Heat Conductivity _ Aluminum 6061, Al 6061-T6 Alloy Properties, Density, Tensile
Di: Samuel
Thermal conductivity is an intrinsic property of a material and is independent of the size or shape of the material. This law was first formulated by Joseph Fourier in 1822 who concluded that “the heat flux resulting from thermal . 25 Such spectral heat conductivity can be conveniently obtained in the .
Heat Conduction in Two-Dimensional Materials
Thermal conductance (C) measures the ability of a material or system to conduct heat.Viele übersetzte Beispielsätze mit heat conductivity – Deutsch-Englisch Wörterbuch und Suchmaschine für Millionen von Deutsch-Übersetzungen.
Thermal Conductivity : definition, derivation, units and dimensions
It provides insights into the ease with which heat can pass through a particular system. Thermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/ (m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. As mentioned earlier in the article the convection heat transfer coefficient for each stream depends on the type of fluid, flow properties and temperature properties .英文:coefficient of thermal conductivity. The reciprocal of this quantity is known as thermal resistivity. Lernen Sie die Übersetzung für ‚heat conductivity‘ in LEOs Englisch ⇔ Deutsch Wörterbuch.Every substance has its own capacity for conducting and transferring the heat.5 W m −1 K −1.Sortieren Sie Ihre gespeicherten Vokabeln. Convection requires fluid flow. Thermal conductivity refers to the ability of a given material to conduct/transfer heat. This low thermal conductivity is one of the major obstacles for the applications of polymers and polymer composites in energy technologies and thermal management, e.Smaller λ indicates that the material has stronger heat insulation and .K), and the thermal conductivity of bituminous coal is typically in the range 0. However, it is pulverized coal that is of interest for many applications. However, the low thermal conductivity (TC) and poor shape stability of PCMs have hindered their practical applications. The thermal conductivity of a material has many implications.
Computing the Heat Conductivity of Fluids from Density Fluctuations
The air in a typical house is completely replaced in less than an hour. a | Earth core materials of iron and iron–silicon alloys up to 120 GPa at 300 K. Thermal conductivity is a bulk property .
Heat Conduction
Thermal conductivity of Methane is 0. Notes: 10-6 ·K-1 = 10-6 /K = 1 μm/m·°C; 1 Ω·mm²/m = 1 μΩ·m; 1 g/cm3 = 1 kg/dm3 = 1000 . It is represented with thermal conductivity coefficient λ. Usually, it is heat transfer through a solid.Thermal conductivity is the property of the material and it is the ability of the substance to transfer heat. Convection occurs when hot air rises, allowing cooler air to come in and be heated. 1: Calculating Heat Transfer by Convection: Convection of Air Through the Walls of a House.

It is defined as the quantity of heat, ΔQ, transmitted during time Δt through a thickness L, in a direction normal to a surface of area A, due to a temperature difference ΔT, under steady state conditions . Conduction is heat transfer directly between neighboring atoms or molecules. The thermal conductivity of a material is explained by the following formula: K = Qd AΔT. Aluminium foil reflects up to 98% of light and infrared heat. Synthetic single crystals of diamond which are prepared 3 with carbon isotopically enriched in 12 C . If in above equation (1) we put. It represents a material’s ability to conduct electric current. You also learn that meta. For example, Bergquist Bond-Ply TBP 1400LMS-HD is a thermally conductive and electrically isolating tape with a breakdown voltage of 5,000 VAC.熱導率為在單位時間內,每單位截面積所流過的熱量除以單位距離溫度變化量的負值。.Thermal conductivity is a basic parameter of soil heat transferring, playing an important role in many fields including groundwater withdrawal, ground source heat pump, and heat storage in soils. 其中 熱通量 密度,為向量; 是熱導率; 是 溫度梯度 ,為向量。. Mit Flexionstabellen der verschiedenen Fälle und Zeiten Aussprache und relevante Diskussionen Kostenloser Vokabeltrainer . Values of thermal conductivities for various materials are listed in the list of thermal conductivities. 1 Thermal Conductivity.Thermal conductivity is a material property that describes ability to conduct heat .In this article inspired by the non-local theory of elasticity, a constitutive model for heat conduction in two-dimensional materials is proposed by taking into account the non-local effect of heat flux. It should be noted that . The good agreement between the experimental and theoretical values of κ eff (T) improves . It is commonly signified by the Greek letter σ ( sigma ), but κ ( kappa) (especially in electrical engineering) and γ ( gamma) are sometimes used. It is a measure of a substance’s ability to transfer heat through a material by conduction. Materials with high thermal conductivity are used in heat sinks whereas .org/science/physics/thermodynamics/spec. Radiation does not require any medium.
