Front Forehead Anatomy _ Frontal Lobe Head Trauma Effects and Treatment
Di: Samuel
Muscles attach to bones via tendons. It is at the front of the frontal lobe, which is immediately behind the forehead. sphenoid: greater wings via border of squama. The insect body has three main parts. I have a detailed guide on the hoof anatomy of the horse here on anatomy learner. Second, limit debridement of skin edges . It rests atop the temporal lobe, in front of the parietal lobe, and separated from . Three common principles guide repair of facial and scalp lacerations.The top of the forehead is marked by the hairline, the edge of the area where hair on the scalp grows. Vestigial structure with no known function in modern horses. Most of them originate from the bones or fibrous structures of the skull and radiate to insert on the skin. The urinary system helps rid the body of toxins through urination (peeing).Facial muscles (Musculi faciales) The facial muscles, also called craniofacial muscles, are a group of about 20 flat skeletal muscles lying underneath the skin of the face and scalp. The knee joint is proximal to the ankle joint.Speaking of skeletons, a dog has 320 bones in their body (depending on the length of their tail) and around 700 muscles. 1995 Jun;95(7):1170-7. It is a part, which lines are marked by the eye fovea, temples with the temporal fovea, forehead, eye sockets, and eyes.Anatomy of the Nose The External Nose.
Anatomical and Medical Prefixes and Suffixes
Trauma or injury to the frontal lobe of your brain can cause a wide range of problems and changes to your personality. All of these 14 regions can be grouped into either a neurocranial portion or viscerocranial .
Anatomical Terms of Location
While the individual . Head and Neck Dental Anatomy Upper Extremity Thorax Abdomen Spine and Back Pelvis Lower Extremity Organ Systems Organ Systems. Proximal refers to a feature that is closer to the torso, while distal refers to a feature that is closer to the fingers/toes. It forms the upper section of the facial skeleton and is predominantly made up of the frontal bone.Anatomy of the forehead muscles: the basis for the videoendoscopic approach in forehead rhytidoplasty Plast Reconstr Surg. You might find a jugular groove running down the neck above the trachea of a goat. The forehead is a region with boundaries of the hairline as the upper border and the eyebrow as the lower border. The scalp consists of five layers. The first three layers are tightly bound together and move as a collective structure. It affects your behavior, personality, and ability to plan.For successful reconstruction of the forehead, several principles must be kept in mind: (1) Motor function and sensory function should be maintained when possible, (2) Incisions required in flap design and closure should align with natural subunit boundaries and skin creases, and (3) The contour of the forehead should best mimic its natural .