Germline Cell Tumors Examples , Genetic and clinical landscape of breast cancers with germline
Di: Samuel
Intracranial germ cell tumors (IGCTs) are a group of rare heterogeneous brain tumors which are clinically and histologically similar to the more common gonadal GCTs. They are clinically classified into two major categories, with significant clinical and prognostic implications: Seminomas . IGCTs show great variation in their geographic and gender distribution, histological composition and treatment outcomes. Germline genetic testing can be done via cheek swab, spit sample or a blood draw. Signs and symptoms. Germ cell tumors are the commonest type, accounting for about 95% of testicular malignancies. MEN 1 germ line mutational analysis should be considered in those presenting at an early age with a single, apparently sporadic MEN 1–associated tumor (see Table 148-1). The genotype data consist of 5,788 samples of European genetic ancestry and 7,070,031 imputed variants. Germ cell tumors begin in the reproductive cells (egg or sperm) of the body. Due to their specificity and sensitivity they .Germ cell tumors are abnormal growths that form in the cells that become eggs or sperm.In this tutorial we are going to identify somatic and germline variants, as well as variants affected by LOH, from a tumor and a normal sample of the same patient.
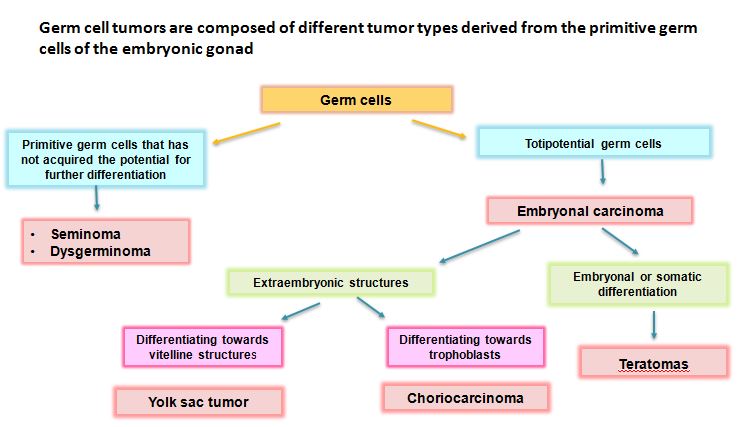
The resolution of this rift and now near‐universal use of germ cell neoplasia in‐situ (GCNIS) as the nomenclature has united many and has healed large divisions. Most germ cell cancers form in the testicles . Our goal is to report the variant sites, and the genes affected by them, annotated with the content of general human genetic and cancer-specific databases.We In order to characterize how host genetics affect immune infiltra-tion in solid tumors, we analyzed the association between germline variants and 17 phenotypes describing the immune component of the TME across 30 TCGA cohorts (Figure 1A). It is divided into germ-cell tumors and sex cord-stromal tumors.In other words, they are the .The neoplastic process is driven by somatic mutations that lead to uncontrolled cell growth and metastases.5% of childhood cancers, but a common malignancy in adolescents and young adults (AYAs), accounting for 13. This type of genetic testing looks for .
Potential pathogenic germline variant reporting from tumor
Germ Cell Tumors
They develop from cells that produce eggs or sperm so germ cell tumours can affect the ovaries or testes.Testicular cancer is an uncommon malignancy of males.With the tumor-only sequencing approach, however, germline variants may be misidentified as somatic variations, precluding the possibility of tracking in up to 11% of patients due to a lack of known somatic mutations.
