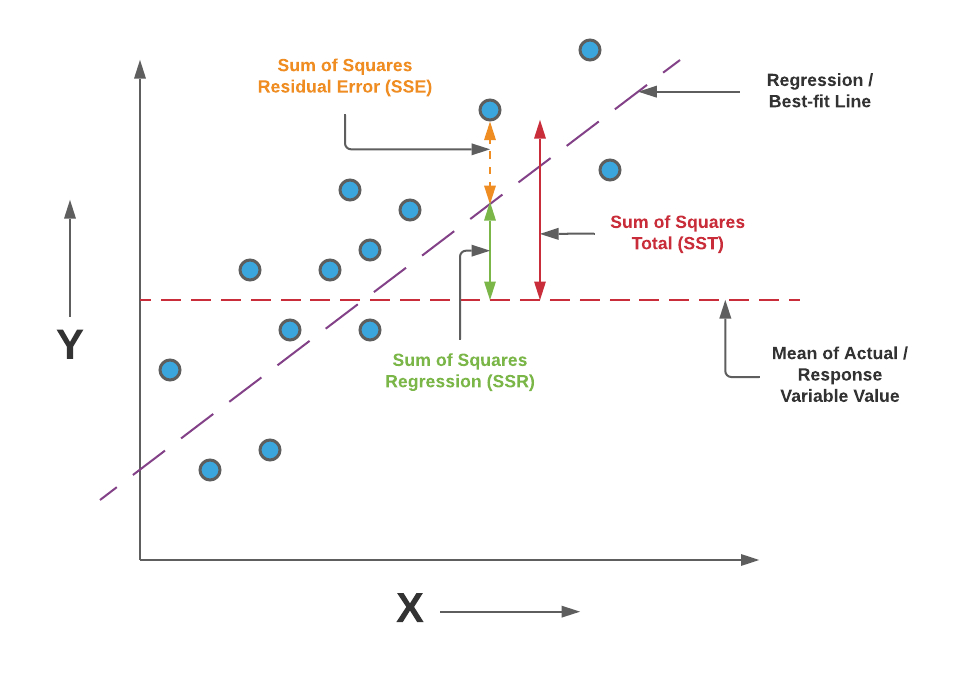
SStot: It represents the total . Previously, we learned about the coefficient of determination, [latex]r^2[/latex], for simple linear regression, which is the proportion of variation in the dependent variable that can be explained by the simple linear regression model based on the independent variable.
Calculating R-squared (video)
In this post, I focus on VIFs and how they detect multicollinearity, . Rsquared, a property of the fitted model, is a structure with two fields: Ordinary — Ordinary (unadjusted) R-squared.Variance Inflation Factors (VIFs) measure the correlation among independent variables in least squares regression models.Autor: Sal Khan
How to Calculate Adjusted R-Squared in R
, predicted) values of y.Example: Calculating R-Squared in Excel. 113) writes that if you multiply [adjusted R-squared] by 100%, it can be interpreted as ‚% variance reduction‘.
Coefficient of determination
The coefficient of .R-squared is a statistical measure that represents the goodness of fit of a regression model.head = TRUE) I am trying to fit multiple linear regression.
How to Perform Multiple Linear Regression in R
As I understand it this would create a linear model based on my data of y=ax+b, but would have values for a,b of other than, 1,0. Perhaps that will point .