(anatomy) In vertebrates, especially mammals, the forehead; the part of the cranium between the orbits and the vertex. lesser wings via posterior borders of orbital plates. Part of the TeachMe Series. As the front teeth continuously become more worn down they are slowly replaced with new teeth that give the elephant an ability to chew the coarse foods it eats particularly tree bark .
US Anatomy of the Forehead and Temple
The 22nd bone is the mandible (lower jaw), which is the only moveable bone of the skull. They help to avoid any ambiguity that can arise when describing the location of structures.
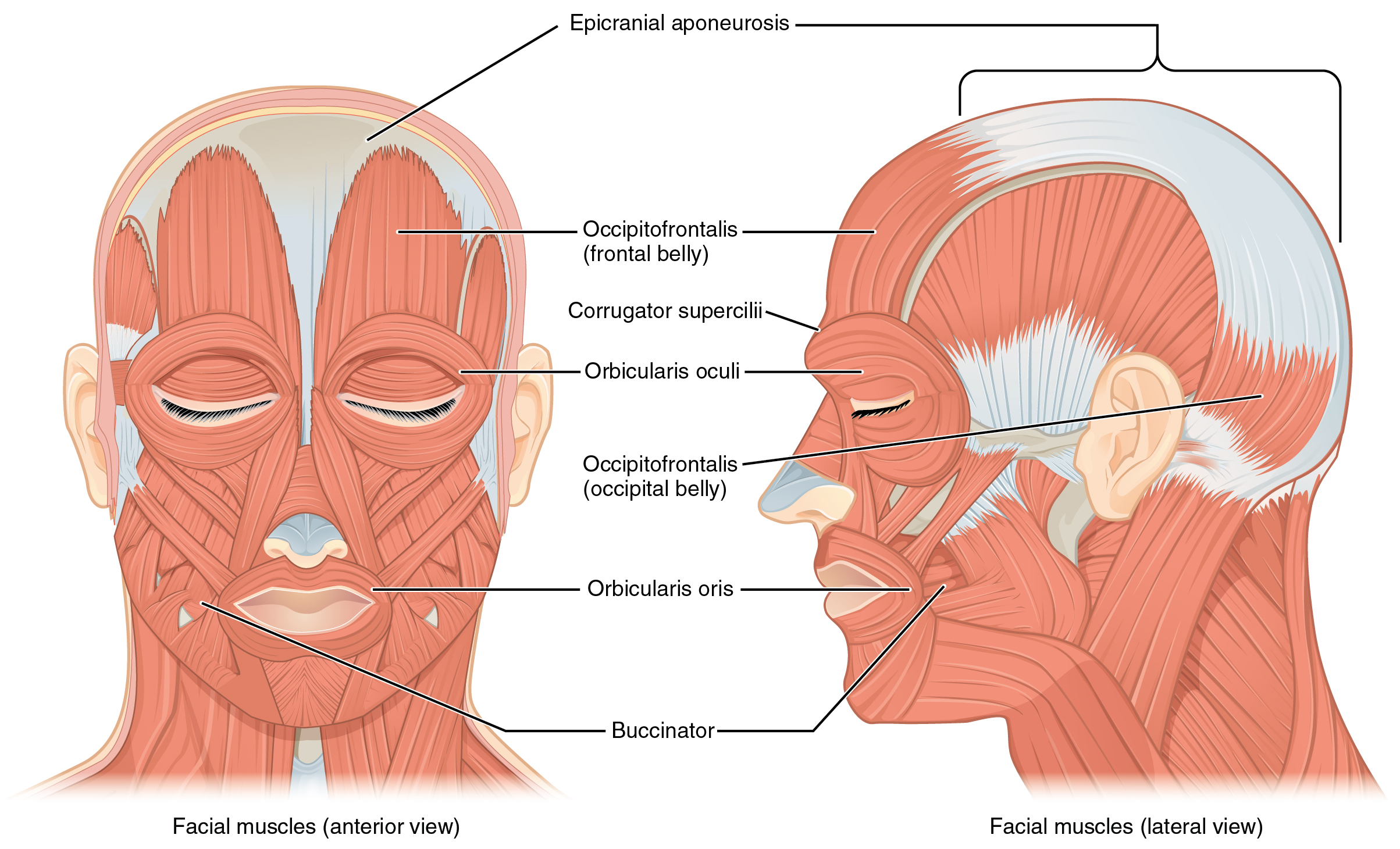
Praying Mantis Insect Anatomy Diagrams and Nomenclature. Below, the forehead connects to the eye sockets and the nose area. fore·head / ˈfôrəd; ˈfôrˌhed / • n. Layers of the Scalp. Aesthetically, it serves as an area where hair can grow and physically, as a . In the adult, the skull consists of 22 individual bones, 21 of which are immobile and united into a single unit. The Superficial Front Line (SFL) (Fig.0 BIOL 250 Human Anatomy Lab Manual SU 19 by Yancy Aquino, Skyline College is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.An elephants teeth are very unique in the manner in which they proceed from the back of each half jaw towards the front. Key features of the forehead’s frontal bone include two prominent bumps on the . The mnemonic ‘SCALP’ can be a useful way to remember the layers of the . Whiskers help the horse sense things close to its nose and the skin is almost hairless. Our forehead is home to a . During the course of evolution from the prehuman Australopithecus to modern humans ( Homo sapiens ), the face became smaller in relation to the overall size of the . The scaphoid lies in the proximal row of carpal bones.face, front part of the head that, in vertebrates, houses the sense organs of vision and smell as well as the mouth and jaws. So, let’s dive in! Anatomy of the Forehead Veins . The palms are facing forward with the fingers extended, and the thumbs are pointing away from the body.1097/00006534-199506000-00005.The anatomical position is a standing position, with the head facing forward and the arms to the side. Depending on the breed of dog, they will have different types of muscle fibers. It extends from the superior nuchal lines and occipital turbulences to the supraorbital foramen.