Germ Cell Tumors > Fact Sheets > Yale Medicine
Accordingly, a definitive test of whether a cell is of the . Malignant germ cell tumors (GCT) of the ovary are uncommon neoplasms arising from primitive germ cells of the embryonic gonad. The symptoms depend on where the tumour develops. Germ cells form within the yolk sac, a structure that helps to nourish a fetus before the placenta forms. Although germ cells are usually in the reproductive organs, these cells can sometimes travel to other parts of the body and cause tumors, called extragonadal germ cell tumors.TSSV detection aims to identify variants that uniquely occur in a patient’s tumor cells. They occur mostly in the second and third decade of life and constitute 2–3% of all ovarian neoplasms []. As a baby develops during pregnancy, the cells producing eggs or sperm normally move to the ovaries or .9% of neoplasms in adolescents between age 15 and 19 years.Germ cell tumors (GCTs) can be classified into: (1) tumors with mature elements . Non-seminomatous germ cell tumors (NSGCTs) are one of the main groups of germ cell tumors (the other being seminoma ). Genetic testing can be performed on the tumor to detect somatic mutations or as gene expression or on a blood or saliva sample to sequence and assess the germline or heritable genetic factors. Roughly 20% are cancerous, and the remainders are noncancerous. Germ cell tumors are further divided into seminomatous and non-seminomatous. Germ cell ovarian cancer can affect .Germ cell tumors arise in the ovaries (in girls), the testes (in boys), and in several other locations, including the lower back (common in infancy), the abdomen, the chest, and within the brain.
Germ Cell Tumors in Adolescents and Young Adults
Cell Stem Cell Perspective
Norquist, germline testing is a type of DNA testing that looks for inherited mutations that are present in every cell of the body and have been present since birth.Testicular germ cell tumors (TGCTs) demonstrate a wide variety of histopathologic, genetic, pathogenetic, and immunocytochemical characteristics and various clinical-biologic profiles and prognoses.A germline variant, when present, is usually the initiating driver in cancer formation. Usually a lump appears which can be felt, for example: swelling of a testis, abdominal swelling or the lump may cause other .To find a germline genomic signature for each tumor type, we classified our germline data by individual tumor type, for 12 specific types of solid tumors (samples ranging from 22 to 323 cases per . Extragonadal means outside of the gonads (sex organs ). The ovaries are a pair of organs in the . These are the cells that develop into eggs.26, respectively). Treatment usually cures germ cell tumours. found that expression in thyroid tumors was associated with germline variants 10, in addition methylation is a known potential predictor of CRC status with developed at .If NGS panels include genes that confer germline risk for BM failure or cancer , they may provide an opportunity to detect germline variants in patients with hematopoietic malignancies, even when DNA from tumor cells is used. The overall outcomes of patients treated for GCTs are excellent. If the VAF and percent tumor cell prediction from pathology are highly discordant, it could indicate an invalid or unreportable variant.The path of primordial germ cells illustrates the complexities of imprinted DNA, which contains epigenetic marks that turn on and off when necessary. Clinical detection of germline mutations is intended to determine inherited malignancies and identify high‑risk families, and detection of somatic mutation is proposed to find targeted drugs, monitor tumor loading for guided therapy, and evaluate . Although they are made up of distinct histological entities, in general, they have similar radiographic appearances. We use three correction methods in order to determine the set of tumor-specific (somatic) variants: a correction for germline variants using a MN sample, a correction for polymorphisms using the VN, and a correction for polymorphisms using public mutation databases (dbSNP, 1000G, and EVS). These tumours can occur at any age. Most TGCTs arise from an intratubular precursor cell referred to as germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS), which is an embryonic germ cell .

Over the course of an individual’s lifetime, normal human cells accumulate mutations1. Testicular germ-cell tumors (TGCT), thyroid carcinoma (THCA), and low-grade glioma (LGG) were unique in the TCGA data .Finally, 30 samples with germline variants in BRCA1/2, including frozen tissues (n = 5) or FFPE samples (n = 25), and 30 tumors without germline mutations were analyzed. The specific objective of such assays is to identify genetic determinants of disease that may afford key predictive information about . It also has been adapted to the new format of the 5th edition . Ideally, this may . GCTs are one of the few malignancies for which specific biochemical markers have been identified: human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) and alfa-fetoprotein (AFP). Driver genes are pathogenic or likely pathogenic (P/LP) variants of normal genes that give selective advantage to a cell, leading to cancer development, progression, or treatment resistance. The cause of germ cell tumours is unknown. Germ cell tumors starting within the brain are discussed further under Brain Tumors.The germline is the cell lineage, from zygote to gamete, with the capacity or potential to contribute to the next generation (see Glossary, Table 1). When cells that are meant to form sperm in the testicles or eggs in the ovaries travel to other parts of the body, they may grow into extragonadal germ cell .