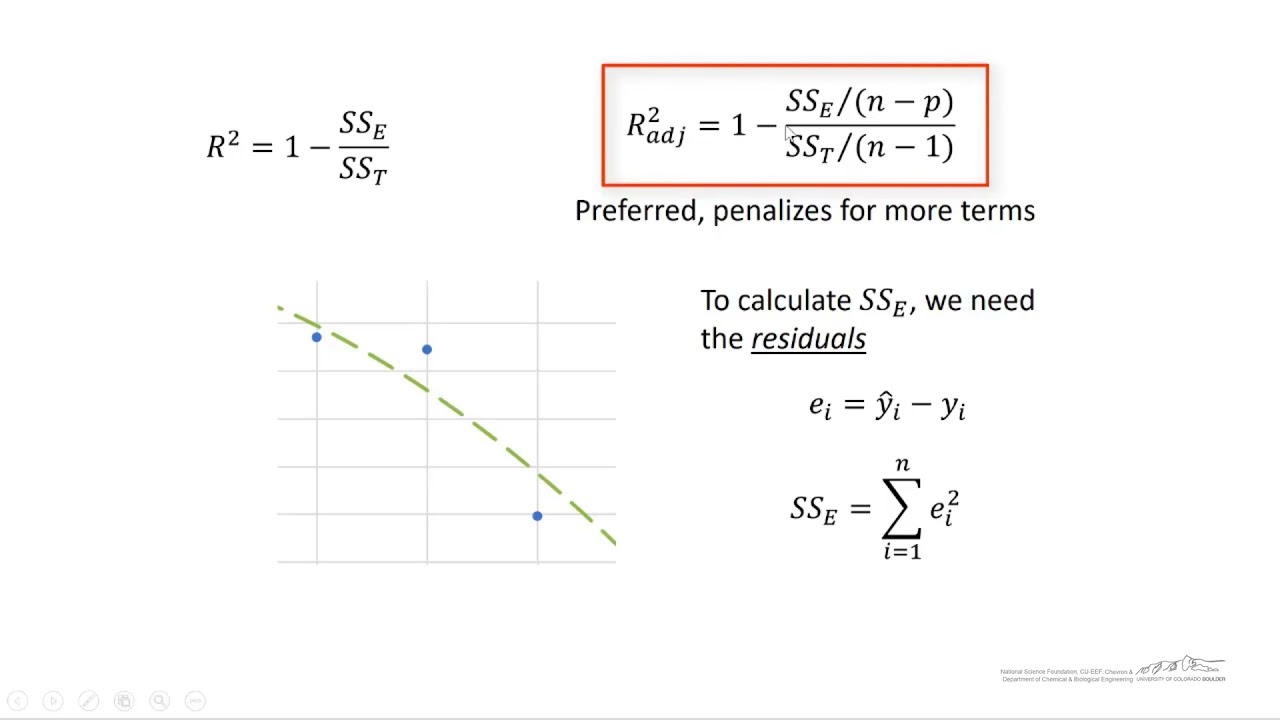
The R squared value ranges between 0 to 1 and is represented by the below formula: R2= 1- SSres / SStot. R 2 = S S R S S T = 1 − S S E S S T.R-squared, often written R 2, is the proportion of the variance in the response variable that can be explained by the predictor variables in a linear regression model. Df Sum Sq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F) I belief, thus the SS are Brain, Height | Brain, Weight | (Brain, Weight) and residuals respectively. For this reason, the value of R will always be positive and will range from zero to one.1% of the variance in mpg can be explained by the predictors in . That problem is that the r-squared naturally increases as you add more independent variables, even if those independent variables aren’t relevant . Using package car we can also get type II sum of square. Then I have measured the traits extraversion, openness and intellect to predict creativity in a multiple linear regression. What are the differences between them? X X X X. 4) Video, Further Resources . 3) Example 2: Extracting Adjusted R-squared from Linear Regression Model.Multiple R is not a standard measure for regression and it is difficult to interpret. For the R-squared calculation, one must estimate the correlation coefficient and then square the result. So let me write it right over here.
R-squared or coefficient of determination (video)
See it’s getting baffling already! The technical definition of R² is that it is the proportion of . Well, the adjusted R-squared considers exactly that. Coefficient of Determination (R Squared) What is the Adjusted Coefficient of Determination? Coefficient of Determination (R Squared) The coefficient of determination, R 2, is used to analyze how differences in one variable can be explained by a difference in a second variable. The algebra shows that R2 = 0. Then take the remaining IVs and regress that on the new DV (the former IV). Ping Yin & Xitao Fan, J. What is the formula / . The adjusted R squared can also be written as a function of the unadjusted sample variances: Proof. The predictor x accounts for all of the variation in y!; If r 2 = 0, the estimated regression line is perfectly horizontal.Here are some basic characteristics of the measure: Since r 2 is a proportion, it is always a number between 0 and 1. If I square the measured correlation between the two, I get the coefficient of determination.
regression
2) Example 1: Extracting Multiple R-squared from Linear Regression Model.
Adjusted R Squared Calculator for Simple Regression
Multiple R is the square root of R-squared (see below). R2 represents the proportion of variance, in the outcome . Dependent variable Y Y sample data (comma or space . However I do not the R^2 in relation to a linear approximation of my data, I want the R^2 in relation to the line y=x – The definition of R-squared is fairly straight-forward; it is the percentage of the response variable variation that is explained . of Experimental Education 69(2): 203-224, Estimating R-squared shrinkage in multiple regression, compares different methods for adjusting r-squared and concludes that the commonly-used ones quoted above are not good. The tutorial is structured as follows: 1) Example Data.Multiple regression is an extension of simple linear regression. However, there is a problem in using it in multiple regression.83 = R2 1 −R2 × 37 4 84. However, we get R-square equals 0 when the model .Then, it calculates the data that fits the regression model.