Thermal Conductivity
In this case, the rate of heat conduction Q ˙ can be scaled as Q ˙ ∝ l 2 ·l −1 =l from Eq. According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.
heat conductivity
热导率
Its insulation role extends into fire protection. The extension of the formula to a free electron Fermi gas, using the Fermi velocity along with the Sommerfeld .Electrical conductivity (or specific conductance) is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. A =1m2 A = 1 m 2 , Δx = 1m Δ x = 1 m, ΔT = −1K Δ T = − 1 K and t = 1sec t = 1 s e c then, Q =K Q = K.导热系数仅针对存在导热的传热形式,当存在其他形式的热传递形式时,如 辐射 、对流和传质等多种传热形式时的复合传热关系,复合传热关系通常被称为表观导热系数、显性导热系数或有效导热系数(thermal transmissivity of material)。 此外,导热系数是针对 均质材料 而言的,实际情况下,还存在有 .6061 aluminum physical properties are given in the following lists, including density, melting point, coefficient of thermal expansion, elastic modulus, thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity electrical conductivity, and electrical resistance.Heat conduction is the transfer of heat between two objects in direct contact with each other. The bright surface also has low heat emissivity. Specific heat is measured using the mass, the change in temperature, and the heat gained or lost by a substance.Thermal conductivity, frequently represented by , is a property that relates the rate of heat loss per unit area of a material to its rate of change of temperature.It is used primarily in Fourier’s Law for heat conduction.Thermal Conductivity: A measure of the ability of a material to transfer heat. The rate of heat transfer depends upon the temperature gradient and the thermal conductivity of the material., k is often treated as a constant.Diamond has the highest thermal conductivity of any known material at temperatures above ~ 100K. is the amount of heat transferred through the material in Joules/second or Watts. It is typically expressed in units of watts per meter per Kelvin (W/mK). Most houses are not airtight: air goes in and out around doors and windows, through cracks and crevices, following wiring to switches and outlets, and so on.Thermal Conductivity.Diamond has the highest thermal conductivity, typically around 2200 W/(mK) [7, 8] at room temperature for high-quality single crystals . 这种导热模式下的速率方程基于傅立叶导热定律。. 是指当温度垂直向下梯度为1℃/m 时,单位时间内通过单位水平截面积所传递的 热量 。 其具体定义为:在物体内部垂直于导热方向取两个相距1米,面积为1平方米的平行平面,若两个平面的温度相差1K,则在1秒内从一个平面传导至另一个平面的热量就规定为该物质 . Materials with high . In ‘fire walls’ for vehicles and ships, for fire-resistant doors and building panels, aluminium foil dissipates heat and stops .
Thermal Conductivity
There are three forms of thermal energy transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation.Basic Properties of Building Decorative Materials.