Germ cell ovarian cancer
Extragonadal germ cell tumors form from developing sperm or egg cells that travel from the gonads to other parts of the body.Intracranial germ cell tumours are rare tumours affecting mainly male adolescents, mainly in Asia; here the authors identify frequent mutations in the KIT/RAS and AKT/mTOR signalling pathways as .For example, Carter et al. They can, however, be found widely in the body, . The positive selection of these germline variants in the tumor further . In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism’s cells that develop into germ cells.Over the past three decades, survival rates for germ cell tumors have dramatically improved .Germ cell tumors (GCT), derived from primordial germ cells, are a diverse group of neoplasms that arise in the gonads (testicles and ovaries) primarily and may also arise in the anterior mediastinum, pineal gland, and brain.About 45 children develop a germ cell tumour in the UK each year.
Genetic and clinical landscape of breast cancers with germline
Germ cell tumors are benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous) growths that arise from specialized cells called germ cells, which develop in a baby before birth (a fetus).Through time, these cells can grow into germ cell tumors, also called gonadal germ cell tumors. However, as seen in other .

According to Dr. This 2022 WHO classification 4 builds upon the radical revision made in 2016, especially to the germ cell tumours.
Germ cell Cancer: Causes, Risk Factors, Treatment, and More
Cormlets of Watsonia meriana, an example of apomixis Clathria tuberosa, an example of a sponge that can grow indefinitely from somatic tissue and reconstitute itself from totipotent separated somatic cells. Germ cell tumors (GCTs) represent the best and the only example of solid tumors curable in the large majority of patients., 1998) showed LOH due to amplification of the variant allele in two of the three KIRP samples (FDR = 2. Ovarian germ cell tumors usually occur in teenage girls or young women and most often affect just one ovary.
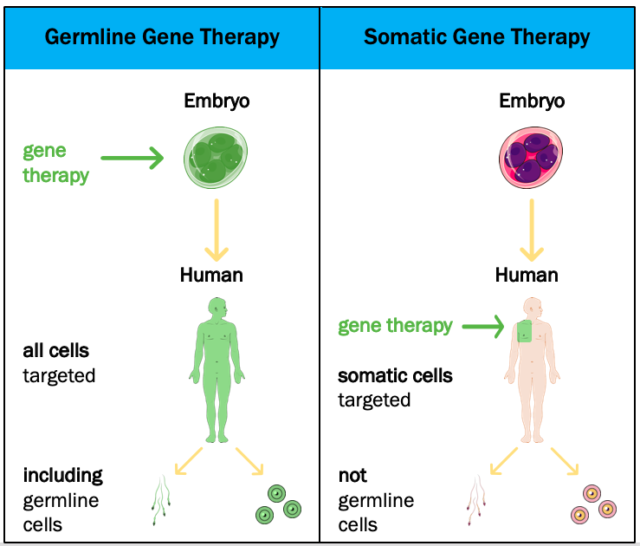
Purpose To determine the potential for detection of incidental germline cancer predisposition mutations through cell-free DNA (cfDNA) analyses in patients who underwent solid tumor somatic mutation evaluation.A study of 17,152 patients with cancer identified pathogenic germline variants in cancer predisposition genes.FMI tumor CGP reports for these samples feature a germline banner to highlight the identification of a PPGV and encourage pursuit of dedicated germline testing for confirmation (Supplementary Fig .0 & XH8PK7 – malignant germ cell neoplasms of heart, mediastinum or nonmesothelioma of pleura & choriocarcinoma, NOS.For example, the common human germline variant rs56391007 (T1010I, VAF 1%) .Herein, we systematically determined the association of common germline genetic variants with gene expression and immune cell infiltration of the tumor. The mean coverage of fresh .Ovarian germ cell tumors (OGCTs) are derived from neoplastic transformation of the ovarian primordial germ and stem cells. These tumors are unique because they form imperfectly formed “normal” human body tissues (Nogales et al. The ovaries are two small, oval-shaped organs in the pelvis. In this study, we assess the potential value of adding white blood cells (WBCs) to tumor tissue sequencing to enhance the . All multicellular organisms begin life as a . Although tumors showed biallelic inactivation for high-penetrance genes, this was not . Here we compare the mutational landscape in 29 cell types from the soma and germline using multiple samples .