R-squared in Regression Analysis in Machine Learning
You survey 500 people whose incomes range from 15k to 75k and ask them to rank their happiness on a scale from 1 to 10.In linear regression, we often get multiple R and R squared.Thus, an R-squared model describes how well the target variable is explained by the combination of the independent variables as a single unit. The predictor x accounts for none of the variation .Simple linear regression example. This is because with each additional variable that you add, the explanatory power may only increase or stay the same.
Calculating R-squared with my own regression model in R
Video ansehen12:41If R-squared is close to zero, a line may not be appropriate (if the data is non-linear), or the explanatory variable just doesn’t do much explaining when it comes to the response .The adjusted R-squared is a modified version of R-squared that adjusts for the number of predictors in a regression model.
Multiple Regression Analysis using SPSS Statistics
To find the r 2 for .
How to Read and Interpret a Regression Table
Thus, the R-squared is 0.You can try calculating the VIF yourself to see where the problem lies.
Variance Inflation Factors (VIFs)
This indicates that 60. You can write the coefficient-of-determination as a simple quadratic form of the correlation values between the individual variables (see this answer for details).Multiple R is also the square root of R-squared, which is the proportion of the variance in the response variable that can be explained by the predictor variables. However, there are important . R-squared is the proportion of the total sum of squares explained by the model.

R-squared is a statistical measure of how close the data are to the fitted regression line. The R-squared relevance in regression is the capability to search the probability of the future event happening in the forecasted results or the outcomes.8% of the dependent variable’s variance. Multiple regressions are always better than simple ones. Here, SSres: The sum of squares of the residual errors. The value for R-squared can range from 0 to 1 where: 0 indicates that the response variable cannot be explained by the predictor variable at all.83 = R 2 1 − R 2 × 37 4. In this example, . It is also known as the coefficient of determination, or the coefficient of multiple determination for multiple regression. For example, when a person gets pregnant has a . Where we get R-square equals 1 when the model perfectly fits the data and there is no difference between the predicted value and actual value.59) claim it’s Theil’s adjusted R-squared and don’t say exactly how its interpretation varies from the multiple R-squared. In multiple regression models, R2 corresponds to the squared correlation between the observed outcome values and the . We’ll randomly split the data into training set (80% for building a predictive model) and test set .; If r 2 = 1, all of the data points fall perfectly on the regression line. Statisticians refer to this type of correlation as multicollinearity.9016794217687075. They recommend the Olkin & Pratt . Take one of the IVs and use that as the DV. It can be through of as percentage of .Instructions: Use this calculator to compute the adjusted R-Squared coefficient for a simple linear regression. Comparison of the Theil–Sen estimator (black) and .Statology Study is the ultimate online statistics study guide that helps you study and practice all of the core concepts taught in any elementary statistics course and makes your life so much easier as a student.R-squared is a goodness-of-fit measure that tends to reward you for including too many independent variables in a regression model, and it doesn’t provide any incentive to stop adding more.R-squared: In multiple linear regression, the R2 represents the correlation coefficient between the observed values of the outcome variable (y) and the fitted (i. This is almost the same as the value from the other method, and if you consider only the three significant figures in the given R2 adj R a d j 2 value, they are the same: 0. The variables we are using to predict the value . From that regression take the R-squared and calculate the VIF: 1 / (1 – R Square). Can I take those observed . function of the independent variable. It is calculated as: Adjusted R2 = 1 – [ (1-R2)* (n-1)/ (n-k-1)] where: Because R-squared always increases as you add more predictors to a model, the adjusted R-squared can tell you how useful a model is, .A small sample will give a deceptively large R-squared.