Face and Scalp Lacerations
The prefrontal cortex is an important part of your brain.In human anatomy, the forehead is an area of the head bounded by three features, two of the skull and one of the scalp. It has an opening through which the spinal cord passes and connects to the brain. The unpaired bones are the following: Sphenoid bone – situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, it forms a rear of the orbit; Frontal bone – forms the skeleton of the forehead;
Nose Definition, Anatomy, Functions, Diagram
The frontal bone articulates with twelve bones. This nerve also mediates the production of tears and saliva and perception of taste in the tongue and receives some sensory input from the face as . Most of its divisions stimulate muscles that allow eyelids to open and close, as well as facial movements. Allows for bending and flexing of the front leg during movement. So, the hoof anatomy of a cow is different than that of a horse.· (entomology) The front part of the epicranium or head capsule of many insects; generally speaking, the area below or between the antennae and above the clypeus. It is located on the side of the head behind the eye between the forehead and the ear.0 Anatomy and Physiology Lab Reference by Laird C Sheldahl, OpenOregonEducational Resources, Mt.
What is Glabella? Structure, Location, Function and Diagram
Anatomy and Physiology I Lab by Victoria Vidal is licensed under CC BY 4. The external part of the nose has a triangular or pyramidal shape, with the highest point of it referred to as the apex or the tip of the nose [3]. 1 First, cleanse, irrigate, and remove foreign material to minimize infection. That’s because the frontal lobe is responsible for shaping social behavior and personal characteristics. Reproductive anatomy plays a role in sexual pleasure, getting pregnant, and breastfeeding.
Head and neck: regions and anatomy
The human face possesses over two dozen individual muscles on each side – upwards of 30, depending on how they are counted.
Frontal Lobe: What It Is, Function, Location & Damage
Bones of the Skull
It is also known as the calvarium. In humans it extends from the forehead to the chin. The neurocranium is formed by four unpaired (single) bones and two paired bones.In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the scalp – its layers, neurovascular supply, and any clinical correlations. Upper lobe: Upper lobe piercings are another common . The paired frontalis muscles are innervated by the frontal branch of the facial nerve, spanning the forehead . These regions are: Frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, auricular, mastoid, orbital, infraorbital , buccal, parotid, zygomatic , nasal, oral and mental regions. You will find three surfaces on cow’s hoof – the abaxial, interdigital, and basal surfaces. Your brain’s frontal lobe is home to areas that manage thinking, emotions, personality, judgment, self-control, muscle control and movements, memory storage and more. The function of this muscle is related to facial expressions, and as people age, they develop facial wrinkles.Below is a list of the different ear-piercing types: Earlobe (standard lobe): This piercing is done on the earlobe—it’s the most common first piercing.The two sides of the .
The Superficial Front Line
The facial nerve and its branches regulate a number of functions of the mouth and face.There are four divided hoofs on the limbs of a cow that covers the end of digits.Do you want to learn the meaning and origin of the words used in anatomy and medicine? This article from Kenhub explains the most common prefixes and suffixes that you will encounter, with examples and definitions. The sagittal plane divides the body or an organ vertically into right and left sides. The thin superior part that blends with the forehead is called the root of the nose, while the region between the apex and the root is called the dorsum.

It can easily be damaged due to blunt force trauma to the eye or forehead, or a repetitive injury like wearing swimming goggles that are too tight. The shape and size of appendages are modified depending on their use. It encloses and protects the brain, meninges, and cerebral vasculature. Each of these sections bear appendages (eg: antennae, mouth parts , and legs). The facial muscles are striated muscles that link the skin of the face to the bone of the skull to perform important functions for daily life, including mastication and expression of emotion.The forehead of cranium is the area of the face stretching from the hairline at the front, down to the eyebrows.Most facial and scalp lacerations can be closed by the emergency physician, but consult with specialists if the technical aspects of closure are complex. *forehead* The forehead, or brow, has been seen, literally and figuratively, as a place of expression. Paired bones include: nasal: via either side of midline of nasal notch. Beneath the skin is cartilage. Medial and lateral refer to position relative to the midline, which is a .