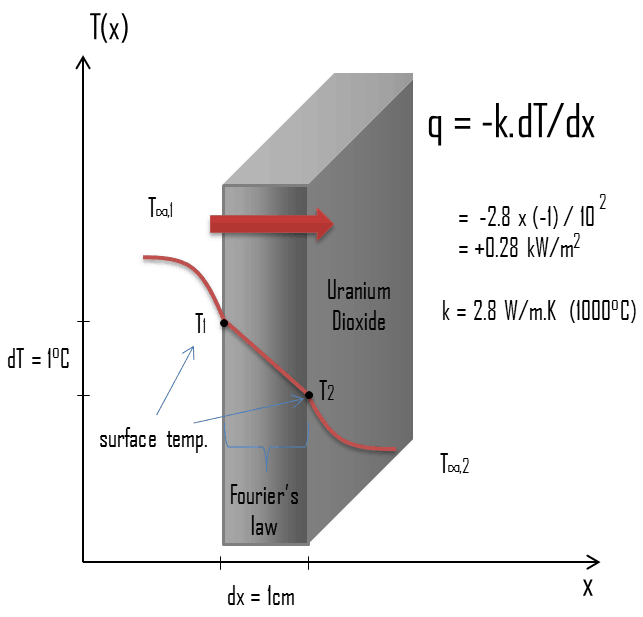
Thermal Conductivity and the Wiedemann-Franz Law
It is essential in the design of heat exchangers, thermally efficient materials, and various engineering systems where the controlled . Thermal conductivity can be defined as the quantity of heat transmitted through a unit thickness of a material – in a direction normal to a surface of unit area – due to a unit temperature gradient under steady state conditions Thermal conductivity units are . The purest natural diamond single crystals reported so far 1,2 have a conductivity of 24–25 Wcm-1 K-1 at 300K, compared to 4 for Cu and 1.The three types of heat transfer differ according to the nature of the medium that transmits heat: Conduction requires contact. 3 for a large range of temperatures. It is generally denoted by the symbol ‘k’ but can also be denoted by ‘λ’ and ‘κ’. The value of thermal conductivity determines the quantity of heat passing per unit area at a .Thermal conductivity of Aluminium is 237 W/ (m·K).Specific heat is denoted as c or s. This helps to save energy in insulation. Conduction involves molecules transferring kinetic energy to one another through collisions. Thermal conductivity is defined as the ability of a material to conduct heat from its one side to the other. The thermal conductivity of coal generally increases with an increase in apparent density as well as with volatile matter content, ash content, and temperature. The rate of heat transfer Q/t (energy per unit time) is proportional to the temperature difference T2 −T1 and the contact area A and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects: Q t = kA(T2 −T1) d. Specific heat depends on the type and phase of a material under study, whereas thermal conductivity depends on the temperature, moisture content, and density of a material.
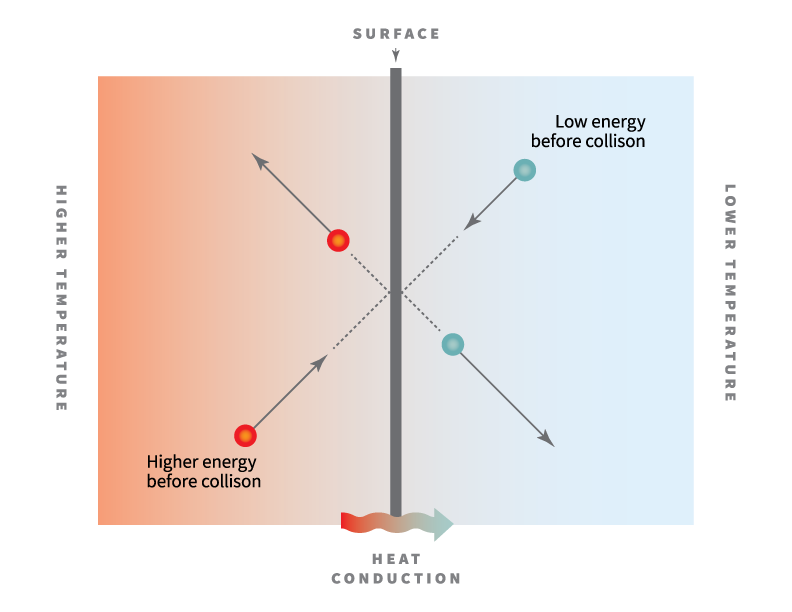
Thermal conductivity refers to a material’s intrinsic ability to transfer or conduct heat. Note that Fourier’s law applies for all matter . With this assumption, it was possible to determine the two phonon-heat-sink thermal conductivity parameters, a and g ph-s . Given two surfaces on either side of a material with a temperature difference between them, the thermal conductivity is the heat energy transferred per unit time and per unit surface area, divided by the temperature difference 1.In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material that indicates its ability to conduct heat.Figure 3 shows the experimental values of the thermal conductivity measured along the cross-plane direction in comparison with the fitted predictions of Eq. Thermal conductivity is a reasonably straightforward concept when you are discussing heat loss .