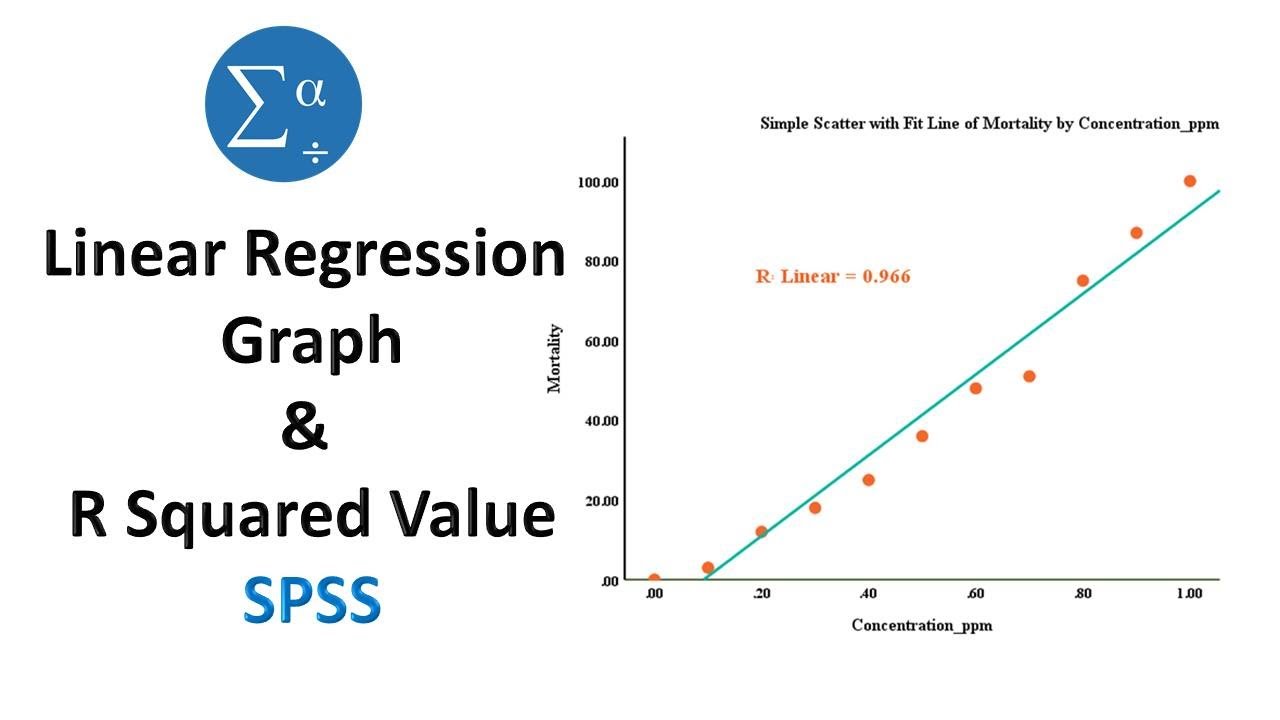
In regression model, the most commonly known evaluation metrics include: R-squared (R2), which is the proportion of variation in the outcome that is explained by the predictor variables.I proved that the percentage of variation explained by a given predictor in a multiple linear regression is the product of the slope coefficient and the correlation of the predictor with the fitted values of the dependent variable (assuming that all variables have been standardized to have mean zero and variance one; which is without loss of generality). Please input the data for the independent variable (X) (X) and the dependent variable ( Y Y ), in the form below: Independent variable X X sample data (comma or space separated) =. Dalgaard, Introductory Statistics with R (2008, p. However, in order to achieve that, we need to calculate two things: Variance of the target variable: var (avg) = ∑ (yi – Ӯ)2.R-squared (or the coefficient of determination) measures the variation that is explained by a regression model.Autor: Sal Khan Suppose we have the following data for the number of hours studied and the exam score received for 20 students: Now suppose we are interested in fitting a simple linear regression model to this data, using “hours” as the predictor variable and “score” as the response variable. The ratio used in the formula above is often called a degrees .Calculate and interpret the coefficient of multiple determination.Preparing the data. Don’t include the original DV at all.For a multiple regression model, R-squared increases or remains the same as we add new predictors to the model, even if the newly added predictors are independent of the target variable and don’t add any value to the . Adjusted R-squared and predicted R-squared use different approaches to help you fight that impulse to add too many.Our R-squared calculator determines the coefficient of determination, R2, for you if you are working with a simple linear regression, Y ~ aX + b: Input your data points into the appropriate rows. The regression mean squares is calculated by regression SS / regression df. Consider a multiple linear regression with m m explanatory vectors and an intercept term. To learn more about making custom functions in R, read the chapter on Functions in Hadley Wickham’s online book R for Data Science. The value of R-square lies between 0 to 1.Model performance metrics. Adjusted — R-squared adjusted for the number of coefficients.In this tutorial you’ll learn how to return multiple and adjusted R-squared in the R programming language.Since the regression line does not miss any of the points by very much, the R 2 of the regression is relatively high. Extra rows will appear as you write; When at least three points are in place, our coefficient of determination calculator will return the value of R2 .