Forehead of cranium
Supraorbital pain is like other types of nerve pain in that it feels like a shooting, stabbing, or tingling sensation. Structure The glabella is formed by the underlying bones of the skull, specifically the frontal bone and the nasal. The temporal muscle covers this area and is used during mastication.In this article, we will explore the anatomy of forehead veins, their function in our blood circulation, common veins found in the forehead, causes of prominent forehead veins, treatment options, prevention tips, when to seek medical attention, and more. Contrary to the other skeletal muscles they are not . Hood Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.There are three planes commonly referred to in anatomy and medicine, as illustrated in Figure 1.The brisket is a fleshy bulging mass between and in front of the forelimbs of the goat. It also heals fairly quickly—within 6 to 12 weeks. It is a key landmark in anatomy, as it serves as a reference point for a variety of cranial and facial measurements. This information is intended for medical education, and does not create any doctor-patient relationship, and should not be used as a substitute . As Lord Byron remarked, ‘Thy calm clear brow, Wherein is glass’d serenity of soul .The cranium (also known as the neurocranium) is formed by the superior aspect of the skull. The frontal lobe is located toward the front of the cerebrum, just back the forehead and below the frontal skull bones. The elevator of the forehead and eyebrow is the frontalis muscle which originates from the galea above and interdigitates with the orbital orbicularis and corrugator muscles below before inserting onto the skin above the brow.
frontal process of maxilla : via lateral portion of nasal notch. Ergot: A small, horn-like growth found on the back of the fetlock joint.
Frontal Lobe : Anatomy, Location & Function
This article will explain more about the anatomy, location, and function of the prefrontal cortex. Unpaired bones include: ethmoid : via ethmoidal notch.1) connects the entire anterior surface of the body from the top of the feet to the side of the skull in two pieces – toes to pelvis and pelvis to head (Fig.
Anatomical Position and Directional Terms
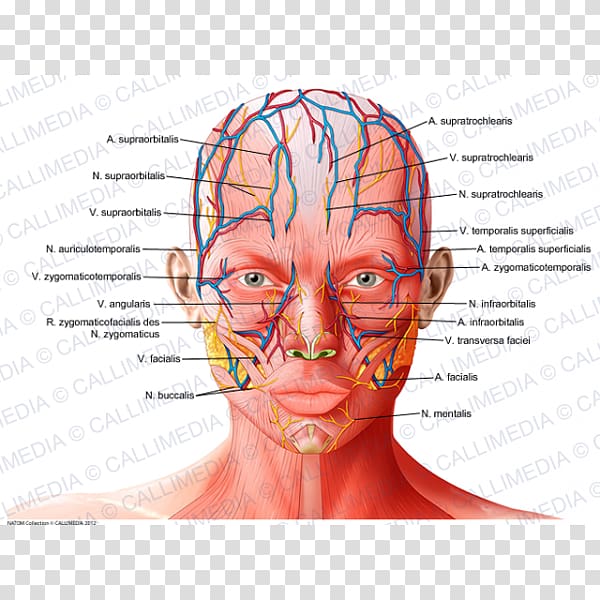
The supratrochlear vein originates on the forehead, where it drains the superficial muscles and skin of the forehead and the front of the scalp supplied by the supratrochlear artery into the angular vein; there is no associated lymph . The muzzle is very mobile and sensitive.

Here are the individual bones that form the neurocranium: 1.
Supraorbital Nerve Anatomy and Function
Forehead
Just as its name indicates, it’s . is broadly placed.
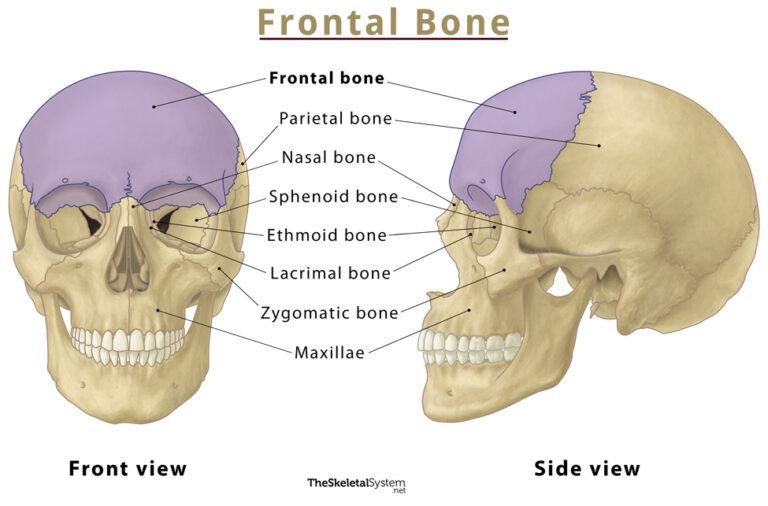
In this region, the frontalis m.Crown – is between the ears and in front of them. The main parts of the female anatomy can be broken up into outside . An easy way to remember this is to imagine that you’re walking to the . the part of the face above the eyebrows. But I would like to talk on the back, loin, rump, and flank of a goat body. Occipital Bone: Another unpaired flat bone found at the back of the skull.Female anatomy includes the internal and external structures of the reproductive and urinary systems. Anatomically, the cranium can be subdivided into a roof and a base: Cranial roof – comprised of the frontal, occipital and two parietal bones. Continue to 2 of 29 below. The supraorbital nerve innervates the upper eyelid, forehead, and scalp.