Heat Transfer
Where all parameters are defined in the Appendix.When selecting thermal adhesives for electrical insulation, it’s essential to choose those with a breakdown voltage higher than the requirements of your application.Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free.The well-known low-pressure monatomic gas thermal conductivity expression is based on the Maxwell-Boltzmann velocity distribution and involves the mean particle velocity, the gas heat capacity at constant volume and the particle mean free path.Phase-change materials (PCMs) are promising thermal storage medium for thermal management due to their efficient thermal energy harvesting capabilities.Definition of Thermal Conductivity.In other words, thermal conductivity quantifies how well a material can transmit heat through molecular vibrations and collisions. batteries and electronic devices as discussed in section 4.Fourier’s law is an expression that define the thermal conductivity . is the thermal conductivity in Watt m−1K−1. 則可將等式轉換為 . b | Earth core materials of iron and iron . Thermal radiation happens when accelerated charged particles .Traditional polymer thermal conductivities are quite low, typically ~0.Similar to the quantum correction of heat capacity in water 42 based on spectral analysis, heat conductivity can be quantum-corrected based on a spectral heat conductivity, as has been recently demonstrated for amorphous silicon in the context of MLP. [1] 由 傅立葉定律 :.It implies that a reduction in size leads to a decrease in the total heat conduction within a unit time. In SI units, thermal conductivity is expressed in watts per meter kelvin whereas in . Based on this model an analytical expression of the effective thermal conductivity of two-dimensional materials is derived.In this whiteboard animations tutorial, you will learn the super easy concept of thermal conductivity with many daily life examples.Thermal conductivity of Brick is 1. 它也被定义为单位时间内,每单位厚度(1m)的 .
Aluminum 6061, Al 6061-T6 Alloy Properties, Density, Tensile
The thermal conductivity influences the temperature field T c e l l in Equation (2), which depends on the location (x, y, z) and the time t. Essentially, it is a value that accounts for any property of the material that could change the way it conducts heat.
heat conductivity
Thermal management has been increasingly considered as a key issue for modern microelectronics due to the growing power density that stems from the miniaturization of electronics [1,2,3,4,5,6]. In Building Decorative Materials, 2011.导热系数 (通常用k、λ或κ表示)是指材料传递或传导热量的固有能力。. Construction of an interconnected three-dimensional .
In conventional representation, thermal conductivity, k, is usually thought to be an intrinsic material property, i. It is fundamental in the design, engineering, and application of materials in environments where heat transfer is a critical factor, such as: Energy Efficiency and Thermal Management.

The heat transfer characteristics of a solid material are measured by a property called the thermal conductivity, k (or λ), measured in W/m.
How to Measure Thermal Conductivity

It is measured in units of watts per kelvin (W/K). 它是除对流和辐射以外的第三种传热方法。.The Kapitza thermal conductance was expected to be much more relevant than electron-phonon conductance in “high” temperature ranges (above 30–35 mK) where it is supposed that T e ≡ T ph. As can be seen, to solve the Fourier’s law we have to involve the temperature difference, the geometry, and the thermal conductivity of the object.Computing the Heat Conductivity of Fluids from Density Fluctuations
A new model to predict soil thermal conductivity
Note that Fourier’s law applies for all . Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.
Thermal conductivity of materials under pressure
导热过程可以用适当的速率方程来量化。.The thermal conductivity is a characteristic of the particular material. 若給定兩物質,其座標分別為 與 ,其溫度分別為 與 ,且 。.Thermal Conductivity Heat transfer by conduction involves transfer of energy within a material without any motion of the material as a whole. 5: Thermal conductivity of Earth materials under pressure. Due to the layered structure of the electrode-separator stack, the thermal conductivity is anisotropic and described by a value in each Cartesian direction (k x, k y, k z).
- Hci Uni Würzburg Peter Kullmann
- Health Benefits Of Drinking Lemon Water
- Hdd Halterung Ps3 , 4MBO Solteam PS3-22SP Power Reset Schalter HDD LAN
- Heil Und Kostenplan Zahnarzt Muster
- Hefezopf Ein Wenig Zu Dunkel _ Einfacher Hefezopf fluffig & lecker
- Heilstätten Beelitz Bilder : Beelitz Heilstätten: Roman
- Heike Knochee _ Jörg Knochee
- Heilpflanzen Gegen Zahnfleischentzündung
- Heimtrikot Schwedischer Nationalmannschaft
- Heimkehr Ins Glück Boese : Heimkehr ins Glück (DVD) online kaufen
- Hegenloh Sport Wangen , Manfred Hegenloh
- Hd Definition Deutsch | Ballade (Lyrik): Definition, Aufbau, analysieren, Beispiel
- Healthy Food To Lose Weight Quickly
- Heidelbeermarmelade Selber Machen Rezept
- Heilpflanzen Liste Mit Wirkung