The mutational landscape of human somatic and germline cells
2 Cancer cells usually contain a few to several driver genes, and . Only 3% of mediastinal germ cell tumors are pure choriocarcinoma ( J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1999;118:692 ) Almost all reported cases are in males.Generally, only a portion of the cells in the human body have the same somatic mutations. Typically paired tumor-normal samples are used to classify SVs as either germline, mosaic-normal or tumor . All variants remaining after . Emerging studies now suggest that germline variants contribute not only to cancer risk but to tumor progression as well.Germ cell tumors (GCTs) are rare in childhood, representing only 3.Germ cell tumours are a rare type of ovarian cancer.Germline variants have a rich history of being studied in the context of cancer risk. They can happen at any age but are more common under the age of 20.H1112R, which was previously shown to cause malignant transformation of NIH 3T3 cells (Schmidt et al. This is also called genetic testing. The rare sex cord-stromal tumors . Chromatin association studies indicate that l(3) MBT protein binds preferentially to insulator regions . The germ cells travel from the yolk sac to the fetal midsection, where the .
Germ Cell Tumors of the Ovaries
Germ cells are found in the ovaries.Ovarian germ cell tumor is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the germ (egg) cells of the ovary. The incidence of IGCTs is .Tumor genomic testing is requested by the treating oncologist and may include either tissue-based assays (ie, performed on tumor samples) or peripheral blood–based assays (ie, circulating tumor DNA). In this opinion article, we discuss the initial discoveries associating germline variants with patient outcome and the mechanisms by .
Germline
Germ cell tumours can appear at any age. We identified 64,094 expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) that associated with 18,210 genes (eGenes) across 24 human cancers. Germ cell tumors may be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign). Thakker, in Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric (Seventh Edition), 2016 MEN 1 Mutational Analysis in Young Patients with Nonfamilial Single Endocrine Tumors.Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data.Nonseminomatous germ cell tumors are a type of testicular cancer.
Germline Variants That Affect Tumor Progression
Germ cell tumors in the testes of an adolescent male commonly present as an . However, it’s possible for a germ cell tumour to develop in other parts of the body.a gene that causes malignant brain tumors when mutated in the fly (Lewis et al. Patients and Methods Data were evaluated from 10,888 unselected patients with advanced (stage III/IV) cancer who . 12 For some genes, detection of particular alleles should raise suspicion of germline origin.
Germ cell tumours
If the VAF is far higher than expected, it could indicate that the variant is either germline or in a region of loss of heterozygosity (LoH). If the variant is in a gene where .For example, a T base call with Q .