The protection that adjusted . In this example, the multiple R-squared is 0. In this example, regression MS = 546. R a d j 2 = 1 − ( n − 1 n . The value for R-squared can .For example, I measured trait openness to predict creativity in a simple linear regression.858 indicates that our model accounts for about 85. It is used when we want to predict the value of a variable based on the value of two or more other variables.53308 / 2 = 273.
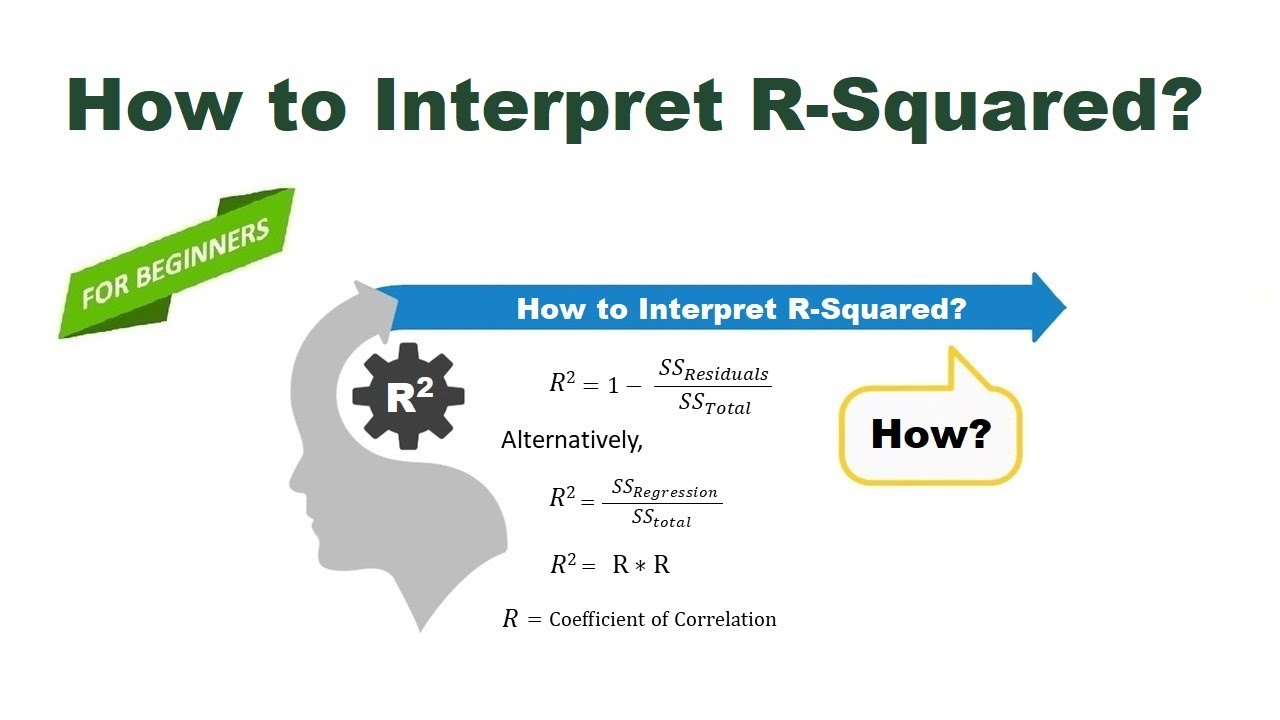
The R-squared measures how much of the total variability is explained by our model.For my own understanding, I am interested in manually replicating the calculation of the standard errors of estimated coefficients as, for example, come with the output of the lm() function in R, but haven’t been able to pin it down. Usually, higher R-squared values are better. Then my R^2 would depend on that regression model.where, n represents the number of data points.
- How Many Users Does Facebook Have In 2024?
- How Many Super Bowls Did The 49Ers Win?
- How Do You Make An Electrolyte In A Lead Acid Battery?
- How Many People Are Colorblind
- How Many Capsules Does A London Eye Have?
- How Do You Write A Sop? | How to Format a Statement of Purpose: Quick and Easy Guide
- How Many Instagram Captions Are There?
- How Do You Play Ping Pong? : How to Play Beer Pong
- How Has Deforestation Impacted The World?
- How Do You Modulate The Colour Of An Electroluminescent Device?
- How Many Free Images Of Business Woman Are There?
- How Long Does Sperm Live Outside
- How Do You Use A Comma In A Sentence?
- How Far Can The New Astra Electric Go?