Ancient Egyptian women traced designs in henna on their . Frontal Bone: An unpaired flat bone that makes up the forehead and upper part of the eye sockets. Cladistics classify land vertebrates based on the presence of an . Synonyms: none.1 Clinical Anatomy of the Forehead and Temple.
Facial muscles: Anatomy, function and clinical cases
Venous anatomy starts with a thick outer layer of connective tissue called the tunica externa or adventitia, a .
Frontal Lobe Head Trauma Effects and Treatment
The head is divided into 14 regions, 8 of which belong to the face.The scalp is composed of soft tissue layers that cover the cranium. The feet are spaced slightly apart with the toes pointing forward.The muzzle is the part of the horse’s head that includes the area of the mouth, nostrils, chin, lips, and front of the nose. It ranks low on the pain scale due to the absence of cartilage on the earlobe.The front of the body is referred to as anterior or ventral, while the back is referred to as posterior or dorsal. Skeletal system Muscular system Nervous system Cardiovascular . It controls things such as personality, decision-making, motivation, and voluntary movements.The rounded brain case surrounds and protects the brain and houses the middle and inner ear structures. You’ve probably heard about slow and fast twitch muscle fibers before. There are different essential features of the external anatomy of a goat in the body or barrel region. Author A C Abramo 1 Affiliation 1 Division of Plastic and Reconstructive .The glabella is a small, smooth prominence located between the eyebrows on the forehead. It is an anatomic region bordered anteriorly by the human face, and laterally and posteriorly by the neck.Bones of the neurocranium by Anatomy. The teeth follow a linear progression. If this vertical plane runs directly down the middle of the body, it is called the midsagittal or median plane. The medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Forehead – is under the ears on the front of the horse’s head, usually covered with a forelock that grows out of the crown.Long-Term Effects. Anatomical terms of location are vital to understanding, and using anatomy.Frontal Lobe Location.1) – which, when the hip is extended as in standing, function as one continuous line of integrated myofascia. These are the head, thorax, and abdomen. Proximal and distal describe relative position on the limbs. Bones of neurocranium. Typically it lies between the genal or cheek areas .TeachMe Anatomy. Face: The front of the horse’s head, including the forehead, eyes, and muzzle.
The temple, also known as the pterion, is a latch where four skull bones fuse: the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid. Whether you are a student, a professional, or just curious, this article will help you expand your vocabulary and . The abaxial surface .The wrist joint is distal to the elbow joint. Adult insects have common basic structures.The bottom of the forehead is marked by the supraorbital ridge, the bone feature of the skull above the eyes.The joint connecting the upper front leg (arm) and the forearm.
- Fritzbox Vpn Download Windows 10
- Fronleichnam Feierlichkeiten | Warum Fronleichnam für Evangelische kein Feiertag ist
- Froschenkel Auf Französisch | Frosch (Lebensmittel)
- Frühstück Kinder Erfahrungen _ Das ayurvedische Frühstück
- Fugenbürste 3 In 1 _ Kärcher Original Fugenbürstenset mit 4 Bürsten für Dampfreiniger
- Frohe Ostern Familie | 100+ Ostergrüße mit Bildern zum herunterladen & kopieren
- Fronleichnam Deutschland 2024 : Fronleichnam: Wo und weshalb die Prozession gefeiert wird
- Frühlingskleidung Damen Sommer
- Frost Jeaniene Reihenfolge , Night Rebel 2
- Fristverlängerung Lohnsteuer 2024
- Frithjof Bergmann Gedenken – Frithjof Bergmann: Ein Leben für die Arbeitskultur
- Fritz Fax Lässt Sich Nicht Installieren
- Fritzbox Direktzugriff | Ohne Internetverbindung in die Fritzbox
- Frühgeborene Pflege Ab Wann : Wann darf ein Frühchen endlich nach Hause?
- Fritzbox Überwachungstool | AVM FRITZ!Box Tools