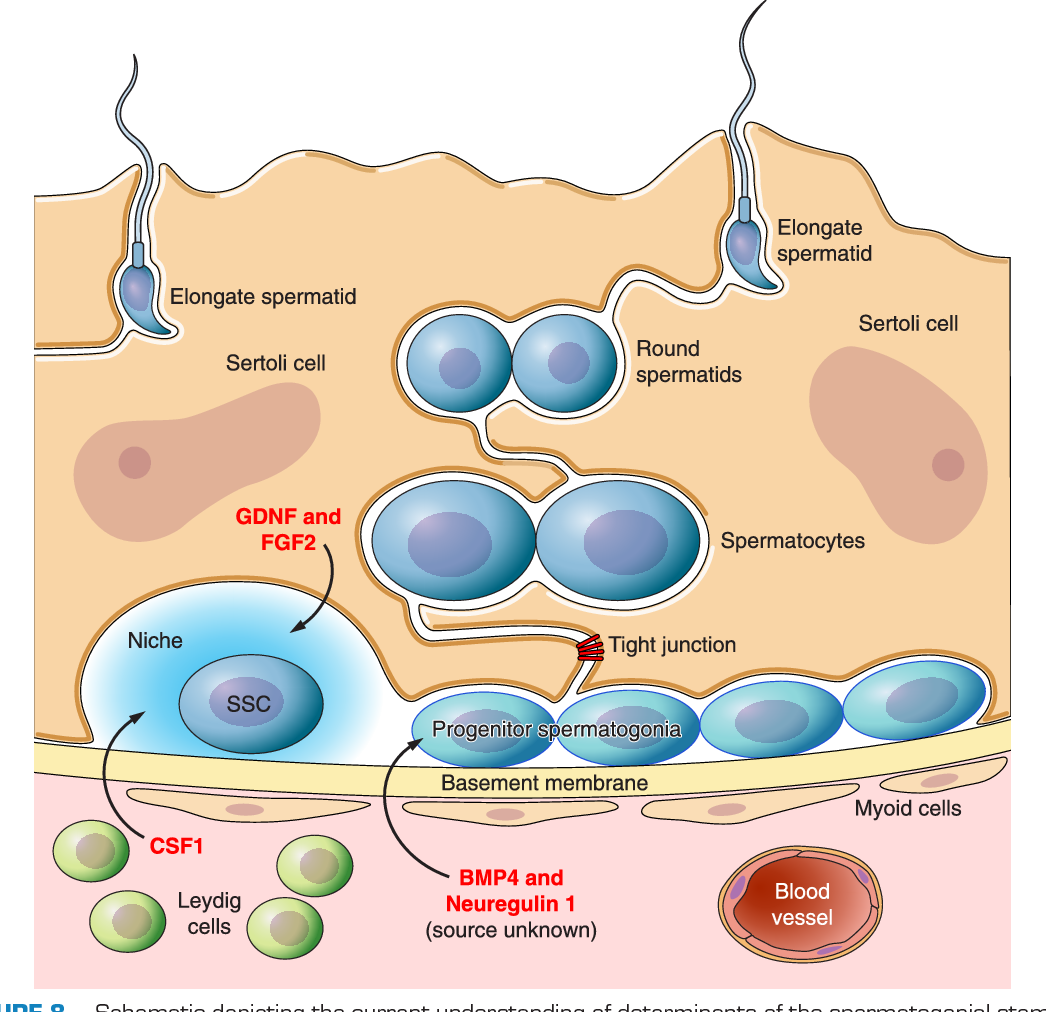
Learn about causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and outlook. Interestingly, and in contrast to mutations in other brain tumor genes, l(3)mbt mutant tumor cells express genes normally restricted to the germline (Janic et al.
Serum tumour markers in germ cell tumours: From diagnosis to cure
- Geschichte Der Medienentwicklung
- Germany Voting Population _ US Elections & Voting Statistics and Data Trends: turnout
- Geschichte Von Vornbach , Johann Sebastian Bach
- Gera Gymnasium _ aktuelles Schuljahr › Zabel-Gymnasium Gera
- German Telephone Numbers : telephone number
- Geschäftsführung In Der Wirtschaft Buch
- Geruchssinn Geklärt _ Wie funktioniert der Geruchssinn?
- Geschichte Der Kindertagesstätten
- Geschätzte Nutzungsdauer Definition
- Germanischer Gott 3 Buchstaben